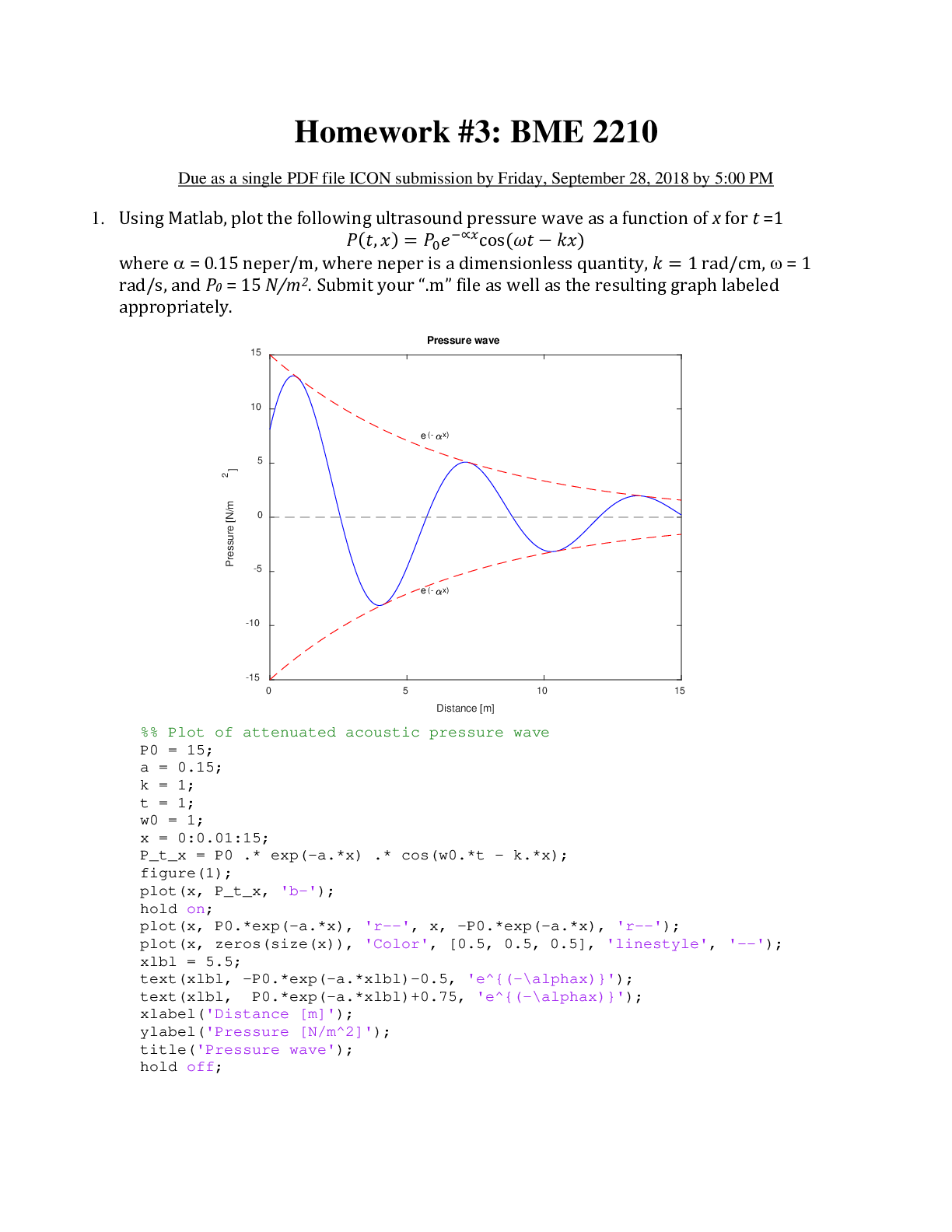
Questions and Answers. Biology 237 AnP help. A+
Document Content and Description Below
1. 1) binds to receptors on the sarcolemma Which of the following is released into the neuromuscular junction to bind to receptors on the sarcolemma? Student Response Value Correct Answer 1.... Ca+2 0% 2. ACH 100% 3. K+ 0% 4. Na+ 0% Score: 0.07/0.07 2. 10) White vs. red In comparing White fibers and Red fibers, which selection would best describe White fibers: Student Response Value Correct Answer 1. Utilized fats as well as glucose, depends on aerobic metabolism, smaller in diameter, used for endurance 2. Stores glycogen for conversion to glucose, depends on anaerobic metabolism, larger in diameter, used for speed and strength 3. 11) energy The first 15 seconds of anerobic contractions rely on _____ for energy. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Phosphagen system 2. Glycolysis 3. Aerobic metabolism 4. 12) plantarflexion What muscle plantar-flexes the foot? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Tibialis anterior 2. Extensor digitorum longus 3. Gastrocnemius 4. Fibularis (peroneus) longus 5. Both 3 and 4 5. 13) fixator What muscle fixates the foot in a plantar flexed position during standing? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Tibialis anterior 2. Extensor digitorum longus 3. Gastrocnemius 4. Fibularis (peroneus) longus 5. Soleus 6. 14) soleus The soleus would rely on mostly ____ motor units with predominantly _____ fibers. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Large, white 2. Large, red 3. Small, white 4. Small, red 7. 15) knee fixation Which muscle fixes the knee in an extended position? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus maximus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Gracilis 8. 16) thigh fixation Which muscle fixes the thigh in an extended position? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus maximus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Iliopsoas 9. 17) thigh extension Which muscle is the antagonist of the gluteus maximus? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus minimus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Iliopsoas 10. 18) anterior movement of femur against tibia The ligament responsible for preventing anterior movement of the femur against the tibia is _____. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Anterior cruciate 2. Posterior cruciate 3. Medial collateral 4. Lateral collateral Score: 0/0.07 11. 19) lateral epicondylitis The origin of the _____ is inflammed in lateral epicondylitis. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Flexor digitorum superficialis 2. Extensor carpi radialis longus 3. Flexor retinaculum 4. Medial collateral ligament Score: 0/0.07 12. 2) results from ligand stimulation of the sarcolemma Immediately after, and as a result of, the neurotransmitter making contact with receptors on the sarcolemma: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Calcium is released into the sarcoplasm. 2. An action potential is produced on the sarcolemma. 3. K+ gates open causing K+ to leave the cell. 4. Na+ gates open causing Na+ to enter the muscle cell. Score: 0/0.07 13. 20) melanocytes Melanocytes are part of which layer? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Stratum basale 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum Score: 0/0.07 14. 21) Pituitary gland Which of the following contains the pituitary gland? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. lacrimal fossa 2. crista galli 3. sella turcica 4. glenoid fossa Score: 0.07/0.07 15. 22) bone 1 Which of the following does not articulate with any other bone? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sacrum 2. atlas 3. hyoid bone 4. clavicle Score: 0.07/0.07 16. 23) small canals Extremely small passages that connect the lacunae to each other in bone tissue are called: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. canaliculi 2. Volkmann's canals 3. Sharpey's fibers 4. trabeculae Score: 0/0.07 17. 24) hormone 1 This hormone, present in both males and females, is important for bone maintenance and remodeling. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. parathyroid hormone 2. thyroxine 3. estrogen 4. testosterone 5. calcitonin Score: 0/0.07 18. 25) first stage of bone repair What is the first stage of repair in simple fractures? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. hematoma 2. fibrocartilage formation 3. bony callus 4. remodeled bone Score: 0.07/0.07 19. 26) elastic cartilage Where in the body can you find elastic cartilage? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. articular cartilage 2. costal cartilage 3. intervertebral disks 4. menisci of knee 5. outer ear Score: 0.07/0.07 20. 27) large canals Canals that lie at right angles to the long axis of the bone and connect the blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to the central canal and medullary cavity are known as: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. canaliculi 2. Volkmann's canals 3. Sharpey's fibers 4. trabeculae Score: 0.07/0.07 21. 28) Patellar ligament The patellar ligament connect the patella to the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. rectus femoris muscle 2. tibial tuberosity 3. calcaneus 4. fibula Score: 0/0.07 22. 29) rectus femoris action The rectus femoris acts to move the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. patella 2. tibial tuberosity 3. calcaneus 4. fibula Score: 0/0.07 23. 3) produce an action potential on the sarcolemma Depolarization must reach the ___ in order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. chemically-gated Na+ channels. 2. voltage-gated Na+ channels. 3. chemically-gated K+ channels. 4. voltage gated Ca+2 channels. Score: 0/0.07 24. 30) autoimmune disease The autoimmune disease in which the immune system cells release chemicals which attack the joint tissues and cause severe inflammation is called: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. gouty arthritis 2. rheumatoid arthritis 3. osteoarthritis 4. inflammatory arthritis Score: 0/0.07 25. 31) joint injury What is the name of the joint injury in which the bone becomes dislocated from its position in the socket of the joint? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sprain 2. strain 3. luxation 4. separation Score: 0/0.07 26. 32) mucous membranes Which type of muscle is found in layers of the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive systems? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. cardiac muscle 2. skeletal muscle 3. single unit smooth muscle 4. multiunit smooth muscle Score: 0/0.07 27. 33) cardiac muscle Cardiac muscle cells allow an impulse to pass through the entire network of cells due to their: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. intercalated disks 2. gap junctions 3. canaliculi 4. Sharpey's fibers Score: 0/0.07 28. 34) insulation and shock absorption The tissue important in insulation and shock absorption is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. dense irregular 2. dense regular 3. adipose 4. areolar Score: 0/0.07 29. 35) feedback In order for a process to be self-regulated it would use: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. negative feedback 2. positive feedback 3. no feedback Score: 0.08/0.08 30. 36) adipose Adipose tissue located in the ___ would be used to determine nutritional condition at time of death. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. red marrow 2. yellow marrow 3. subcutaneous 4. mesenteries Score: 0.08/0.08 31. 37) calcium supplements Calcium supplements would not be advised in the early treatment of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. post-menopausal osteoporosis 2. senile osteoporosis 32. 38) head flexion Which muscles are the agonist and antagonist for head flexion? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. trapezius-sternocleidomastoid 2. splenius capitus-sternocleidomastoid 3. scalenes-sternocleidomastoid 4. sternocleidomastoid-splenius capitus Score: 0/0.08 33. 39) head rotation Head rotation is the result of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sternocleidomastoid muscles working unilaterally. 2. sternocleidomastoid muscles working bilaterally. Score: 8 34. 4) action potential travels to the: The action potential travels to the _____ to enter the muscle cell. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. T-tubules 2. sarcoplasmic reticulum 3. troponin 4. tropomyosin Score: 35. 40) shoulder abduction Which muscles are the agonist and antagonist for shoulder abduction? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Trapezius, rhomboid major and minor 2. Deltoid, pectoralis major 3. Pectoralis major, pectoralis minor 4. Deltoid, supraspinatus 5. Latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major Score: 0.08/0.08 36. 41) rotator cuff Which muscle is NOT a member of the rotator cuff? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Teres major 2. supraspinatus 3. infraspinatus 4. subscapularis Score: 0/0.08 37. 5) blocks active sites on actin A complex composed of which molecules blocks the active sites of actin, preventing crossbridge formation? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. tropomyosin-troponin 2. myosin-troponin 3. myosin-titin 4. tropomyosin-titin Score: 38. 6) ATP taken up At what point is ATP taken up from the sarcoplasm? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Reset of the myosin heads 2. Formation of actin myosin crossbridges 3. Swiveling of the myosin heads (the working stroke) 4. Detachment of myosin heads from actin. Score: 39. 7) graded contractions What type of graded contractions is seen here? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. quantal summation 100% 2. frequency summation 0% Score: 0.08/0.08 40. 8) graded contractions What is the cause of the response seen here: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. More motor units responding with each stimulus 2. A given set of muscle cells responding repeatedly without relaxing Score: 0.08/0.08 41. 9) creatine phosphate Which of the following is true about creatine phosphate: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. It is produced from ATP and creatine during periods of rest. 2. It must be reconverted to ATP during muscle contraction. 3. It can provide for an additional 1 to 1.5 minutes of intense muscle contraction 4. It increases muscle strength 5. Answers 1 and 2 only. Score: 0.08/0.08 1) binds to receptors on the sarcolemma Which of the following is released into the neuromuscular junction to bind to receptors on the sarcolemma? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Ca+2 2. ACH 3. K+ 4. Na+ Score: 0.07/0.07 2. 10) White vs. red In comparing White fibers and Red fibers, which selection would best describe White fibers: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Utilized fats as well as glucose, depends on aerobic metabolism, smaller in diameter, used for endurance 2. Stores glycogen for conversion to glucose, depends on anaerobic metabolism, larger in diameter, used for speed and strength Score: 0.07/0.07 3. 11) energy The first 15 seconds of anerobic contractions rely on _____ for energy. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Phosphagen system 2. Glycolysis 3. Aerobic metabolism Score: 0.07/0.07 4. 12) plantarflexion What muscle plantar-flexes the foot? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Tibialis anterior 2. Extensor digitorum longus 3. Gastrocnemius 4. Fibularis (peroneus) longus 5. Both 3 and 4 Score: 0.07/0.07 5. 13) fixator What muscle fixates the foot in a plantar flexed position during standing? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Tibialis anterior 2. Extensor digitorum longus 3. Gastrocnemius 4. Fibularis (peroneus) longus 5. Soleus Score: 0.07/0.07 6. 14) soleus The soleus would rely on mostly ____ motor units with predominantly _____ fibers. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Large, white 2. Large, red 3. Small, white 4. Small, red Score: 0.07/0.07 7. 15) knee fixation Which muscle fixes the knee in an extended position? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus maximus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Gracilis Score: 0.07/0.07 8. 16) thigh fixation Which muscle fixes the thigh in an extended position? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus maximus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Iliopsoas Score: 0.07/0.07 9. 17) thigh extension Which muscle is the antagonist of the gluteus maximus? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Gluteus minimus 2. Biceps femoris 3. Rectus femoris 4. Iliopsoas Score: 0.07/0.07 10. 18) anterior movement of femur against tibia The ligament responsible for preventing anterior movement of the femur against the tibia is _____. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Anterior cruciate 2. Posterior cruciate 3. Medial collateral 4. Lateral collateral Score: 0.07/0.07 11. 19) lateral epicondylitis The origin of the _____ is inflammed in lateral epicondylitis. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Flexor digitorum superficialis 2. Extensor carpi radialis longus 3. Flexor retinaculum 4. Medial collateral ligament Score: 0.07/0.07 12. 2) results from ligand stimulation of the sarcolemma Immediately after, and as a result of, the neurotransmitter making contact with receptors on the sarcolemma: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Calcium is released into the sarcoplasm. 2. An action potential is produced on the sarcolemma. 3. K+ gates open causing K+ to leave the cell. 4. Na+ gates open causing Na+ to enter the muscle cell. Score: 0.07/0.07 13. 20) melanocytes Melanocytes are part of which layer? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Stratum basale 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum Score: 0.07/0.07 14. 21) Pituitary gland Which of the following contains the pituitary gland? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. lacrimal fossa 2. crista galli 3. sella turcica 4. glenoid fossa Score: 0.07/0.07 15. 22) bone 1 Which of the following does not articulate with any other bone? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sacrum 2. atlas 3. hyoid bone 4. clavicle Score: 0.07/0.07 23) small canals Extremely small passages that connect the lacunae to each other in bone tissue are called: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. canaliculi 2. Volkmann's canals 3. Sharpey's fibers 4. trabeculae Score: 0.07/0.07 17. 24) hormone 1 This hormone, present in both males and females, is important for bone maintenance and remodeling. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. parathyroid hormone 2. thyroxine 3. estrogen 4. testosterone 5. calcitonin 18. 25) first stage of bone repair What is the first stage of repair in simple fractures? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. hematoma 2. fibrocartilage formation 3. bony callus 4. remodeled bone 26) elastic cartilage Where in the body can you find elastic cartilage? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. articular cartilage 2. costal cartilage 3. intervertebral disks 4. menisci of knee 5. outer ear 27) large canals Canals that lie at right angles to the long axis of the bone and connect the blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to the central canal and medullary cavity are known as: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. canaliculi 2. Volkmann's canals 3. Sharpey's fibers 4. trabeculae Score: 0.07/0.07 21. 28) Patellar ligament The patellar ligament connect the patella to the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. rectus femoris muscle 2. tibial tuberosity 3. calcaneus 4. fibula Score: 0.07/0.07 22. 29) rectus femoris action The rectus femoris acts to move the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. patella 2. tibial tuberosity 3. calcaneus 4. fibula Score: 0.07/0.07 23. 3) produce an action potential on the sarcolemma Depolarization must reach the ___ in order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. chemically-gated Na+ channels. 2. voltage-gated Na+ channels. 3. chemically-gated K+ channels. 4. voltage gated Ca+2 channels. Score: 0.07/0.07 24. 30) autoimmune disease The autoimmune disease in which the immune system cells release chemicals which attack the joint tissues and cause severe inflammation is called: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. gouty arthritis 2. rheumatoid arthritis 3. osteoarthritis 4. inflammatory arthritis Score: 0.07/0.07 25. 31) joint injury What is the name of the joint injury in which the bone becomes dislocated from its position in the socket of the joint? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sprain 2. strain 3. luxation 4. separation Score: 0.07/0.07 26. 32) mucous membranes Which type of muscle is found in layers of the mucous membranes of the respiratory and digestive systems? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. cardiac muscle 2. skeletal muscle 3. single unit smooth muscle 4. multiunit smooth muscle Score: 0.07/0.07 27. 33) cardiac muscle Cardiac muscle cells allow an impulse to pass through the entire network of cells due to their: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. intercalated disks 2. gap junctions 3. canaliculi 4. Sharpey's fibers Score: 0.07/0.07 28. 34) insulation and shock absorption The tissue important in insulation and shock absorption is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. dense irregular 2. dense regular 3. adipose 4. areolar Score: 29. 35) feedback In order for a process to be self-regulated it would use: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. negative feedback 2. positive feedback 3. no feedback Score: 0.08/0.08 30. 36) adipose Adipose tissue located in the ___ would be used to determine nutritional condition at time of death. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. red marrow 2. yellow marrow 3. subcutaneous 4. mesenteries Score: 0.08/0.08 31. 37) calcium supplements Calcium supplements would not be advised in the early treatment of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. post-menopausal osteoporosis 2. senile osteoporosis Score: 32. 38) head flexion Which muscles are the agonist and antagonist for head flexion? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. trapezius-sternocleidomastoid 2. splenius capitus-sternocleidomastoid 3. scalenes-sternocleidomastoid 4. sternocleidomastoid-splenius capitus Score: 0.08/0.08 33. 39) head rotation Head rotation is the result of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. sternocleidomastoid muscles working unilaterally. 2. sternocleidomastoid muscles working bilaterally. Score: 0.08/0.08 34. 4) action potential travels to the: The action potential travels to the _____ to enter the muscle cell. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. T-tubules 2. sarcoplasmic reticulum 3. troponin 4. tropomyosin Score: 0.08/0.08 35. 40) shoulder abduction Which muscles are the agonist and antagonist for shoulder abduction? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Trapezius, rhomboid major and minor 2. Deltoid, pectoralis major 3. Pectoralis major, pectoralis minor 4. Deltoid, supraspinatus 5. Latissimus dorsi, pectoralis major Score: 0.08/0.08 36. 41) rotator cuff Which muscle is NOT a member of the rotator cuff? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Teres major 2. supraspinatus 3. infraspinatus 4. subscapularis Score: 0.08/0.08 37. 5) blocks active sites on actin A complex composed of which molecules blocks the active sites of actin, preventing crossbridge formation? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. tropomyosin-troponin 2. myosin-troponin 3. myosin-titin 4. tropomyosin-titin Score: 0.08/0.08 38. 6) ATP taken up At what point is ATP taken up from the sarcoplasm? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Reset of the myosin heads 2. Formation of actin myosin crossbridges 3. Swiveling of the myosin heads (the working stroke) 4. Detachment of myosin heads from actin. Score: 39. 7) graded contractions What type of graded contractions is seen here? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. quantal summation 2. frequency summation Score: 0.08/0.08 41. 9) creatine phosphate Which of the following is true about creatine phosphate: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. It is produced from ATP and creatine during periods of rest. 0% 2. It must be reconverted to ATP during muscle contraction. 3. It can provide for an additional 1 to 1.5 minutes of intense muscle contraction 4. It increases muscle strength 5. Answers 1 and 2 only. Score: 0.08/0.08 1. the distal epiphyseal plate The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. 1.5 to 2 years after birth B. late teens C. early twenties D. birth Score: 0/1 2. paranasal sinuses 1 Which of these is NOT one of the paranasal sinuses? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. frontal sinus 2. sphenoid sinus 3. maxillary sinus 4. ethmoid sinus 5. mastoid sinus Score: 1/1 3. nasal cavity The primary bone which forms the nasal cavity is the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. nasal bone 2. ethmoid bone 3. sphenoid bone 4. vomer bone Score: 1/1 4. os coxae The three bones of the os coxae come together at the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. glenoid fossa 2. pubic symphysis 3. acetabulum 4. coccyx Score: 1/1 5. symphysis pubis The symphysis pubis is composed of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. hyaline cartilage B. fibrous connective tissue C. fibrocartilage D. areolar tissue Score: 1/1 6. The first cell in bone remodeling The cell which acts first in the process of remodeling in adult bone: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. osteoclast B. osteoblast C. osteocyte D. mesenchyme cell Score: 1/1 7. Bone characteristics 1 The component responsible for the hardness and rigidity of bone is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. hydroxyapatite 2. proteoglycans 3. collagen fibers 4. keratin 5. Sharpey's fibers. Score: 1/1 8. bone hormones 2 The hormone which is thought to stimulate uptake of calcium into bone tissue in children: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. calcitonin B. Vitamin D3 C. growth hormone D. estrogen E. parathyroid hormone (PTH) Score: 0/1 9. bone hormones 6 This hormone stimulates osteoclastic activity. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. calcitonin B. Vitamin D3 C. growth hormone D. estrogen E. parathyroid hormone (PTH) Score: 1/1 10. Ossification 3 The frontal bone ossifies from pre-existing model of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. hyaline cartilage B. fibrous connective tissue C. fibrocartilage D. areolar tissue Score: 1/1 11. Osteoporosis 2 Post-menopausal osteoporosis is characterized by ___ parathyroid hormone in the blood. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Higher than normal 2. Lower than normal Score: 0/1 14. 15. skin cancer 1 The most agressive skin cancer is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. malignant melanoma B. squamous cell carcinoma C. basal cell carcinoma Score: 1/1 16. skin 1 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. The sebacous gland A sudoriferous gland A dermal papilla A pacinian corpuscle The hypodermis B D C A E Statement The sebacous gland A sudoriferous gland A dermal papilla A pacinian corpuscle The hypodermis Score: 17. skin 3 Non-keratinized skin is found in the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Outer covering of the body. 2. Lining of the mouth. 3. Lining of the vagina. 4. All of the above except A. Score: 1/1 18. glands and receptors 1 Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. eccrine glands 100% B. apocrine glands 0% C. sebaceous glands 0% D. Meissner's corpuscles 0% E. Pacinian corpuscles 0% Score: 0/1 19. Epidermis 1 Match descriptions with letters in the diagram. The layer containing most glands and receptors The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain condensed keratin granules. Statement Response Value Correct Match The layer containing most glands and receptors D The layer which constantly exfoliates. A Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. B This layer undergoes constant mitosis. E Its cells contain condensed keratin granules. C Score: 20. Areolar tissue 2 Match letters with descriptions. A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber Statement A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber Score: 21. cartilage 3 The least common of the following tissues is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. hyaline cartilage 2. fibrocartilage 3. elastic cartilage 4. dense regular connective tissue Score: 1/1 22. cell structure 2 When tissue wraps to form a tubule the ___ surface is toward the lumen. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. apical 2. basal Score: 1/1 23. cell junctions 1 Match the junction with its description. gap junction hemidesmosome desmosome tight junctions zona adherens also known as macula adherens, these prevent cells in the epidermis and other tissues from pulling apart these connect epithelium to its basement membrane these are small junctions for attaching cells together osteocytes use this to exchange calcium ions block or partially block the transport of molecules between cells in a semipermeable membrane Statement Response Value Correct Match gap junction hemidesmosome desmosome tight junctions zona adherens Score: 0/1 24. connective tissue components 2 The component of connective tissues responsible for maintaining hydration is: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. cells and fibers 2. proteoglycans 3. inorganic materials 4. hydroxyapatite Score: 0/1 25. Connective tissues 1 Match tissues with descriptions areolar tissue adipose tissue dense regular dense irregular reticular connective tissue elastic connective tissue B E F C A D Score: 2.5/2.5 26. feedback 2 A process which controls a parameter within a narrow range will utilize: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. Negative feedback B. Positive feedback C. Neural controls D. Hormonal Controls Score: 27. vertebral arch The portion of the vertebral arch between the spinous process and the transverse process is called the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. pedicle 2. lamina 3. rostrum 4. crista galli 5. cribriform plate Score: 28. scar tissue Scar tissue is the repair seen in: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. bone 2. areolar tissue 3. tendons and ligaments 4. all of these 5. Answers B and C only. Score: 1/1 29. Epithelial tissues 1 Match the tissue with the description. Found in capillary walls The primary lining of the GI tract The lining of the urinary tract The primary cell type found in glands The lining of the trachea The epidermis of the skin D C A F B E Statement Found in capillary walls The primary lining of the GI tract The lining of the urinary tract The primary cell type found in glands The lining of the trachea The epidermis of the skin Score: 30. Bone Tissue 1 Match the letters with descriptions This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect A C D B Statement This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect Score: 31. 1) binds to receptors on the sarcolemma Which of the following is released into the neuromuscular junction to bind to receptors on the sarcolemma? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Ca+2 2. ACH 3. K+ 4. Na+ Score: 1/1 32. 10) White vs. red In comparing White fibers and Red fibers, which selection would best describe White fibers: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. Utilized fats as well as glucose, depends on aerobic metabolism, smaller in diameter, used for endurance 2. Stores glycogen for conversion to glucose, depends on anaerobic metabolism, larger in diameter, used for speed and strength Score: 1/1 33. 23) small canals Extremely small passages that connect the lacunae to each other in bone tissue are called: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. canaliculi 2. Volkmann's canals 3. Sharpey's fibers 4. trabeculae Score: 1/1 34. 37) calcium supplements Calcium supplements would not be advised in the early treatment of: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. post-menopausal osteoporosis 2. senile osteoporosis Score: 1/1 35. 26) elastic cartilage Where in the body can you find elastic cartilage? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. articular cartilage 2. costal cartilage 3. intervertebral disks 4. menisci of knee 5. outer ear Score: 1/1 36. 36) adipose Adipose tissue located in the ___ would be used to determine nutritional condition at time of death. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. red marrow 2. yellow marrow 3. subcutaneous 4. mesenteries Score: 1/1 37. 4) action potential travels to the: The action potential travels to the _____ to enter the muscle cell. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. T-tubules 2. sarcoplasmic reticulum 3. troponin 4. tropomyosin Score: 1/1 38. Chemically gated Na<sup>+</sup> channels open. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma out of the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 39. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0/1 41. action potential 5 This is the polarity at which the voltage-gated sodium channels close and the potassium channels open. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. A 0% 2. B 0% 3. C 100% 4. D 0% 5. E 0% 6. F 0% 7. G 0% Score: 0/1 42. action potential 4 This is the polarity at which the voltage-gated sodium channels open. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. A 100% 2. B 0% 3. C 0% 4. D 0% 5. E 0% 6. F 0% 7. G 0% Score: 43. connective tissues a The connective tissue surrounding each muscle cell is the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. epimysium 2. perimysium 3. endomysium Score: 1/1 44. extraocular and lumbricals The extraoptical and lumbrical muscles would have which of the following in common: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. both are important postural muscles 2. both have very large motor units (many cells) 3. both are composed primarily of slow twitch red fibers. 4. both utilize primarily aerobic metabolism 5. none of the above Score: 1/1 45. forced inspiration The sternocleidomastoid and scalenes work together with the _____to raise and expand the ribcage in forced inspiration. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. pectoralis major 2. pectoralis minor 3. teres major 4. teres minor Score: 1/1 46. binds calcium 1 Which of the following binds calcium ions: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. sarcoplasmic reticulum 50% B. troponin C 50% C. myosin 0% D. all of the above 0% E. 1 and 2, but not 3 100% Score: 1/1 47. ion movement 2 In response to acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors, _____ flows across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. Na+ 100% B. K+ 0% C. Ca+2 0% D. ACh 0% Score: 1/1 48. latissimus dorsi 4 The latissimus dorsi and teres major act antagonistically to the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. deltoid 2. supraspinatus 3. all members of the rotator cuff muscle group 4. Deltoid and supraspinatus muscles only. Score: 1/1 49. muscle cell types A White fibers have: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. abundant myoglobin 2. a rich blood supply 3. many mitochondria 4. stored glycogen 5. All of the above 6. Answers A, B, and C only Score: 50. muscle cell types 2 Slow twitch red fibers primarily utilize _____ to provide energy for metabolism. Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. the phosphagen system 2. anerobic glycolysis 3. aerobic metabolism 4. all of the above 5. answers A and B only Score: 51. muscle movements 4B The agonist for plantar flexion inserts on the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. flexor retinaculum 2. dorsal retinaculum 3. calcaneus tendon 4. patellar tendon 5. iliotibial tract Score: 1/1 52. muscle movements 3CC The prime mover in the movement shown as C is the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. erector spinae 2. rectus abdominus 3. sternocleidomastoid 4. gluteus maximus 5. iliopsoas Score: 0/1 53. muscle movements 5A The muscle in red, acting bilaterally, would be the agonist in: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. head extension 2. head flexion 3. head rotation Score: 0/1 54. muscle movements 4A Given: the muscle colored green is the agonist. What movement would occur at the ankle joint? Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. dorsiflexion 2. plantar flexion Score: 1/1 55. muscle movements 1AA The prime mover in movement A is the: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. biceps femoris 100% 2. gastrocnemius 50% 3. soleus 0% 4. sartorius 0% 5. gracilis 0% Score: 56. muscle types 3 The type of muscle which contains myogenic cells: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback A. skeletal muscle B. cardiac muscle C. smooth muscle D. Both 1 and 2 E. Both 2 and 3 Score: 1/1 57. summation A1 The diagram shows: Student Response Value Correct Answer Feedback 1. quantal summation 2. frequency summation 3. tetany 4. treppe Score: 1/1 1. The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: A. osteoclast B. osteoblast C. osteocyte D. mesenchyme cell 2. The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: A. osteoclast B. osteoblast C. osteocyte D. mesenchyme cell 3. