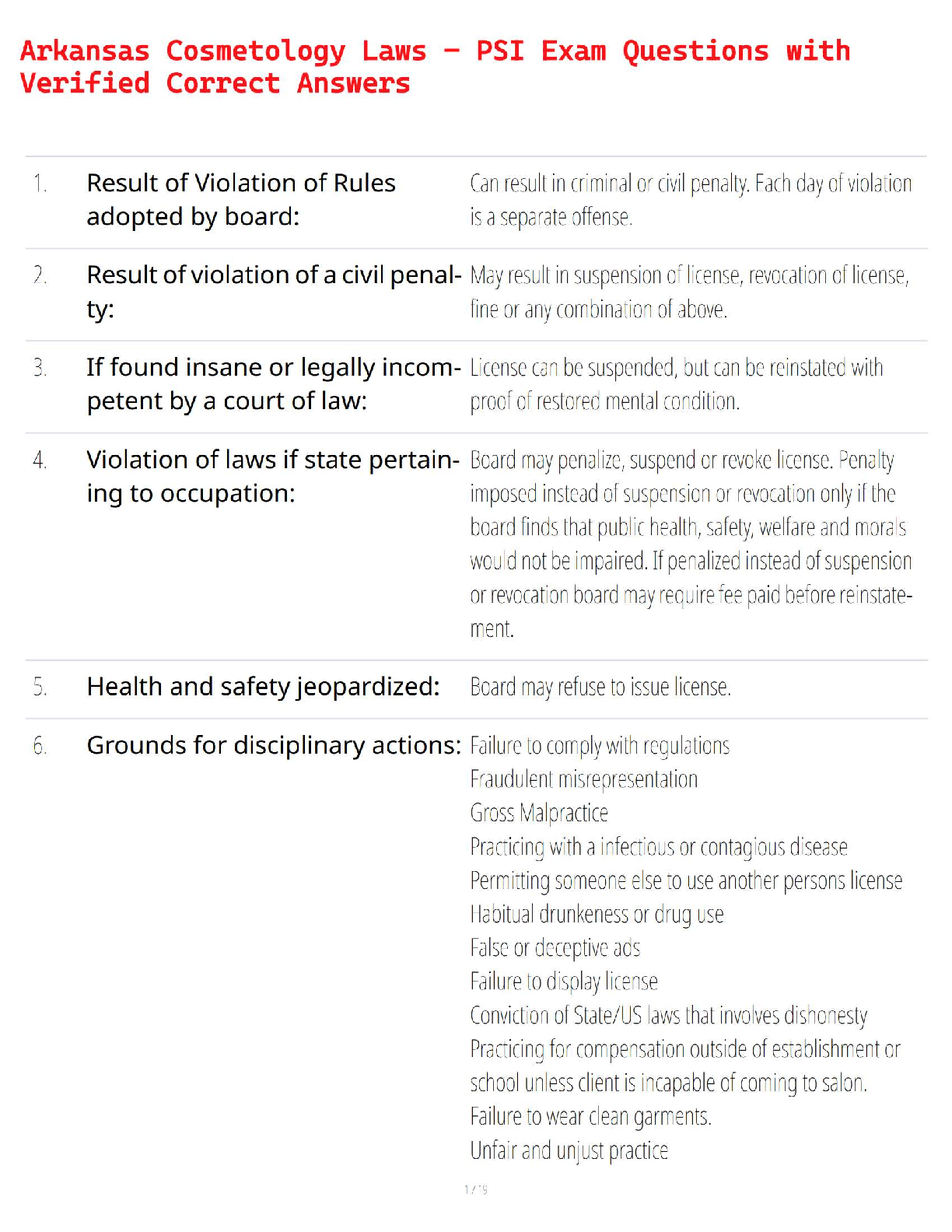
Arkansas Cosmetology Laws – PSI Exam Questions with Verified Correct Answers
*NURSING > EXAMs > Sarah Michelle FNP Practice Final Test/Exam, Complete Questions With 100% Rated Correct Explained An (All)
Sarah Michelle FNP Practice Final Test/Exam, Complete Questions With 100% Rated Correct Explained Answers, Latest Update (From Actual Test)-Which of the following is a nonstimulant drug that may be pr ... escribed for treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? A.Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin XR) B.Mixed salts of amphetamine (Adderall) C.Methylphenidate (Ritalin) D.Atomoxetine (Strattera) - Answer: D. Atomoxetine (Strattera) Atomoxetine is classified as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, not a stimulant. Atomoxetine may be prescribed for patients for who do not experience adequate ADHD symptom relief from stimulant medications such as dexmethylphenidate, amphetamine, or methylphenidate. The nurse practitioner (NP) advises a patient who is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) to avoid foods that contain high levels of tyramine. Which food would the NP include in a list of examples? A.Chicken B.Beer C.Cottage cheese D.Spinach - Answer: B. Beer Fermented food items, including fermented beverages such as beer, tend to be high in tyramine. Although cured meats are high in tyramine, noncured proteins such as chicken are not. Pasteurized cheeses, such as cottage cheese, tend to be lower in tyramine than aged cheeses. Fresh vegetables tend to be low in tyramine. What symptom would be unexpected in a diagnosis of depression? A.Anhedonia B.Low self-esteem C.Apathy D.Apraxia - Answer: D. Apraxia Apraxia is characterized by loss of the ability to execute or carry out learned purposeful movements despite the desire and the physical ability to perform the movements. Apraxia is not a sign or symptom of depression; it is a disorder of motor planning caused by damage to specific areas of the cerebrum. Common signs of depression include anhedonia (loss of interest in activities that the patient normally finds pleasurable), unintentional weight loss or gain, fatigue, change in appetite, insomnia or hypersomnia, feelings of guilt and worthlessness, and recurrent thoughts of suicide The nurse practitioner is reviewing the medical record of a 6-month-old infant with normocytic hemolytic anemia and notes an electrophoresis result of hemoglobin S with a 20% concentration of hemoglobin F (fetal hemoglobin). Which additional diagnosis is most likely? A.Aplastic anemia B.Hemolytic anemia C.Sickle cell anemia D.Thalassemia major - Answer: C. Sickle cell anemia A patient with normocytic hemolytic anemia who has electrophoresis results of hemoglobin S with a 20% concentration of hemoglobin F has sickle cell anemia. Electrophoresis is not used to diagnose hemolytic or aplastic anemia. Thalassemia major appears within the first 2 years of life and is associated with