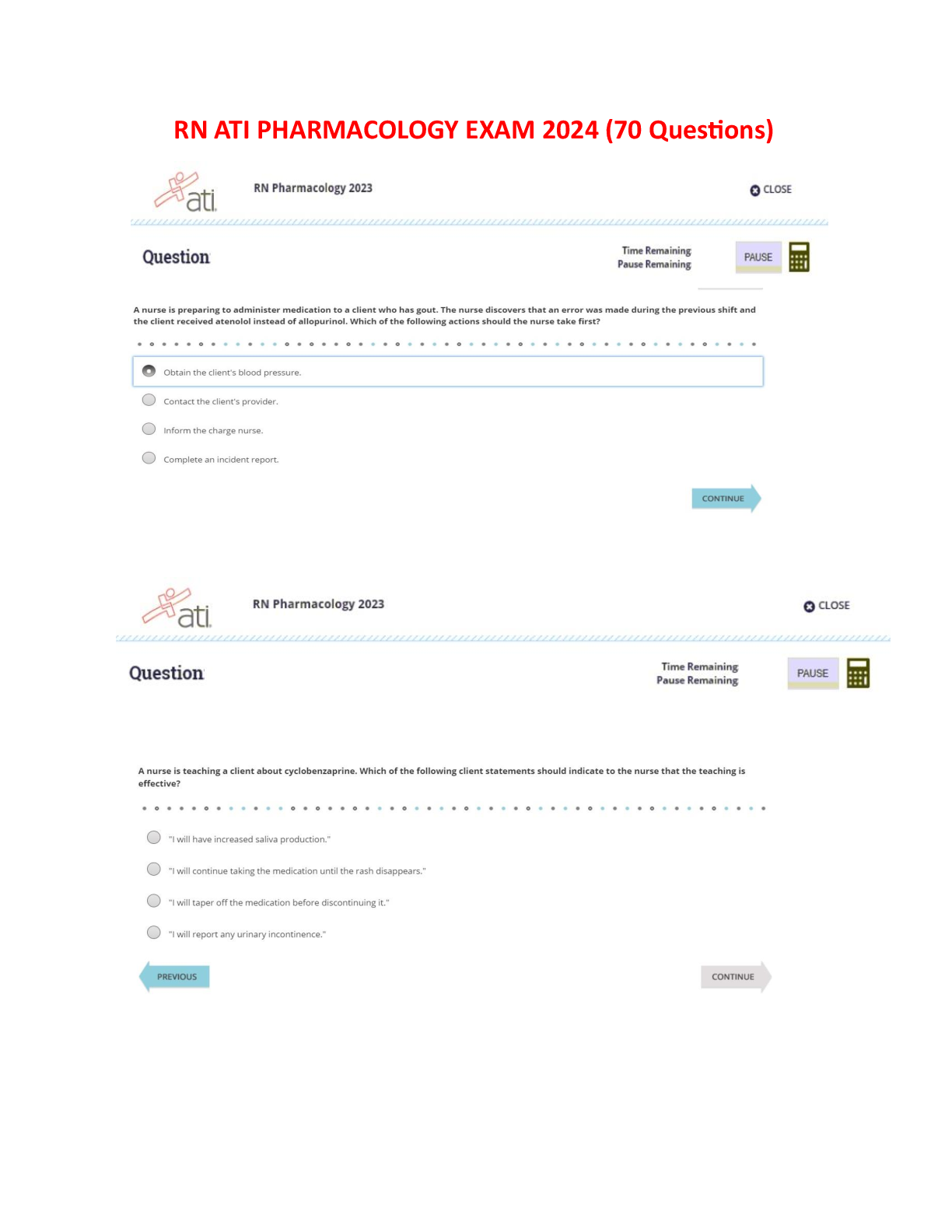
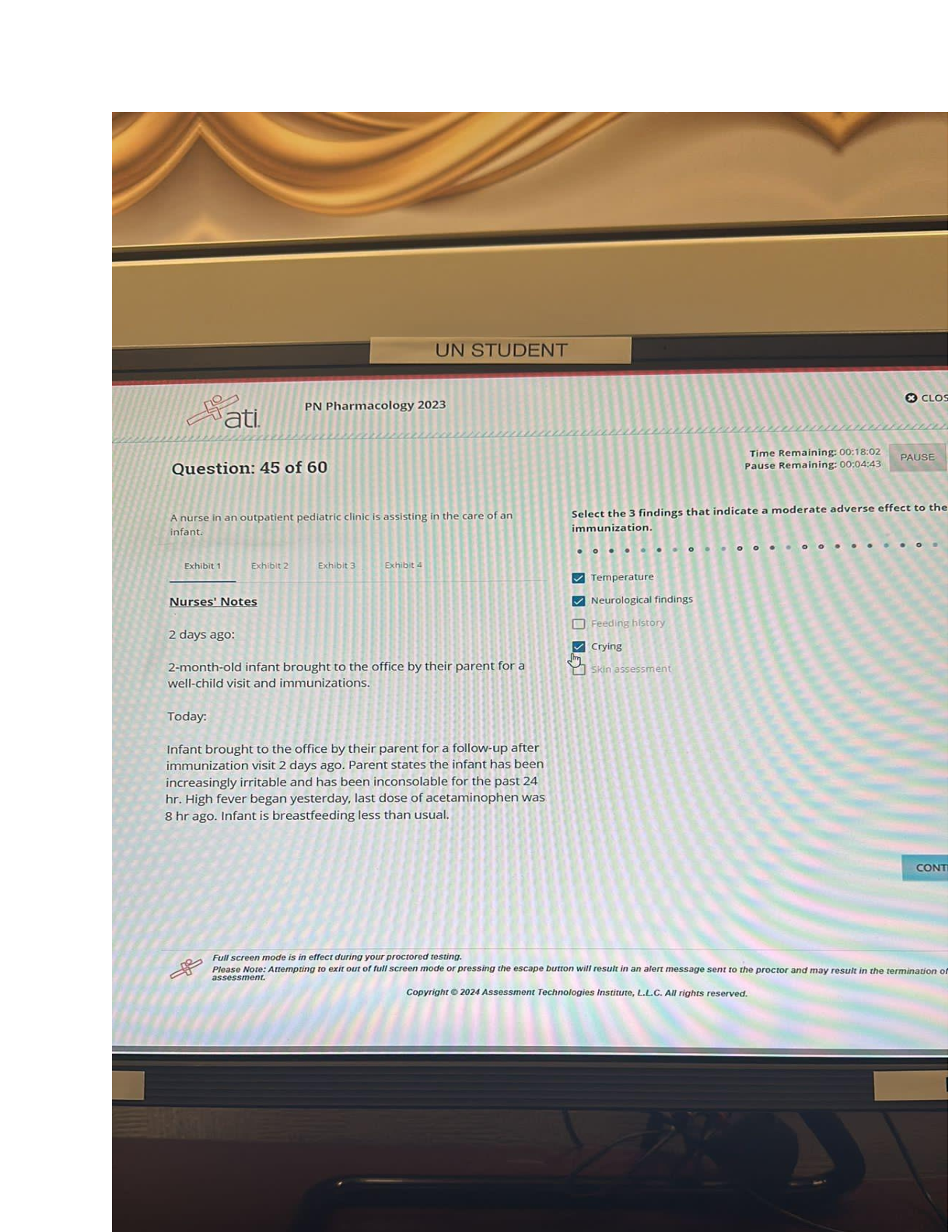
Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions: 1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) Gained more than 15 pounds (7kg) 3.) Had a full t
...
Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions: 1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) Gained more than 15 pounds (7kg) 3.) Had a full term pregnancy
4.) Had a second term abortion
When you use a diaphragm, you need to use spermicide with every act of coitus (withdrawal of penis from vagina prior to ejaculation). Every time you withdrawl, instill more spermicide
Diaphragm must stay inserted for 6hrs after act of coitus
Hormonal Contraceptives (Oral)
Side effects: Chest pain, SOB, Leg pain (from a possible clot), headache or eye problems (from a stroke or hypertension)
Contraindications: Women with a history of blood clots, stroke, cardiac problems, smoker, breast or estrogen related cancers (pill contains estrogen)
Depo-Provera/Medroxyprogesterone
Injectable progestin
Can cause decreased bone mineral density or loss of calcium
Nursing action: Ensure patient has adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
IUD
Increase risk for PID
Can cause uterine perforation or ectopic pregnancy (increases risk for ectopic pregnancy)
Look out for/Notify PCP:
Change in string length IUD is moving and not in the right place
Foul smelling vaginal discharge
Pain with intercourse
Fever/Chills (infection)
Infertility is defined as an inability to conceive desire engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse for a prolonged period of time or at least 12 months.
Common factors associated with infertility include:
Decreased sperm production (Sperm analysis)
Endometriosis
Ovulation disorders
Tubal occlusions If you test and use DYE (used in the fallopian tubes), make sure the woman is not allergic to iodine or shellfish/seafood
Video #2: Signs of Pregnancy
Presumptive: Can be defined by things/reasons other than pregnancy
Amenorrhea Can be anorexic or exercising too much
Fatigue Didn’t sleep well
Nausea/Vomiting Sick
Urinary Frequency UTI
Quickening/Fluttering in stomach Gas
Probable: Changes that make the examiner suspect a woman is pregnant (primarily related to physical changes of the uterus).
Abdominal enlargement: Related to changes in uterine size, shape, and position
Hegar’s Sign: Softening and compressibility of the lower uterus
Chadwick’s Sign: Deepend violet bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa
Goodell’s Sign: Softening of cervical tip
Ballottement: Rebound of unengaged uterus
Braxton Hicks Contractions: False contractions that are painless, irregular, and usually relieved by walking
Positive Pregnancy Test: Woman’s hormonal level may not be normal
Fetal Outline:
Positive: Very distinct things.
Fetal Heart Sounds
Fetal Heart Beat can be heard
Can see the baby with ultrasound
Can feel movement in the uterus
Naegele’s Rule: LMP – 3 months + 7 days + 1 year Cathy’s Rule: + 9 months + 1 week
Know how to find out GTPAL numbers
G= Gravidity (# of times a woman has been pregnant PLUS current pregnancy) T= Term Births (How many baby’s were delievered at term 38 WEEKS OR MORE) P= Preterm Births (Below 38 weeks)
A= Abortion (spontaneous or not) or miscarriages
L= Living children
Video #3: Weight Gain & Nutrition During Pregnancy AND Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy
Weight Gain & Nutrition
Normal weight gain = 25- 35 pounds
Overweight person weight gain = 15- 25 pounds
Underweight person weight gain = 28-40 pounds
During 1st trimester A woman should only gain 1-2 kg (2-4 pounds); A woman should not gain 1 pound per week.
During 2nd trimester 1 pound per week is normal; increase caloric intake by 340 calories per day
During 3rd trimester 1 pound per week is normal ; increase caloric intake by 450 calories per day
If you are breastfeeding after pregnancy You still need to eat an extra 300-400 calories per day
Intake of FOLIC ACID Helps prevent Neural Tube Defects (NTD) Sources: dark green leafy veggies; orange juice
Women should increase their fluid intake to 2-3L per day
Women should limit their caffeine intake to 300 mg per day
No amount of alcohol is okay
Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy Noninvasive = Full Bladder
Invasive = Empty Bladder
Ultrasound Bladder should be full to help sound waves resonate better
Amniocentesis Bladder should be empty
Biophysical Profile (BPP): Scored from 0-10
Score between 8-10 Healthy Baby
Tests Measures 5 things
Reactive HR (0/2)
Breathing (0/2)
Body Movement (0/2)
Fetal Tone (0/2)
Amniotic Fluid Volume (0/2)
Non-Stress Test (NST)
Non-invasive
[Show More]





.png)