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: A. mesenchyme cells B. monocytes C. osteoprogenitor cells D. all of the above E. Answers 1 and 2 only. 4. The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: Student Response A. 1.5 to 2 years after birth B. late teens C. early twenties D. birth Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Cranial bones start out as a: Student Response A. hyaline cartilage plate B. fibrous connective tissue membrane C. membrane of areolar and dense irregular tissue. D. membrane of stratified squamous epithelium Score: 0.5/0.5 6. There are _____ pair of ribs. Student Response A. 7 B. 5 C. 12 D. 10 Score: 0.5/0.5 7. The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: Student Response A. calcitonin B. parathyroid hormone C. estrogen D. growth hormone E. Vitamin D3 Score: 0.5/0.5 8. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: Student Response A. Sharpey's fibers B. red marrow C. yellow marrow D. periosteum Score: 0.5/0.5 9. The first location of ossification in long bones is the: Student Response A. diaphysis bone collar B. epiphyseal plate C. proximal epiphysis D. distal epiphysis Score: 0.5/0.5 10. All ribs articulate with the: Student Response A. thoracic vertebrae B. sternum C. lumbar vertebrae D. Both answers 1 and 2 Score: 0.5/0.5 11. Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus Statement Response Value Frontal Sinus A Ethmoid sinus B Sphenoid sinus C Maxillary sinus D Mastoid sinus C Score: 1. The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. Student Response A. sella turcica, sphenoid bone B. sella turcica, ethmoid bone C. cribriform plate, ethmoid bone D. cribriform plate, sphenoid bone Score: 0.5/0.5 2. Spongy bone lacks: Student Response A. osteocytes B. lacunae C. blood vessels D. Haversian systems Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: Student Response Value A. osteoclast B. osteoblast C. osteocyte D. mesenchyme cell Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: Student Response Value A. external callus of bone B. bud of new blood vessels C. hematoma D. internal callus Score: 0.5/0.5 5. The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: Student Response Value A. bone collar B. epiphyseal plate C. medullary canal D. trochanter Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: Student Response Value A. Sharpey's fibers B. red marrow C. yellow marrow D. periosteum Score: 0.5/0.5 7. All ribs articulate with the: Student Response Value A. thoracic vertebrae B. sternum C. lumbar vertebrae D. Both answers 1 and 2 Score: 0.5/0.5 8. The first location of ossification in long bones is the: Student Response A. diaphysis bone collar B. epiphyseal plate C. proximal epiphysis D. distal epiphysis Score: 0.5/0.5 9. The large anterior fontanel hardens at: Student Response A. 1.5 to 2 years after birth B. late teens C. early twenties D. birth Score: 0.5/0.5 10. Both cartilage and bone possess: Student Response A. lacunae B. a basement membrane C. canaliculi D. internal blood vessels Score: 0.5/0.5 Total score: 10.05/10.05 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10.05 1. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Student Response A. epimysium B. perimysium C. endomysium D. retinaculum Score: 0.67/0.67 2. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? Student Response A. rheumatoid arthritis B. osteoarthritis C. bursitis D. gouty arhtritis Score: 0.67/0.67 3. The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: Student Response A. skeletal muscle B. cardiac muscle C. smooth muscle D. Both 1 and 2 E. Both 2 and 3 Score: 0.67/0.67 4. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. Student Response A. tendon B. ligament C. aponeurosis D. retinaculum Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: Student Response A. rheumatoid arthritis B. osteoarthritis C. bursitis D. gouty arthritis Score: 0.67/0.67 6. The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Student Response A. contractility B. excitability C. elasticity D. extensibility Score: 0.67/0.67 7. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. Student Response A. myosin B. actin C. titin D. collagen E. elastin Score: 0.67/0.67 8. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: Student Response A. serous membrane B. a ligament C. a retinaculum D. synovial membrane Score: 0.67/0.67 9. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. Student Response A. medial and lateral collateral ligaments B. medial and lateral retinacula C. medial and lateral menisci D. anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments Score: 0.67/0.67 10. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Student Response A. Ca+2 B. ATP C. ADP and Pi D. ACh Score: 0.67/0.67 11. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? Student Response A. fibrous B. cartilaginous C. synovial Score: 0.67/0.67 12. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Student Response A. AChase B. Ca+2 C. Na+ D. K+ Score: 0.67/0.67 13. In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Student Response A. myofilaments B. myofibrils C. myofibers D. myosin Score: 0.67/0.67 14. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: Student Response A. single unit smooth muscle B. multi-unit smooth muscle C. sphincter muscle Score: 0.67/0.67 15. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. Student Response A. flexion B. extension C. abduction D. adduction Score: 0.67/0.67 View Attempt 1 of 3 Title: Quiz #5 - Stimulus-Contraction Coupling Started: October 3, 2008 11:09 AM Submitted: October 3, 2008 11:30 AM Time spent: 00:21:56 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Student Response Value A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Student Response Value A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.67/0.67 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.66/0.66 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.66/0.66 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma out of the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.66/0.66 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Student Response A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions enter the sarcoplasm from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma out of the muscle cell. F. Opening of the chemically-gated sodium channels. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0.66/0.66 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: Student Response A. sarcoplasmic reticulum B. troponin C C. myosin D. all of the above E. 1 and 2, but not 3 Score: 0.66/0.66 Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. Adducts and fixates the scapula. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. Score: 2/2 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. Score: 2/2 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Elbow extensor. Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Score: 2/2 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Statement Response Value Score: 2/2 1. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: Student Response Value A. spinal gray matter B. spinal white matter C. dorsal root ganglion D. ventral root ganglion Score: 1/1 2. Multipolar neurons function as: Student Response Value A. spinal and cranial nerve sensory neurons B. spinal and cranial nerve motor neurons C. spinal and cranial interneurons D. all of the above E. #2 and #3 only Score: 1/1 3. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Student Response A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 1/1 4. Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Student Response A. Motor control on the same side of the body as their origin. B. Motor control on the opposite side of the body from their origin. C. Motor control for equilibrium and balance. D. Proprioception and muscle sense. E. Both answers #3 and #4. Score: 1/1 5. The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Student Response A. possessing chemically-gated ion channels B. possessing voltage-gated ion channels C. having both chemically-gated and voltage-gated ion channels D. being able to propagate an action potential Score: 1/1 6. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: Student Response A. outside the dura mater B. between the dura mater and arachnoid C. in the subdural space D. in the central canal of the spinal cord Score: 1/1 7. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Student Response A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 1/1 8. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Student Response A. Upper motor neurons B. Lower motor neurons C. Second order neurons D. Third order neurons. Score: 1/1 9. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: Student Response A. gray matter B. white matter C. dorsal root ganglion D. ventral root ganglion Score: 1/1 10. Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? Student Response A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 1/1 View Attempt 2 of 2 Title: Quiz #7 Neurology Started: November 3, 2008 11:32 AM Submitted: November 3, 2008 11:35 AM Time spent: 00:02:53 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: Student Response A. ascending and sensory B. ascending and motor C. descending and sensory D. descending and motor Score: 1/1 2. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Student Response A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 1/1 3. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Student Response Value A. Upper motor neurons B. Lower motor neurons C. Second order neurons D. Third order neurons. Score: 1/1 4. The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Student Response Value A. possessing chemically-gated ion channels B. possessing voltage-gated ion channels C. having both chemically-gated and voltage-gated ion channels D. being able to propagate an action potential Score: 1/1 5. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Student Response Value A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 1/1 6. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: Student Response A. outside the dura mater B. between the dura mater and arachnoid C. in the subdural space D. in the central canal of the spinal cord Score: 1/1 7. Multipolar neurons function as: Student Response A. spinal and cranial nerve sensory neurons B. spinal and cranial nerve motor neurons C. spinal and cranial interneurons D. all of the above E. #2 and #3 only Score: 1/1 8. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: Student Response A. gray matter B. white matter C. dorsal root ganglion D. ventral root ganglion Score: 1/1 9. The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: Student Response Value A. the dendrites B. the cell body C. the axon hillock D. all of the above E. #1 and #2 only Score: 1/1 10. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: Student Response A. spinal gray matter B. spinal white matter C. dorsal root ganglion D. ventral root ganglion Score: 1/1 View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #8 Neurophysiology Started: November 6, 2008 1:47 PM Submitted: November 6, 2008 1:51 PM Time spent: 00:04:21 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Student Response A. facilitation B. inhibition C. divergence D. convergence Score: 1/1 2. Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: Student Response A. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate open, K+ gate closed. B. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate closed, K+ gate closed. C. Na+ activation gate open, Na+ inactivation gate open, K+ gate closed. D. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate closed, K+ gate open. Score: 1/1 3. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Student Response A. depolarization B. hyperpolarization C. EPSP D. IPSP E. Both #1 and #3. F. Both #2 and #4. Score: 1/1 4. The crossed extensor reflex consists of: Student Response Value A. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a stretch reflex on the other side. B. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a tendon reflex on the other side. C. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and extension on the other side. D. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a flexor reflex on the other side. Score: 1/1 5. Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: Student Response Value A. chemically-gated ion channels only B. voltage-gated ion channels only C. Both chemically-gated and voltage-gated ion channels. D. The receptive region. Score: 1/1 6. Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Student Response Value A. facilitation B. inhibition C. divergence D. convergence Score: 1/1 7. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: Student Response Value A. paraplegia B. quadriplegia C. multiple sclerosis D. Paget's disease Score: 1/1 8. When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: Student Response Value A. learned reflex B. post-tetanic potentiation C. divergence D. convergence Score: 1/1 9. If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. Student Response Value A. temporal summation B. spatial summation C. action potential D. All of the above. E. #1 and #3 only. Score: 1/1 10. When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: Student Response Value A. Muscle contraction in the initiating muscle and reciprocal inhibition. B. Muscle contraction in the initiating muscle and reciprocal activation. C. Muscle relaxation in the initiating muscle and reciprocal inhibition. D. Muscle relaxation in the initiating muscle and reciprocal activation. Score: 1/1 View Attempt 2 of 2 Title: Quiz #8 Neurophysiology Started: November 10, 2008 2:02 PM Submitted: November 10, 2008 2:15 PM Time spent: 00:12:05 Total score: 8/10 = 80% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: Student Response A. EPSP B. IPSP C. graded potential D. all of the above E. #1 and #2 only. Score: 2. Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: Student Response A. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate open, K+ gate closed. B. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate closed, K+ gate closed. C. Na+ activation gate open, Na+ inactivation gate open, K+ gate closed. D. Na+ activation gate closed, Na+ inactivation gate closed, K+ gate open. Score: 1/1 3. Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: Student Response A. saltatory conduction B. post-tetanic potentiation C. temporal summation D. spatial summation Score: 1/1 4. The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: Student Response A. absolute refractory period B. relative refractory period C. period of depolarization D. period of hyperpolarization E. Both answers 1 and 3 F. Both answers 2 and 4 Score: 0/1 5. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: Student Response A. paraplegia B. quadriplegia C. multiple sclerosis D. Paget's disease Score: 1/1 6. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. Student Response A. temporal summation B. spatial summation C. action potential D. All of the above. E. #1 and #3 only. Score: 1/1 7. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Student Response A. depolarization B. hyperpolarization C. EPSP D. IPSP E. Both #1 and #3. F. Both #2 and #4. Score: 1/1 8. The relative refractory period occurs during: Student Response A. opening of Na+ gates B. opening of K+ gates C. closing of K+ gates when excess K+ has left the neuron. D. opening of K+ gates when excess K+ has left the neuron. Score: 1/1 9. Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: Student Response A. chemically-gated ion channels only B. voltage-gated ion channels only C. Both chemically-gated and voltage-gated ion channels. D. The receptive region. Score: 1/1 10. When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: Student Response A. Muscle contraction in the initiating muscle and reciprocal inhibition. B. Muscle contraction in the initiating muscle and reciprocal activation. C. Muscle relaxation in the initiating muscle and reciprocal inhibition. D. Muscle relaxation in the initiating muscle and reciprocal activation. Score: 1/1 View Attempt 2 of 2 Title: Quiz #9 The Brain Started: November 10, 2008 2:51 PM Submitted: November 10, 2008 2:57 PM Time spent: 00:05:37 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: Student Response Value B. pons varoli C. pineal body D. midbrain E. corpora quadrigemia Score: 1/1 2. The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: Student Response Value B. hypothalamus C. substantia nigra D. basal nuclei E. pons Score: 1/1 3. Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: Student Response Value Student Response A. choroid plexus 1 B. falx cerebri C. superior sagittal sinus D. septum pellucidum Score: 1/1 4. The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Student Response Value B. fornix C. choroid plexus D. arbor vitae Score: 1/1 5. The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: Student Response Value A. thalamus B. hypothalamus C. substantia nigra D. basal nuclei Score: 1/1 6. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Student Response Value A. thalamus 0% Student Response B. C. substantia nigra D. basal nuclei E. pons Score: 1/1 7. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 8. The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. Student Response Value Score: 1/1 9. The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. Student Response Value Score: 1/1 10. The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. Student Response D. Score: 1/1 Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 2. Pain stimuli terminate in the: Score: 1/1 3. Broca's area is located alongside the: Score: 1/1 4. The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. Score: 1/1 5. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: Score: 1/1 6. The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 7. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Score: 1/1 8. The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 9. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: Score: 1/1 10. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: Score: 1/1 As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. Score: 1/1 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 10. Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. Score: 1/1 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. Score: 1/1 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 10. Score: 1/1 Jump to Navigation Frame Your location: Assessments › View All Submissions › View Attempt View Attempt 2 of 2 Title: Quiz #2: The Skeletal System Started: February 19, 2007 12:28 AM Submitted: February 19, 2007 12:33 AM Time spent: 00:05:14 Total score: 9.5/10 = 95% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 2. Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. Increased calcium absorption is produced by: Student Response Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: 5. The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. 6. Spongy bone lacks: 7. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 8. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 9. The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 0.5/0.5 10. Both cartilage and bone possess: 1. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 2. Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 3. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 4. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: Value Correct Answer Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 6. Although the joints between the clavicle and scapula are only slightly movable, according to Marieb they are classified as _____ joints. 7. A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 8. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 9. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 10. The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 11. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 12. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 13. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 14. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 15. In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 2. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 3. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 4. The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: 5. Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 6. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 7. In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 8. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 9. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 10. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 11. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 12. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 13. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 14. A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 15. The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Jump to Navigation Frame Your location: Assessments › View All Submissions › View Attempt View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #5 - Stimulus-Contraction Coupling Started: March 15, 2007 9:23 PM Submitted: March 15, 2007 9:52 PM Time spent: 00:29:33 Total score: 5.34/10 = 53.4% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Student Response Value Correct Answer Score: 0.67/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Student Response Value Correct Answer Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 8. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 9. Epidermis Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. D C B E A 10. diarthrotic joints All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 11. types of tissues Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: 12. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence medial condyle lateral malleolus medial malleolus 13. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E parietal bone lacrimal bone zygomatic bone zygomatic arch sphenoid bone 14. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus B A D E C 15. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 16. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 17. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 18. elbow Match the part with its letter. tendon of the biceps brachii lateral epicondyle lateral collateral ligament annular ligament radial tubercle bursa tendon of the triceps brachii olecranon process trochlea synovial membrane of joint capsule F D C E B J A G I H 19. spinocerebellar tract Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? 20. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #9 The Brain Started: November 27, 2007 9:58 PM Submitted: November 27, 2007 10:03 PM Time spent: 00:04:07 Total score: 1/10 = 10% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: Score: 0/1 2. Broca's area is located alongside the: 3. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 4. The upper motor neurons originate in the: 5. Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 6. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 7. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 8. The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 9. Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 10. The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. Title: Quiz #8 Neurophysiology Started: November 18, 2007 1:14 PM Submitted: November 18, 2007 1:27 PM Time spent: 00:12:50 Total score: 4/10 = 40% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 2. Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 3. Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 4. When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 5. In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. 6. The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 7. The relative refractory period occurs during: 8. If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 9. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 10. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: itle: Quiz #8 Neurophysiology Started: November 25, 2007 2:18 PM Submitted: November 25, 2007 2:40 PM Time spent: 00:22:10 1. High frequency stimuli result from: 2. Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 3. The relative refractory period occurs during: 4. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 5. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 6. Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 7. When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 8. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 9. Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 10. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #9 The Brain Started: November 29, 2007 3:35 PM Submitted: November 29, 2007 3:46 PM Time spent: 00:10:49 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 2. The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: 3. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 4. The upper motor neurons originate in the: Score: 1/1 5. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 6. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: Score: 1/1 7. A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: 8. Broca's area is located alongside the: 9. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 10. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #10: Autonomic Nervous System Started: November 29, 2007 3:50 PM Submitted: November 29, 2007 4:04 PM Time spent: 00:14:27 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. Score: 1/1 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 8. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 9. Epidermis Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. D C B E A 10. diarthrotic joints All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 11. types of tissues Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: 12. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence medial condyle lateral malleolus medial malleolus 13. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E parietal bone lacrimal bone zygomatic bone zygomatic arch sphenoid bone 14. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus B A D E C 15. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 16. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 17. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 18. elbow Match the part with its letter. tendon of the biceps brachii lateral epicondyle lateral collateral ligament annular ligament radial tubercle bursa tendon of the triceps brachii olecranon process trochlea synovial membrane of joint capsule F D C E B J A G I H 19. spinocerebellar tract Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Score: 0.5/0.5 20. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. View Attempt 1 of 2 Title: Quiz #9 The Brain Started: November 27, 2007 9:58 PM Submitted: November 27, 2007 10:03 PM Time spent: 00:04:07 Total score: 1/10 = 10% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: Student Response Value A. reticular formation 0% B. cerebral cortex 0% C. limbic system 100% D. thalamus 0% Score: 0/1 2. Broca's area is located alongside the: 3. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 4. The upper motor neurons originate in the: 5. Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 6. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 7. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 8. The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 9. Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 10. The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 1. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 2. Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 3. Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 4. When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 5. In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. Score: 1/1 6. The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 7. The relative refractory period occurs during: 8. If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 9. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 10. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 1. High frequency stimuli result from: 2. Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 3. The relative refractory period occurs during: 4. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 5. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 6. Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 7. When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 8. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 9. Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 10. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: View Attempt 1 of 2 1. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 2. The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: 3. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 4. The upper motor neurons originate in the: 5. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 6. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 7. A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: 8. Broca's area is located alongside the: 9. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: Score: 1/1 10. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. Score: 1/1 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 10. Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. 1. myeloid tissue1 The ____ is the location of production of blood cells: 2. The first cell in bone remodeling The cell which acts first in the process of remodeling in adult bone: 3. spongy bone 1 Spongy bone lacks: 4. first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 5. humerus 1 The trochlea articulates with the _____ of the ulna in a hinge joint. 6. nasal cavity The primary bone which forms the nasal cavity is the: 7. sella turcica The sella turcica lies directly above the: 8. conchae The superior and middle conchae are part of the ___ bone. 9. symphysis pubis The symphysis pubis is composed of: 10. occipital condyles The occipital condyles articulate with superior surfaces on the: 11. paranasal sinuses 1 Which of these is NOT one of the paranasal sinuses? Score: 1/1 12. sacrum The sacrum articulates laterally with the _____ of the os coxae. Score: 13. All the ribs articulate with the: All ribs articulate with the: Score: 1/1 14. Bone characteristics 1 The component responsible for the hardness and rigidity of bone is: Score: 1/1 15. bone hormones 7 An excess or abuse of this hormone can lead to acromegaly and sometimes pituitary diabetes. Score: 1/1 16. bone hormones 3 A reduction in this hormone is the cause of post-menopausal osteoporosis: Score: 1/1 17. bone hormones 1 18. Ossification 3 The frontal bone ossifies from pre-existing model of: Score: 1/1 19. Osteoporosis 3 Senile (age-related) osteoporosis is characterized by ___ parathyroid hormone in the blood. Score: 1/1 20. Osteoporosis 1 Post-menopausal osteoporosis is characterized by ___ calcium in the blood. Score: 1/1 21. