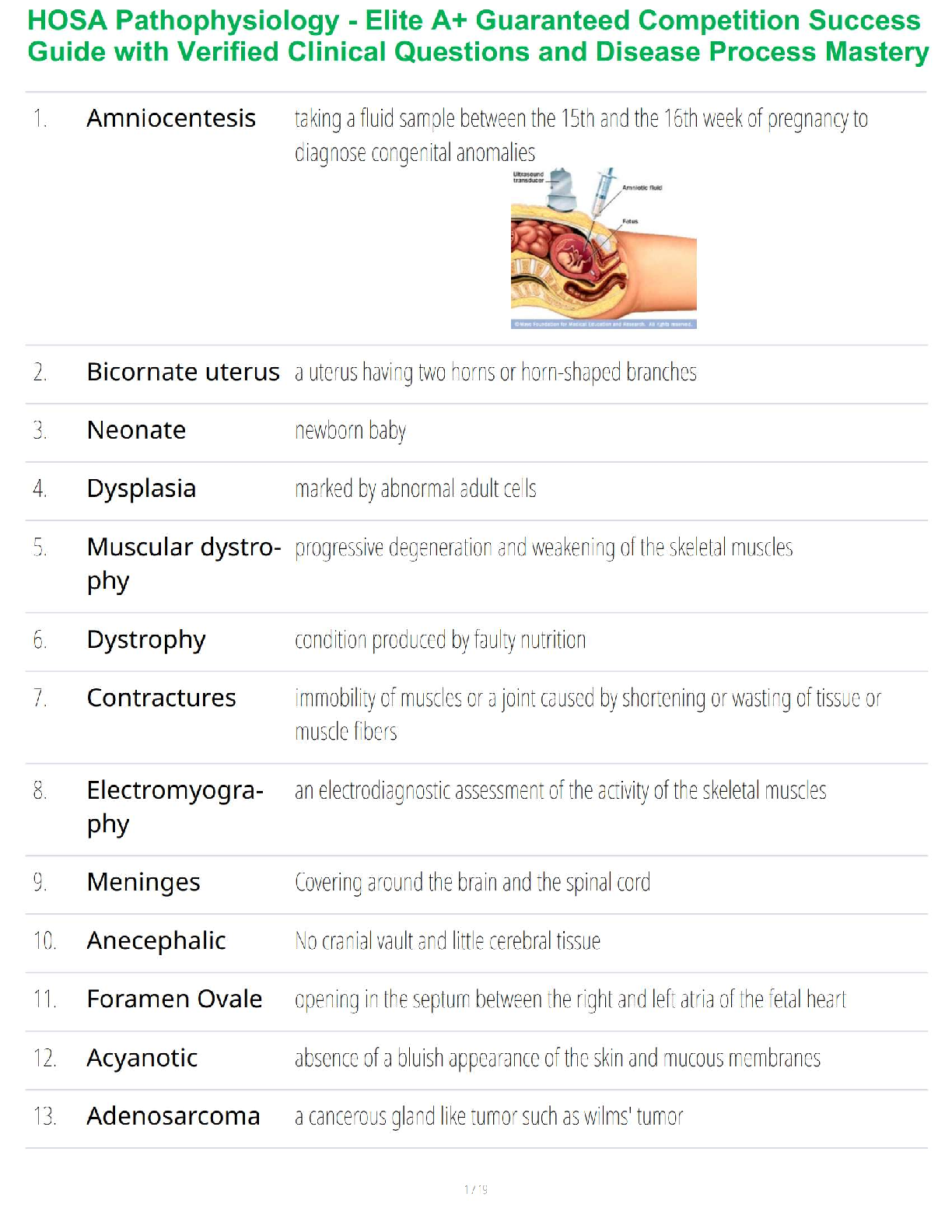
NURS 6550 MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE
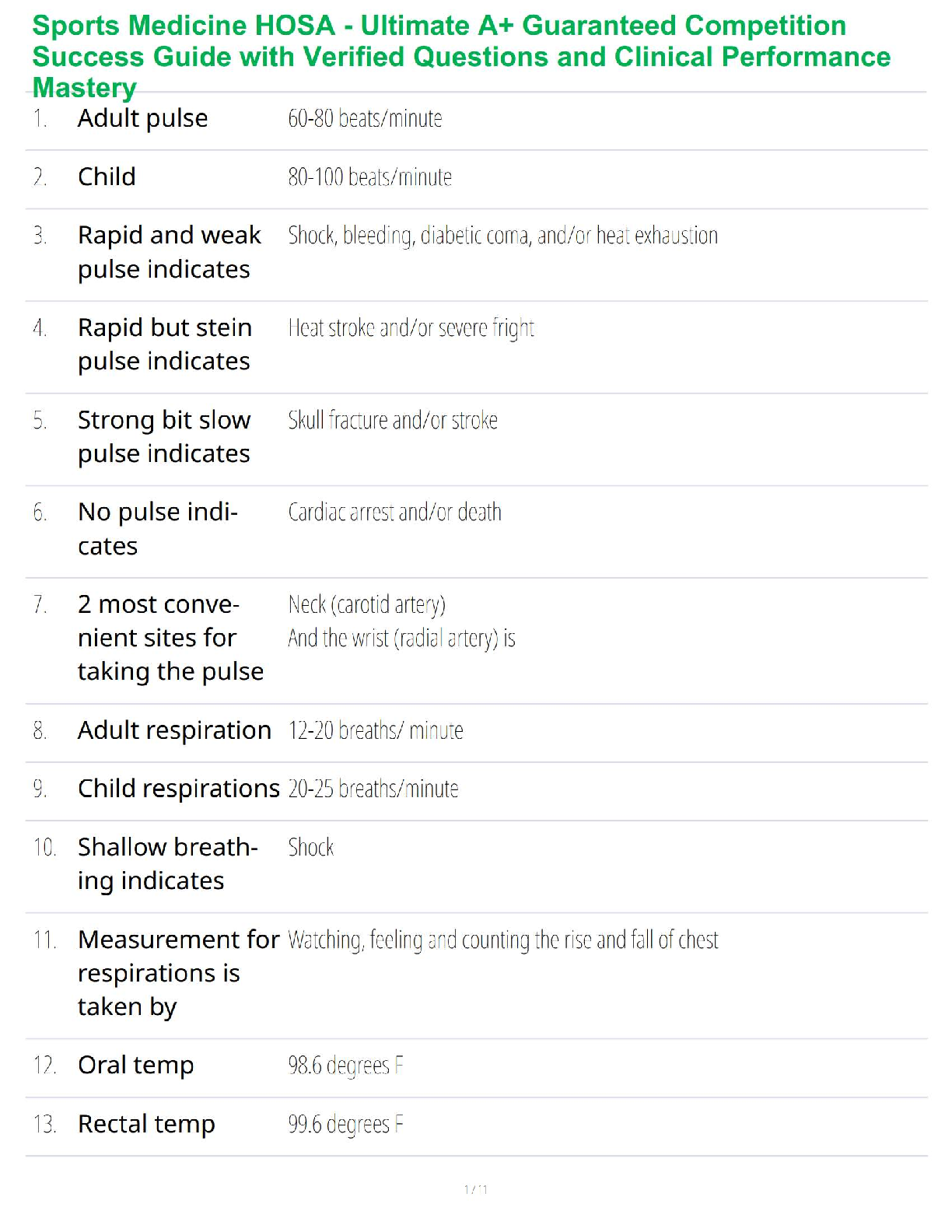
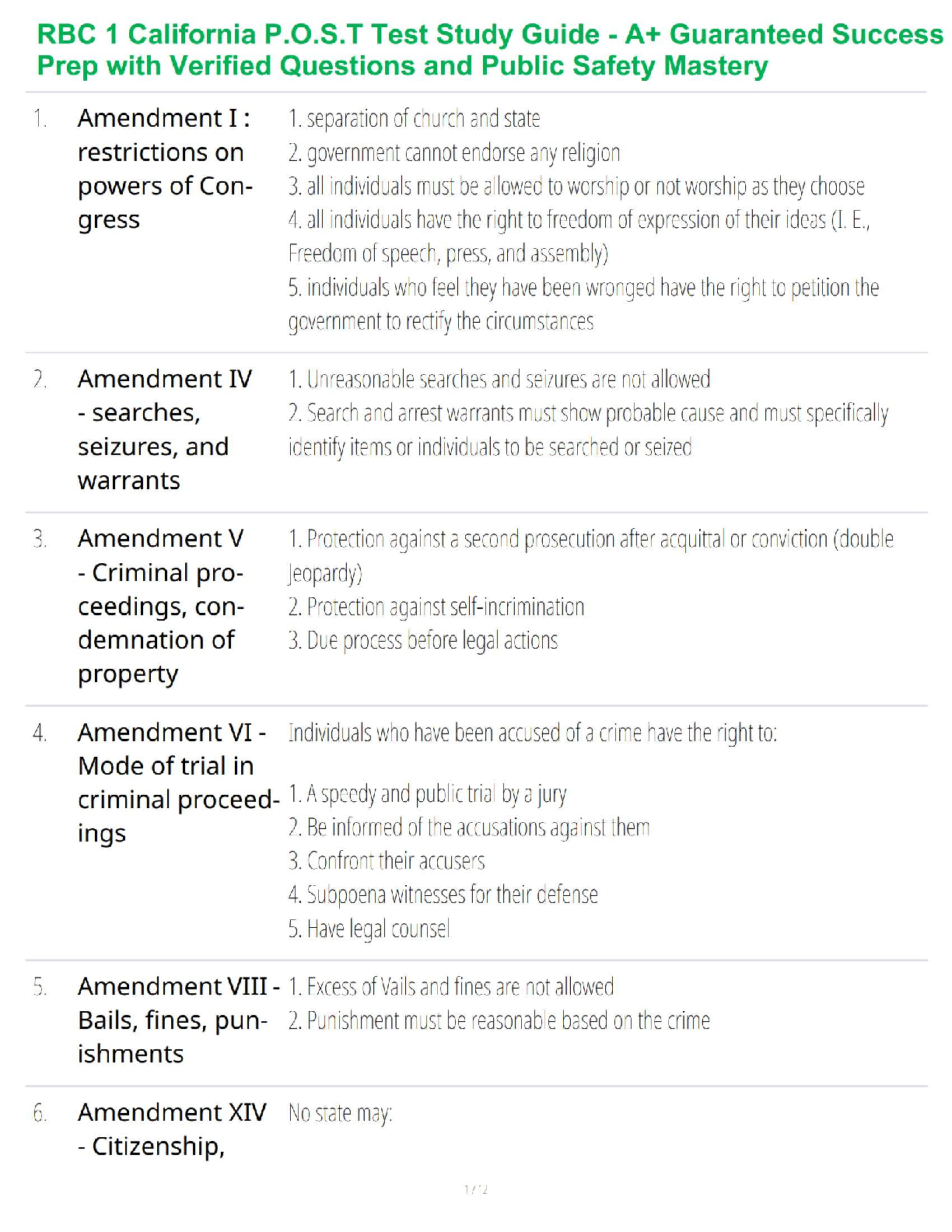
