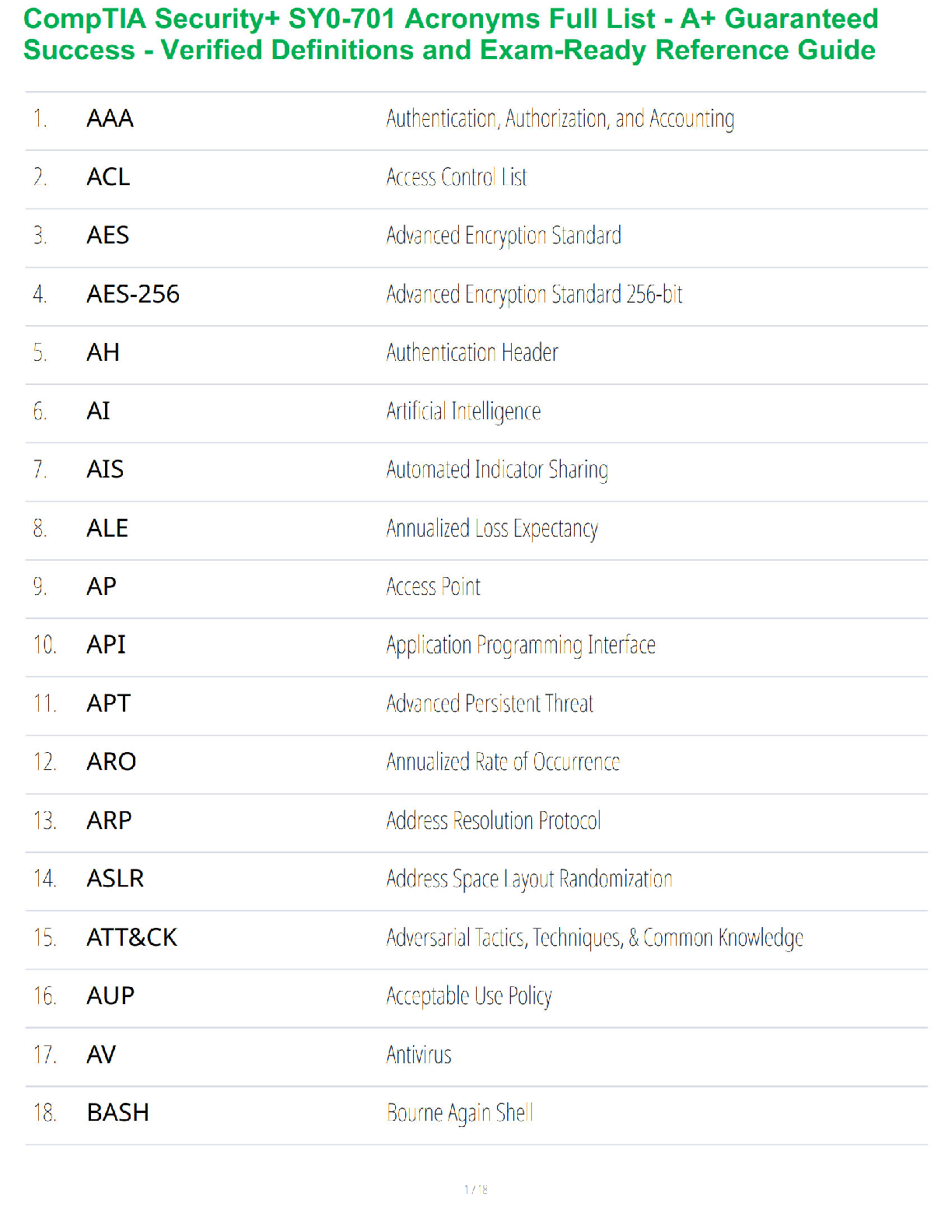
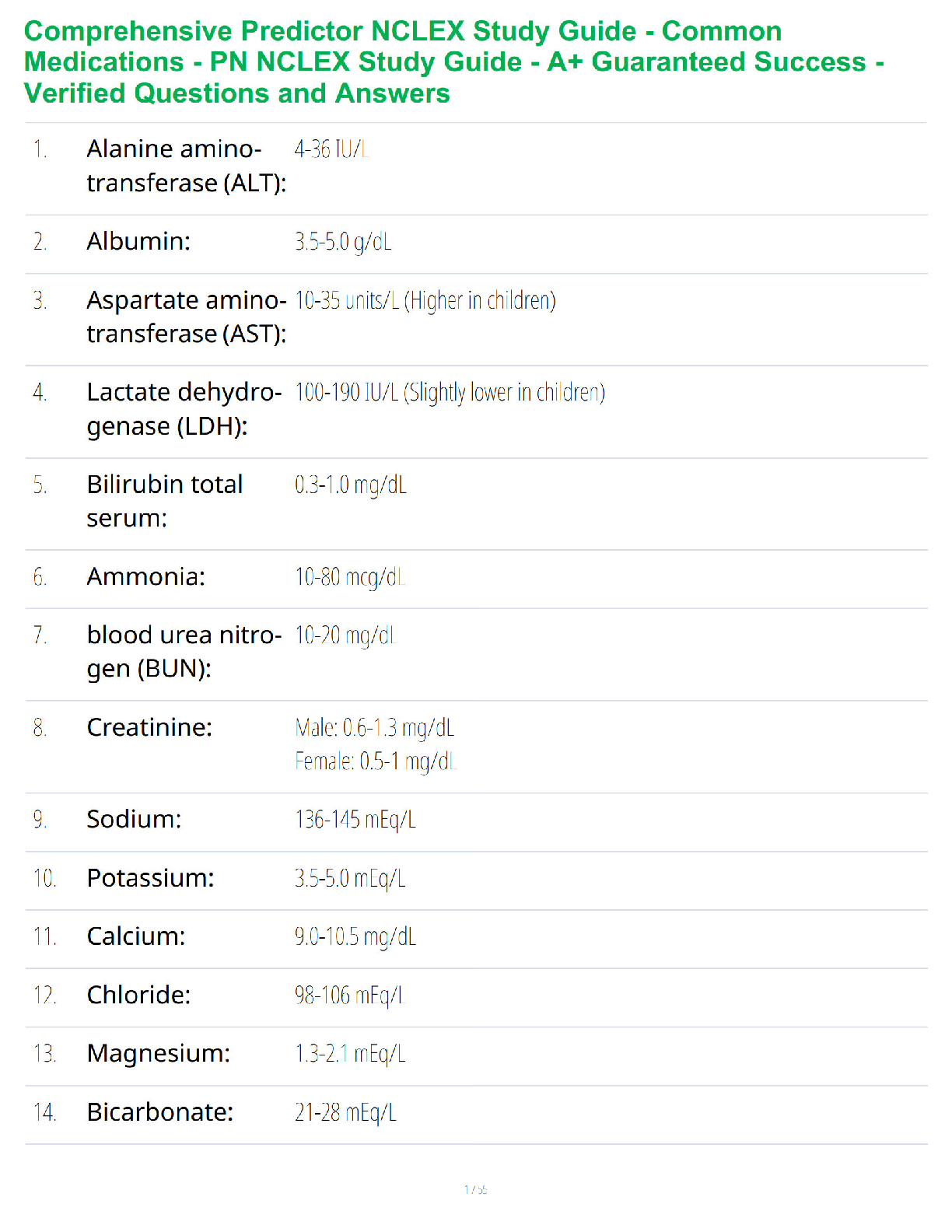
Med/Surg Final Exam Review
A patient is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization with coronary angiography. Before the test, the
nurse informs the patient that?
A warm feeling may be noted when the contrast dye is inje
...
Med/Surg Final Exam Review
A patient is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization with coronary angiography. Before the test, the
nurse informs the patient that?
A warm feeling may be noted when the contrast dye is injected- A sensation of warmth or flushing is
common when the iodine-based contrast material is injected, which can be anxiety-producing unless it
has been discussed with the patient. The patient may receive a sedative drug before the procedure, but
monitored anesthesia care is not used. ECG monitoring is used during the procedure to detect
dysrhythmias, but there is not a risk for dysrhythmias after the procedure. The patient is not immobile
during cardiac catheterization and may be asked to cough or take deep breaths.
A patient with a history of hypertension treated with a diuretic and an angiotensin-converting enzyme
(ACE) inhibitor arrives in the emergency department complaining of a severe headache and has a BP of
240/118 mm Hg. Which question should the nurse ask first?
Have you been consistently taking your medications? Sudden withdrawal of antihypertensive
medications can cause rebound hypertension and hypertensive crisis.