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial malleolus tibial tuberosity medial condyle intercondylar eminence lateral malleolus Score: 3/3 22. anterior skull Match parts with letters. A B C D E nasal bone mandible maxilla zygomatic bone frontal bone Score: 3/3 23. skin cancer 2 What normally prevents keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum from becoming cancerous due to mutation from uv radiation is: Score: 1/1 24. skin 3 Non-keratinized skin is found in the: Score: 1/1 25. skin 2 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. Score: 1/1 26. glands and receptors 2 Which of the following signaling chemicals called pheromones? Score: 1/1 27. glands and receptors 3 Which of the following is a receptor for non-discriminative touch? Score: 1/1 28. Epidermis 1 Match descriptions with letters in the diagram. The layer containing most glands and receptors The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain condensed keratin granules. D A B E C Score: 3/3 29. Areolar tissue 2 Match letters with descriptions. A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber B D C A Score: 1.5/3 30. cartilage 3 The least common of the following tissues is: Score: 1/1 31. cartilage 2 The intervertebral disks are composed of: Score: 1/1 32. cell structure 3 Keratin filaments are the primary structural component in: Score: 1/1 33. cell structure 2 When tissue wraps to form a tubule the ___ surface is toward the lumen. Score: 1/1 34. columnar epithelium 2 Match letters with descriptions. This surface might have hemidesmosomes Secretes mucus This surface might have microvilli This has a characteristic shape and location in the cell D A B C Score: 3/3 35. connective tissue components 1 The two primary components of all connective tissues are: Score: 0/1 36. complementarity 1 The term "complementarity" used in Anatomy and Physiology refers to the deterministic relationship between: Score: 1/1 37. Connective tissues 1 Match tissues with descriptions areolar tissue adipose tissue dense regular dense irregular reticular connective tissue elastic connective tissue C A D E F B Score: 3/3 38. feedback 2 A process which controls a parameter within a narrow range will utilize: Score: 1/1 39. scar tissue Scar tissue is the repair seen in: Score: 1/1 40. nucleus pulposus The nucleus pulposus is the spongy center of: Score: 0/1 41. functional repair Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences functional repair? Score: 1/1 42. ligamentum flavum Unlike most other ligaments, the ligamentum flavum in the vertebral column contains: Score: 1/1 43. Epithelial tissues 2 Match the tissue with the description. A F B C D E 44. Bone Tissue 1 Match the letters with descriptions This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect B A D C Score: 3/3 1. first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 1/1 2. The first cell in bone remodeling The cell which acts first in the process of remodeling in adult bone: Score: 1/1 3. bone cells The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: Score: 1/1 4. the epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone to harden is the: Score: 1/1 5. humerus 2 The capitulum articulates with the _____ to form a pivot joint. Score: 1/1 6. os coxae The three bones of the os coxae come together at the: Score: 0/1 7. All the ribs articulate with the: All ribs articulate with the: Score: 0/1 8. Sharpey's fibers 1 Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: Score: 1/1 9. sacrum The sacrum articulates laterally with the _____ of the os coxae. Score: 1/1 10. sella turcica The sella turcica lies directly above the: Score: 1/1 11. symphysis pubis The symphysis pubis is composed of: Score: 1/1 12. paranasal sinuses 1 Which of these is NOT one of the paranasal sinuses? Score: 1/1 13. anterior fontanel 1 The large anterior fontanel hardens at: Score: 1/1 14. Bone characteristics 1 The component responsible for the hardness and rigidity of bone is: Score: 15. bone hormones 4 This hormones stimulates closure (hardening) of the epihyseal plates and end to growth of the long bones. Score: 16. bone hormones 1 The primary hormone in adult calcium homeostasis is: Score: 1/1 17. bone hormones 6 This hormone stimulates osteoclastic activity. Score: 1/1 18. Ossification 2 A lumbar vertebra ossifies from pre-existing model of: Score: 1/1 19. Osteoporosis 4 Senile (age-related) osteoporosis is characterized by ___ calcium levels in the blood. Score: 1/1 20. Osteoporosis 1 21. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial malleolus intercondylar eminence medial condyle tibial tuberosity lateral malleolus 22. tibia-fibula1 Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E tibial tuberosity lateral malleolus medial condyle intercondylar eminence medial malleolus Score: 0/3 23. skin cancer 3 The primary characteristic which causes melanocytes to metastasize is their: Score: 1/1 24. skin 4 Skin is designated as thick if it: Score: 1/1 25. skin 1 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. The sebacous gland A sudoriferous gland A dermal papilla A pacinian corpuscle The hypodermis D B E C A Score: 26. glands and receptors 1 Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? Score: 0/1 27. glands and receptors 3 Which of the following is a receptor for non-discriminative touch? Score: 1/1 28. Epidermis 1 Match descriptions with letters in the diagram. The layer containing most glands and receptors The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain condensed keratin granules. C D E A B Score: 3/3 29. Areolar tissue 2 Match letters with descriptions. A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber C A D B Score: 30. cartilage 1 Chondrocytes are found within fluid-filled spaces called: Score: 31. cartilage 4 The most common of the cartilage is: Score: 1/1 32. cell structure 1 Microvilli increase area on the _____ surface. Score: 1/1 33. cell structure 4 Channels called connexons are the primary structural component in: Score: 0/1 34. columnar epithelium 2 Match letters with descriptions. This surface might have hemidesmosomes Secretes mucus This surface might have microvilli This has a characteristic shape and location in the cell B C A D Score: 3/3 35. connective tissue components 1 The two primary components of all connective tissues are: Score: 1/1 36. connective tissue derivation All connective tissues are derived from ____ cells which come from the mesoderm. Score: 0/1 37. Connective tissues 1 Match tissues with descriptions areolar tissue adipose tissue dense regular dense irregular reticular connective tissue elastic connective tissue A B E F C D Score: 1.5006/3 38. feedback 1 A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: Score: 1/1 39. smallest bones The smallest standard bones found in the body are the: Score: 1/1 40. osteoporosis 01 Low _____ and high _____ is a characteristic of senile osteoporosis. Score: 1/1 41. scar tissue Scar tissue is the repair seen in: Score: 1/1 42. functional repair Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences functional repair? Score: 1/1 43. Epithelial tissues 2 Match the tissue with the description. Shows a capillary wall The mucous membrane of the GI tract The lining of the urinary tract The primary cell type found in glands The primary lining of the respiratory tract The epidermis of the skin C F A E B D Score: 0.9996/3 44. Bone Tissue 1 Match the letters with descriptions This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect D A C B Score: 1.5/3 1. arthritis 3 Which type of arthritis is caused by damage to the articular cartilage from injury or excessive use? Score: 2. tennis elbow The disorder known as tennis elbow is due to an irritation around the _____ which is the origin for the _____. Score: 1/1 3. syndesmosis 1 A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones at a non-movable joint. Score: 0/1 4. the knee The knee is a joint of condyloid structure in which ligaments force the knee to be: Score: 1/1 5. hand rotation 1 Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: Score: 1/1 6. carpal tunnel The carpal tunnel is a narrowed area enclosing tendons between the carpal bones and the _____. Score: 0/1 7. joint capsule The joint capsule of a synovial joint is composed of: Score: 1/1 8. joint examples 2 Match the joint type with the example. tibiofibular joint (distal) pubic symphysis talus-calcaneous (ankle) joint diarthrotic joint synarthrotic joint amphiarthrotic joint Score: 3/3 9. joint examples 1A Match the joint type with the example. knee atlas-axis intercarpal joint occipital conndyles-atlas hip (coxal) joint hinge joint ball-and-socket gliding joint pivot joint condyloid joint Score: 3/3 10. joint injuries 2 A dislocation is defined as: Score: 1/1 11. joint movements 2 Condyloid joints move in: Score: 0/1 12. joint movements 3A Movements at ball and socket joints include: Score: 1/1 13. joint strength 1 The _____ has a fibrocartilaginous labrum which grips the head of the femur, securing it in place. Score: 14. joint structures 1 Non-movable joints are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. Score: 1/1 15. joint structures 1A Non-movable joints are classified as _____ joints. Score: 1/1 16. Knee 1A Match the letters with descriptions. patellar retinaculm collateral ligament patellar ligament extensor tendon the insertion of the rectus femoris muscle keeps the tibia from abducting inserts on the tibial tuberosity keeps the patella from sliding laterally Score: 3/3 17. Knee 2B Match the letters with descriptions articular cartilage posterior cruciate ligament anterior cruciate ligament medial meniscus patellar ligament fomposed of fibrocartilage prevents the forward sliding of the femur against the tibia prevents the forward sliding of the tibia against the femur inserts on the tibial tuberosity osteoarthritis begins with damage to this structure Score: 1.8/3 18. knee 3 Match letters with descriptions. posterior cruciate ligament anterior cruciate ligament extensor tendon patellar ligament articular cartilage B C A E D Score: 19. action potential 3 Which letter indicates the absolute refractory period? Score: 20. action potential 7 This is the point where repolarization begins. Score: 0/1 21. action potential 6 The ion gates will not respond to a depolarizing stimulus during this period. Score: 22. extraocular and lumbricals 2 The extraoptical and lumbrical muscles would have which of the following in common: Score: 1/1 23. forced inspiration The sternocleidomastoid and scalenes work together with the _____to raise and expand the ribcage in forced inspiration. Score: 24. length-tension Muscles achieve their greatest tension: Score: 1/1 25. binds calcium 1 Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 1/1 26. myosin head reset 1 In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 1/1 27. extraocular and lumbricals The extraoptical and lumbrical muscles would have which of the following in common: Score: 1/1 28. erector spinae and soleus The erector spinae and soleus would have which of the following in common: Score: 1/1 29. ion movement 2 In response to acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors, _____ flows across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. Score: 1/1 30. latissimus dorsi 2 The latissimus dorsi: Score: 1/1 31. muscle cell types 3 Fast twitch red (intermediate) fibers can utilize _____ to provide energy for metabolism. Score: 1/1 32. muscle cell types C Fast twitch red (intermediate) fibers have: Score: 1/1 33. muscle movements 1B The movement shown as B is ___ of the knee. Score: 34. muscle movements 2AA The prime mover for the movement shown at A is: Score: 1/1 35. muscle movements 3CC The prime mover in the movement shown as C is the: Score: 1/1 36. muscle movements 4A Given: the muscle colored green is the agonist. What movement would occur at the ankle joint? Score: 1/1 37. muscle movements 4B The agonist for plantar flexion inserts on the: Score: 1/1 38. muscle movements 5A The muscle in red, acting bilaterally, would be the agonist in: Score: 1/1 39. muscle movements 5D If the head is fixed, the muscles shown here would: Score: 1/1 40. connective tissues c The _____ surrounds each fasciculus of muscle cells. Score: 1/1 41. muscle types 2 The type of muscle possessing striations: Score: 1/1 42. Stimulus-Contraction 4 As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 1/1 43. Stimulus-Contraction 5 What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 1/1 44. Stimulus-Contraction 9 What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 1/1 45. Stimulus-Contraction 10 What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 1/1 46. Stimulus-Contraction 3 Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Score: 1/1 47. Stimulus-Contraction 6 As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 1/1 48. Stimulus-Contraction 7 As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 0/1 49. summation A1 The diagram shows: Score: 0/1 50. summation B2 The diagram shows: Score: Jump to Navigation Frame Your location: Assessments › View All Submissions › View Attempt View Attempt 1 of 1 Title: Unit Test #2 Started: April 10, 2008 5:28 PM Submitted: April 10, 2008 5:52 PM Time spent: 00:23:50 Total score: 53.83/60 = 89.7167% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 60 1. arthritis 4 This is inflammation of a synovial membrane located outside the actual joint. Score: 1/1 2. joint capsule The joint capsule of a synovial joint is composed of: Score: 1/1 3. tennis elbow The disorder known as tennis elbow is due to an irritation around the _____ which is the origin for the _____. Score: 1/1 4. diarthrotic joints 1 All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: Score: 1/1 5. intracapsular ligaments 1 The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. Score: 1/1 6. atlas-axis 1 The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint which performs a movement called _____. Score: 1/1 7. head of radius The _____ holds the head of the radius in place while allowing it to turn. Score: 8. joint examples 1 Match the joint type with the example. suture intervertebral disk intercarpal joint synarthrotic joint amphiarthrotic joint diarthrotic joint Score: 3/3 9. joint examples 3A Match the joint type with the example. humerus-ulna atlas-axis clavicular-acromion metatarsal-phalangeal metacarpal-carpal of thumb condyloid joint gliding joint saddle joint hinge joint pivot joint Score: 3/3 10. joint injuries 1 A separation (e.g. shoulder separation) is defined as: Score: 0/1 11. joint movements 2 Condyloid joints move in: Score: 1/1 12. joint movements 2A Movements at hinge joints include: Score: 1/1 13. joint strength 1 The _____ has a fibrocartilaginous labrum which grips the head of the femur, securing it in place. Score: 1/1 14. joint structures 3 Semimovable joints are classified structurally as _____ joints. Score: 1/1 15. joint structures 3A Semi-movable joints are classified as _____ joints. Score: 1/1 16. Knee 1 Match the letters with descriptions. patellar retinaculum collateral ligament patellar ligament extensor tendon A C B D Score: 3/3 17. Knee 2 Match the letters with descriptions articular cartilage posterior cruciate ligament anterior cruciate ligament medial meniscus patellar ligament B E C D A Score: 3/3 18. knee 3A Match letters with descriptions. posterior cruciate ligament anterior cruciate ligament extensor tendon patellar ligament articular cartilage its damage causes osteoarthritis the insertion of the quadriceps muscles inserts on the tibial tuberosity prevents the anterior sliding of the femur against the tibia prevents posterior sliding of the femur against the tibia Score: 1.8/3 New score: 3/3 This score has been adjusted by the grader. 19. action potential 2 Which letter indicates the point where the membrane is hyperpolarized? Score: 1/1 20. action potential 6 The ion gates will not respond to a depolarizing stimulus during this period. Score: 0/1 21. action potential 5 This is the polarity at which the voltage-gated sodium channels close and the potassium channels open. Score: 1/1 22. extraocular and lumbricals 2 The extraoptical and lumbrical muscles would have which of the following in common: Score: 1/1 23. energy source The "working stroke" of muscle contraction depends directly on _____ for energy. Score: 0/1 24. extraocular and lumbricals The extraoptical and lumbrical muscles would have which of the following in common: Score: 1/1 25. rotator cuff Which muscle listed is not a member of the rotator cuff muscles? Score: 1/1 26. binds calcium 1 Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.5/1 27. myosin head reset 1 In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 1/1 28. contraction trigger 1 The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Score: 1/1 29. ion movement 1 The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. Score: 1/1 30. latissimus dorsi 4 The latissimus dorsi and teres major act antagonistically to the: Score: 1/1 31. muscle cell types 3 Fast twitch red (intermediate) fibers can utilize _____ to provide energy for metabolism. Score: 0.33/1 32. muscle cell types B Slow twitch red fibers have: Score: 1/1 33. muscle movements 1BB The prime mover in movement B is the: Score: 1/1 34. muscle movements 2BB The prime mover for the movement shown at B is: Score: 1/1 35. muscle movements 3C The movement shown as C is ___ of the vertebral column. Score: 1/1 36. muscle movements 4B The agonist for plantar flexion inserts on the: Score: 1/1 37. muscle movements 4A Given: the muscle colored green is the agonist. What movement would occur at the ankle joint? Score: 38. muscle movements 5A The muscle in red, acting bilaterally, would be the agonist in: Score: 1/1 39. muscle movements 5D If the head is fixed, the muscles shown here would: Score: 1/1 40. connective tissues b The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Score: 1/1 41. muscle types 2 The type of muscle possessing striations: Score: 1/1 42. Stimulus-Contraction 5 What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 1/1 43. Stimulus-Contraction 12 As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Score: 1/1 44. Stimulus-Contraction 7 As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 1/1 45. Stimulus-Contraction 3 Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Score: 1/1 46. Stimulus-Contraction 11 As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 1/1 47. Stimulus-Contraction 9 What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 1/1 48. Stimulus-Contraction 4 As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 1/1 49. summation A1 The diagram shows: Score: 1/1 50. summation B2 The diagram shows: Score: 1/1 1. Which of the following secretes pheromones? Score: 0.5/0.5 2. Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: Score: 0.5/0.5 3. Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The most agressive skin cancer is: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa found as costal cartilage found in the epiglottis and ear found in symphysis pubis a lining and covering membrane all connective tissues are derived from this Score: 7. Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. gap junction tight junction desmosome keratin filaments hemidesmosome Allows ions to pass between cells. fibers which hold cells together laterally Called macula adherens because they are like spot welds which adhere cells together. adheres cells to the basement membrane Called the zona occludens because it blocks passage of substances between cells. Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. C D E A B Score: 1. Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? Score: 0.5/0.5 2. Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? Score: 0/0.5 6. Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. gap junction tight junction desmosome keratin filaments hemidesmosome fibers which hold cells together laterally adheres cells to the basement membrane Allows ions to pass between cells. Called macula adherens because they are like spot welds which adhere cells together. Called the zona occludens because it blocks passage of substances between cells. Score: 2.5/2.5 7. Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa found in symphysis pubis a lining and covering membrane found in the epiglottis and ear found as costal cartilage all connective tissues are derived from this Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. C D A E B Score: 2.5/2.5 1. Once completely hardened, osteoprogenitor cells must come from the _____ for bone repair. Score: 0.5/0.5 2. Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Score: 0/0.5 4. The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Cranial bones start out as a: Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Spongy bone lacks: Score: 0/0.5 7. The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: Score: 0/0.5 8. The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: Score: 0.5/0.5 9. The large anterior fontanel hardens at: Score: 0.5/0.5 10. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: Score: 0/0.5 11. Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process D C A B Score: 2.5/5 Increased calcium absorption is produced by: Score: 0.5/0.5 2. There are _____ pair of ribs. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 0.5/0.5 4. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Once completely hardened, osteoprogenitor cells must come from the _____ for bone repair. Score: 0.5/0.5 7. Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Score: 0.5/0.5 8. The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. Score: 0.5/0.5 9. Cranial bones start out as a: Score: 0.5/0.5 10. the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: Score: 0.5/0.5 11. Match the parts of the temporal bone with the letters. external acoustic meatus styloid process mastoid process zygomatic process mandibular fossa A C D B E Score: 5/5 Jump to Navigation Frame 1. Match parts with letters. A B C D E glenoid fossa acromion coracoid process subscapular fossa spinous process Score: 2.5/2.5 2. Match the parts shown. A B C D E zygomatic arch zygomatic bone parietal bone sphenoid bone lacrimal bone Score: 2.5/2.5 3. Match parts with letters. A B C D E F G H I medial condyle medial epicondyle intercondylar notch head of femur linea aspera anatomical neck lesser trochanter patellar articular surface greater trochanter Score: 2.5/2.5 4. Match parts with letters. A B C D E occipital condyle foramen magnum zygomatic arch vomer bone hard palate of maxilla Score: 2.5/2.5 1. A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 2. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. Score: 0/0.67 3. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. Score: 0.67/0.67 4. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. Score: 0.67/0.67 6. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Score: 0.67/0.67 7. The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? Score: 0.67/0.67 10. In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: Score: 0.67/0.67 11. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? Score: 0.67/0.67 12. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 0.67/0.67 13. The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Score: 0.67/0.67 14. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. Score: 0.67/0.67 15. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? Score: 0.67/0.67 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 0/0.67 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.67/0.67 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Score: 0/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 0.67/0.67 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Score: 0.67/0.67 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Score: 0.66/0.66 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: Score: 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 0/0.66 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.66/0.66 Jump to Navigation Frame Time spent: 00:02:42 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.67/0.67 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 0.67/0.67 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Score: 0.67/0.67 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Score: 0.67/0.67 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 0.66/0.66 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Score: 0.66/0.66 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: Score: 0.66/0.66 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.66/0.66 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.66/0.66 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.67/0.67 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 0.67/0.67 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Score: 0.67/0.67 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Score: 0.67/0.67 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 0.66/0.66 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Score: 0.66/0.66 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: Score: 0.66/0.66 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.66/0.66 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.66/0.66 1. Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. Adducts and fixates the scapula. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. Score: 1.2/2 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. Score: 1.2/2 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. Score: 2/2 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Elbow extensor. Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Score: 2/2 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Score: 2/2 Time spent: 00:02:54 Total score: 9.6/10 = 96% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. Adducts and fixates the scapula. Score: 2/2 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. Score: 2/2 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. Score: 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris Elbow extensor. Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Score: 2/2 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Score: 2/2 Jump to Navigation Frame 1. The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Score: 1/1 2. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: Score: 3. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Score: 1/1 4. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Score: 1/1 5. Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? Score: 6. A multipolar neuron has: Score: 1/1 7. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: Score: 1/1 8. Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Score: 9. The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: Score: 10. Multipolar neurons function as: Score: 0/1 Time spent: 01:21:10 1. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: Score: 1/1 2. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Score: 0/1 3. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: Score: 1/1 4. The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: Score: 1/1 5. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: Score: 1/1 6. Multipolar neurons function as: Score: 1/1 7. A multipolar neuron has: Score: 1/1 8. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: Score: 1/1 9. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Score: 1/1 10. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Score: 1/1 Jump to Navigation Frame Your location: Assessments › View All Submissions › View Attempt View Attempt 1 of 2 Time spent: 00:21:37 1. The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: Score: 1/1 2. The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Score: 3. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: Score: 4. Broca's area is located alongside the: Score: 5. The upper motor neurons originate in the: Score: 6. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. Score: 0/1 7. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: Score: 1/1 8. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: Score: 9. The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. Score: 10. Pain stimuli terminate in the: Score: 1. The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: Score: 1/1 2. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Score: 1/1 3. Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: Score: 1/1 4. Pain stimuli terminate in the: Score: 1/1 5. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: Score: 1/1 6. The upper motor neurons originate in the: Score: 1 7. The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. Score: 1 8. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: Score: 1 9. The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. Score: 1/1 10. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: Score: 1/1 Epithelial Tissue Histology - Template Tissue Type Characteristics Functions Locations Simple Squamous Flat, thin cells Used for membranes Walls of capillaries and air sacs of lungs Simple Cuboidal Cube shaped Secretory and absorptive In glands and liver and kidneys Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous epithelium Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Transitional epithelium Connective Tissue Histology Tissue Type Characteristics Functions Locations Loose: Areolar Most common, contains all 3 types of fibers, ground substance has most of body’s water It’s the body’s interstitial tissue Part of dermis of skin, underlying supportive layer of GI, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts, serous membranes Loose: Adipose Loose: Reticular Dense regular connective tissue Dense irregular connective tissue Dense elastic connective tissue Hyaline Cartilage Elastic cartilage Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue Histology-EMILY WISDOM Tissue Type Characteristics Functions Locations Areolar Three types of fibers and contains interstitial fluid Underlying supportive layer Dermis of the skin, GI,respiratory and genitourinary tracts, serous membranes Adipose Cells store lipids in a large vacuole Shock absorption and insulation Many organs including the heart, eyes, kidneys, and spleen. Dense regular Arranged in an irregular pattern Provides strength and withstands stress. Deep layers of the skin’s dermis, GI tract, capsules of synovial joints. Dense irregular Almost entirely collagen fibers, densely packed Strongest connective tissue Tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses, fascia, fibrous joints Reticular Delicate fibers forming interlacing networks Internal support Kidneys, spleen, liver and other soft organs Cartilage (hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage) Avascular, gel like Cushioning, and joint lubrication Hyaline-nose, ribs, articular cartilage. Elastic- epiglottis and ear Fibrocartilage- intervertebral disks and the symphysis pubis The Skin Match the number of each structure in the skin diagram with its name on the chart, then describe the characteristics or functions of each. The first one has been done as an example. Number Characteristics epidermis 1 The outer layer of the skin, composed of stratified squamous epithelium Reticular layer of dermis 2 Made of areolar and dense irregular connective tissue. Contains many of the nerves, sensory corpuscles, hair follicles, and numerous glands. Sebaceous gland 3 Secrete oily substance called sebum which prevents dehydration. They connect to hair follicles over most of the skin Hair root 4 Anchors hair, area of new hair cell growth Hypodermis (as well as adipose tissue) 5 The hypodermis is mostly made up of adipocytes. It is also called the subcutaneous layer Dermal papillae 6 Extension of dermis into epidermis. Contain vascular loops and specialized nerve endings Meissner’s corpuscle 7 Light touch receptors that are attached to nerve endings that produce action potentials. Eccrine glands 8 Found extensively in skin and aids in thermoregulation. It secretes primarily water with little amounts of salts and urea. Arrector pili muscle 9 Found in dermis and attached at one end to the hair root and the other end to basement membrane of epidermis. Able to raise hairs during thermoregulation and stressful situations Pacinian corpuscle 10 Responds to pressure and vibration. Found in subcutaneous tissue as well as mesenteries and near joints. BIOL 237 Case History 1 A 27 year old man, who works outdoors, notices a growth on the skin which includes a darkly pigmented spot surrounded by a halo of inflamed skin. This man has a very fair complexion, with numerous freckles and blond hair. Because of his job and recreational interests he spends a great deal of time outdoors and often gets sunburned in the summer time. The pigmented spot was removed surgically and sent for biopsy. It was determined to be malignant, but there was no evidence of metastasis. 1. What is the most likely diagnosis of the condition described. Explain. 2. Describe the normal histology of the epidermis which relates to this condition. 3. Where do melanocytes originate, and where do they reside after migration. 4. Describe the differences in metabolism of melanocytes in healthy vs. response to UV radiation to produce malignancy. 5. What are the major criteria for determining malignancy in melanotic tumors? 1) Impulse arrives at axon terminus causing Ca++ to enter axon 2) Ca++ bind to ACh vesicles causing a release of Acetylcholine (ACh) into the synapse by exocytosis 3) d and the energy transferred to the myosin heads as they cock and reset for next stimulus. Antagonists I. Tricepts Brachii is an antagonist to the biceps brachii, brachialis. a. II. Internal intercostals is an antagonist to the External intercostals, pectoralis minor, diaphragm, scalenes, sternocleidomastoid a. Action is the compression of the thorax. III. Extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis is an antagonist to flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus a. Action is the extension and abduction of the wrist. IV. Infraspinatus, teres minor are……………….. V. , rhomboid major a. Action is the abduction of the scapula. Synergists I. Temporalis and masseter II. Splenius capitus and trapezius III. Rhomboid minor and rhomboid major a. IV. Deltoid and supraspinatus a. V. Biceps brachii and brachialis a. Fixators I. Rhomboid major and rhomboid minor a. Fixates……….. II. Supraspinatus a. Fi……. III. Levator scapulae a. Fixates scapula IV. Semispinalis capitis, semispinalis cervicis, semispinalis thoracis, multifidis, rotators a. Fixates torso during standing Stimulus-contraction 1. Impulse arrives at axon terminus. 2. Calcium ion influx into axon. 3. Calcium binds to vesicles containing acetylcholine (Ach) and causes the vesicles to traverse to the axon terminal. 4. The vesicles bind to the terminal membrane, which in turn releases the Ach into the synapse. 5. Ach diffuses across synapse and binds to Ach receptors on the sarcolemma, which causes the chemically-gated sodium channels to open, allow for a sudden influx of sodium, causing depolarization. 6. The depolarization causes an action potential to propagate along the sarcolemma by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. 