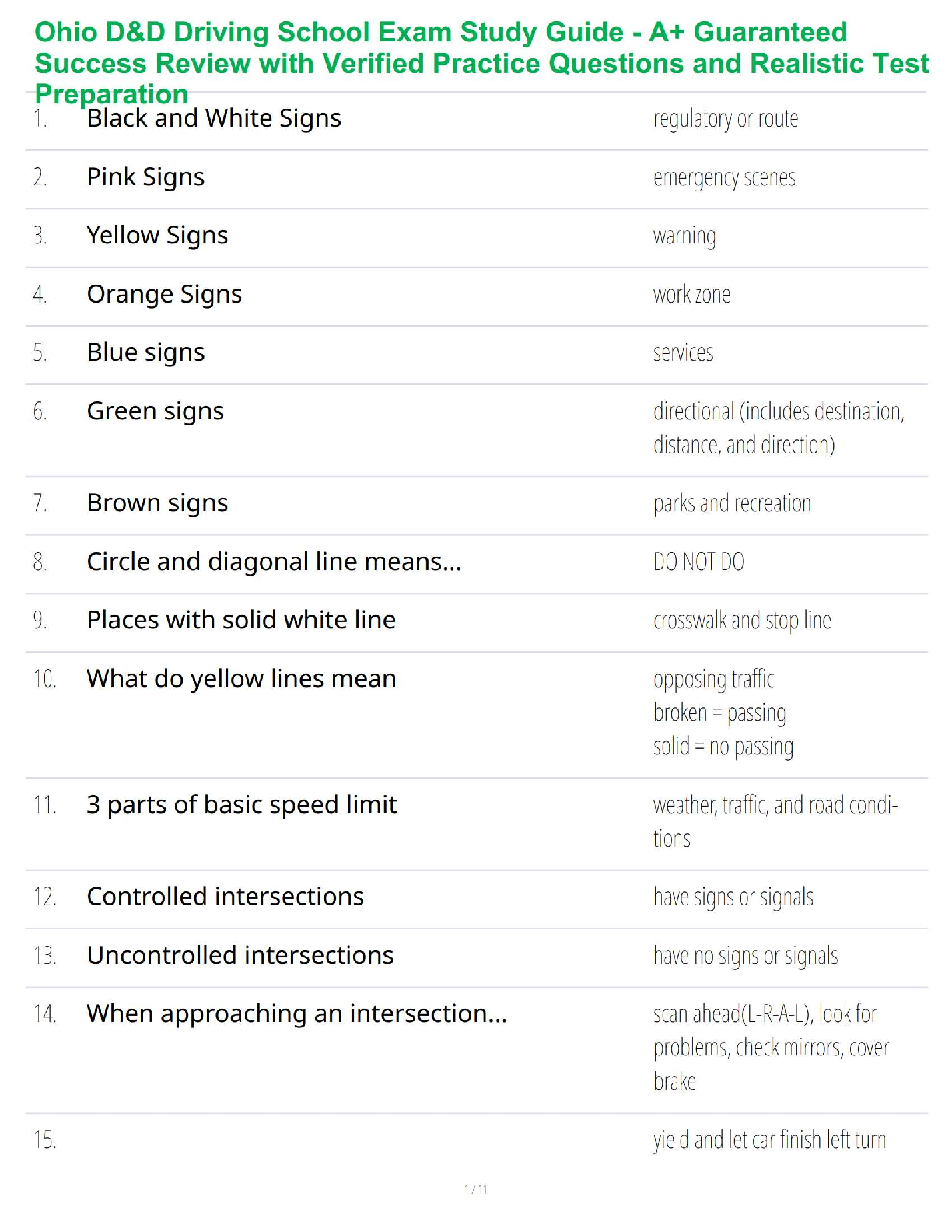
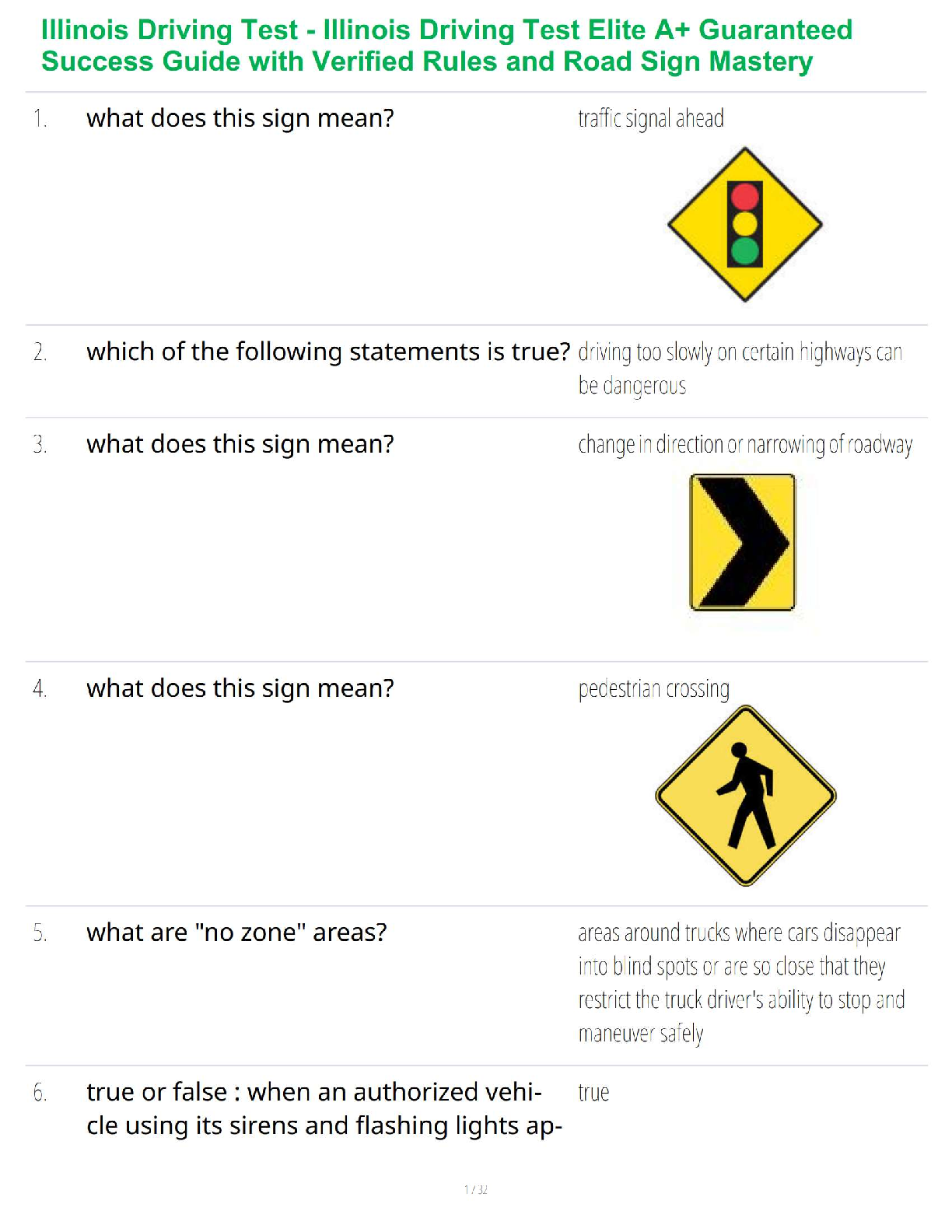
Generalized anxiety disorder diagnosis criteria
(1)
Primary neurotransmitter in PTSD
* PTSD diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of acute panic attacks- What are the medications
...
NURS 6550 MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE
Generalized anxiety disorder diagnosis criteria
(1)
Primary neurotransmitter in PTSD
* PTSD diagnosis and treatment
Treatment of acute panic attacks- What are the medications for initial/first line
Inpatient treatment of depression- ECT
Venlafaxine dosing
Endogenous depression pathophysiology is best described as?
Differences between panic attacks and panic disorder?
