MCA II Exam 3 | Questions, Answers and Rationales
Document Content and Description Below
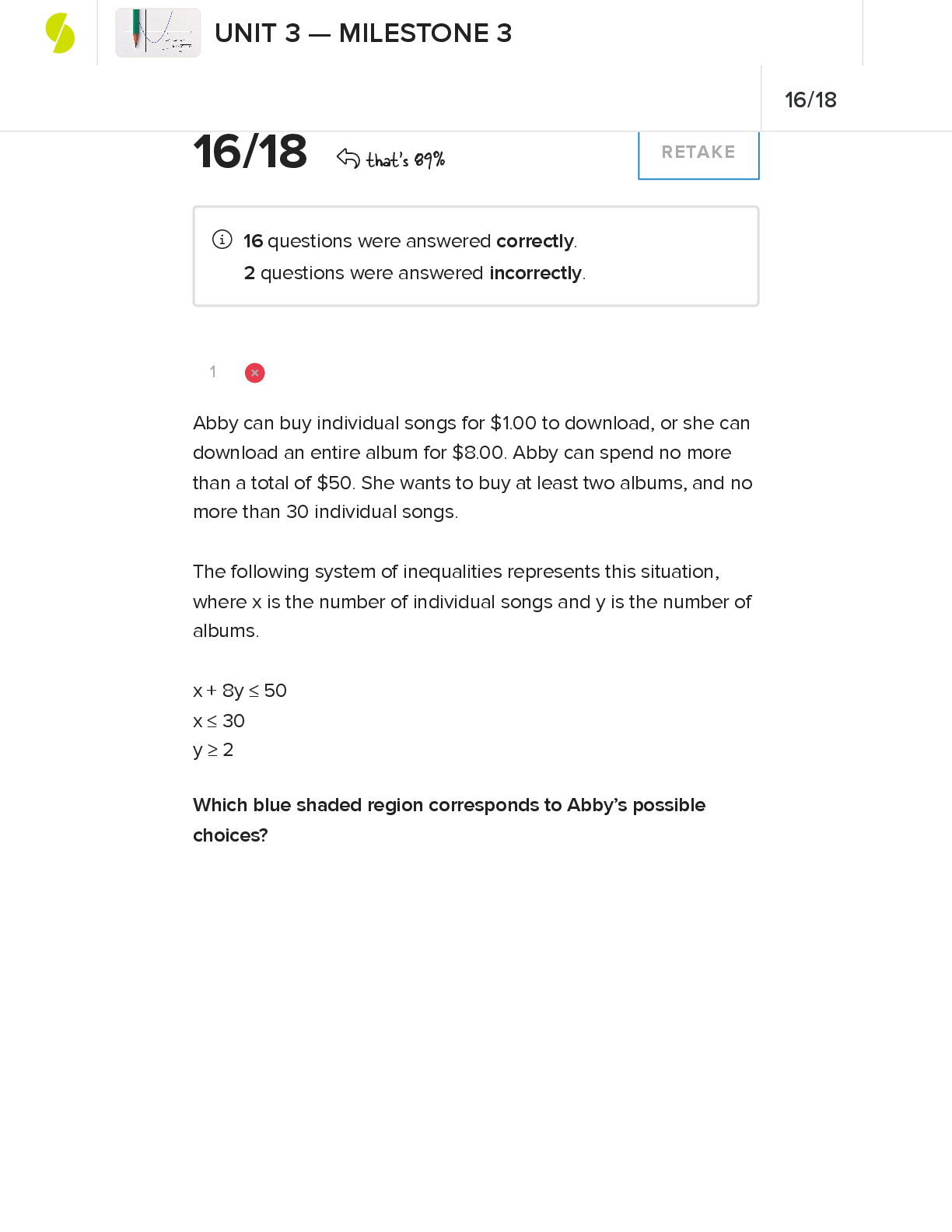
MCA II Exam 3 | Questions, Answers and Rationales Which type of hepatitis develops into a chronic form of the disease? select all that apply. a. hepatitis A b. hepatitis B c. hepatitis C d. hepati... tis D e. hepatitis E Hepatitis B and C generally develop into chronic hepatitis. Hepatitis D is an incomplete virus that can become chronic and is dependent on the presence of hepatitis B to survive. Hepatitis A and E are acute, self-limiting infections that resolve over time and do not develop with chronic hepatitis. A nurse is providing postoperative care for a client who has begun taking levothyroxine after undergoing a thyroidectomy. Which findings in the client may indicate potential thyrotoxic crisis? a. Elevated serum calcium b. Sudden drop in pulse rate c. Hypothermia and dry skin d. Rapid heartbeat and tremors Thyrotoxic crisis (thyroid storm) refers to a sudden and excessive release of thyroid hormones, which causes pyrexia, tachycardia, and exaggerated symptoms of thyrotoxicosis; surgery, infection, and ablation therapy can precipitate this life-threatening condition. Hypercalcemia is not related to thyrotoxic crisis; hypocalcemia results from accidental removal of the parathyroid glands. Tachycardia is an increased, not decreased, heart rate, which occurs with thyrotoxic crisis because of the sudden release of thyroid hormones; thyroid hormones increase the basal metabolic rate. Fever, not hypothermia, and diaphoresis, not dry skin, occur with thyrotoxic crisis because of the sudden release of thyroid hormones, which increase the basal metabolic rate. Which questions would the nurse ask when assessing a client diagnosed with acromegaly? select all that apply. a. "have you noticed any changes to your vision?" b. "have you ever been told that you snore loudly?" c. "have you had any changes in your menstrual cycle?" d. "have you noticed any chances to your bowel movements?" e. "have you noted you consume excess amount of cruciferous vegetables?" It is reasonable to ask a client with acromegaly if he or she has experienced changes in his or her vision, because pressure on the optic nerve from a pituitary adenoma can occur. some clients with acromegaly will develop sleep apnea, secondary to upper airway narrowing and obstruction from increased amounts of pharyngeal soft tissues. clients with acromegaly are at an increased risk of colorectal cancer. it is not necessary to ask the client with acromegaly about her menstrual cycle; acromegaly is the overgrowth of soft tissue and bone in the hands, feet, and face, and does not affect the reproductive organs as some other excesses of tropic hormones do. intake of cruciferous vegetables will not affect acromegaly; the goitrogens in these vegetables contain thyroid-inhibiting substance and can lead to goiter if eaten in excessive amounts. The nurse is admitting a client with severe myxedema coma. Which interventions would the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct. a. Administer intravenous (IV) levothyroxine. b. Avoid use of corticosteroids. c. Give IV normal saline. d. Wait for laboratory results before treating. e. Monitor blood pressure every 4 hours. myxedema coma is a major complication of poorly treated hypothyroidism. interventions include administering IV levothyroxine. this promotes the return of normal thyroid hormone levels. IV normal saline corrects dehydration. corticosteriods are administered as part of the treatment. levothyroxine is initiated before obtaining laboratory results because waiting can cause death. the blood pressure should be monitored hourly. Which clinical findings correspond with the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? select all that apply. a. edema b. polyuria c. bradycardia d. muscle cramps e. hyponatremia muscle cramps occur when sodium level is less than 124 mEq/L and are caused by osmotic fluid shift. ADH causes water retention, which dilutes serum electrolytes such as sodium, with a resultant hyponatremia. edema is not usually seen in syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) because water retention is not extracellular.. a decreased urine output occurs with SIADH because ADH causes reabsorption of fluid in the kidney glomeruli. the increased fluid volume associated with SIADH results in tachycardia, tachypnea and crackles. A client with cirrhosis of the liver has a prolonged prothrombin time and a low platelet count. A regular diet is prescribed. What should the nurse instruct the client to do