7. The sarcolemma will then repolarize by opening potassium channels as the sodium channels close. Since more potassium leaves than is needed, a period of hypolarization occurs, causing a relative refractory period. 8. The sodium-potassium pump will then restore the regular ion distribution. 9. As all this is going on, the Ach will detach from the receptors and either get broken down by acetylcholinesterase or recycled via the Ach re-uptake channels. 10. As the action potential passes along the sarcolemma, it comes across T-tubules and enters them. The T-tubules run transverse to the length of the muscle, so it is very useful for carrying the action potential to the muscle cell’s interior. T-tubules also attach to the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), which stores calcium. 11. When the action potential moves down the T-tubules, it causes the SR to release calcium ions into the sarcoplasm. 12. The calcium ions in the sarcoplasm will bind to Troponin C, causing a conformation shift that moves the tropomyosin away from the active site on actin filaments. 13. With the active site on the actin exposed, myosin molecules eagerly binds to actin with the energy from bound ATP. 14. The myosin heads then swivel, pulling the Z-lines closer together and shortening the sarcomeres. As this occurs, ADP and Pi are released. Heat is also released. 15. ATP is taken up by myosin heads as the crossbridges detach. 16. ATP is then hydrolyzed and energy transferred to myosin heads as they cock and reset for next stimulus. Antagonists 1. Biceps brachii and triceps brachii – frm at the elbow, respectively. 2. Quadriceps femoris and hamstrings ee, respectively. 3. Rectus abdominus and erector spinak, respectively. 4. Masseter and platysma – opens and 5. Rhomboids (major and minor) and sprotraction of the scapula, respectively. Synergists 1. Masseter and temporalis – closes th……………………….. 2. Supraspinatus and deltoid – abducts………………… 3. Biceps brachii and brachialis – flexio…………………… 4. Internal oblique and external oblique…………………. 5. Adductor brevis and adductor longu………………… Fixators 1. The pectoralis major, rhomboids, anhen the deltoids abduct the arm…………………………… 2. Soleus – fixes foot in a plantar flexe………………………….. 3. Brachioradialis – fixates forearm in flmething……………………………. 4. Gemellus – stabilize head of femur 5. Gluteus medius – steadies and plac…………………………….. Spinal Tracts Assignment Name of Tract (3 Sensory, 1 Motor) Information Carried and Destination 1o, 2 o, 3 o with pathway Spinocerebellar Tract (sensory) Spinothalamic Tract (Sensory) Fasciculus Cuneatus and Fasciculus Gracilis (sensory) Corticospinal Tracts (motor) Walking Right Knee Extended going to Flexed 1. Contraction of rectus femoris (quadriceps) stretches tendon. 2. Tendon stretch causes Golgi tendon organ to send message to spinal cord, which in turn: a. Inhibits contraction of rectus femoris b. Activates contraction of biceps femoris (hamstrings) 3. Contraction of biceps femoris causes right knee to flex Right Knee Flexed going to Extended 4. Extension of rectus femoris causes muscle to stretch. 5. Stretched muscle activates muscle spindle to send message to spinal cord, which in turn: a. Inhibits contraction of biceps femoris b. Activates contraction of rectus femoris 6. Contraction of rectus femoris causes right knee to extend. Repeat for walking! Brain Assignment NAME OF AREA FUNCTION OF AREA A Visual areas B Parietal lobe C Primary somatosensory area D Auditory area E Primary motor area F Pre-motor area G Pre-frontal lobe H Broca’s area I Wernike’s area Language comprehension and elaboration; important for all aspects of language, reading, and speech J Cerebellum Responsible for fine motor movements, integration of sensory perception and motor control. Spinal Tracts Assignment Name of Tract (3 Sensory, 1 Motor) Information Carried and Destination 1o, 2 o, 3 o with pathway Spinocerebellar Tract Conducts proprioception (muscle sense) from spinal cord to the cerebellum where subconscious senses are perceived 1°= Begins with the unipolar sensory neuron which synapses with the second order neuron in the spinal gray matter 2°= Neuron travels in the spinocerebellar tract to the cerebellum Spinothalamic Tract Conducts pain, temperature, touch, and pressure from the spinal cord to the thalamus and the cerebral cortex where conscious senses are perceived. The Fasciculus Cuneatus and Fasciculus Gracilis Conducts discriminative touch and conscious proprioception from spinal cord to the cerebral cortex Corticospinal (Pyramidal) Tract Carries voluntary motor stimuli from ceberal cortex to the spinal cord and the motor neurons which innervate skeletal muscles Brain Assignment NAME OF AREA FUNCTION OF AREA A Pre frontal lobe B Pre motor area C Post-Central Gyrus The somatosensory area; It receives conscious sensations from the musculocutaneous regions of the body. D Brodmann’s Area (Primary Auditory Area) The area receives auditory stimuli, processes them into recognized sounds, and associates them with other functions such as speech and the memory necessary to speak and understand speech. E Pre-Central Gyrus The primary motor area; The center for voluntary control of the skeletal muscles. F Frontal Eye Field Synchronizes eye movements. G Visual areas H Broca’s Area The motor speech area for control of the muscles of speech. I Wernicke’s Area Language comprehension and elaboration; Important for all aspects of language, reading, and speech. J NAME OF AREA FUNCTION OF AREA A Corpus Callosum Connects the cerebral hemispheres. B Cingulate Gyrus Conscious manifestations of emotion. C D Corpora Quadrigemina The center for visual reflexes (superior colliculi) and the center for auditory reflexes (inferior colliculi) E F Thalamus Receives all conscious sensations and acts as a relay center. G Pons Connects to the medulla for respiratory control. Other functions bridge voluntary and involuntary control. Connection of cranial nerves V, VI VII, VIII. H Medulla Oblongata The center for control of respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure. Connection for cranial nerves VIII, IX, X, XI, XII. I Arbor Vitae (of the Cerebellum) The white matter of the cerebellum (coordinates voluntary muscle action and connects to incoming and outgoing fibers to provide constant update adjustments) J 9. Match the part with the letter. spinous process transverse process lamina foramen body A D C E B 10. There are _____ pair of ribs. 11. Match the bone with its letter. frontal bone nasal bone mandible maxilla zygomatic bone B A E C D 12. The last part of a long bone to harden is the: 13. Almost all growth of the _____ occurs by 2 years of age. Time spent: 00:08:27 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. All ribs articulate directly with the: 2. Match the bone part with its letter. articular surface for patella medial condyle greater trochanter lesser trochanter head neck linea aspera epicondyle intercondylar notch A G C E I F B D H 3. The socket for the head of the humerus is called the: 4. Match the bone with the letter. pubic tubercle greater sciatic notch iliac crest acetabulum ischial tuberosity A B C E D 5. Match the bone marking with its letter. radial head radial tuberosity trochlear notch coronoid process olecranon process styloid process D G F B A E 6. Match the part of the scapula with its name. glenoid fossa subscapular fossa coracoid process acromion process scapular spine C E D B A 7. Match the bone part with its letter. tibial condyle tibial tuberosity medial malleolus lateral malleolus intercondylar eminence D B E C A 8. The pulley-shaped process on the humerus which articulates with the ulna is the: 9. Match the part with the letter. spinous process transverse process lamina foramen body E A C B D 10. There are _____ pair of ribs. 11. Match the part with its letter. foramen magnum foramen ovale cribriform plate crista galli sella turcica B E A C D 12. The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 13. The last part of a long bone to harden is the: Time spent: 00:22:53 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Match the parts with the correct letters. medial collateral ligament tibial tuberosity medial retinaculum lateral collateral ligament lateral retinaculum tendon of rectus femoris patella patellar ligament D F H C B E A G 2. Match the letter with the description or identification patellar ligament articular cartilage of patella quadriceps tendon medial meniscus medial collateral ligament posterior cruciate ligament tibiofibular ligament lateral meniscus lateral collateral ligament anterior cruciate ligament C E F I B G A J H D 3. The movement shown at C is: 4. The movement shown at A is: 5. match the movement with the illustration (NOTE: D is not used) abduction adduction circumduction medial rotation lateral rotation E F B C A 6. What type of muscle moves your femur? 7. Name the type of muscle tissue that has intercalated discs. View Attempt 2 of 2 1. Match the muscle name with the letter from the diagram. serratus anterior rectus abdominus external oblique transverse abdominus internal oblique E B C D A 2. Which muscle (s) below play a role in inspiration (i.e., drawing air into the lungs)? 3. Match the muscle names with letter from diagram. E D B C A 4. Match the muscle name with letters from the diagram. brachioradialis pronator teres palmaris longus flexor carpi ulnaris flexor carpi radialis C E A D B 5. Match the muscle names with letters from the diagram. trapezius infraspinatus coracobrachialis supraspinatus subscapularis Inserts on E Lies above C Lies below C Lies in fossa D Originates on B 6. True or False: the gastrocnemius is a synnergist to the soleus. 7. Match the muscle names with letters from the diagram. quadratus lumborum psoas major iliacus tensor facia latae sartorius D A B C E 1. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 2. action potential In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 5 3. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 4. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters 5. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 6. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 7. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 8. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 9. voltage-gated ion channels Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 10. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 11. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 5 12. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 13. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 14. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: 15. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 16. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 17. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 18. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 19. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: Student Response Value Feedback A. elastic B. reticular C. keratin D. collagen Score: 20. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. Back Your location: Assessments › View All Submissions › View Attempt crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 2. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 3. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon 0% B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. 0% K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 4. vascularization Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? Score: 0/0.5 5. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. scapula.jpg subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process D C B A 6. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: Student Response Value Feedback A. supination B. pronation C. elevation D. depression Score: 0.5/0.5 7. upper motor neurons Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Student Response Value Feedback A. Upper motor neurons B. Lower motor neurons C. Second order neurons D. Third order neurons. Score: 0.5/0.5 8. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. Student Response Value Feedback A. True B. False 9. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Student Response Value Feedback A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 10. pyramidal tract fibers Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Student Response Value Feedback A. Motor control on the same side of the body as their origin. B. Motor control on the opposite side of the body from their origin. C. Motor control for equilibrium and balance. D. Proprioception and muscle sense. Student Response E. Both answers #3 and #4. 11. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Student Response Value Feedback A. 4 weeks B. 8 weeks C. birth D. 1.5 to 2 years after birth Score: 12. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Scor 13. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 14. septum pellucidum The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Student Response Value Feedback A. septum pellucidum 100% Student Response B. fornix 0% C. choroid plexus 0% D. arbor vitae 0% Score: 0/0.5 15. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: Student Response Value Feedback A. Many dendrites and axons attached to the cell body. 0% Student Response B. Many dendrites and only one axon attached to the cell body. 100% C. One dendrite and many axons attached to the cell body 0% D. One process attached to the cell body. 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 16. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. 17. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 18. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 19. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 20. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. View 1. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 2. action potential In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 3. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 4. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters A B C D E cribriform plate foramen magnum sella turcica crista galli sphenoid 5. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 6. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 7. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 8. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 9. voltage-gated ion channels Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 10. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 11. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 12. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 13. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 14. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: 15. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 16. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 17. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 18. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 19. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: Score: 0.5/0.5 20. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process C A D B Score: View Attempt 2 of unlimited 1. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: Student Response Value Feedback A. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a stretch reflex on the other side. B. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a tendon reflex on the other side. C. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and extension on the other side. D. A withdrawal reflex on one side of the body and a flexor reflex on the other side. Score: 2. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. Student Response Value Feedback A. synovial B. cartilaginous C. fibrous Score: 3. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 4. vascularization Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? Student Response Value Feedback A. bone B. adipose C. cartilage D. all of the above E. Answers 1 and 2, but not 3. Score: 5. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process Statement Response Value subscapular fossa D coracoid process C glenoid fossa A acromion process B Score: 6. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: Student Response Value Feedback A. supination B. pronation C. elevation D. depression Score: 0.5/0.5 7. upper motor neurons Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Student Response Value Feedback A. Upper motor neurons B. Lower motor neurons C. Second order neurons D. Third order neurons. 8. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. Student Response Value Feedback A. True B. False Score: 9. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Student Response Value Feedback A. spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus and fasciculus gracilis C. spinothalamic tract D. both #2 and #3 Score: 0.5/0.5 10. pyramidal tract fibers Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Student Response Value Feedback A. Motor control on the same side of the body as their origin. B. Motor control on the opposite side of the body from their origin. C. Motor control for equilibrium and balance. D. Proprioception and muscle sense. E. Both answers #3 and #4. Score: 0/0.5 11. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Student Response Value Feedback A. 4 weeks B. 8 weeks C. birth D. 1.5 to 2 years after birth Score: 0/0.5 12. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. Binding of calcium ions to Troponin C. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 0/0.5 13. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. Student Response Value Feedback A. flexion 100% B. extension 0% C. abduction 0% D. adduction 0% Score: 14. septum pellucidum The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Student Response Value Feedback A. septum pellucidum B. fornix C. choroid plexus D. arbor vitae Score: 0/0.5 15. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: Student Response Value Feedback A. Many dendrites and axons attached to the cell body. B. Many dendrites and only one axon attached to the cell body. C. One dendrite and many axons attached to the cell body D. One process attached to the cell body. Score: 16. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. H. Opening of potassium channels. I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. Score: 17. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Student Response Value Feedback A. facilitation B. inhibition C. divergence D. convergence Score: 18. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Student Response Value Feedback A. possessing chemically-gated ion channels B. possessing voltage-gated ion channels C. having both chemically-gated and voltage-gated ion channels D. being able to propagate an action potential Score: 19. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: Student Response Value Feedback A. spinal and cranial nerve sensory neurons B. spinal and cranial nerve motor neurons C. spinal and cranial interneurons D. all of the above E. #2 and #3 only Score: 0.5/0.5 20. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Student Response Value Feedback A. areolar connective tissue B. elastic connective tissue C. fibrous connective tissue D. dense irregular connective tissue Score: 0.5/0.5 View QUIZ 2. Action is elbow flexion. Which number shows the Inhibitory pathway frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 3. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 4. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 6. limbic system Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 7. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: 8. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 9. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 11. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 5 12. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 13. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 14. first, second, and third order neurons Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? 15. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 16. gray matter Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: 7. 18. hypothalamus The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 19. post-central gyrus Pain stimuli terminate in the: 20. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 1. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 2. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 5 3. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 4. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 5. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 6. myogenic The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 7. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 8. cell hierarchy The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 9. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 10. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 11. Corpora quadrigemina Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 12. disk movement The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 14. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: Student Response Value Feedback A. Upper portion of the pre-central gyrus. 0% B. Lower portion of the pre-central gyrus. 100% C. Upper portion of the post-central gyrus. 0% D. Lower portion of the post-central gyrus. 0% Score: 0/0.5 15. epidural An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 16. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 17. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 18. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: Student Response Value Feedback A. dense irregular tissue 0% Student Response B. reticular tissue 100% C. areolar tissue 0% D. dense regular tissue 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 19. complementarity The term "complementarity" used in Anatomy and Physiology refers to the deterministic relationship between: 20. spongy bone The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 1. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 2. first cell in bone remodeling The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 3. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 4. pheromomes Which of the following secretes pheromones? 5. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 6. disk movement The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 7. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. 8. receptive region location The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: 9. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process C D A B 10. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 11. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 12. complementarity The term "complementarity" used in Anatomy and Physiology refers to the deterministic relationship between: 13. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 14. Breakdown of ACh by Achase Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? 15. olfactory nerves The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. 16. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 17. the scapula Match parts with letters. A B C D E spinous process acromion glenoid fossa subscapular fossa coracoid process 19. meissner's corp which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? 20. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 1. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 2. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 3. Adipose Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? 5 4. Ca<sup>+2</sup> release Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: 5. contractile elements In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: 5 7. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 8. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 9. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 10. graded potential A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 11. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 12. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 13. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 14. first, second, and third order neurons Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? 15. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 16. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 17. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: 18. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 20. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: View Attempt 1. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 2. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 3. Adipose Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? 4. Ca<sup>+2</sup> release Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: 5. contractile elements In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: 6. Breakdown of ACh by Achase Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? 7. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 8. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 9. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 10. graded potential A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 11. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 12. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 13. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 14. first, second, and third order neurons Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? 15. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 16. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 17. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: 18. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 19. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 20. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: View Attempt Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 2. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 3. myogenic The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 4. voltage-gated ion channels Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 5. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 6. Hierarchy Organs are groupings composed of _____ which work together. 7. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 8. disk structure The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 10. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 11. disk movement The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 12. upper motor neurons Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: 13. basal nuclei Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 14. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 15. Sarcolemma repolarization What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 16. central sulcus The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 17. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. c31ec184-c0a8-518f-017b-57568f158c2b.11472558011_R.jpg A B C D E medial condyle intercondylar eminence medial malleolus tibial tuberosity lateral malleolus 18. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 5 19. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: Student Response Value Feedback A. Upper portion of the pre-central gyrus. 0% 20. hypothalamus The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Student Response Value Feedback A. thalamus 0% Total score: 9.5/10 = 95% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 2. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 3. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 4. synovial sack A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 5. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 6. Junctions Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. gap junction tight junction desmosome keratin filaments hemidesmosome fibers which hold cells together laterally Called the zona occludens because it blocks passage of substances between cells. Allows ions to pass between cells. adheres cells to the basement membrane Called macula adherens because they are like spot welds which adhere cells together. 7. inferior view of skull Match parts with letters. c31ec184-c0a8-518f-017b-57568f158c2b.11472552011_R.jpg A B C D E foramen magnum zygomatic arch occipital condyle hard palate of maxilla vomer bone 8. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 9. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 10. vascularization Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? 11. inhibitory to heart The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 12. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 13. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 14. sodium pump The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 15. central sulcus The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 16. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 17. Impulse enters the T-Tubules What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? 18. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 19. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 20. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: View Attempt Title: Alternate Substitute Quiz connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 2. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 3. medulla The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 4. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: Student Response Value Feedback 5. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 6. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. 7. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 8. desmosomes Which type of cell junction is important in preventing cells from tearing apart from one another when subjected to stress? Student Response Value Feedback 9. receptive region location The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: 10. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: Student Response Value Feedback A. The autonomic system is motor only, while the somatic is both motor and sensory. 0% B. The autonomic system has two motor neurons, the somatic has only one, in each reflex arc. 0% C. The autonomic system has a ganglion in each motor pathway from the CNS, the somatic nervous system does not. 0% D. All of the above. 0% 11. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 12. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 13. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Student Response Value Feedback 14. spinocerebellar tract Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Student Response Value Feedback 15. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 16. graded potential A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 17. Sarcolemma repolarization What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 18. temporal bone Match the parts of the temporal bone with the letters. temporal.jpg external acoustic meatus styloid process mastoid process zygomatic process mandibular fossa C B E A D 19. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. Student Response Value Feedback 20. Breakdown of ACh by Achase Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon 0% B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 0% C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. 0% D. Acetylcholine binds to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. 0% E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. 0% View Attempt Time spent: 00:16:54 Total score: 10/10 = 100% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: Student Response Value Feedback A. bone collar 0% hanter 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 2. spinocerebellar tract Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Student Response Value Feedback 3. relative refractory period The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: Student Response Value Feedback A. absolute refractory period 0% B. relative refractory period 0% C. period of depolarization 0% D. period of hyperpolarization 0% E. Both answers 1 and 3 0% 4. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 5. anterior skull Match parts with letters. c31ec184-c0a8-518f-017b-57568f158c2b.11472550011_R.jpg A B C D E maxilla zygomatic bone mandible frontal bone nasal bone 6. Tissues vs. Characteristics 1 Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional comprises the deep dermis normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract the most abundant connective tissue stretchable epithelium tendons are made of this type 5 7. Epidermis Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. D A C E B 8. Resting membrane potential Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 9. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 10. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 11. contraction trigger The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Student Response Value Feedback 12. pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 13. inferior view of skull Match parts with letters. c31ec184-c0a8-518f-017b-57568f158c2b.11472552011_R.jpg A B C D E zygomatic arch occipital condyle foramen magnum hard palate of maxilla vomer bone 14. myogenic The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 15. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 16. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 17. