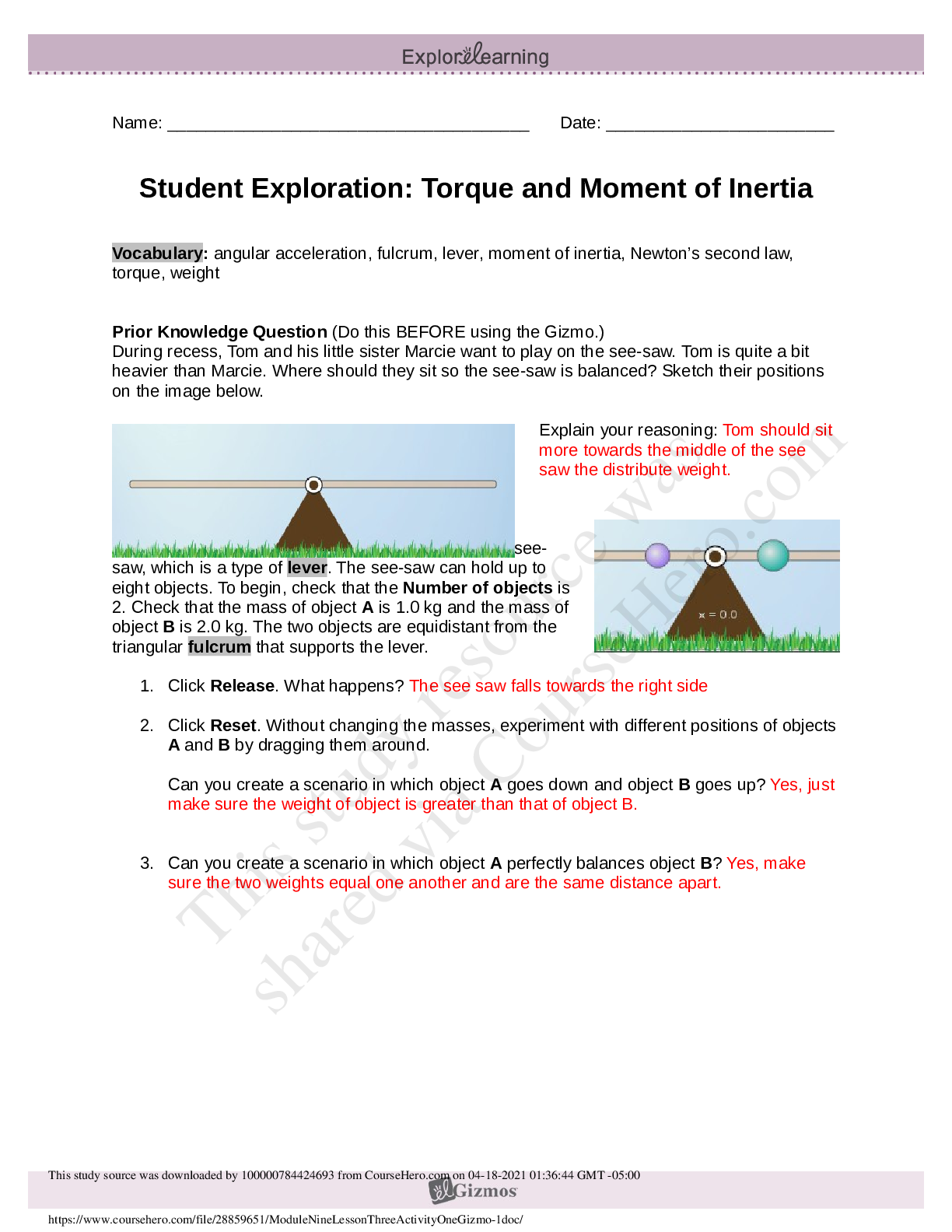
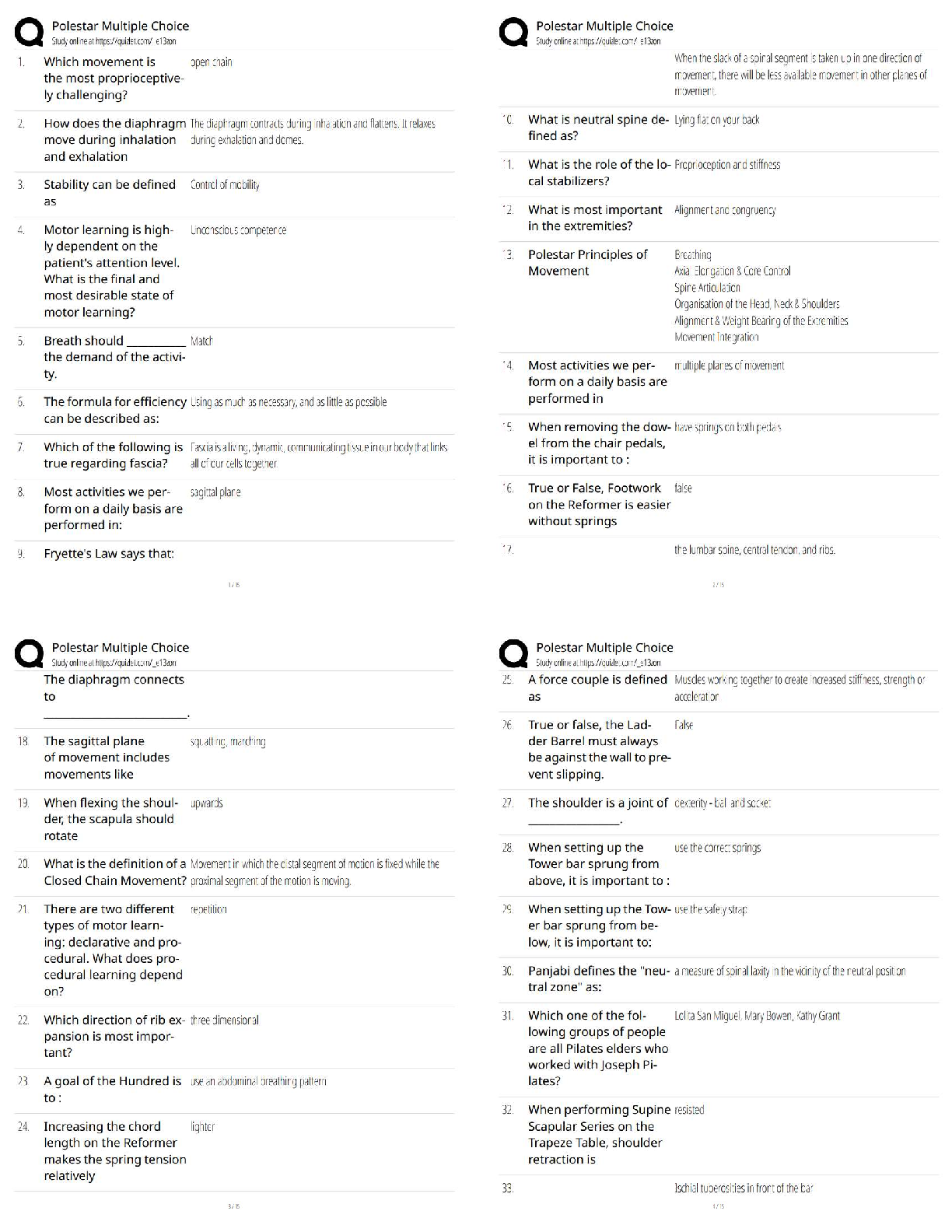
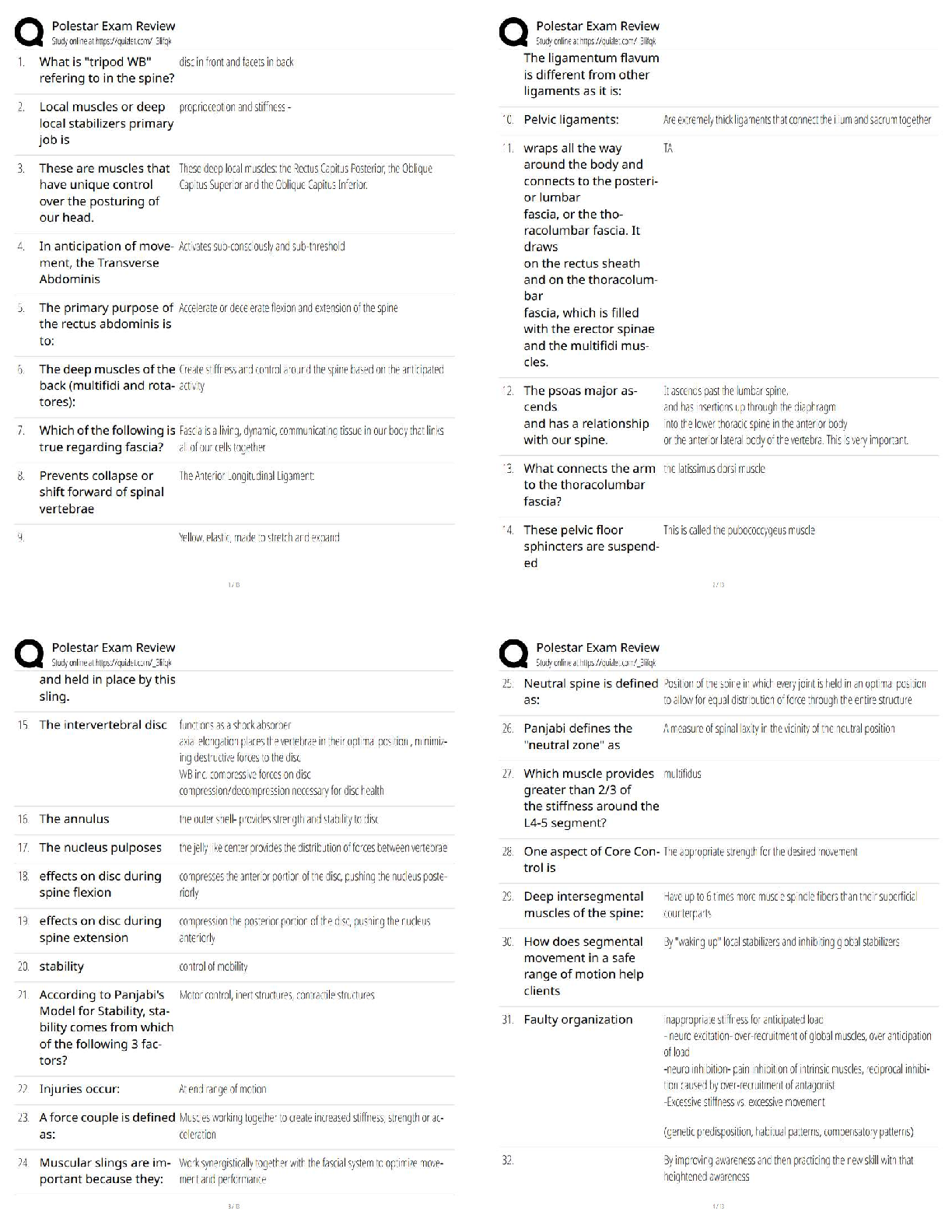
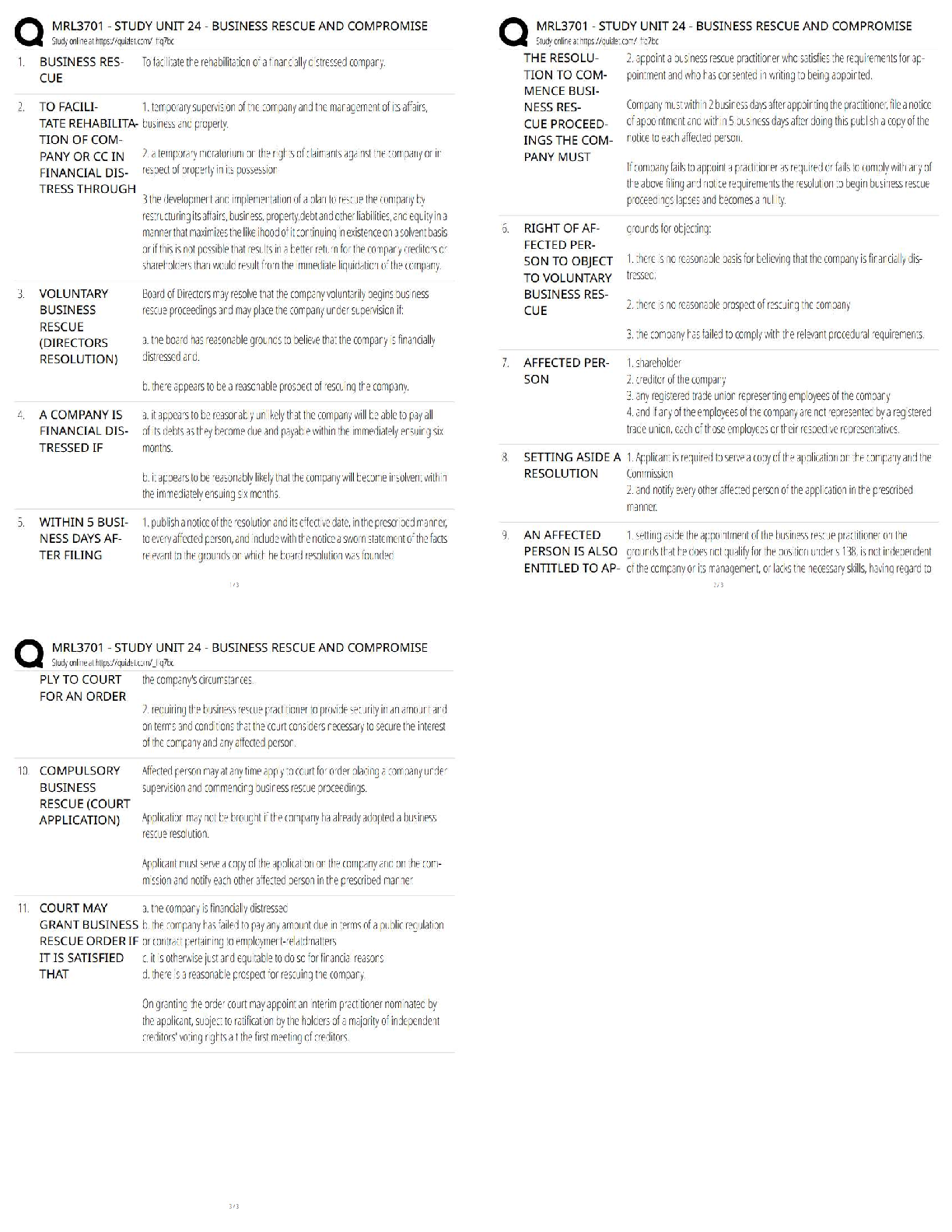
Virtual Lab: Velocity and Acceleration on a Frictionless
Inclined Plane, and Free Fall
Theory:
The Italian scientist Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) discovered mathematical relationships that
describe the motion of falli
...
Virtual Lab: Velocity and Acceleration on a Frictionless
Inclined Plane, and Free Fall
Theory:
The Italian scientist Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) discovered mathematical relationships that
describe the motion of falling objects, and the motion of objects rolling down inclined planes.