considering the client's condition? a. Avoid foods high in phytonadione b. Check the pulse several times a day. c. Drink a glass of milk when taking aspirin. d. Report signs of bleeding no matter how slight. One of the many functions of the liver is the manufacture of clotting factors; there is interference in this process with cirrhosis of the liver, resulting in bleeding tendencies. The storage of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), water-soluble vitamins (B1, B2, folic acid, and cobalamin), and minerals (including iron) is compromised in cirrhosis; therefore, these nutrients, including phytonadione, should not be limited. Should the client bleed, the pulse rate may be increased, but it is not necessary for the client to check the pulse rate several times daily. A client whose prothrombin time is prolonged and platelet count is low should not be taking aspirin, even with milk. While assessing a postpartum client who is suspected of having a thyroid disorder, the nurse suspects that the client has autoimmune thyroiditis. Which diagnostic studies are most suitable for confirming the diagnosis? a. Radioactive iodine uptake b. computed tomography scan c. magnetic resonance imaging d. thyroid-stimulating hormone the postpartum client may have silent, painless thyroiditis. radioactive iodine uptake is suppressed in silent thyroiditis, so this test would be beneficial in diagnosing the thyroiditis. a computed tomography scan is used to detect thyroid nodules. magnetic resonance imaging is also used in evaluating thyroid nodules. a blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormone is used to evaluate thyroid function. Which action is the function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? a. reduces blood volume b. decreases water loss in urine c. increases urine output d. initiates the thirst mechanism ADH is released by the posterior pituitary gland. it is released mainly in response to either a decrease in blood volume or an increased concentration of sodium or other substances in the plasma. ADH acts to decrease the production of urine by increasing the reabsorption of water by renal tubules. A decrease in ADH would cause reduced blood fluid volume; decreased ability of the kidneys to reabsorb water, resulting in increased urine output; and an increase in the thirst mechanism. The nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing an underproduction of thyroxine (T4). with what diagnosis is this associated? a. myxedema b. acromegaly c. Graves disease d. Cushing disease myxedema is the severest form of hypothyroidism. decreased thyroid gland activity means reduced production of thyroid hormones. acromegaly results from excess growth hormone in adults once the epiphyses are closed. graves disease results from an excess, not a deficiency, of thyroid hormones. cushing disease results from excess glucocorticoids. Which clinical indicator would the nurse expect to find when assessing a client with excess antidiuretic hormone? a. polyuria b. dehydration c. hyponatremia d. hyperglycemia antidiuretic hormone (ADH) causes increased resorption of water by renal tubules, which dilutes sodium levels, causing hyponatremia. ADH will decrease urine volume. ADH causes fluid retention. ADH does not alter glucose metabolism. A client with hyperthyroidism asks the nurse about the tests that will be prescribed. Which diagnostic tests should the nurse include in a discussion with this client? a. thyroxine (T4) and x-ray films b. thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) assay and triiodothyronine (T3) c. thyroglobulin level anad PO2 d. protein-bound iodine and sequential multichannel autoanalyzer (SMA) a decreased TSH assay together with an elevated T3 level may indicate hyperthyroidism. x-ray films will not indicate thyroid disease, and elevation of T4 level might indicate hyperthyroidism. However, this may be a false reading because of the presence of thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) and is inadequate for diagnosis when used alone. PO2 is not specific to thyroid disease, and the thyroglobulin level is most useful to monitor for recurrence of thyroid carcinoma or response to therapy. the results with the SMA are not specific to thyroid disease; the protein-bound iodine test is not definitive because it is influenced by the intake of exogenous iodine. The nurse is assessing a client with a suspected thyroid disorder. Which= diagnostic studies will be most appropriate to confirm that the thyroid disorder is autoimmune in origin? Select all that apply. a. Free thyroxine b. Thyroglobulin antibody