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 18. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 19. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. 20. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Student Response Value Feedback Given: muscle where stimulus occurs is the biceps brachii, Action is elbow flexion. What type of reflex is produced here? Given: muscle where stimulus occurs is the biceps brachii, Time spent: 00:40:32 Total score: 1. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 2. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. 3. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: 4. Impulse enters the T-Tubules What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? 5. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 6. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 7. sodium pump The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 8. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 9. Exocytosis of ACh into the synaptic cleft. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 10. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 11. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 12. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 13. multiple sclerosis A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: 14. spinal ganglion The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 15. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters A B C D E crista galli sphenoid foramen magnum cribriform plate sella turcica 16. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 17. Sarcolemma repolarization What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 18. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 19. third ventricle The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 20. temporal bone Match the parts of the temporal bone with the letters. external acoustic meatus styloid process mastoid process zygomatic process mandibular fossa E A C B D View Attempt Total score: 1. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process B A C D 2. Junctions Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. gap junction tight junction desmosome keratin filaments hemidesmosome Allows ions to pass between cells. Called macula adherens because they are like spot welds which adhere cells together. fibers which hold cells together laterally adheres cells to the basement membrane Called the zona occludens because it blocks passage of substances between cells. 3. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: 4. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 5. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 6. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 7. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? 8. parenchymal repair When a tissue experiences parenchymal repair the new tissue _____ produce the tissue's orignal function. 9. binds calcium Which of the following binds calcium ions: 10. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 11. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 12. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 13. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 14. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 15. muscle spindle A muscle spindle receptor responds to: 16. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 17. Crossbridge attachment As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: 18. pelvis Match letters with parts. A B C D E ischial tuberosity greater sciatic notch pubic crest iliac crest acetabulum 19. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 20. thalamus The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: View Attempt 1. radius-ulna Match letters with bone parts. A B C D E F G styloid process olecranon process interosseus membrane trochlear notch head of radius coronoid process radial tuberosity 2. sodium pump The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 3. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E zygomatic arch sphenoid bone parietal bone zygomatic bone lacrimal bone 4. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 5. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 6. Tissues vs. Characteristics 1 Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract the most abundant connective tissue stretchable epithelium tendons are made of this type comprises the deep dermis 7. thalamus The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: 8. spinal ganglion The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 9. distal epiphyseal plate The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: 10. pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 11. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 12. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 13. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 14. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 15. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 16. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 17. Hierarchy Organs are groupings composed of _____ which work together. 18. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: 19. septum pellucidum The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. 20. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: View Attempt 1. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process B A D C 2. pre-central gyrus The upper motor neurons originate in the: 3. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 4. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 5. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 6. pyramidal tract fibers Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: 7. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 8. contraction trigger The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 9. binds calcium Which of the following binds calcium ions: 10. elbow Match the part with its letter. tendon of the biceps brachii lateral epicondyle lateral collateral ligament annular ligament radial tubercle bursa tendon of the triceps brachii olecranon process trochlea synovial membrane of joint capsule C G J A E B F I D H 11. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus C B D A E 12. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 13. inferior view of skull Match parts with letters. A B C D E hard palate of maxilla foramen magnum zygomatic arch occipital condyle vomer bone 14. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial malleolus intercondylar eminence medial condyle tibial tuberosity lateral malleolus 15. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 16. spinocerebellar tract Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? 17. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E parietal bone sphenoid bone lacrimal bone zygomatic bone zygomatic arch 18. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 19. distal epiphyseal plate The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: 20. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: View Attempt Title: Started: Submitted: Time spent: 1. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 2. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 3. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 4. post-central gyrus Pain stimuli terminate in the: 5. contraction trigger The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 6. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 7. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus A B C E D 8. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 9. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 10. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 11. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 12. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 13. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 14. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. 15. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 16. basal nuclei Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 17. femur Match parts with letters. A B C D E F G H I anatomical neck lesser trochanter medial epicondyle linea aspera head of femur intercondylar notch medial condyle greater trochanter patellar articular surface 18. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Student Response Value Feedback A. epimysium 100% B. perimysium 0% C. endomysium 0% D. retinaculum 0% Score: 0/0.5 19. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 20. pelvic bone Match the bone parts with the letters. iliac crest greater sciatic notch acetabulum pubic tubercle ischial tuberosity D B A C E View Attempt Total score: 1. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 2. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 3. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 4. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 5. relative refractory period The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: 6. myeloid tissue the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: 7. melanoma The most agressive skin cancer is: 8. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 9. Exocytosis of ACh into the synaptic cleft. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 10. pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: Student Response Value Feedback A. cholinergic, nicotinic 0% B. cholinergic, muscarinic 0% C. adrenergic, alpha 100% D. adrenergic, beta 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 11. anterior fontanel The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 12. types of tissues Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: 13. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 14. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 15. disk structure The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 16. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E zygomatic bone sphenoid bone lacrimal bone zygomatic arch parietal bone 17. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters A B C D E foramen magnum sphenoid sella turcica cribriform plate crista galli 18. first cell in bone remodeling The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 19. basement membrane All epithelial cells have: 20. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? View Attempt Time spent: Total score: 1. Tissues vs. Characteristics 1 Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional the most abundant connective tissue tendons are made of this type comprises the deep dermis stretchable epithelium normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract 2. voltage-gated ion channels Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 3. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. 4. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. osteoclasts Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 6. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 7. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 8. melanoma The most agressive skin cancer is: 9. distal epiphyseal plate The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: 10. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 11. first cell in bone remodeling The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 12. anterior external knee Match the parts with the correct letters. medial collateral ligament tibial tuberosity medial retinaculum lateral collateral ligament lateral retinaculum tendon of rectus femoris patella patellar ligament A F E H C B D G 13. myeloid tissue the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: 14. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 15. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 16. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 17. Corpora quadrigemina Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 18. first, second, and third order neurons Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? 19. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 20. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: View Attempt 1. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 2. spongy bone The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 3. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 4. inhibitory to heart The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 5. the cerebellum A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: 6. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 7. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 8. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 9. vascularization Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? 10. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 11. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 12. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 13. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 14. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 15. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 16. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 17. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 18. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 19. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 20. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. View Attempt Time spent: 00:04:03 1. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 2. spongy bone The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 3. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 4. inhibitory to heart The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 5. the cerebellum A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: 6. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 7. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 8. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 9. vascularization Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences true parenchymal repair? 10. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 11. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 12. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 13. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 14. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 15. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 16. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 17. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 18. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 19. Cartilage and bone Both cartilage and bone possess: 20. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. View Attempt 1. Impulse enters the T-Tubules What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? 2. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. 3. meissner's corp which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? 4. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 5. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus A D E B C 6. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 7. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 8. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 9. the scapula Match parts with letters. A B C D E acromion coracoid process glenoid fossa spinous process subscapular fossa 10. Tissues vs. Characteristics 2 Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa found in symphysis pubis a lining and covering membrane found as costal cartilage all connective tissues are derived from this found in the epiglottis and ear 11. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 12. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 13. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 14. diarthrotic joints All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 15. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 16. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: 17. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 18. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 19. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 20. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. View Attempt Time spent: 00:05:15 Total score: 7/10 = 70% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 2. anterior fontanel The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 3. pre-central gyrus The upper motor neurons originate in the: 4. voltage-gated ion channels Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: 5. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 6. parenchymal repair When a tissue experiences parenchymal repair the new tissue _____ produce the tissue's orignal function. 7. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 8. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 9. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: 10. striations The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: 11. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 12. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 13. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 14. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 15. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 16. autonomic ganglion As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. 17. Resting membrane potential Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 18. cranial bone ossification Cranial bones start out as a: 19. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 20. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: Time spent: 00:05:30 Total score: 9/10 = 90% Total score adjusted by 0.0 Maximum possible score: 10 1. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 2. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. 3. Exocytosis of ACh into the synaptic cleft. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 4. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 5. lateral skull Match the parts shown. A B C D E sphenoid bone zygomatic arch parietal bone zygomatic bone lacrimal bone 6. inflammatory arthritis Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 7. Sarcolemma repolarization What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 8. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 9. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 10. Resting membrane potential Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 11. binds calcium Which of the following binds calcium ions: 12. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 13. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 14. anterior fontanel The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 15. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 16. neural tube The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 17. pyramidal tract fibers Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: 18. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 0.5/0.5 19. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 20. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: 1. relative refractory period The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: 2. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 3. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 4. synovial sack A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 5. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 6. limbic system Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 7. receptive region location The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: 8. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 9. osteoclastic activity osteoclasts are stimulated by: 10. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 11. myeloid tissue the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: 12. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 13. elbow Match the part with its letter. tendon of the biceps brachii lateral epicondyle lateral collateral ligament annular ligament radial tubercle bursa tendon of the triceps brachii olecranon process trochlea synovial membrane of joint capsule D H I G E J C A F B 14. autonomic ganglion As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. 15. Chemically gated Na<sup>+</sup> channels open. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? 16. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 17. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 18. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 19. crossed extensor reflex The crossed extensor reflex consists of: 20. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: View Attempt 16 of unlimited 1. paranasal sinuses Match the sinus with its letter. paranasal_sinuses.jpg Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus D E B A C 2. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 3. Uptake of ATP by myosin heads. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 4. eccrine glands Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 5 5. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Student Response Value Feedback 6. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Student Response Value Feedback 7. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 8. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 9. olfactory nerves The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. 10. types of tissues Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: 11. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 12. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 13. osteoclastic activity osteoclasts are stimulated by: 14. anterior skull 15. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 16. spatial summation If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 17. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 18. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 19. spinal ganglion The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 20. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 2. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 4. eccrine glands Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 6. multiple sclerosis A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: 7. saltatory conduction When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 8. complementarity The term "complementarity" used in Anatomy and Physiology refers to the deterministic relationship between: 5 9. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 10. atlas-axis The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 11. third ventricle The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 12. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 13. pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 14. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 15. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. 16. calcium absorption Increased calcium absorption is produced by: Student Response Value Feedback A. calcitonin 0% Student Response B. parathyroid hormone 0% C. estrogen 0% D. growth hormone 0% E. Vitamin D3 100% Score: 0/0.5 17. post-central gyrus Pain stimuli terminate in the: Student Response Value Feedback A. temporal lobe 0% B. basal nuclei 0% C. pre-central gyrus 0% 18. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of 19. cranial bone ossification Cranial bones start out as a: 20. cell hierarchy The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 1. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 2. thalamus The brain center which filters out sensory stimuli and sends it to appropriate locations is the: 3. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 4. striations The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: 5. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: 6. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters A B C D E foramen magnum sphenoid sella turcica crista galli cribriform plate 7. anterior knee intracapsular Match the letter with the description or identification patellar ligament articular cartilage of patella quadriceps tendon medial meniscus medial collateral ligament oosteruir cruciate ligament tibiofibular ligament lateral meniscus lateral collateral ligament anterior cruciate ligament I J H F E A C G D B 8. neural tube The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 9. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 10. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 11. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. 12. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 13. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process C D A B 14. Corpora quadrigemina Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 15. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 16. sympathetic effect on glands Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. 17. reative refractory period The relative refractory period occurs during: 18. myogenic The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 19. upper motor neurons Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: 20. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. View Attempt Total score: 1. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 2. anterior knee intracapsular Match the letter with the description or identification patellar ligament articular cartilage of patella quadriceps tendon medial meniscus medial collateral ligament oosteruir cruciate ligament tibiofibular ligament lateral meniscus lateral collateral ligament anterior cruciate ligament I F C J G D A H E B 3. tibia-fibula Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E lateral malleolus medial malleolus medial condyle tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence 4. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 6. Chemically gated Na<sup>+</sup> channels open. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? 7. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 8. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 9. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 10. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 11. choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: 12. binds calcium Which of the following binds calcium ions: 13. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 14. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 15. autonomic ganglion As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. 16. pheromomes Which of the following secretes pheromones? 17. central sulcus The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 19. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 20. scapula Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process D B A C 1. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 2. Adipose Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? 3. post-central gyrus Pain stimuli terminate in the: 4. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 5. hypothalamus The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 6. Tissues vs. Characteristics 1 Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional the most abundant connective tissue tendons are made of this type stretchable epithelium normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract comprises the deep dermis 7. sympathetic effect on glands Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. 8. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 9. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 11. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 12. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 13. 14. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 16. eccrine glands Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 17. action potential In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 18. melanoma The most agressive skin cancer is: 19. Voltage gated Na+ channels open. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 20. medulla The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: Student Response Value Feedback A. medulla oblongata 100% B. pons varoli 0% C. pineal body 0% D. midbrain 0% E. corpora quadrigemia 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 1. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 2. recoil The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. 3. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 4. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. 5. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 7. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 8. types of tissues Which of the following is NOT one of the basic tissue types into which all other tissues fall: 9. saltatory conduction When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 10. anterior external knee Match the parts with the correct letters. medial collateral ligament tibial tuberosity medial retinaculum lateral collateral ligament lateral retinaculum tendon of rectus femoris patella patellar ligament F E B C H D G A 11. limbic system Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 12. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 13. 14. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 15. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 16. receptive region location The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: 17. spatial summation If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 18. synovial sack A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 19. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 20. epidural An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 2. diarthrotic joints All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 3. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Student Response Value Feedback 4. third ventricle The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. Student Response Value Feedback 5. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 6. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 7. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 8. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 9. neural tube The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 10. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Student Response Value Feedback A. Calcium ions enter the axon 0% B. Calcium ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 0% C. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. 0% Student Response D. Acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. 100% E. Na+ moves across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. 0% F. Breakdown of ACh by AChase. 0% G. Opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels. 0% H. Opening of potassium channels. 0% I. The troponin-tropomyosin complex shifts, exposing the active sites on actin. 0% J. Uptake of ATP by the myosin heads. 0% K. Attachment of actin-myosin crossbridges and swiveling of the myosin heads. 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 11. basal nuclei Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: Student Response Value Feedback A. pre-motor cortex 0% Student Response B. basal nuclei 100% C. pre-central gyrus 0% D. post-central gyrus 0% E. pre-frontal lobes 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 12. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 13. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 14. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 15. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 18. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 19. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 20. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 3. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 4. basement membrane All epithelial cells have: 5. hypothalamus The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 6. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 7. atlas-axis The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 8. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 9. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 10. osteoclasts Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: Student Response Value Feedback 11. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 12. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 13. cell hierarchy The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 14. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 17. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 2. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 3. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 4. Syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 6. limbic system Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 7. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: 8. Inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 9. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 11. Wernicke's area The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 12. facilitation Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 13. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 14. first, second, and third order neurons Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? 15. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 16. gray matter Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: 17. Action potential An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 18. hypothalamus The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 19. post-central gyrus Pain stimuli terminate in the: 20. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 1. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 2. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 3. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 4. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 5. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 6. myogenic The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 7. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 8. cell hierarchy The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 9. collagen fibers The predominant fibers in dense regular connective tissue are: 10. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Student Response Value Feedback 11. Corpora quadrigemina Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 12. disk movement The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? Student Response Value Feedback A. synarthrosis 0% Student Response B. amphiarthrosis 100% C. diarthrosis 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 14. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 15. epidural An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 16. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 17. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 18. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: 19. complementarity The term "complementarity" used in Anatomy and Physiology refers to the deterministic relationship between: 20. spongy bone The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 2. diarthrotic joints All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 3. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 4. third ventricle The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 5. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 6. excitation of heart Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 7. bone repair The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 8. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 9. neural tube The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. 10. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 11. basal nuclei Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 12. series elastic elements The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 13. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 14. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 15. inhibition Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 18. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 19. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 20. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 1. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 2. The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 3. Cranial bones start out as a: 4. There are _____ pair of ribs. 5. Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 6. Both cartilage and bone possess: 7. Spongy bone lacks: 8. The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 9. The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: 10. Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 11. Match the parts of the temporal bone with the letters. external acoustic meatus styloid process mastoid process zygomatic process mandibular fossa B E A D C Skelatel Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 2. There are _____ pair of ribs. 3. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 4. the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: 5. osteoclasts are stimulated by: 6. The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 7. Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 8. All ribs articulate with the: 9. The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 10. The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 11. Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process B C A D 1. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial condyle tibial tuberosity medial malleolus intercondylar eminence lateral malleolus 2. Match parts with letters. A B C D E F G H I lesser trochanter anatomical neck linea aspera intercondylar notch greater trochanter medial epicondyle patellar articular surface medial condyle head of femur 3. Match parts with letters. A B C D E zygomatic bone frontal bone maxilla mandible nasal bone 4. Match letters with parts. A B C D E iliac crest pubic crest ischial tuberosity acetabulum greater sciatic notch 1. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial malleolus lateral malleolus medial condyle tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence 2. Match parts with letters. A B C D E occipital condyle vomer bone hard palate of maxilla foramen magnum zygomatic arch 3. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E lateral malleolus medial malleolus medial condyle intercondylar eminence tibial tuberosity 4. Match bone parts with letters A B C D E crista galli sella turcica foramen magnum sphenoid cribriform plate 1. Match parts with letters. A B C D E spinous process acromion coracoid process glenoid fossa subscapular fossa 2. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E lateral malleolus medial condyle medial malleolus tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence 3. Match the parts shown. A B C D E zygomatic bone parietal bone sphenoid bone zygomatic arch lacrimal bone 4. Match letters with bone parts. A B C D E F G coronoid process head of radius trochlear notch styloid process radial tuberosity olecranon process interosseus membrane 1. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 2. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 3. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 4. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 5. The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 6. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 7. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 8. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 9. The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: 10. Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 11. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 12. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 13. Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: 14. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 15. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 1. In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 2. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 3. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 4. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 5. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 6. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 7. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 8. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 9. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 10. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 11. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 12. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 13. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 14. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 15. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: CONTRACTION COUPLING 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: 1. Muscle identification Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. Adducts and fixates the scapula. Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris Elbow extensor. Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Title: Quiz #1 Intro-Histology-Integument 1. Organs are groupings composed of _____ which work together. Score: 0.5/0.5 2. The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Which type of cell junction is important in preventing cells from tearing apart from one another when subjected to stress? Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. Score: 2.5/2.5 7. Match each type of tissue with its description. Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. Score: 2.5/2.5 2. When a tissue experiences parenchymal repair the new tissue _____ produce the tissue's orignal function. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. Score: 0.5/0.5 4. In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. A C E B D Score: 2.5/2.5 7. Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional tendons are made of this type stretchable epithelium normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract the most abundant connective tissue comprises the deep dermis Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. gap junction tight junction desmosome keratin filaments hemidesmosome adheres cells to the basement membrane Called the zona occludens because it blocks passage of substances between cells. fibers which hold cells together laterally Called macula adherens because they are like spot welds which adhere cells together. Allows ions to pass between cells. Score: 1.5/2.5 . A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: Score: 0.5/0.5 2. The most agressive skin cancer is: Score: 0.5/0.5 3. Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 4. The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Organs are groupings composed of _____ which work together. Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa found in symphysis pubis found as costal cartilage a lining and covering membrane all connective tissues are derived from this found in the epiglottis and ear Score: 2.5/2.5 7. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. B C A D E Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match each type of tissue with its description. areolar p.c.c.e. dense regular dense irregular transitional comprises the deep dermis normally the the most abundant lining in the respiratory tract stretchable epithelium tendons are made of this type the most abundant connective tissue Score: 2.5/2.5 . The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: Score: 0.5/0.5 2. There are _____ pair of ribs. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: Score: 0.5/0.5 4. Cranial bones start out as a: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: Score: 0.5/0.5 6. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: Score: 0.5/0.5 7. The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: Score: 0.5/0.5 8. Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. Score: 0.5/0.5 9. The first location of ossification in long bones is the: Score: 0.5/0.5 10. The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 0.5/0.5 11. Match the sinus with its letter. Frontal Sinus Ethmoid sinus Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus Mastoid sinus E A B D C Score: 5/5 1. Both cartilage and bone possess: Score: 0.5/0.5 2. Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Cranial bones start out as a: Score: 0.5/0.5 6. The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. Score: 0.5/0.5 7. Increased calcium absorption is produced by: Score: 0.5/0.5 8. the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: Score: 0.5/0.5 9. The first location of ossification in long bones is the: Score: 0.5/0.5 10. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: Score: 0.5/0.5 11. Match the bone parts with the letters. iliac crest greater sciatic notch acetabulum pubic tubercle ischial tuberosity C B A E D Score: 5/5 1. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: Score: 0.67/0.67 2. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. Score: 0.67/0.67 3. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: Score: 0.67/0.67 4. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 6. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? Score: 0.67/0.67 7. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 0.67/0.67 8. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. Score: 0.67/0.67 9. The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: Score: 0.67/0.67 10. In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Score: 0.67/0.67 11. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Score: 0.67/0.67 12. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. Score: 0.67/0.67 13. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Score: 0.67/0.67 14. Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 15. The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: Score: 0.67/0.67 1. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. Score: 0/0.67 2. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: Score: 0.67/0.67 3. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. Score: 0.67/0.67 4. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. Score: 0.67/0.67 6. A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 7. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Score: 0.67/0.67 10. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? Score: 0/0.67 11. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? Score: 0.67/0.67 12. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. Score: 0.67/0.67 13. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: Score: 0.67/0.67 14. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. Score: 0.67/0.67 15. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Score: 0.67/0.67 1. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: Score: 0.67/0.67 2. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. Score: 0.67/0.67 3. Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: Score: 0.67/0.67 4. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: Score: 0.67/0.67 5. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. Score: 0.67/0.67 6. In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Score: 0.67/0.67 7. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? Score: 0/0.67 8. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. Score: 0.67/0.67 9. The term _____ means that a muscle will tend to return to its resting length after contracting. Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? Score: 0.67/0.67 11. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. Score: 0.67/0.67 12. In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: Score: 0/0.67 13. A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: Score: 0.67/0.67 14. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. Score: 0.67/0.67 15. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. Score: 0.67/0.67 . What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? Score: 0.67/0.67 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.67/0.67 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? Score: 0.67/0.67 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: Score: 0.67/0.67 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? Score: 0.67/0.67 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 0.67/0.67 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 0.67/0.67 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? Score: 0.67/0.67 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? Score: 0.67/0.67 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 0.66/0.66 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Score: 0.66/0.66 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: Score: 0.66/0.66 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? Score: 0.66/0.66 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.66/0.66 . Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius Adducts and fixates the scapula. Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. Score: 2/2 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. Score: 2/2 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. Score: 2/2 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Elbow extensor. Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. Score: 2/2 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Score: 2/2 Na+ is pumped out, K+ in at 3:2 producing unequal distribution which leads to a polarized membrane, ~ -65mv.1) An impulse arrives at the neuromuscular junction causing Ca+2 to enter the axon terminus. 2) Ca+2 causes exocytosis of Ach vesicles into synaptic cleft. 3) Ach diffuses across the synapse to contact post-synaptic receptors on the sarcolemma. Ach causes Na+ to enter sarcolemma causing depolarization. 4) If depolarization is threshold a new impulse is produced on the sarcolemma by depolarization of voltage-regulated ion gates. 5) Sarcolemma repolarizes, K+ leaves the cell, pump restores distribution.6) Achase (a.k.a. ACh-E) breaks down Ach so the NMJ can function again. 1. Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 2. The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 3. Cranial bones start out as a: 4. There are _____ pair of ribs. 5. Increased calcium absorption is produced by: 6. Both cartilage and bone possess: 7. Spongy bone lacks: 8. The first step in bone repair is the formation of a: 9. The distal epiphyseal plate of long bones hardens at: 10. Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 11. Match the parts of the temporal bone with the letters. external acoustic meatus styloid process mastoid process zygomatic process mandibular fossa B E A D C Score: 5/5 Skelatel Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 2. There are _____ pair of ribs. 3. The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 4. the myeloid tissue responsible for hematopoiesis is found in the: 5. osteoclasts are stimulated by: 6. The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 7. Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 8. All ribs articulate with the: 9. The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 10. The large anterior fontanel hardens at: 11. Match the parts of the scapula with the letters. subscapular fossa coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion process B C A D 1. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial condyle tibial tuberosity medial malleolus intercondylar eminence lateral malleolus 2. Match parts with letters. A B C D E F G H I lesser trochanter anatomical neck linea aspera intercondylar notch greater trochanter medial epicondyle patellar articular surface medial condyle head of femur 3. Match parts with letters. A B C D E zygomatic bone frontal bone maxilla mandible nasal bone 4. Match letters with parts. A B C D E iliac crest pubic crest ischial tuberosity acetabulum greater sciatic notch 1. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial malleolus lateral malleolus medial condyle tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence Score: 2.5/2.5 2. Match parts with letters. A B C D E occipital condyle vomer bone hard palate of maxilla foramen magnum zygomatic arch 3. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E lateral malleolus medial malleolus medial condyle intercondylar eminence tibial tuberosity 4. Match bone parts with letters A B C D E crista galli sella turcica foramen magnum sphenoid cribriform plate 1. Match parts with letters. A B C D E spinous process acromion coracoid process glenoid fossa subscapular fossa 2. Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E lateral malleolus medial condyle medial malleolus tibial tuberosity intercondylar eminence 3. Match the parts shown. A B C D E zygomatic bone parietal bone sphenoid bone zygomatic arch lacrimal bone 4. Match letters with bone parts. A B C D E F G coronoid process head of radius trochlear notch styloid process radial tuberosity olecranon process interosseus membrane 1. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: 2. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 3. The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 4. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 5. The type(s) of muscle which have myogenic cells: 6. The series elastic elements of a muscle are composed of the various connective tissues and proteins including the protein _____. 7. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 8. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 9. The types of muscle which exhibit striations are: 10. Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 11. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 12. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 13. Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: 14. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 15. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 1. In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 2. The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 3. Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 4. In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 5. The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 6. The intervertebral disks are what type of joint, classified by movement? 7. The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. 8. Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 9. The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 10. A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 11. The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 12. The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 13. Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 14. The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 15. All true diarthrotic joints have a joint capsule composed of: CONTRACTION COUPLING 1. What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? 2. What is the next thing which happens after an impulse enters the T tubules? 3. What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 4. As a result of threshold depolarization at the neuromuscular junction, what happens on the adjacent sarcolemma? 5. As soon as Ca++ ions enter the axon: 6. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 7. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 8. As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: 9. Which event is required for detachment of the crossbridges? 10. Which event, required for continued function of the neuromuscular junction, is prevented by certain pesticide and nerve gas poisons? 11. As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 12. Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 13. An action potential is generated on the sarcolemma by which event of the following: 14. What event causes depolarization of the sarcolemma at the neuromuscular junction? 15. Which of the following binds calcium ions: 1. Muscle identification Match the muscle with its description. serratus anterior rhomboid major and minor infraspinatus levator scapulae trapezius Instrumental in shrugging the shoulder. The only muscle of the group which does not move the scapula. protracts the scapula, as in throwing a punch. Adducts and fixates the scapula. Retracts and fixates the scapula if the head is fixed. 2. Match the muscles with their descriptions. sternocleidomastoid splenius capitus scalenes trapezius temporalis The upper portion of this muscle extends the head only if the scapula is fixed. Elevates the mandible to close the jaw. Acting bilaterally with its pair it extends the head and neck. Acting bilaterally with its pair it protracts and flexes the head. Elevates the ribcage in forced inspiration if head is fixed. 3. Match the muscles with their descriptions. pectoralis major latisimus dorsi teres minor supraspinatus deltoid Adducts and laterally rotates the humerus. The primary adductor of the humerus. A rotator cuff muslce which also abducts the humerus. The primary abductor of the shoulder joint. A back muscle which adducts and medially rotates the humerus. 4. extensor carpi radialis longus brachioradialis brachialis triceps brachii flexor carpi ulnaris Elbow extensor. Maintains the wrist in a partially abducted position when carrying something. Its origin is on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The primary synergist of the biceps brachii Inflammation of the origin of this muscle on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus produces "tennis elbow". 5. Match the muscles with their descriptions. quadratus lumborum iliopsoas gluteus maximus gluteus minimus tensor fascia latae Flexes the thigh (hip joint). Inserts on the iliotibial tract along with the gluteus maximus to abduct and fixate the knee Unilaterally abducts (laterally flexes) the trunk Extends the thigh for running and climbing; fixates in an extended position when standing. Abducts and rotates the thigh when walking Title: Quiz #1 Intro-Histology-Integument 1. Organs are groupings composed of _____ which work together. Score: 0.5/0.5 2. The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: Score: 0.5/0.5 3. The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. Score: 0.5/0.5 4. The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. Score: 0.5/0.5 5. Which type of cell junction is important in preventing cells from tearing apart from one another when subjected to stress? Score: 0.5/0.5 6. Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. Score: 2.5/2.5 7. Match each type of tissue with its description. Score: 2.5/2.5 8. Match the cell junctions and other structures with their descriptions. Junctions may be used more than once. 1. The relationship between the alpha-helix structure of proteins and their function as structural components in tendons and ligaments is described as: 2. The control mechanism maintaining the normal level of a substance or process in would be: 3. Which type of feedback might temporarily oppose homeostasis? 4. The control mechanism activated to produce a rapid response would be: . 5. The anatomical level which is composed of different tissues working together is the: 6. The skin, capillary walls, and the lining of the intestine are all example of which basic function of life? 7. Most of the respiratory tract has a lining of: (A) simple columnar epithelium, (B) simple squamous epithelium, ( 8. The most complex (has the most components) of the epithelial membranes is the: 9. Mesenteries are made of ____________ which connect and lubricate movement of the intestinal organs. 10. The basic types of tissue into which all specific tissues fall include all the following except: 11. All epithelial cells have: (A) a basement membrane, (B) cell junctions, (C) microvilli, (D) all of the above, (E) A and B only. ________________________________________ 12 through 16 Matching: Use each answer once only. (A) desmosomes, ) tight junctions, basement membrane, () gap junctions, microvilli, 12. These anchor the cell's basal surface. 13. These increase the surface area for secretion and absorption. 14. These anchor the intercellular membranes in stretchable tissues. 15. These allow electrolytes and impulses to pass between cells. 16. These produce a semipermeable membrane of cells. ________________________________________ 17 through 21 Matching: Use each answer once only. 17. Found as the stroma supporting the soft organs. 18. Found in the periosteum of bone. 19. Found in the outer dermis of the skin, contains most of the body's water. 20. Does not have the structural arrangement of cells and matrix typical of other connective tissues. 21. Functions to permit arteries to expand and recoil. ________________________________________ 22. Which of the following is most poorly supplied with blood vessels: ) adipose, () fibrous connective tissue, areolar tissue, epidermis ________________________________________ 23 through 27 Matching: Use each answer once only. (A) elastic connective tissue, (B) fibrous connective tissue, (C) fibrocartilage, (D) hyaline cartilage, (E) areolar connective. 23. Produces the articular cartilage found at the ends of bones. 24. Found in the intervertebral disks. 25. The tissue which allows arteries to have flexible walls. 26. The best vascularized of the tissues listed above. 27. The tissue which makes up tendons and ligaments. ________________________________________ 28. The tissue type found lining the stomach and intestines: (A) simple columnar epithelium, pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, ) transitional epithelium, ) simple cuboidal epithelium, () serous membrane. 29. Goblet cells are functionally important to: ) synovial membranes, () mucous membranes, () joints, 30. Stretchable tissue in the urinary bladder is made of: (A) simple columnar epithelium, (B) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, (C) transitional epithelium, (D) simple cuboidal epithelium, (E) serous membrane. 31. Most peritoneal organs are covered with: (A) simple columnar epithelium, (B) serous membrane, (C) mucous membrane, (D) simple cuboidal epithelium, (E) synovial membrane. The Integument Questions 1 through 5 utilize letters from the diagram of the epidermis shown below: Letters are used only once. 1. The stratum lucidum. B 2. This layer undergoes constant mitosis to replace the cells above it. 3. Keratin and keratohyaline accumulate in granules of cells in this layer. 4. This area represents a dermal papilla. 5. This cell secretes melanin. 6. This layer is called the stratum spinosum 7. This layer is constantly exfoliating. A 8. Skin is classified as “thick” when it has: (A) a very thick cornified layer which produces callouses. (B) the stratum lucidum (C) the stratum basale (D) ketatinocytes 9. The turnover time for replacement of the epidermis averages: 10. Sudoriferous glands are: 11. The _____ are glands most important in thermoregulation. 12. The _____ are glands which secrete a viscous fluid containing pheromones. ( 13. The skin cancer with the greatest danger of metastasis is: (A) basal cell carcinoma, (B) squamous cell carcinoma, (C) melanoma. 14. The _____ secrete an oil important in waterproofing the skin. (A) eccrine sweat glands, (B) apocrine sweat glands, (C) sebaceous glands, (D) synovial glands. 15. The _____ raise the hair follicles to produce “goosebumps” on the surface of the skin. (A) hair papillae, (B) vellus hairs, (C) arrector pili muscles, (D) merkel disks. The Skeletal System 1. The very last cranial region to harden is the: 2. The tiny canals which allow osteocytes to connect with one another: 3. The unit of structure of cortical bone tissue is the: ____________________________________________________________________________________ 4 through 8 Matching: Use each answer once only. (A) macrophages, (B) osteoblasts, (C) osteoclasts, (D) osteocytes, (E) fibroblasts. 4. These cells perform phagocytosis in the early stages of bone repair. 5. These cells produce new bone tissue. 6. These cells are stimulated by parathryroid hormone. 7. These cells aid in calcium homeostasis but neither break down nor produce bone tissue. 8. These cells are important in producing an early bone callus. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 9. The very last bone region of the following to harden is the: (A) anterior fontanel, ) diaphysis, ) distal epiphyseal plate, (D) proximal epiphyseal plate, () pubic symphysis. 10. The type of osteoporosis related to excess parathyroid hormone secretion is: 11. Lacunae are spaces enclosing the _____: 12. Which of the following exhibits endochondral ossification? (A) the vertebrae, (B) the scapulae, (C) the ribs, (D) the cranial bones, (E) all of the above, (F) all except D. ____________________________________________________________________________________ Mechanism for Control of Adult Calcium Homeostasis Stimulus Sensor, Control Center and Effector Response Effects Questions 13 through 16 are based on the diagram at left. 13. What is the stimulus for this mechanism? (D) exercise. 14. The sensor, control center, and effector are all located in the: . 15. The response of the effector is to secrete: 16. The hormone secreted in the previous question does which of the following: 17. What tissue is shown at left: 18. What would you find inside A in living tissue: . Arthrology Sample Questions class=Section2> 1. When the radius medially rotates from anatomical position, the movement of the hand is described as: ( -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 through 7 Matching: Answers may be used more than once or not at all. 2. An intracapsular structure which cushions the joint.F 3. An intracapsular ligament which helps to prevent posterior sliding of the femur against the tibia.C 4. Both the knee and elbow have this to prevent medial or lateral movement. A 5. One of these helps prevents the patella from moving laterally out of position D 6. Ligament which helps to stabilize the head of the femur. E 7. This helps reduce friction when tendons and ligaments move against one another G Figure 1 Lateral View -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8. The action illustrated in Figure 1 in which the thigh is raised anteriorly as shown is of the hip: 9. Which of the following would be an agonist in the above action: ( 10. An antagonist to #9 specifically forceful in running, climbing, and jumping would be: Figure 1 Lateral View 11. The movement illustrated by Figure 2 in which the chin is raised from the chest to put the head in anatomical position is of the head. 12. Which of the following would be a prime mover of the head in the above action:, ( 13. What muscle would be a synergist with #24: Figure 2 Lateral View 14. The prime mover in abducting the femur is the: (. 15. Which of the following acts synergistically with #14 in placing the leg when walking: 16. Uniaxial joints can: 17. The intervertebral discs and symphysis pubis are both: Muscular System Sample Questions 1, 2. The soleus is a muscle primarily used in ___(1)____ and would therefore tend to have ___(2)____ size motor units. class=Section3> Answers for #1: 3. The rotator cuff includes all but which of the following muscles: class=Section4> 4. The muscle which helps stabilize the femur and is often the cause of spasm leading to sciatica is: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Questions 5 through 9 utilize the sarcomere diagram which follows: Use only letters indicated. 