These equations paved the way for the subsequent development of the field of classical
mechanics (the science of forces and motion) by the English physicist, Sir Isaac Newton, who
was born the same year Galileo died. This short PBS video describes Galileo’s groundbreaking
work on inclined planes:
https://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/phy03.sci.phys.mfw.galileoplane/galileos-inclinedplane/
In this lab, we will explore the motion of objects on inclined planes just like Galileo did, some
400 years ago.
Definitions:
Speed: a measure of how fast an object moves, or how much distance it covers in a given
amount of time. The units for speed are m/s.
Velocity (v): the quantity that describes the speed of an object as well as the direction in which
it is traveling. The units for velocity are m/s.
Acceleration (a): a measure of how much the velocity of an object changes in a given amount
of time (or how fast its velocity is changing). The change in velocity may be due to change(s) in
the object’s speed, or due to change(s) in the object’s direction. The units for acceleration are
m/s2
.
Free fall: motion of an object that falls under the influence of the force of gravity alone, with
other forces such as air resistance being so small that they can be ignored. In the absence of air
resistance all objects, heavy or light, fall at the same speed and with the same acceleration,
whose value is g = 9.80 m/s2
. This acceleration experienced by all objects on our planet is
called the acceleration due to gravity, and it can be rounded off to: g = 10.0 m/s2
.
To study an object’s motion, we measure quantities such as the height it falls through, its
velocity, the time it takes, and so on. The height through which an object falls is denoted by the
symbols h or d, and is measured in meters.
In free fall, the above three quantities are related through the equation:
v
2 = 2gh … Equation [1]
Taking the square root of both sides, this equation can also be written as:
v=√2 gh
(remember, this is only for free fall, where we can ignore air resistance.)
[Show More]







.png)