A 52-year-old patient who has no previous history of hypertension or other health problems suddenly
develops a BP of 188/106 mm Hg. After reconfirming the BP, it is appropriate for the nurse to tell the
patient that
More diagnostic testing may be needed to determine the cause of the hypertension- A sudden increase
in BP in a patient over age 50 with no previous hypertension history or risk factors indicates that the
hypertension may be secondary to some other problem.
To determine the effects of therapy for a patient who is being treated for heart failure, which
laboratory result will the nurse plan to review?
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)- Increased levels of BNP are a marker for heart failure. The other
laboratory results would be used to assess for myocardial infarction (myoglobin) or risk for coronary
artery disease (Hcy and LDL).
When planning care for a patient hospitalized with a streptococcal infective endocarditis (IE), which
intervention is a priority for the nurse to include?
Arrange for placement of a long-term IV catheter- Treatment for IE involves 4 to 6 weeks of IV antibiotic
therapy in order to eradicate the bacteria, which will require a long-term IV catheter such as a
peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line. Rest periods and limiting physical activity to a
moderate level are recommended during the treatment for IE. Oral antibiotics are not effective in
eradicating the infective bacteria that cause IE. Blood cultures, rather than antibody levels, are used to
monitor the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy.
When the nurse is monitoring a patient who is undergoing exercise (stress) testing on a treadmill,
which assessment finding requires the most rapid action by the nurse?
Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes indicating coronary ischemia- ECG changes associated with coronary
ischemia (such as T-wave inversions and ST segment depression) indicate that the myocardium is not
getting adequate oxygen delivery and that the exercise test should be terminated immediately. Increases
This study source was downloaded by 100000821916538 from CourseHero.com on 03-26-2021 14:58:34 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/14912652/MedSurg-Final-Exam-Review-1/
This study resource was
shared via CourseHero.com
in BP and heart rate (HR) are normal responses to aerobic exercise. Tiredness also is normal as the
intensity of exercise increases during the stress testing.
A 19-year-old student comes to the student health center at the end of the semester complaining that,
"My heart is skipping beats." An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows occasional premature ventricular
contractions (PVCs). What action should the nurse take next?
Ask the patient about current stress level and caffeine use- In a patient with a normal heart, occasional
PVCs are a benign finding. The timing of the PVCs suggests stress or caffeine as possible etiologic factors.
It is unlikely that the patient has coronary artery disease, and this should not be the first question the
nurse asks. The patient is hemodynamically stable, so there is no indication that the patient needs to be
seen in the ED or that oxygen needs to be administered.
? Difficulty swallowing may occur with a thoracic aneurysm because of pressure on the esophagus.
When evaluating the red cell indices of a patient, the nurse knows that a low mean corpuscular
volume (MCV) indicates?
Small size of the red blood cells (RBCs)- The MCV is low when the RBCs are smaller than normal.
Inadequate numbers of RBCs are an indication of anemia. Low levels of hemoglobin in the RBCs and
hypochromic RBCs result in a low mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH).
A diabetic patient's arterial blood gas (ABG) results are pH 7.28; PaCO2 34 mm Hg; PaO2 85 mm Hg;
HCO3- 18 mEq/L. The nurse would expect which finding?
**36. Kussmaul respirations-Kussmaul (deep and rapid) respirations are a compensatory mechanism for
metabolic acidosis. The low pH and low bicarbonate result indicate metabolic acidosis. Intercostal
retractions, a low oxygen saturation rate, and a decrease in venous O2 pressure would not be caused by
acidosis.
When assessing the respiratory system of an older patient, which finding indicates that the nurse
should take immediate action?
Bilateral crackles at lung bases. Crackles in the lower half of the lungs indicate that the patient may have
an acute problem such as heart failure. The nurse should immediately accomplish further assessments,
such as oxygen saturation, and notify the health care provider. A barrel-shaped chest, hyperresonance to
percussion, and a weak cough effort are associated with aging. Further evaluation may be needed, but
immediate action is not indicated. An older patient has a less forceful cough and fewer and less
functional cilia. Mucous membranes tend to be drier.
While caring for a patient with respiratory disease, the nurse observes that the patient's SpO2 drops
from 93% to 88% while the patient is ambulating in the hallway. What is the priority action of the
[Show More]
.png)











.png)
.png)