5. The dark striations are produced by D 6. Troponin and tropomyosin are part of: 7. Which band shortens when the muscle contracts? 8. Which protein is part of serial elastic elements of the muscle? 9. ATP binds to: Use E, F, or G only Questions 10 through 12 apply to diagrams below. Assume electrical stimulation of a muscle. Diagram A 10. Which of these diagrams shows a controlled, graded, contraction? 11. Which diagram shows an increase in the number of cells or motor units responding? 12. Which of the diagrams shows a warmup of a given set of muscle cells? A or B Diagram B 13. Tetanus is: 14. Lactic acid oxygen debt must be paid back by: 15. A cholinesterase inhibitor results in: 16. Slow twitch fibers utilize which of the following for their extended ATP supply: 17. Training increases the number of mitochondria in: 18. Creatine phosphate is extensively stored in: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 19 through 24 Matching: Answers may be used more than once or not at all. 19. Carries the action potential to the interior of the muscle fiber. 20. Before calcium release this blocks the active sites on actin molecules. 21. Consists of three proteins. 22. Its heads swivel to provide the “working stroke” in muscle contraction. 23. Releases calcium when signaled by an action potential. 24. Their opening produces the action potential on the sarcolemma. The action potential is a self-propagated, all-or-none movement of depolarization along the membrane.All-or-none means that there are not different size action potentials. You either have one or you don't. 1) Depolarization speads from previous ion channel. 2) When this depolarization reaches threshold, the Na+ channel opens, allowing Na+ ions into the cell and causing a reversal of potential. 3) As the Na+ channels close, K+ channels open allowing K+ ions to leave the cell causing repolarization. 4) Resting potential is reached, but so much K+ leaves the cell that there is a brief hyperpolarization 5) The hyperpolarization ends as K+ channels close. 1. Sharpey's fibers 1 Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: Score: 1/1 2. bone remodeling The primary stimulus for adult bone remodeling is: Score: 1/1 3. All the ribs articulate with the: All ribs articulate with the: Score: 1/1 4. myeloid tissue1 The ____ is the location of production of blood cells: Score: 1/1 5. occipital condyles The occipital condyles articulate with superior surfaces on the: Score: 0/1 6. first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: Score: 1/1 7. Bone characteristics 1 The component responsible for the hardness and rigidity of bone is: Score: 0/1 8. bone hormones 7 An excess or abuse of this hormone can lead to acromegaly and sometimes pituitary diabetes. Score: 1/1 9. bone hormones 1 The primary hormone in adult calcium homeostasis is: Score: 0/1 10. Ossification 1 Endochondral ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. Score: 0/1 11. Osteoporosis 2 Post-menopausal osteoporosis is characterized by ___ parathyroid hormone in the blood. Score: 1/1 12. inferior view of skull Match parts with letters. A B C D E hard palate of maxilla foramen magnum occipital condyle vomer bone zygomatic arch Score: 1/1 13. pelvis Match letters with parts. A B C D E ischial tuberosity greater sciatic notch iliac crest pubic crest acetabulum Score: 1/1 14. cranial floor Match bone parts with letters A B C D E sphenoid foramen magnum crista galli cribriform plate sella turcica Score: 1/1 15. skin cancer 2 What normally prevents keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum from becoming cancerous due to mutation from uv radiation is: Score: 1/1 16. skin 1 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. The sebacous gland A sudoriferous gland A dermal papilla A pacinian corpuscle The hypodermis B C A E D Score: 0.6/1 17. skin 2 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. Secretes an oily waterproofing Produces sweat Area which contains capillaries and touch receptors Responds to deep pressure and vibration A hypodermic syringe injects into this area A C D E B Score: 1/1 18. glands and receptors 3 Which of the following is a receptor for non-discriminative touch? Score: 1/1 19. Epidermis 2 Match descriptions with letters in the diagram. Also called keratinocytes due to the large number of keratin fibers which anchor them together This is a specialized phagocytic cell A cell derived from neurons These cells are dead This cell responds to fine, discriminative touch D E C B A Score: 1/2.5 20. Areolar tissue 2 Match letters with descriptions. A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber C A B D Score: 0.5/1 21. cartilage 4 The most common of the cartilage is: Score: 1/1 22. cell structure 1 Microvilli increase area on the _____ surface. Score: 0/1 23. cell junctions 1 Match the junction with its description. gap junction hemidesmosome desmosome tight junctions zona adherens these are small junctions for attaching cells together osteocytes use this to exchange calcium ions block or partially block the transport of molecules between cells in a semipermeable membrane also known as macula adherens, these prevent cells in the epidermis and other tissues from pulling apart these connect epithelium to its basement membrane Score: 1/1 24. connective tissue components 2 The component of connective tissues responsible for maintaining hydration is: Score: 1/1 25. Connective tissues 1 Match tissues with descriptions areolar tissue adipose tissue dense regular dense irregular reticular connective tissue elastic connective tissue B C D E F A Score: 0.834/2.5 26. feedback 1 A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: Score: 1/1 27. nucleus pulposus The nucleus pulposus is the spongy center of: Score: 0/1 28. osteoporosis 01 Low _____ and high _____ is a characteristic of senile osteoporosis. Score: 1/1 29. Epithelial tissues 2 Match the tissue with the description. Shows a capillary wall The mucous membrane of the GI tract The lining of the urinary tract The primary cell type found in glands The primary lining of the respiratory tract The epidermis of the skin B E F A C D Score: 0/1 30. Bone Tissue 1 Match the letters with descriptions This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect C A D B Score: 0.5/1 31. 40) shoulder abduction Which muscles are the agonist and antagonist for shoulder abduction? Score: 1/1 32. 30) autoimmune disease The autoimmune disease in which the immune system cells release chemicals which attack the joint tissues and cause severe inflammation is called: Score: 1/1 33. 16) thigh fixation Which muscle fixes the thigh in an extended position? Score: 1/1 34. 19) lateral epicondylitis The origin of the _____ is inflammed in lateral epicondylitis. Score: 1/1 35. 15) knee fixation Which muscle fixes the knee in an extended position? Score: 1/1 36. 41) rotator cuff Which muscle is NOT a member of the rotator cuff? Score: 1/1 37. 4) action potential travels to the: The action potential travels to the _____ to enter the muscle cell. Score: 1/1 38. binds calcium Which of the following binds calcium ions: Score: 0.5/1 39. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? Score: 1/1 40. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: Score: 0/1 41. action potential 7 This is the point where repolarization begins. Score: 1/1 42. action potential 3 Which letter indicates the absolute refractory period? Score: 1/1 43. connective tissues d A _____ is a tendinous structure that prevents the displacement of other tendons or ligaments and holds them in their normal positions. Score: 0/1 44. forced inspiration The sternocleidomastoid and scalenes work together with the _____to raise and expand the ribcage in forced inspiration. Score: 0/1 45. contractile elements 1 In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: Score: 1/1 46. resting length Muscle fibers will return to their resting length due to their: Score: 1/1 47. ion movement 1 The sarcolemma is polarized because more _____ are pumped out than ___ are pumped in. Score: 1/1 48. latissimus dorsi 1 Which muscle is a synergist with the latissimus dorsi in its action on the brachium? Score: 0/1 49. muscle cell types C Fast twitch red (intermediate) fibers have: Score: 0.75/1 50. muscle cell types 2 Slow twitch red fibers primarily utilize _____ to provide energy for metabolism. Score: 1/1 51. muscle movements 5B An antagonist to the muscle shown in red (bilateral action) would: Score: 0/1 52. muscle movements 4C The agonist for dorsiflexion would be: Score: 0/1 53. muscle movements 1B The movement shown as B is ___ of the knee. Score: 1/1 54. muscle movements 1AA The prime mover in movement A is the: Score: 1/1 55. muscle movements 3AA In movement A, performed from a standing position as shown, the _____ is contracting (generating tension) eccentrically. Score: 0/1 56. muscle types 2 The type of muscle possessing striations: Score: 1/1 57. summation A2 The diagram shows: Score: 1/1 1. occipital condyles The occipital condyles articulate with superior surfaces on the: Score: 1/1 2. conchae The superior and middle conchae are part of the ___ bone. Score: 1/1 3. humerus 2 The capitulum articulates with the _____ to form a pivot joint. Score: 0/1 4. Sharpey's fibers 1 Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: Score: 1/1 5. The first cell in bone remodeling The cell which acts first in the process of remodeling in adult bone: Score: 0/1 6. the epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone to harden is the: Score: 1/1 7. Bone characteristics 2 The component responsible for the flexibility and resilience of bone is: Score: 0/1 8. bone hormones 5 This hormone is directly necessary for calcium absorption from the gut. Score: 1/1 9. bone hormones 1 The primary hormone in adult calcium homeostasis is: Score: 0/1 10. Ossification 2 A lumbar vertebra ossifies from pre-existing model of: Score: 1/1 11. Osteoporosis 1 Post-menopausal osteoporosis is characterized by ___ calcium in the blood. Score: 1/1 12. anterior skull Match parts with letters. A B C D E nasal bone frontal bone zygomatic bone mandible maxilla Score: 1/1 13. the scapula Match parts with letters. A B C D E coracoid process glenoid fossa acromion subscapular fossa spinous process Score: 1/1 14. tibia-fibula1 Match the bone parts with their letters. A B C D E medial condyle medial malleolus lateral malleolus intercondylar eminence tibial tuberosity Score: 1/1 15. skin cancer 2 What normally prevents keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum from becoming cancerous due to mutation from uv radiation is: Score: 0/1 16. skin 1 Match the letters from the diagram with their descriptions. The sebacous gland A sudoriferous gland A dermal papilla A pacinian corpuscle The hypodermis E B D C A Score: 0.6/1 17. skin 3 Non-keratinized skin is found in the: Score: 1/1 18. glands and receptors 1 Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? Score: 1/1 19. Epidermis 2 Match descriptions with letters in the diagram. Score: 1/2.5 20. Areolar tissue 2 Match letters with descriptions. A fibroblast Reticular fiber Elastic fiber Collagen fiber D A B C Score: 0.5/1 21. cartilage 1 Chondrocytes are found within fluid-filled spaces called: Score: 1/1 22. cell structure 1 Microvilli increase area on the _____ surface. Score: 1/1 23. columnar epithelium 2 Match letters with descriptions. This surface might have hemidesmosomes Secretes mucus This surface might have microvilli This has a characteristic shape and location in the cell D B A C Score: 1/1 24. connective tissue components 1 The two primary components of all connective tissues are: Score: 0/1 25. Connective tissues 1 Match tissues with descriptions areolar tissue adipose tissue dense regular dense irregular reticular connective tissue elastic connective tissue B A C F D E Score: 0.4175/2.5 26. feedback 1 A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: Score: 1/1 27. parenchymal repair 1 True parenchymal repair occurs in _____ tissue. Score: 0/1 28. functional repair Which of the following tissues is well vascularized and experiences functional repair? Score: 1/1 29. Epithelial tissues 2 Match the tissue with the description. Shows a capillary wall The mucous membrane of the GI tract The lining of the urinary tract The primary cell type found in glands The primary lining of the respiratory tract The epidermis of the skin B D A F C E Score: 0.6668/1 30. Bone Tissue 1 Match the letters with descriptions This carries a blood vessel This contains a bone cell This is left over from a previous osteon This allows processes from osteocytes to connect B C A D Score: 1/1 31. 21) Pituitary gland Which of the following contains the pituitary gland? Score: 1/1 32. 28) Patellar ligament The patellar ligament connect the patella to the: Score: 1/1 33. 11) energy The first 15 seconds of anerobic contractions rely on _____ for energy. Score: 1/1 34. 16) thigh fixation Which muscle fixes the thigh in an extended position? Score: 1/1 35. 13) fixator What muscle fixates the foot in a plantar flexed position during standing? Score: 1/1 36. 20) melanocytes Melanocytes are part of which layer? Score: 1/1 37. 8) graded contractions What is the cause of the response seen here: Score: 1/1 38. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: Score: 1/1 39. Crossbridge attachment As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: Score: 0/1 40. Sarcolemma repolarization What event causes repolarization of the sarcolemma? Score: 1/1 41. action potential 4 This is the polarity at which the voltage-gated sodium channels open. Score: 1/1 42. action potential 2 Which letter indicates the point where the membrane is hyperpolarized? Score: 1/1 43. connective tissues d A _____ is a tendinous structure that prevents the displacement of other tendons or ligaments and holds them in their normal positions. Score: 0/1 44. rotator cuff Which muscle listed is not a member of the rotator cuff muscles? Score: 1/1 45. erector spinae and soleus The erector spinae and soleus would have which of the following in common: Score: 0.75/1 46. contraction trigger 1 The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: Score: 1/1 47. ion movement 2 In response to acetylcholine binding to post-synaptic receptors, _____ flows across the sarcolemma into the muscle cell. Score: 0/1 48. latissimus dorsi 3 The latissimus dorsi and teres major are: Score: 0/1 49. muscle cell types B Slow twitch red fibers have: Score: 1/1 50. muscle cell types 1 White fibers utilize _____ to provide energy for metabolism. Score: 1/1 51. muscle movements 3AA In movement A, performed from a standing position as shown, the _____ is contracting (generating tension) eccentrically. Score: 0/1 52. muscle movements 2B The movement shown as B is ___ of the thigh. Score: 1/1 53. muscle movements 4D The agonist for dorsiflexion would be: Score: 1/1 54. muscle movements 3C The movement shown as C is ___ of the vertebral column. Score: 1/1 55. muscle movements 1A The movement shown as A is ___ of the knee. Score: 1/1 56. muscle types 2 The type of muscle possessing striations: Score: 0.5/1 57. summation B1 The diagram (all parts) shows: Score: 1/1 1. As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. Score: 1/1 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. Score: 0/1 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: Score: 1/1 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: Score: 1/1 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: Score: 1/1 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division Score: 1/1 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. Score: 1/1 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: Score: 1/1 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: Score: 1/1 10. Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. Score: 1/1 1. As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. Score: 1/1 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. Score: 1/1 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: Score: 1/1 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: Score: 1/1 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: Score: 1/1 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division Score: 1/1 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. Score: 1/1 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: Score: 1/1 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: Score: 1/1 10. Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. Score: 1/1 1. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: Score: 1/1 2. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: Score: 1/1 3. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: Score: 1/1 4. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Score: 0/1 5. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: Score: 1/1 6. A multipolar neuron has: Score: 1/1 7. Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? Score: 1/1 8. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Score: 1/1 9. The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Score: 1/1 10. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: Score: 1/1 1. The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: Score: 1/1 2. Which of the following tracts has first order, second order, and third order neurons? Score: 1/1 3. The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: Score: 0/1 4. Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Score: 1/1 5. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? Score: 1/1 6. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: Score: 1/1 7. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: Score: 1/1 8. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Score: 1/1 9. Multipolar neurons function as: Score: 1/1 10. A multipolar neuron has: Score: 1/1 1. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: Score: 1/1 2. Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Score: 1/1 3. High frequency stimuli result from: Score: 1/1 4. Threshold depolarization will result in an action potential when it occurs at: Score: 1/1 5. Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: Score: 1/1 6. The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: Score: 1/1 7. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. Score: 1/1 8. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: Score: 1/1 9. When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: Score: 1/1 10. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. Score: 1/1 1. A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: Score: 1/1 2. The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. Score: 1/1 3. Pain stimuli terminate in the: Score: 1/1 4. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Score: 1/1 5. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: Score: 1/1 6. Broca's area is located alongside the: Score: 1/1 7. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: Score: 1/1 8. The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Score: 1/1 9. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. Score: 0/1 10. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: Score: 1/1 1. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. Score: 1/1 2. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: Score: 1/1 3. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: Score: 1/1 4. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: Score: 1/1 5. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: Score: 1/1 6. Cerebrospinal fluid is a filtrate from the capillaries of the: Score: 1/1 7. The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. Score: 1/1 8. The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. Score: 1/1 9. The _____ is derived from the canal within the primitive neural tube. Score: 1/1 10. Broca's area is located alongside the: Score: 1/1 Score: 2.5/2.5 Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? 2. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 3. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: 4. A multipolar neuron has: 5. Multipolar neurons function as: 6. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 7. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: 8. The receptive region of a multipolar neuron would include: 9. Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: 10. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 2. Which of the following tracts does not send impulses ultimately to the cerebral cortex? 3. Multipolar neurons function as: 4. Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: 5. Unmyelinated fiber, synapses, and cell bodies in the brain and spinal cord are located in: 6. Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? 7. The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 8. An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 9. Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: 10. A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 2. The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: 3. A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: 4. High frequency stimuli result from: 5. The relative refractory period occurs during: 6. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 7. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 8. Prior sub-threshold depolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 9. When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 10. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: 2. Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 3. The relative refractory period occurs during: 4. A small local depolarization or hyperpolarization is known as: 5. The period during which the trigger region is effectively inhibited but not prevented from generating an action potential is the: 6. Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Score: 1/1 7. Prior sub-threshold hyperpolarization of a reflex pathway produces: 8. When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 9. Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 10. If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. A constantly updating control of muscles which provides coordination is centered in the: 2. The brain center which controls much of the endocrine and sympathetic systems is the: 3. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 4. The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 5. Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 6. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 7. The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 8. The area said to represent intelligence and an interpretive area for language is the: 9. The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 10. The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 2. Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 3. Broca's area is located alongside the: 4. The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 5. The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 6. The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 7. The _____ separates the mainly motor from the mainly sensory portions of the cerebrum. 8. The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. 9. Reflexes such as blinking and pupilary reflex is centered in the: 10. Repetitive movements of a skilled nature are facilitated in the: 2. The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 3. The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 4. The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 5. Receptors which mediate excitation of the heart in response to stress are: 6. Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 7. Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 8. The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 9. The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 10. Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? 2. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 3. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? 4. spongy bone The spaces in spongy bone are initially filled with: 5. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Feedback Score: 0/0.5 6. autonomic vs. somatic The autonomic nervous system differs from the somatic nervous system in which of the following ways: 7. Tissues vs. Characteristics 2 Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa all connective tissues are derived from this found as costal cartilage found in the epiglottis and ear a lining and covering membrane found in symphysis pubis 8. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 9. Crossbridge attachment As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: 10. contractile elements In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: 11. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 12. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. 13. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 14. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division 15. Epidermis Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. B C E A D 16. Positive feedback A process which requires rapid response will usually utilize: 17. osteoclastic activity osteoclasts are stimulated by: 18. foot movement The movement of the foot in which the sole is turned inward is correctly termed: 19. Ossification Ossification begins at about _____ in the developing embryo. 20. sympathetic effect on glands Most glands are _____ by the sympathetic nervous system. 1. olfactory nerves The olfactory nerves pass through the ____ of the _____ on their way to the brain. 2. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 3. medulla The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 4. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 5. pons The brain center which mediates functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary is: 6. myosin head reset In order for myosin heads to detach from actin and reset, _____ must be available. 7. atlas-axis The joint between the atlas and axis is a _____ joint with the movement performed called _____. 8. thigh movement Movement in which the thigh is raised toward the abdomen is _____ of the hip. 9. There are _____ pair of ribs. There are _____ pair of ribs. 10. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 12. Adipose Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? 13. epidural An epidural injection of anesthetic would be administered: 14. synovial sack A sack made of synovial membrane which lies between tendons, ligaments, and nearby bones is called: 15. vascular stimulation Most blood vessels are innervated only by the _____ division Score: 0.5/0.5 17. spatial summation If several inputs to a reflex pathway each produce simultaneous sub-threshold depolarizations, it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 18. Gates at Nodes In myelinated peripheral nerves the voltage gates are located only at the Nodes of Ranvier. 19. saltatory conduction When an action potential spreads from one node of Ranvier to the next it is called _______ and it travels _________ than other forms of transmission. 20. spinal ganglion The cell bodies of spinal sensory neurons are located in: 1. syndesmosis A syndesmosis is actually a small _____ which connects bones in a non-movable way. 2. conscious sensations Which of the following tracts is responsible for conscious sensations? Score: 0.5/0.5 3. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 4. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: Student Response Value Feedback A. spinal and cranial nerve sensory neurons 0% B. spinal and cranial nerve motor neurons 0% C. spinal and cranial interneurons 0% D. all of the above 0% E. #2 and #3 only 100% Score: 0/0.5 5. elastic connective tissue The stroma of the lungs contains _____ which permits its expansion and recoil. 6. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 7. Resting membrane potential Once an action potential is generated, another cannot be generated until the ion gates return to the following configuration: 8. inhibitory to heart The fibers which control the heart in the absence of stress come from the _____ portion of the CNS as part of the _____ division of the autonomic nervous system. 9. pheromomes Which of the following secretes pheromones? 10. osteoclasts Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 11. frequency summation High frequency stimuli result from: 12. contraction trigger The trigger which causes vesicles of acetylcholine to move to the axon membrane and release ACh is: 13. contractile elements In the structural hierarcy of a muscle, each cell is filled with contractile structures called: 14. eccrine glands Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 15. glossopharyngeal nerve The autonomic function of the glossopharyngeal nerve is: 16. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: 17. primary auditory area The primary auditory area is located in the _____ lobe. 18. negative feedback In order for a regulatory process to be self controled it must utilize: 19. haversian systems Spongy bone lacks: 20. receptive region criterion The criterion for an area being the neuron receptive region is: 1. medulla The centers which control the heart, respiratory muscle contraction, and vascular smooth muscle are located in the: 2. autonomic ganglion As a result of an autonomic ganglion located _____ the _____ is alble to produce mass activation. 5. post-tetanic potentiation Repeated use of a particular neural pathway, such as in a rote task, will result in a temporary facilitation of the pathway called: 7. reticular tissue The stroma of the body's soft organs is made of: 9. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 10. septum pellucidum The _____ covers the entrance to the lateral ventricle. 11. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: 12. Ca++ binds to troponin C As soon as Ca++ ions are released into the sarcoplasm: 13. inflammatory arthritis Which type of arthritis involves the greatest degree of inflammation and disability? 14. stretch reflex When a stretch reflex is initiated it produces: 15. meissner's corp which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? 16. Adipose Which tissue is important in being an insulator and shock absorber for the organs? 17. cranial bone ossification Cranial bones start out as a: 18. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 20. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 1. Sharpey's fibers Collagen fibers which run from the fibrous bone covering into the bone itself are called: 2. upper motor neurons Fibers in the corticospinal tract are known as: 3. epiphyseal plate The last location within a long bone of cartilage formation is: 4. desmosomes Which type of cell junction is important in preventing cells from tearing apart from one another when subjected to stress? 5. substantia nigra The brain region involved when insufficient dopamine production produces Parkinson's disease: 6. Broca's area Broca's area is located alongside the: 7. specialization The hierarchy organization which produces body systems results in _____ specialization. 8. learned reflex When a pathway is automatically facilitated by the brain, when the proper circumstances are present, it is called: 9. elbow Match the part with its letter. tendon of the biceps brachii lateral epicondyle lateral collateral ligament annular ligament radial tubercle bursa tendon of the triceps brachii olecranon process trochlea synovial membrane of joint capsule E F B H J G D A I C 10. Impulse reaches the axon terminus What is the first thing that happens when an impulse reaches the axon terminus of a neuromuscular junction? 11. pyramidal tract fibers Fibers which cross in the pyramids are concerned with: Score: 0/0.5 12. eccrine sweat glands Sympathetic stimulation of the eccrine sweat glands is through _____ fibers. 13. hyperpolarization Opening of the chemically-gated K+ channels would produce: Score: 0.5/0.5 14. first cell in bone remodeling The cell which initiates the process of remodeling in adult bone: 15. Ca<sup>+2</sup> release Ca+2 is released into the sarcoplasm when an action potential stimulates the: 17. intracapsular ligaments The _____ are intracapsular ligaments which help to prevent anteroposterior displacement and twisting of the knee. 18. fibrocartilage Which of the following forms the structure of the intervertebral disks? 19. multipolar neuron A multipolar neuron has: 20. pheromomes Which of the following secretes pheromones? 1. Curare Curare acts as a muscle relaxant by competing with this process: Score: 2. limbic system Functions such as emotional motor responses and short term memory both reside in the: 3. disk structure The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? 4. Tissues vs. Characteristics 2 Match each type of tissue with its description. fibrocartilage elastic cartilage hyaline cartilage mesenchyme serosa found in the epiglottis and ear a lining and covering membrane found as costal cartilage found in symphysis pubis all connective tissues are derived from this 5. non-movable joints Joints which non-movable are usually classified structurally as _____ joints. 