life-threatening anemia. Thalassemia major is associated with nonhemolytic, normocytic anemia. The nurse practitioner (NP) notices a gray ring on the edge of both irises of an 81-year-old female patient. The patient denies visual changes or pain. She reports that she has had the "ring" for many years. What would the clinical significance of this same finding be in a 35-year-old patient? A.The patient would have a higher risk of blindness. B.The patient should be evaluated for hyperlipidemia. C.The patient should be evaluated by an ophthalmologist. D.The patient should be evaluated for acute glaucoma. - Answer: B. The patient should be evaluated for hyperlipidemia. Arcus senilis is caused by lipid deposits deep in the edge of the cornea and is quite commonly present in older adults. However, since it can also appear earlier in life as a result of hypercholesterolemia, the NP should order a fasting lipid profile in patients younger than 40 years. The condition is not associated with visual changes, so referral to an ophthalmologist is unnecessary. A female multigravida patient who is at 34 weeks' gestation wants to know at what level her uterine fundus should be. The best answer is to advise the patient that her fundus is: A.Midway between the umbilicus and the lower ribs B.At the level of the umbilicus C.From 33 to 35 cm D.From 32 to 34 cm - Answer: C. From 33 to 35 cm After 20 weeks' gestation, fundal height in centimeters should measure approximately the same as the number of weeks of gestation. When evaluating the blood pressure on both the arms and the legs of an infant who has a diagnosis of coarctation of the aorta, which of the following is the expected finding? A.The systolic blood pressure is higher in the arms than in the legs. B.Only the diastolic blood pressure is higher in the legs than in the arms. C.The blood pressure is higher in the legs than the arms. D.The systolic blood pressure is lower in the arms than in the legs. - Answer: A. The systolic blood pressure is higher in the arms than in the legs. In coarctation of the aorta, blood pressure is higher in the arms than in the legs because of the narrowing in the aorta. Blood pressure must rise to get adequate blood flow to the lower extremities; therefore, the blood pressure above the coarctation rises to compensate for this [Show More]
Last updated: 9 months ago
Preview 5 out of 101 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:


BUNDLE: SARAH MICHELLE FNP Exams (From Actual Test) All Rated 100%
By PROF 9 months ago
$32.5
4
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 26, 2025
Number of pages
101
Written in
All
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 26, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
40
Scholarfriends.com Online Platform by Browsegrades Inc. 651N South Broad St, Middletown DE. United States.
We're available through e-mail, Twitter, and live chat.
FAQ
Questions? Leave a message!
Copyright © Scholarfriends · High quality services·