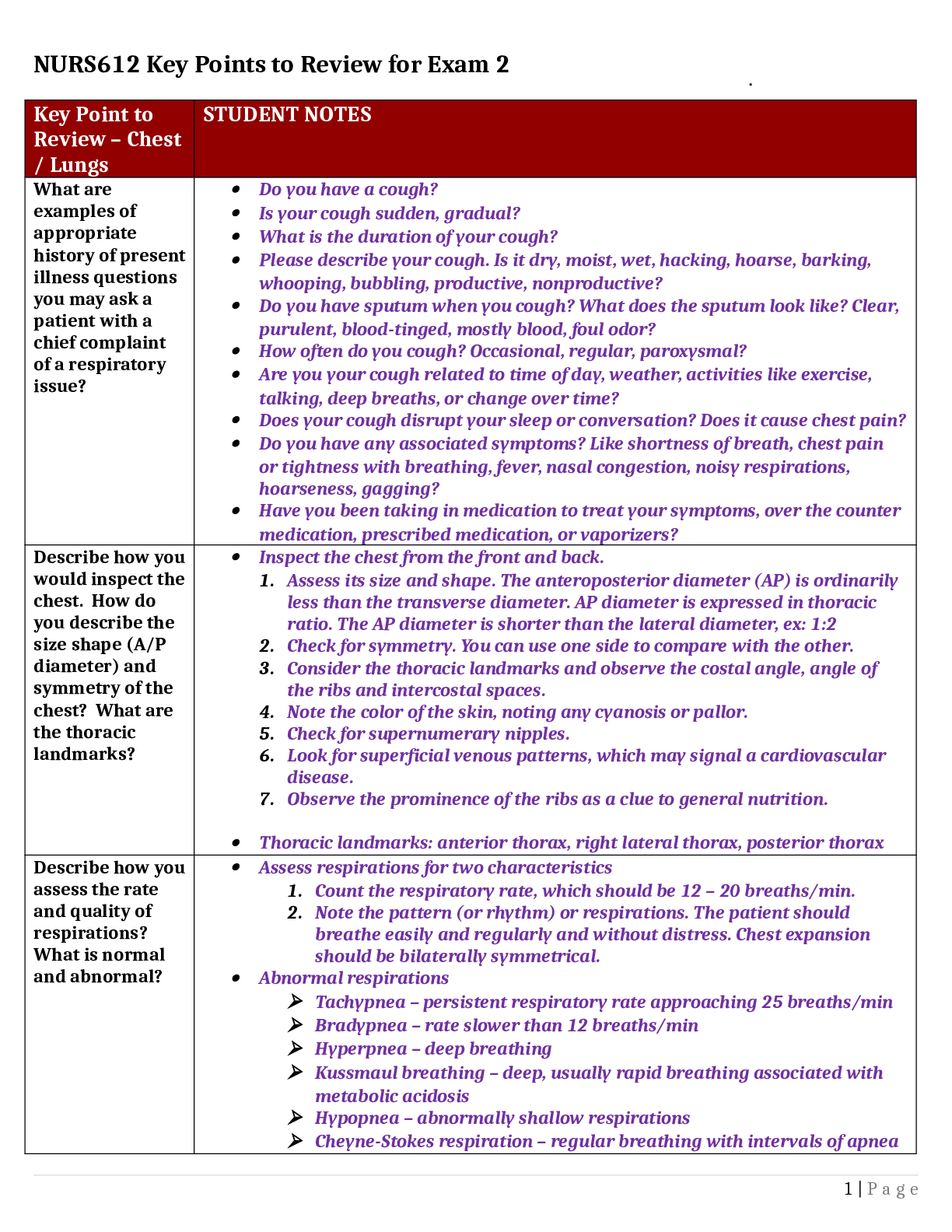
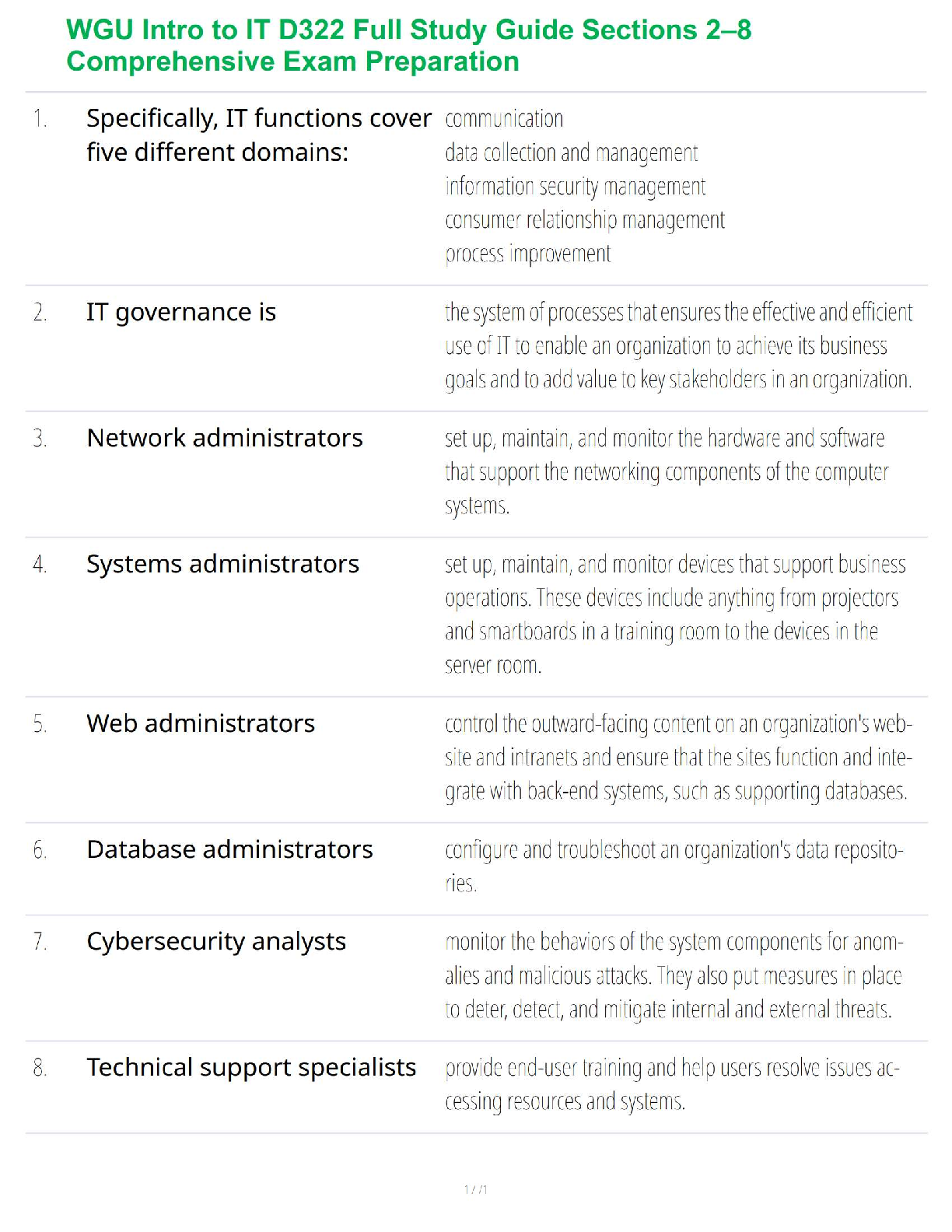
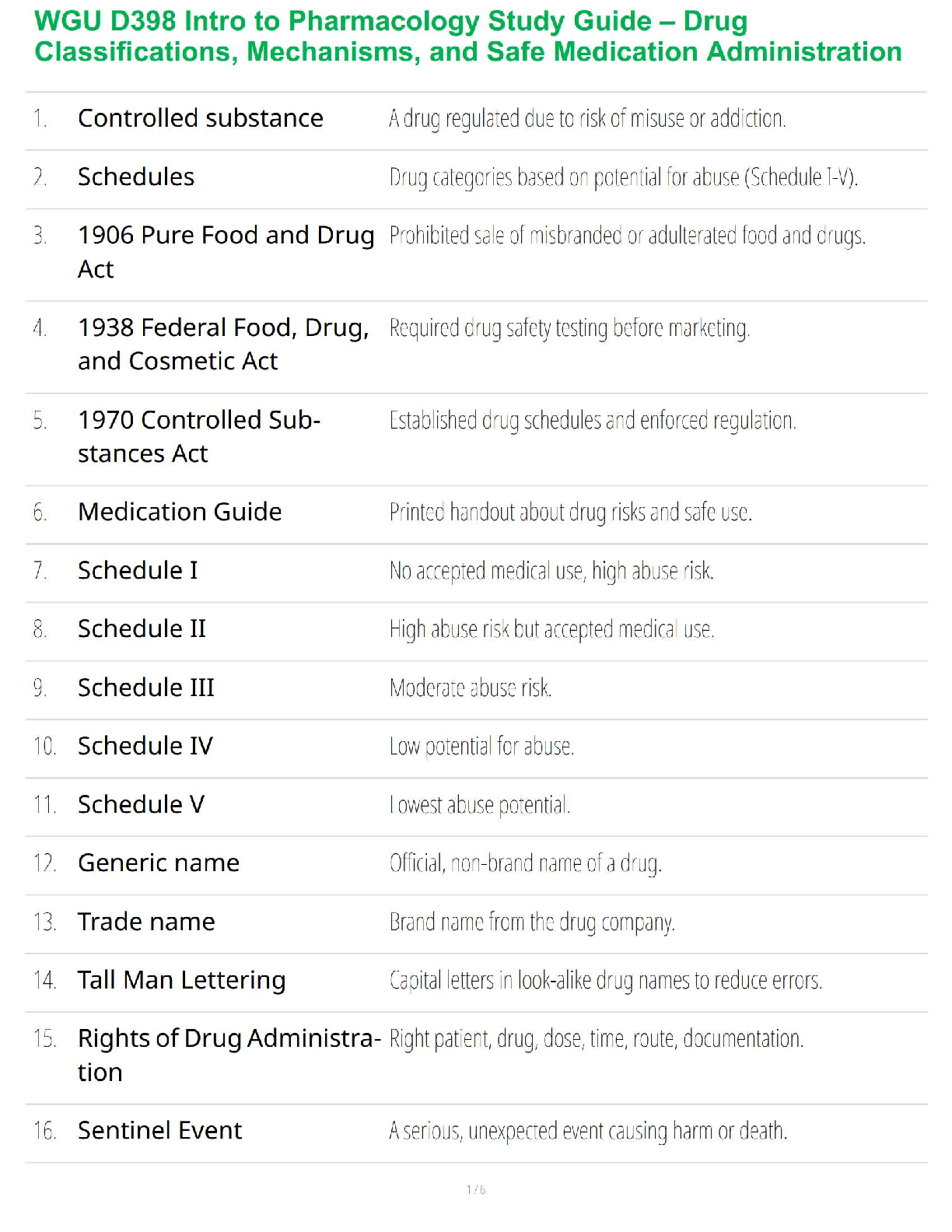
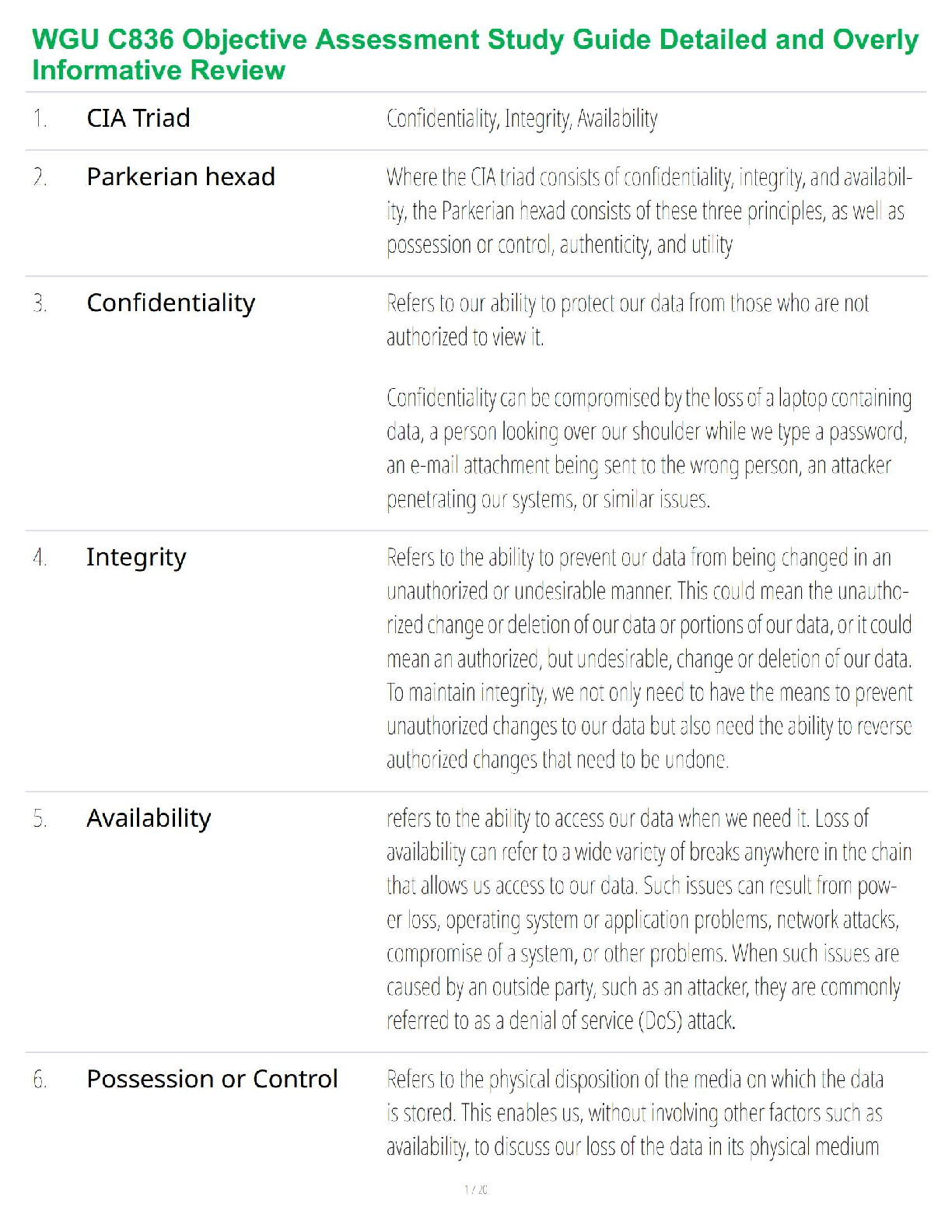
• Glucocorticoids type of Corticosteroids
Stimulate an increase in glucose levels for energy
Prednisone: generic Replacement therapy in adrenal cortical insufficiency, short term management of inflammation and a
...
• Glucocorticoids type of Corticosteroids
Stimulate an increase in glucose levels for energy
Prednisone: generic Replacement therapy in adrenal cortical insufficiency, short term management of inflammation and allergic disorders.
Adverse effects: vertigo, headache, hypotension, shock, sodium and fluid retention, amenorrhea, increased appetite, weight gain, immunosuppression, aggravation or masking of infections, impaired wound healing.