c. Thyroid peroxidase antibody d. Thyroid-stimulating antibody e. Thyroid-stimulating hormone Thyroglobulin, thyroid peroxidase, and thyroid-stimulating antibodies are assessed in a thyroid antibody test. This test helps to differentiate other forms of thyroiditis from autoimmune thyroid disease. An active component of total T4 is measured by free thyroxine but cannot differentiate the origin. Thyroid-stimulating hormone levels are used to evaluate a thyroid dysfunction but cannot differentiate the origin. while reviewing the client's laboratory reports, the nurse finds that there is an elevation in the client's growth hormone levels. which key physical changes would the nurse expect to find if acromegaly is suspected? select all that apply a. facial shape b. body weight c. chest shape d. lip thickness e. length of hands acromegaly may occur as a result of overproduction of growth hormone by the pituitary gland, which results in a few physical changes. the client with acromegaly would experience a barrel-shaped chest, enlarged facial features including bones and thickened lips, and enlarged hands and feet. clients who have hyperfunction of adrenocorticotropic hormone have weight gain. A client with a family history of goiter is experiencing changes in voice and breathing. Which diagnostic study does the nurse consider to be beneficial in confirming a diagnosis? a. thyroglobulin b. thyroid antibodies c. thyroxine (free T4), total d. thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Changes in voice and breathing can be seen in Hashimoto's thyroiditis if the thyroid gland enlarges rapidly and constricts the trachea and laryngeal nerves. Clients with a family history of goiter may have this condition. A thyroid antibody test is used diagnose Hashimoto's thyroiditis by differentiating thyroid dysfunction from thyroiditis. A client with a primary brain tumor has developed syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). The nurse will expect to see which clinical findings upon assessment? Select all that apply. a. Vomiting b. Hyperthermia c. Bradycardia d. increased weight e. Decreased serum sodium f. Decreased level of consciousness Water retention and decreased urinary output occur because of excess secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Early manifestations are related to water retention and may include gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances, such as loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. Weight gain occurs because of the water retention. Serum sodium levels are decreased because of fluid retention and sodium loss. Central nervous system changes include headaches, lethargy, and decreased level of consciousness, progressing to coma and seizures. Hypothermia also occurs because of central nervous system disturbance. The pulse is full and bounding because of the increased fluid volume. The nurse would monitor a client for which manifestation indicating a thyroid storm? select all that apply. a. Increased heart rate b. Increased temperature c. Decreased respirations d. Increased pulse deficit e. Decreased blood pressure thyroid storm is severe hyperthyroidism; excessive amounts of thyroxine increase the metabolic rate, thereby causing an increased heart rate (tachycardia). Because of the increased metabolic rate associated with thyroid storm, the respiratory rate increases (tachypnea) to meet the body's oxygen needs. pulse deficit, the difference between apical and peripheral pulse rates, is not indicative of thyroid storm. the blood pressure will increase to meet the oxygen demand caused by the increased metabolic rate during thyroid storm. A paracentesis is prescribed for a client recently admitted to a medical unit. The nurse recalls that the procedure is performed for what reasons? (Select all that apply.) a. extract peritoneal fluid b. improve respiratory status c. decrease intrapleural fluid d. increase intra-abdominal tension e. obtain peritoneal fluid for culture when a client has ascites, a peritoneal tap (paracentesis) may be prescribed to remove fluid for diagnostic purposes and for relief of discomfort. the removal of intra-abdominal fluid relieves pressure against the diaphragm, which will improve the client's respiratory status. a culture of peritoneal fluid may provide information about the cause of the ascites. closed-chest drainage, not paracentesis, removes fluid from the pleural space. paracentesis is done to decrease, not increase, intra-abdominal pressure. A client with esophageal varices has severe hematemesis, and a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is