6. The first cervical vertebra The first cervical vertebra is called the: 7. smooth muscle The type of smooth muscle in which an impulse passes through a large number of cells which subsequently contract in synchrony is: 8. Epidermis Match descriptions with letters in the diagram of the epidermis. (Click on the word "diagram") The layer missing from thin skin. The layer which constantly exfoliates. Its cells contain numerous keratin filaments. This layer undergoes constant mitosis. Its cells contain dense keratin granules. E C A D B 9. temporal summation If one input to a reflex releases a depolarizing neurotransmitter with a high frequency it could result in _____ at the receptive region of the receiving neuron. 11. action potential In order to produce an action potential on the sarcolemma, depolarization at the neuromuscular junction must activate: 12. Function of multipolar neurons Multipolar neurons function as: 13. osteoporosis Insufficient _____ is associated with osteoporosis. 14. meissner's corp which of the following is responsible for crude (non-descriminative) touch? 16. anterior external knee Match the parts with the correct letters. medial collateral ligament tibial tuberosity medial retinaculum lateral collateral ligament lateral retinaculum tendon of rectus femoris patella patellar ligament H D B G F A E C 17. Binding of the ACh to the post-synaptic receptors. What event causes opening of the chemically-gated Na+ channels? 18. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 19. muscle spindle A muscle spindle receptor responds to: 20. multiple sclerosis A demyelination disorder of the CNS which results in impaired and disrupted conduction along axons is: Student Response Value Feedback A. paraplegia 0% B. quadriplegia 0% C. multiple sclerosis 100% D. Paget's disease 0% Score: 0.5/0.5 1. eccrine glands Which of the following is important in thermoregulation? 2. hand rotation Starting in anatomical position, the hand is rotated so that the palm is down (or to the back). This movement is called: 3. third ventricle The _____ surrounds the intermediate mass. 4. connective sheath The _____ surrounds a muscle and fuses with a tendon or aponeurosis. 5. articular cartilage damage The type of arthritis which begins with damage to articular cartilage from stress or injury is called: 6. parenchymal repair When a tissue experiences parenchymal repair the new tissue _____ produce the tissue's orignal function. 7. Shifting of the troponin-tropomyosin complex. As a direct result of Ca+2 binding to troponin: 8. Crossbridge attachment As soon as the active sites are exposed on actin: 9. cell hierarchy The cell derived from osteoprogenitor cels which produces ossification is the: 11. internal capsule Fibers of the _____ carry stimuli from the motor cortex to the corticospinal tracts. 12. Descending tract A tract with the name vestibulospinal would be: 13. osteoclasts Osteoclasts are derived at some point from: 14. inhibition of heart The fibers which control the heart at all times in the absence of stress are: 15. The first location of ossification in long bones The first location of ossification in long bones is the: 18. pupilary dilation The receptors which produce pupilary dilation are: 19. disk structure The intervertebral disks are which type of joint classified according to structure? Student Response Value Feedback A. fibrous 0% B. cartilaginous 100% C. synovial 0% Score: 0/0.5 20. Calcium homeostasis The primary hormone for calcium homeostasis is: 1 In-Class Quiz Neurology Which of the following cells produces the myelin sheath in the CNS? 1)Schwann cells 2)Oligodendrocytes 3)Ependymal cells 4)Astrocytes Which of the following cells is important in nerve fiber regeneration? 1)Schwann cells 2)Oligodendrocytes 3)Ependymal cells 4)Astrocytes A structure in the CNS that is analogous with a nerve? 1)Ganglion 2)Center 3)Tract 4)Fasciculus Which tract carries pain, temperature, touch and pressure? 1)Spinothalamic 2)Spinocerebellar 3)Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus 4)Corticospinal Which tracts reach the cerebral cortex? 1)Spinothalamic 2)Spinocerebellar 3)Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus 4)Corticospinal There are how many pair of spinal nerves? 1)7 2)8 3)31 4)48 The femoral nerve arises from which plexus? 1)Cervical 2)Brachial 3)Lumbar 4)Sacral The axillary nerve arises from which plexus? 1)Cervical 2)Brachial 3)Lumbar 4)Sacral Answer 2 The sciatic nerve forms which of the following? 1)Pudendal and obturator 2)Pudendal and tibial 3)Tibial and peroneal (fibular) 4)Peroneal and obturator 1 BIOL 237 In-Class Quiz The Brain Which part of the brain is the origin of upper motor neurons? A)Pre-central gyrus B)Post-central gyrus C)Pre-frontal lobe D)Wernicke’s area E)Basal Nuclei Answer Which part of the brain would receive stimuli from the spinothalamic tract? A)pre-central gyrus B)Post-central gyrus C)Pre-frontal lobe D)Wernicke’s area E)Basal Nuclei Answer 4 Which part of the brain would connect to both auditory areas and Broca’s area? A)Pre-central gyrus B)Post-central gyrus C)Pre-frontal lobe D)Wernicke’s area E)Basal Nuclei Answer 5 Language Pathways Listening: Speaking: Visual or auditory cortex Wernicke’s area Broca’s area Motor cortex Wernicke’s area is, among other things, the center for language use. It processes input from both visual and auditory sources (reading language and hearing speech) and sends stimuli to Broca’s area and the motor cortex for speech production. 6 Too much dopamine, or malformation of which part is believed to be a cause of schizophrenia? A)Pre-central gyrus B)Post-central gyrus C)Pre-frontal lobe D)Wernicke’s area E)Basal Nuclei Answer 7 Lack of dopamine secreted into the _____ is the cause of Parkinson’s? A)pre-central gyrus B)Post-central gyrus C)Pre-frontal lobe D)Wernicke’s area E)Basal Nuclei Answer 8 3 8 0 9 4 5 7 1 6 2 Which part is the center for the “vital functions” of the heart and respiration.? Answer 9 Which part receives all conscious sensations.? 3 8 0 9 4 5 7 1 6 2 Answer 10 Which part covers the entrance to the lateral 3 8 0 9 4 5 7 1 6 2 Answer 11 3 8 0 9 4 5 7 1 6 2 12 Which part facilitates reflexes of a skilled and repetitive nature? (A) Basal nuclei (B) pineal gland (C) Substantia nigra (D) Corpora qadrigemina Answer A 13 The Basal Nuclei Figure 12.11 a Corona radiata – connect to motor cortex Caudate nucleus Lentiform nucleus Thalamus Amygdaloid nucleus Corpus striatum = striped body Corpus striatum = striped body Internal capsule Pyramidal fibers The basal nuclei (Figure 12.11) (sometimes misnamed the basal ganglia [Q: why is this incorrect?]) consist of a group of structures with both gray and white matter which in various ways modify motor functions coming from the cerebral cortex. Its structures include the 14 Role of the Basal Nuclei • Complex and repetitive movements e.g. 15 Which part would contain the reflex center for blinking? (A) Basal nuclei (B) pineal gland (C) Substantia nigra (D) Corpora qadrigemina Answer 16 Which part contains the respiratory center? (A) Pineal gland (B) Hypothalamus (C) Thalamus (D) Medulla Answer 17 Which part controls most endocrine glands? (A) Pineal gland (B) Hypothalamus (C) Thalamus (D) Medulla Answer 18 Visual signals would travel to which parts? (A) Pineal gland (B) Hypothalamus (C) Thalamus (D) Medulla Answer 19 Which part is is a cortical component of 3 the limbic system? 8 0 9 4 5 7 1 6 2 Answer 20 The part of the limbic system which activates fear and other emotional responses: (A) mammillary body (B) Hypothalamus (C) Amygdala (D) Hippocampus Answer 21 Limbic System Components Figure 12.18 CCoonnsscciioouuss mmaanniiffeessttaattiioonnss ooff eemmoottiioonn Amygdala CCeenntteerr ffoorr eemmoottiioonnaall rreessppoonnsseess Hippocampus Mammillary body MMeemmoorryy Memory, possibly olfactory Memory, possibly olfactory Fornix Part of Thalamus Pleasure center; stress responses Pleasure center; stress responses Hypothalamus Cingulate gyrus The Limbic System is usually considered as composed of the following: The cingulate gyrus The hypothalamus - contains …………………………….. Mamillary body - contains me Hippocampus - responsible fo Amygdaloid nucleus - Part of 22 Pathways of Fear Pre-frontal cortex – Cortex – cingulate gyrus Stimulus Thalamus Hippocampus Amygdala Sympathetic N.S. “Fight or Flight” Hypothalamus Pituitary Fornix Septum Mammillary body “Low Road” “High Road” Evolution has designed the brain so that a frightening stimulus, hearing an explosion for instance, is picked up by the thalamus and sent directly to the amygdala. The amygdala, in turn, communicates with other regions to set in motion the body’s ……………….. There are so-called “high” and “low roads” for the fear response. The low road provides for a quick, perhaps life-saving, response in the face of danger. The high road allows evaluation of the stimulus by the cortex and consideration of the response. PTSD re-activates the low road response from memories. 1 BIOL 237 In-Class Review 2 Which type of tissue is important for holding most of the body’s water: A)Adipose B)Areolar C)Dense irregular D)Reticular E)Hyaline cartilage Answer 3 Which two of these are found in the dermis of the skin and in mucous membranes? A)Adipose B)Areolar C)Dense irregular D)Reticular E)Hyaline cartilage 4 Which substance is most important in hydration of connective tissues: A) Lipid B) Proteoglycans C) Collagen D) The glycocalyx E) NaCl Answer 5 Which layer of the skin contains the most numerous desmosomes? A) stratum basale B) stratum spinosum C) stratum granulosum D) stratum lucidum E) stratum corneum Answer 6 Which junction allows cells to exchange materials directly with one another A) tight junctions B) desmosomes C) hemidesmosomes D) gap junctions E) zona adherens Answer 7 Which tissue lines most of the gastrointestinal tract? A) simple squamous B) simple columnar C) simple cuboidal D) pseudostratified ciliated columnar E) stratified squamous Answer 8 Merkel disks send information through which of the following spinal tracts A) spinothalamic B) spinocerebellar C) fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus D) corticospinal E) extrapyramidal Answer 9 Information originating in the vestibule and semicircular canals would ultimately reach the lower motor neurons through which of the following: A) spinothalamic B) spinocerebellar C) fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus D) corticospinal E) extrapyramidal Answer 10 The joint between the atlas and axis is a: A) condyloid joint B) pivot joint C) hinge joint D) ball-and-socket joint E) planar joint Answer 11 Which of the following can exhibit flexion and extension? A) condyloid joint B) pivot joint C) hinge joint D) ball-and-socket joint E) planar joint Answer 12 Primary muscle for flexing the thigh: A) sternocleidomastoid B) spenius capitus C) iliopsoas D) gluteus maximus E) rectus abdominis Answer 13 Primary muscle for abducting the thigh: A) latissimus dorsi B) deltoid C) tensor fasciae latae D) gluteus minimus and medius E) gracilis Answer 14 Primary muscle for extending the knee: A) biceps femoris B) gastrocnemius C) rectus femoris D) peroneus (fibularis) longus E) soleus What nerve innervates each of the above? Answer C FEMORAL N. –. PERONEAL (FIBULAR) N – TIBIAL N. – 15 What type of ion channels are needed to generate an action potential? A) chemically-gated B) voltage-gated Where are these channels found? Answer CHEMICALLY GATED ON DENDRITES AND CELL BODY TO AXON HILLOCK VOLTAGE GATED FROM AXON HILLOCK TO AXON TERMINUS 16 What causes the actin-myosin crossbridges to attach and then swivel? A) action potential arrives at the T-tubules B) calcium enters the axon terminus C) calcium is released into the sarcoplasm D) ATP attaches to the myosin head E) sodium enters the Answer 17 Which type of muscle fiber responds to appropriate training by building myofibrils? A) white B) slow-twitch red Energy systems and activities characteristic of each type? Answer SEE NOTES 18 Which glial cell would be found associated with the choroid plexus? A) astrocytes B) ependymal cells C) microglia D) oligodendrocytes E) Schwann cells Answer 19 Which type of neuron is only found in the special senses? A) bipolar B) unipolar C) multipolar What function does each type have? Which of these is missing in a 2-neuron reflex? Answer SEE NOTES 20 A muscle contracts, producing a reflex. The reflex would be _____. A) stretch B) tendon C) withdrawal D) crossed-extensor Answer 21 If many EPSPs from different neurons all add together to produce threshold depolarization, the type of summation which is occurring is: A) spatial B) temporal An IPSP occurring at the same time which prevents the above from reaching threshold produces a condition known as: Answer INHIBITION 22 The neuron carrying an impulse from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex travels in the: A) corona radiata B) internal capsule C) medial lemniscus D) pyramidal tract Answer 23 If the information transmitted is from pain in the jaw, it will ultimately reach the: A) superior pre-central gyrus B) superior post-central gyrus C) inferior pre-central gyrus D) inferior post-central gyrus Answer 24 The part of the brain malfunctioning in dyslexia is the: A) pre-central gyrus B) Broca’s area C) visual cortex D) Wernicke’s area E) basal nuclei Answer 25 Visual stimuli will reach the: A) visual cortex B) pineal gland C) superior colliculi D) thalamus E) all of the above Answer 26 The center for the fear response is the: A) hippocampus B) hypothalamus C) amygdala D) thalamus Answer 27 Which cranial nerve(s) mediate taste? A)Facial B)Trigemina C)Vagus D)Glossopharyngeal E)Oculomotor Cardiac control? Salivation? Muscles of facial expression? Chewing? Answer C,D A,D A B 28 Which cranial nerve carries the sense of balance? A) VII B) V C) VIII D) IX E) III Answer 29 Which cranial nerve innervates the sternocleidomastoid? A) hypoglossal B) trochlear C) spinal accessory D) glossopharyngeal E) abducens Answer 30 Which sensory mode has receptors which replace themselves over time? A) Vision B) Hearing C) Olfaction D) Taste E) Two of these Answer 31 Which part of the eye is most important in bending the light rays? A) Cornea B) Lens C) Aqueous humor D) Vitreous humor E) Retina Glaucoma is due to excessive pressure in which of these? Answer C 32 Secretion of apocrine glands in sexual arousal is: A)Parasympathetic B)Sympathetic Answer 33 The receptors on eccrine sweat glands are: A)Cholinergic nicotinic B)Cholinergic muscarinic C)Adrenergic alpha D)Adrenergic beta Answer 34 Vasodilation of blood vessels leading to the skeletal muscles, heart, lungs, and skin is: A)Parasympathetic B)Sympathetic Answer 35 All of the previous functions except vasodilation to the skeletal muscles are: A)Cholinergic nicotinic B)Cholinergic muscarinic C)Adrenergic alpha D)Adrenergic beta Answer 36 Which of these is the area of sharpest vision? A) Optic disk B) Choroid C) Fovea centralis D) Macula lutea Which of these has all of the color receptors? Answer 37 Which tissue is found as the stroma of soft organs? A)Areolar ct B)Dense regular ct C)Dense irregular ct D) Reticular ct E)Elastic ct Answer 38 Which of the following is important in cells which must secrete and absorb substances? A)Cilia B)Microvilli C)Hemidesmosomes D)Pericytes Answer 39 Which tissue forms the symphysis pubis? A)Hyaline cartilage B)Elastic cartilage C)Fibrocartilage D)Fibrous connective tissue Answer 40 Endochondal ossification occurs in all the following except the: A) Wrist bones B) Long bones C) Cranial bones D) Calcaneus Answer 41 Which type of osteoporosis has too much blood calcium: A)Post-menopausal B)Senile Answer 42 The most important hormone in calcium homeostasis in adults is: A)PTH B)Estrogen C)Testosterone D)Calcitonin E)Thyroxine Answer 43 Which set of movements occurs at a pivot joint: A) supination-pronation B) inversion-eversion C) dorsiflexion-plantar flexion D)Both A and B Answer 1 BIOL 237 In-Class Review 2 Cholinergic Rec Nicotinic – found excitatory recept Muscarinic – fou organs and at ce e.g. eccrine swe blood vessels to Types depend o The term cholin transmitter acety types of choliner stimulated by th is that certain cli cholinergic rece 1) nicotinic rece neuromuscular j 2) muscarinic re certain sympath copious secretio skeletal muscles 3 Adrenergic Rece Alpha – mostly excitatory e.g. vasoconstricts blood sphincters, dilates pupils Beta – mostly inhibitory ( increase rate and force) e.g. vasodilation in heart dilation, inhibition of mus Found at most sympathe Adrenergic receptors co These are found at symp excitatory. They cause va blood pressure, dilation o the GI tract as part of its Beta receptors are gener receptors on the heart inc vessels to the heart and l anti-bronchitis drugs whic muscles and glands of th 4 Which cranial nerve(s) mediate taste? A)Facial B)Trigeminal C)Vagus D)Glossopharyngeal E)Oculomotor Answer 5 Which cranial nerve(s) are part of cardiac control? A)Facial B)Trigeminal C)Vagus D)Glossopharyngeal E)Oculomotor Answer 6 Which cranial nerve(s) produce salivation? A)Facial B)Trigeminal C)Vagus D)Glossopharyngeal E)Oculomotor Answer 7 Which is not a parasympathetic nerve? A)Facial B)Trigeminal C)Vagus D)Glossopharyngeal E)Oculomotor Answer 8 Which is not a parasympathetic function? A)Slow heart rate B)Normal motility of GI tract C)Forceful contraction of GI sphincters D)Constriction of the pupil E)Salivation Answer 9 Copious secretion of sweat in thermoregulation is: A)Parasympathetic B)Sympathetic Answer 10 The receptors on eccrine sweat glands are: A)Cholinergic nicotinic B)Cholinergic muscarinic C)Adrenergic alpha D)Adrenergic beta Answer 11 Vasodilation of blood vessels leading to the skeletal muscles, heart, lungs, and skin is: A)Parasympathetic B)Sympathetic Answer 12 All of the previous functions except vasodilation to the skeletal muscles are: A)Cholinergic nicotinic B)Cholinergic muscarinic C)Adrenergic alpha D)Adrenergic beta Answer 13 Which junction produces a semipermeable membrane? A)Tight junctions B)Desmosomes C)Hemidesmosomes D)Gap junctions Answer 14 Which tissue principally lines the respiratory tract? A)Simple squamous epithelium B)Simple cuboidal epithelium C)Simple columnar epithelium D)Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium E)Stratified squamous epithelium Answer 15 Which tissue(s) are found in the dermis? A)Areolar ct B)Dense regular ct C)Dense irregular ct D)Adipose E)Elastic ct Answer 16 Which tissue is found in the epiglottis? A)Hyaline cartilage B)Elastic cartilage C)Fibrocartilage D)Fibrous connective tissue Answer 17 Endochondal ossification begins with: A)Hyaline cartilage B)Elastic cartilage C)Fibrocartilage D)Fibrous connective tissue Answer 18 Which type of osteoporosis has too much PTH: A)Post-menopausal B)Senile Answer 19 Which hinge joint is composed of three bones: A)Knee B)Elbow C)Head-atlas D)Carpo-metacarpal E)Both A and B Answer 20 Which of the following has intracapsular ligaments: A)Knee B)Hip C)Shoulder D)All of the above E)Both A and B Answer 21 The primary abductor of the shoulder: A)Pectoralis major B)Deltoid C)Gluteus maximus D)Iliopsoas E)Gastrocnemius Answer 22 Where is calcium important in muscle contraction: A)Exocytosis of acetylcholine at NMJ B)Production of resting potential C)Depolarization of voltage-gated channels D)Trigger for movement of troponin-tropomyosin E)Repolarization of the sarcolemma Answer 23 Which of these produces the myelin sheath in nerves: A)Oligodendrocyte B)Schwann cell C)Ependymal cell D)Microglia E)Astrocyte Answer 24 The first order neuron in every reflex pathway is: A)Unipolar B)Multipolar Answer 25 Which tracts have third order neurons? A)Spinothalamic B)Spinocerebellar C)Fasciculus gracilis Answer 26 Which of the following correctly describes a pathway for anterior thigh pain: A)Tibial nerve, sacral plexus, f. gracilis B)Tibial nerve, sacral plexus, spinothalamic tract C)Femoral nerve, lumbar plexus, f. gracilis D)Femoral nerve, lumbar plexus, spinothalamic tr. Answer 27 Which part of the brain initiates skeletal muscle contraction: A)Pre-central gyrus B)Pre-motor area C)Broca’s area D)Basal nuclei E)Pyramids All play a role, but the pre-central gyrus initiates the contraction pathway. Neurology and Neurophysiology Questions 1through 5 refer to the diagram below: Assume the threshold for producing an action potential is -15 mv. 1. Response A shows: Choices: (1) hyperpolarization, (2) depolarization, (3) a graded potential, (4) EPSP, (5) IPSP. Answers: (A) 1, 3, and 5, (B) 2, 3, and 4, (C) 1 and 4 only, (D) 2 and 5 only. 2. Response C is caused by only a single input to this neuron . Response C illustrates: (A) temporal summation, (B) spatial summation. 3. In this example an action potential _____ be produced. (A) would, (B) would not. 4. If A and C occurred simultaneously, it would result in: (A) temporal summation to produce threshold depolarization, (B) spatial summation to produce threshold depolarization, (C) no threshold depolarization produced. 5. The response seen in A is due to: (A) Opening of chemically-gated Na+ channels (B) Opening of chemically-gated K+ channels (C) Opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels (D) Opening of voltage-gated K+ channels ¬6 through 11 Matching: Answers may be used more than once or not at all. (A) fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus (considered as a single tract), (B) spinocerebellar tract, (C) spinothalamic tract, (D) all of the above, (E) A and B only, (F) A and C only. 6. First order neuron is a unipolar neuron 7. Makes a stop in the thalamus. 8. Makes a stop in the medulla. 9. Destination is on the other side of the brain from the origin of sensory stimuli. 10. Muscle spindles would send signals through this tract. 11. An interneuron in a withdrawal reflex would send a fiber through this tract. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12. The extrapyramidal tracts: (A) carry signals which go to the voluntary muscles, (B) carry signals which are responsible for maintaining balance and muscle bone, (C) originate in a part of the brain, (D) all of the above, (E) B and C only. 13. The conductive region is characterized by having: (A) chemically-gated ion channels, (B) voltage-gated ion channels, (C) both chemically and voltage gated ion channels, (D) vesicles of neurotransmitter, (E) both C and D. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Questions 14 through 18 Matching: Refer to action potential diagram below: NOTE: A through G indicate levels of membrane polarity; H and I indicate time periods. 14. At this membrane polarity Na+ activation gates open. Use letters A-G from the diagram. 15. This is the point at which voltage-gated K+ channels open. Use letters AG from the diagram. 16. Na+ activation gates are closed and inactivation gates are open at this point. Use letters A-G from the diagram. 17. The membrane cannot be stimulated during this period. Use H or I only 18. This indicates hyperpolariztion. Use letters A-F from the diagram. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 19 through 23 Matching. Match the nerve below with the correct description. Not all letters are used. (A) axillary, (B) phrenic,, (C) pudendal, (D) obturator, (E) radial, (F) ulnar, (G) peroneal. 19. If this nerve is blocked you would loose sensation from the external genitalia. 20. If this nerve is damaged you could not breathe on your own. 21. Inflammation of this nerve would impair elbow extension. 22. The dorsiflexor muscles are innervated by this nerve. 23. This nerve comes from the lumbar plexus. class=Section2> ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Questions 24 through 30 apply to the following diagram of the spinal cord cross section: 24. Which area would contain oligodendrocytes? (A) 6, (B) 7, (C) 8, (D) 9. 25. Which area would contain most astrocytes? (A) 6, (B) 7, (C) 8, (D) 9. 26. Which are multipolar neurons? (A) 3, (B) 10, (C) 14, (D) A and B, (E) B and C. 27. Motor neuron axons are indicated by: (A) 1, (B) 12, (C) 14 28. Ependymal cells would be found in: (A) 6, (B) 7, (C) 8, (D) 9. class=Section3> 29. When a stretch reflex is operating with Muscle A, which of the following is true about its antagonist B? (A) A stretch reflex is also operating with B, (B) a tendon reflex is operating with B, (C) Muscle B will be inhibited, (D) Both A and C, (E) Both B and C. 30. The conus medullaris is found at level what position in the vertebral column? (A) C8, (B) L2, (C) T5, (D) the sacrum -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31 through 35 Matching: Answers may be used more than once. (A) receptive region, (B) trigger region, (C) conductive region, (D) secretory region. 31. This area contains only chemically gated ion channels. 32. Contains vesicles of neurotransmitter. 33. This area possesses only voltage gated ion channels. 34. This area is the long process of the axon. 35. This area is the axon hillock of multipolar neurons. 36. Cerebrospinal fluid is found in which of the following: (A) central canal of spinal cord, (B) subdural space, (C) subarachnoid space, (D) pia mater, (E) all of the above, (F) all except D. 37. An epidural anesthetic is applied: (A) between the dura mater and the arachnoid, (B) outside the dura mater, (C) beneath the arachnoid. 38. In the knee jerk reflex, tapping the patellar tendon with a rubber mallet simulates: (A) tendon and muscle stretch, (B) tendon stretch and muscle contraction, (C) a withdrawal reflex. class=Section4> 39. Saltatory conduction makes impulse transmission faster in the: (A) peripheral nerve, (B) spinal tract. 40. When withdrawal from pain occurs in one limb, _____ will usually occur in the corresponding limb on the other side. (A) flexion, (B) extension, 41. The intensity of a stimulus corresponds to: (A) the frequency of sensory stimuli, (B) the number of sensory neurons involved 42. The event which happens immediately after and as a result of calcium ions released into the axon is: (A) opening of chemically-regulated ion gates, (B) opening of voltage-regulated ion gates, (C) exocytosis of neurotransmitter from pre-synaptic membrane, (D) depolarization of post-synaptic membrane. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Questions 43 through 50 apply to diagram below. Assume a repetitive movement of the elbow such as in rowing. The movement occurring to initiate the reflex is elbow flexion. 43. The receptor for this reflex is: (A) muscle spindle, (B) Golgi tendon organ. 44. This reflex is called a reflex. (A) stretch, (B) tendon, (C) crossed extensor, (D) withdrawal. 45. Neuron #3 is: (A) multipolar, (B) unipolar, (C) bipolar. 46. Neuron #1 is: (A) multipolar, (B) unipolar, (C) bipolar. 47. Neuron #2 is: (A) an inhibitory motor neuron, (B) an excitatory motor neuron. 48. Reciprocal inhibition is shown by: (A) pathway 1, (B) pathway 2, (C) pathway 3, (D) not shown. 49. Reciprocal activation is shown by: (A) pathway 1, (B) pathway 2, (C) pathway 3, (D) not shown. 50. Part 4 is located in: (A) the dorsal root ganglion, (B) the ventral root ganglion, (C) the gray matter. Nervous System 1. A 2. The Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 through 7 Matching: Answers may be used more than once or not at all. (A) vagus, (B) glossopharyngeal, (C) facial, (D) oculomotor, (E) abducens, (F) Both A and B, (G) Both B and C, (H) Both D and E, (I) A, B, C, and D. 1. Part of the sensory component of cardiac control. 2. Produces salivation. 3. Sensory from the taste buds. 4. Controls the heart at all times in the absence of stress. 5. Controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. 6. Controls the medial rectus muscle of the eye 7. Produces secretion of GI tract glands. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8. A voluntary stimulus to pucker the lips originates in the: (A) superior pre-central gyrus, (B) inferior pre-central gyrus, (C) superior post-central gyrus, (D) inferior post-central gyrus, (E) pre-motor cotex. 9. The stimulus which puckers the lips travels through the: (A) trigeminal nerve, (B) facial nerve, (C) oculomotor nerve, (D) vagus nerve, (E) phrenic nerve. 10. Cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed from the: (A) arachnoid villi, (B) choroid plexus, (C) septum pellucidum, (D) pineal body, (E) falx cerebri. 11. Impulses from the retina of one eye travel to the: (A) visual cortex on the opposite side of the brain, (B) visual cortex on the same side of the brain, (C) visual cortex on both sides of the brain. 12. The is the part of the limbic system related to short term memory : (A) basal nuclei, (B) hippocampus, (C) hypothalamus, (D) pre-motor cortex, (E) amygdala. 13. The _____ are fiber tracts connecting the thalamus to the cerebral cortex. (A) basal nuclei, (B) corticospinal tracts, (C) fornix, (D) corona radiata, (E) spinothalamic tracts. 14. The _____ is the center for fear pathways and related responses by the limbic system. (A) basal nuclei, (B) hippocampus, (C) hypothalamus, (D) pre-motor cortex, (E) amygdala. 15. Blood vessels leading to the _____ are dilated by the sympathetic nervous system during “fight or flight”: (A) heart, (B) skeletal muscles, (C) eccrine sweat glands, (D) all of the above, (E) A and B only. 16. The center for both interpretation and elaboration of language (both incoming and outgoing pathways) is: (A) thalamus, (B) Broca’s area, (C) cerebellum, (D) basal nuclei, (E) Wernicke’s area. 17. Insufficient absorption of cerebrospinal fluid causes: (A) glaucoma, (B) hydrocephalus, (C) Huntington’s disease, (D) Parkinson’s disease. 18. Visual stimuli would travel to which of the following: (A) occipital cortex, (B) superior colliculi of the midbrain, (C) thalamus, (D) all of the above, (E) A and B only, (F) A and C only, (G) B and C only. 19. Most endocrine functions are ultimately controlled by the: (A) thalamus, (B) hypothalamus, (C) cerebellum, (D) basal nuclei, (E) pineal gland. 20. Personality as well as advance planning of motor functions resides in the: (A) pre-motor cortex, (B) basal nuclei, (C) pre-frontal lobes, (D) pre-central gyrus, (E) thalamus. 21. “Upper motor neurons” originate in the: (A) pre-motor cortex, (B) basal nuclei, (C) pre-frontal lobes, (D) pre-central gyrus, (E) thalamus. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22. Through 26 Matching: Answers are used once only. (A) medulla oblongata, (B) basal nuclei, (C) pre-frontal cortex, (D) corpora quadrigemina, (E) pons 22. Part of brain involved in functions which are part voluntary and part involuntary, such as urination. 23. Part of brain in which advance planning and reasoning occurs. 24. Facilitates reflexes, especially those that involve repetitive movements of a skilled nature. 25. The blinking reflex is centered in a portion of this area of the brain. 26. Center for control of the heart and blood pressure. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 27, 28. Insufficient production of ___27___ (use A-E) by neurons originating in the ___28___ (use F-I) produces Parkinson’s disease. (A) acetylcholine, (B) glutamate, (C) dopamine, (D) L-dopa, (E) GABA (F) basal nuclei, (G) substantia nigra, (H) Broca’s area, (I) pre-central gyrus. 29. The formation of amyloid plaques and tangles of tau protein are characteristic of: (A) Parkinson’s disease, (B) Huntington’s disease, (C) Alzheimer’s disorder, (D) dyxlexia 30. The separates the temporal from the parietal lobes: (A) longitudinal fissure, (B) central sulcus, (C) transverse fissure, (D) corpus callosum, (E) lateral fissure. BIOL 237 Sample Questions Autonomic Nervous System 1 through 5: Determine in each case if the characteristic or action described is (A) cholinergic, nicotinic, (B) cholinergic, muscarinic, (C) alpha adrenergic, (D) beta adrenergic. 1. Excitatory receptors at the eccrine sweat glands. 2. Excitatory receptors on the heart. 3. Stimulates secretion of glands and increase motility in the gastrointestinal tract. 4. Receptors which cause focusing of the lens for near objects. 5. Receptors which dilate vessels leading to the skeletal muscles. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6, 7. When your ophthalmologist applies drops to your eyes in order to examine the eye, the drug is blocking the ___(6)___ receptors which produce pupillary constriction, while not affecting the ___(7)___ receptors which control contraction in the eye’s extrinsic muscles. (A) cholinergic, nicotinic, (B) cholinergic, muscarinic, (C) alpha adrenergic, (D) beta adrenergic. -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8 through 15 Matching: Choose the correct division for each function listed: (A) sympathetic division, (B) parasympathetic division, (C) somatic division. 8. Increase in heart rate and volume. 9. Release of epinephrine by the adrenal medulla. 10. Blinking. 11. Constriction of vessels leading to the GI tract 12. Foreceful contraction of GI sphincter muscles along with inhibition of motility in other GI muscles. 13. Constriction of the pupil 14. Dilation of vessels leading to the skeletal muscles 15. Salivation [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 826 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$25.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 25, 2021
Number of pages
826
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 25, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
104

 HESI VI EXIT EXAM.png)