Nursing Interventions for Prednisone: Protect from infection, monitor blood glucose levels, monitor for diet as needed, instruct patient not to stop medication suddenly, but should have the medication tapered gradually, do not give live vaccine if patient is immunosuppressed.
Thyroid Hormone: Uses iodine to produce thyroid hormone that regulates body’s metabolism.
Control of thyroid gland involves an intricate balance between TRH, TSH, and circulating levels of thyroid hormone.
• Actions
– Increases the metabolic rate of body tissues, increasing oxygen consumption, respiration, and heart rate; the rate of fat, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism; and growth and maturation
• Indications
– Replacement therapy in hypothyroidism; pituitary TSH suppression in the treatment of euthyroid goiters, management of thyroid cancer; thyrotoxicosis in conjunction with other therapy; myxedema coma
• Pharmacokinetics
– Absorbed in GI tract and binds to serum proteins
– Eliminated in bile
Does not cross the placenta
• Contraindications
– Known allergy
– Thyrotoxicosis
– Acute MI
• Caution
– Lactation
– Hypo-adrenal conditions such as Addison’s disease
Adverse Effects
– Skin reactions
– Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
– Cardiac stimulation
– CNS effects
Drug-to-Drug Interactions
– Cholestyramine: decreased absorption
– Oral anticoagulants: increased bleed times
– Digitalis: decreased effectiveness of Dig
– Theophylline: decreased clearance (which can lead to toxic theophylline levels)
–
Levothyroxine (Synthroid): Replacement therapy in hypothyroidism-suppression of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) release; treatment of myxedema coma or thyrotoxicosis.
Nursing Intervention: Instruct patient to take on an empty stomach (before breakfast daily), contact the provide if having chest pain, palpitations, and rapid HR.
Antithyroid Agents: Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
Thriomide: Propylthiouracil: treatment of hyperthyroidism.
– Thioamides prevent the formation of thyroid hormone within the thyroid cells, lowering the serum level of thyroid hormone
– Partially inhibit the conversion of T4 to T3
• Indications
Hyperthyroidism
[Show More]









.png)