inserted. What design and purpose does the tube have? a. single-lumen; for gastric lavage b. double-lumen; for intestinal decompression c. triple-lumen; for esophageal compression d. multi-lumen; for gastric and intestinal decompression the Sengstaken-Blakemore is a triple-lumen tube; one lumen inflates the esophageal balloon that compresses the esophagus, the second inflates the gastric balloon, and the third is attached to suction to decompress the stomach. The Sengstaken-Blakemore is not a single-lumen tube. The Sengstaken-Blakemore is not a double-lumen tube; the stomach, not the intestine, is decompressed. The intestine is not decompressed with a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube. A nurse is caring for a client with the clinical manifestation of hypotension associated with a diagnosis of Addison disease. Which hormone is impaired in its production as a result of this disease? a. Estrogens b. Androgens c. Glucocorticoids d. aldosterone aldosterone can be impaired in its production because pf Addison disease, although Addison disease itself is caused by a cortisol deficiency. Aldosterone causes the kidneys to retain sodium ions. Increased sodium promotes water retention, which elevates blood pressure. the absence of aldosterone causes hypotension. the major effect of cortisol is on glucose metabolism and not on sodium and water concentrations, so the absence of this hormone will not cause significant hypotension. estrogen and androgens are sex hormones and do not affect blood pressure. A nurse is caring for a client with a diagnosis of Cushing syndrome. What is the most common cause of Cushing syndrome that the nurse should consider before assessing this client for physiological responses? a. pituitary hypoplasia b. hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex c. deprivation of adrenocortical hormones d. insufficient adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) production hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex leads to increased secretion of cortical hormones, which causes signs of Cushing syndrome. pituitary hypoplasia is a malfunction of the pituitary that will result in Simmonds disease (panhypopituitarism), which has clinical manifestations similar to those for Addison disease. Cushing syndrome results from excessive cortical hormones. ACTH stimulates production of adrenal hormones. Inadequate ACTH will result in Addisonian signs and symptoms which situation in a client with hyperthyroidism may precipitate thyroid crisis (thyroid storm)? a. increased iodine in the blood b. removal of the parathyroid glands c. high levels of the hormone triiodothyronine d. rebound increase in metabolism after anesthesia thyroid trauma, thyroid surgery, or physiological stress in a client with hyperthyrodism may lead to a release of abnormally high levels of thyroid hormones. high levels of the hormone triiodothyronine (T3) intensify all the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism (thyroid storm or crisis), such as increased temperature, pulse, and respirations, restlessness, vomiting, and often death. iodine binds with thyroxine, thus decreasing the potential for crisis. tetany, not thyroid crisis, occurs from surgical excision of the parathyroid glands. anesthesia will depress metabolism, not increase it. A patient is scheduled for transsphenoidal hypophysectomy to treat a pituitary adenoma. During preoperative teaching, the nurse instructs the patient about the need to: a. cough and deep breathe every 2 hours postoperatively. b. remain on bed rest for the first 48 hours after the surgery. c. avoid brushing teeth for at least 10 days after the surgery. d. be positioned flat with sandbags at the head postoperatively. To avoid disruption of the suture line, the patient should avoid brushing the teeth for 10 days after surgery. It is not necessary to remain on bed rest after this surgery. Coughing is discouraged because it may cause leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the suture line. The head of the bed should be elevated 30 degrees to reduce pressure on the sella turcica and decrease the risk for headaches. The nurse is planning postoperative care for a patient who is being admitted to the surgical unit from the recovery room after transsphenoidal resection of a pituitary tumor. Which nursing action should be included? a. Palpate extremities for edema. b. Measure urine volume every hour. c. Check hematocrit every 2 hours for 8 hours. d. Monitor continuous pulse oximetry for 24 hours. After pituitary surgery, the patient is at risk for diabetes insipidus caused by cerebral edema. Monitoring of urine output and urine specific gravity is essential. Hemorrhage is not a common problem. There is no need to check the hematocrit hourly. The patient is at risk for dehydration, not volume overload. The patient is not at high risk for problems with oxygenation, and continuous pulse oximetry is not needed. The nurse is assessing a male patient diagnosed with a pituitary tumor causing panhypopituitarism. Assessment findings consistent with panhypopituitarism include: a. high blood pressure. b. decreased facial hair. c. elevated blood glucose. d. tachycardia and palpitations. Changes in male secondary sex characteristics such as decreased facial hair, testicular atrophy, diminished spermatogenesis, loss of libido, impotence, and decreased muscle mass are associated with decreases in follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Fasting hypoglycemia and hypotension occur in panhypopituitarism as a result of decreases in adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol. Bradycardia is likely due to the decrease in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones associated with panhypopituitarism. Which information will the nurse include when teaching a 50-yr-old male patient about somatropin (Genotropin)? a. The medication will be needed for 3 to 6 months. b. Inject the medication subcutaneously every day. c. Blood glucose levels may decrease when taking the medication. d. Stop taking the medication if swelling of the hands or feet occurs. Somatropin is injected subcutaneously on a daily basis, preferably in the evening. The patient will need to continue on somatropin for life. If swelling or other common adverse effects occur, the health care provider should be notified. Growth hormone will increase blood glucose levels. The nurse determines that demeclocycline is effective for a patient with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) based on finding that the patient's a. weight has increased. b. urinary output is increased. c. peripheral edema is increased. d. urine specific gravity is increased. Demeclocycline blocks the action of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on the renal tubules and increases urine output. An increase in weight or an increase in urine specific gravity indicates that the SIADH is not corrected. Peripheral edema does not occur with SIADH. A sudden weight gain without edema is a common clinical manifestation of this disorder. The nurse determines that additional instruction is needed for a patient with chronic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) when the patient makes which statement? a. "I need to shop for foods low in sodium and avoid adding salt to food." b. "I should weigh myself daily and report any sudden weight loss or gain." c. "I need to limit my fluid intake to no more than 1 quart of liquids a day." d. "I should eat foods high in potassium because diuretics cause potassium loss." Patients with SIADH are at risk for hyponatremia, and a sodium supplement may be prescribed. The other patient statements are correct and indicate successful teaching has occurred. A patient who had a subtotal thyroidectomy earlier today develops laryngeal stridor and a cramp in the right hand upon returning to the surgical nursing unit. Which collaborative action will the nurse anticipate next? a. Suction the patient's airway. b. Administer IV calcium gluconate. c. Plan for emergency tracheostomy. d. Prepare for endotracheal intubation. The patient's clinical manifestations of stridor and cramping are consistent with tetany caused by hypocalcemia resulting from damage to the parathyroid glands during surgery. Endotracheal intubation or tracheostomy may be needed if the calcium does not resolve the stridor. Suctioning will not correct the stridor. Which nursing action will be included in the plan of care for a patient with Graves' disease who has exophthalmos? a. Place cold packs on the eyes to relieve pain and swelling. b. Elevate the head of the patient's bed to reduce periorbital fluid. c. Apply alternating eye patches to protect the corneas from irritation. d. Teach the patient to blink every few seconds to lubricate the corneas. The patient should sit upright as much as possible to promote fluid drainage from the periorbital area. With exophthalmos, the patient is unable to close the eyes completely to blink. Lubrication of the eyes, rather than eye patches, will protect the eyes from developing corneal scarring. The swelling of the eye is not caused by excessive blood flow to the eye, so cold packs will not be helpful. A 62-yr-old patient with hyperthyroidism is to be treated with radioactive iodine (RAI). The nurse instructs the patient a. about radioactive precautions to take with all body secretions. b. that symptoms of hyperthyroidism should be relieved in about a week. c. that symptoms of hypothyroidism may occur as the RAI therapy takes effect. d. to discontinue the antithyroid medications taken before the radioactive therapy. There is a high incidence of postradiation hypothyroidism after RAI, and the patient should be monitored for symptoms of hypothyroidism. RAI has a delayed response, with the maximum effect not seen for 2 to 3 months, and the patient will continue to take antithyroid medications during this time. The therapeutic dose of radioactive iodine is low enough that no radiation safety precautions are needed. Which nursing assessment of a 70-yr-old patient is most important to make during initiation of thyroid replacement with levothyroxine (Synthroid)? a. Fluid balance b. Apical pulse rate c. Nutritional intake d. Orientation and alertness In older patients, initiation of levothyroxine therapy can increase myocardial oxygen demand and cause angina or dysrhythmias. The medication also is expected to improve mental status and fluid balance and will increase metabolic rate and nutritional needs, but these changes will not result in potentially life-threatening complications. A patient with primary hyperparathyroidism has a serum phosphorus level of 1.7 mg/dL (0.55 mmol/L) and calcium of 14 mg/dL (3.5 mmol/L). Which nursing action should be included in the plan of care? a. Restrict the patient to bed rest. b. Encourage 4000 mL of fluids daily. c. Institute routine seizure precautions. d. Assess for positive Chvostek's sign. The patient with hypercalcemia is at risk for kidney stones, which may be prevented by a high fluid intake. Seizure precautions and monitoring for Chvostek's or Trousseau's sign are appropriate for hypocalcemic patients. The patient should engage in weight-bearing exercise to decrease calcium loss from bone. A patient develops carpopedal spasms and tingling of the lips following a parathyroidectomy. Which action will provide the patient with rapid relief from the symptoms? a. Administer the prescribed muscle relaxant. b. Have the patient rebreathe from a paper bag. c. Start the PRN O2 at 2 L/min per cannula. d. Stretch the muscles with passive range of motion. The patient's symptoms suggest mild hypocalcemia. The symptoms of hypocalcemia will be temporarily reduced by having the patient breathe into a paper bag, which will raise the PaCO2 and create a more acidic pH. Applying as-needed O2 or range of motion will have no impact on the ionized calcium level. Calcium supplements will be given to normalize calcium levels quickly, but oral supplements will take time to be absorbed. Which finding for a patient who has hypothyroidism and hypertension indicates that the nurse should contact the health care provider before administering levothyroxine (Synthroid)? a. Increased thyroxine (T4) level b. Blood pressure 112/62 mm Hg c. Distant and difficult to hear heart sounds d. Elevated thyroid stimulating hormone level An increased thyroxine level indicates the levothyroxine dose needs to be decreased. The other data are consistent with hypothyroidism and the nurse should administer the levothyroxine. Which finding indicates to the nurse that the current therapies are effective for a patient with acute adrenal insufficiency? a. Increasing serum sodium levels b. Decreasing blood glucose levels c. Decreasing serum chloride levels d. Increasing serum potassium levels Clinical manifestations of Addison's disease include hyponatremia and an increase in sodium level indicates improvement. The other values indicate that treatment has not been effective. Which intervention will the nurse include in the plan of care for a patient with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)? a. Encourage fluids to 2 to 3 L/day. b. Monitor for increasing peripheral edema. c. Offer the patient hard candies to suck on. d. Keep head of bed elevated to 30 degrees. Sucking on hard candies decreases thirst for a patient on fluid restriction. Patients with SIADH are on fluid restrictions of 800 to 1000 mL/day. Peripheral edema is not seen [Show More]
Last updated: 6 months ago
Preview 5 out of 23 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)

MCA II EXAM 1- 4 BUNDLE
MCA II EXAM 1- 4 BUNDLE
By Ajay25 6 months ago
$30
4
Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 16, 2025
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 16, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
5