What are Major Depressive disorder symptoms?-
Familiarize yourself with the side effects of Lithium-
Common adverse effects of atypical antipsychotics-
Mental status changes in elderly… how do you evaluate?
Mental status changes related to UTI in elderly
Assessment of Delirium in geriatric patients-
Elders with dementia and driving
Short Confusion Assessment Method (Short CAM): what things are assessed?
Types of dementia, know differences?
Alzheimer's disease- Alzheimer's disease
Vascular dementia- Vascular dementia
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)- Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) back to top
mixed dementia.
Mixed dementia- Mixed dementia
Parkinson's disease- Parkinson's disease
Frontotemporal dementia- Frontotemporal dementia
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Normal pressure hydrocephalus-Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Huntington's Disease back to top
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndromeback to top
Korsakoff syndrome
Aricept and dosing and patient teaching?
Management of disinhibition in elderly-
• Physical findings when death is imminent
Limits of pain medication on dying patient
Theories about successful aging…familiarize yourself with them-
Education: due to direct beneficial effect or leads to life-long learning?
• Activity theory
• Continuity theory
• Disengagement theory
Psychological abuse of elders
Death and the anxiety related to it, who’s at risk? Age and suicide risk in the different age groups?
Geriatric Depression Screen-
Geriatric Depression Scale: Short Form
Geriatric Depression Scale
Which of the following is not an indication for use of a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor?-
Lucy Garcia is a 42-year-old Hispanic female with a 20-plus-year history of depression. She is currently hospitalized for treatment of progressive, acute-on-chronic depressive symptoms, including refusal to get out of bed and inattentiveness to personal hygiene
Which of the following are risk factors for obesity? (Select all that apply
How should a physician assess the risk for suicide in a depressed adolescent? (Select all that apply.)
Why must a physician assess the risk for suicide in a depressed adolescent?
Advanced practice nursing procedures.
, “
Audiometry Testing”-
“Tympanometry”
Chapter 71, “Visual
Function: Evaluation (Snellen, Illiterate E) Procedures—Eyes”
o Chapter 76, “Eyebrow Laceration Repair”-
o
o Chapter 77, “Eyelid Eversion Procedures: Ears/Nose
Chapter 79, “Cerumen Impaction Removal: Irrigation of the Ear and Curette Technique
o Chapter 80, “Ear Piercing”
o Chapter 88, “Tooth Avulsion and Fracture”
Chapter 7, “Disorders of the Eyes & Lids”
Chapter 8, “Ear, Nose, & Throat Disorders”
EENT EYE
* Cataract Familiarize yourself with Cataracts, presentation? TRX?-
Phacoemulsification is the most widely used cataract surgery in the developed world.[46][47] This procedure uses ultrasonic energy to emulsify the cataract lens. Phacoemulsification typically comprises six steps:
Herpes zoster
Hordeolum
Chalazion
Blepharitis
Ectropion
Vitreous hemorrhage-
* Dacrocystitis-
• What is acute angle glaucoma?
• Chronic uveitis medication management-
• Gonococcal conjunctivitis presentation and medication management-
• Trachoma (chlamydial Kertoconjuctivitis
• Dry eye (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
• Allergic conjunctivitis
• Viral, allergic, bacterial conjunctivitis:
Macular degeneration presentation and S&S, trx
The Macula
Who is at risk?
• Smoking.
• Race
• Family history and Genetics.
Does lifestyle make a difference?
How is AMD detected?
• Visual acuity test.
• Dilated eye exam.
• Amsler grid.
• Fluorescein angiogram.
• Optical coherence tomography.
Diabetic retinopathy
• Orbital fractures
importance of recording visual acuity cannot be overemphasized
Different types of hearing loss and why they occur-
Sensorineural hearing loss-
Weber Test
Acute otitis media:
Vertigo, how do you evaluate and trx?
Epistaxis:
Complications: Nasal Packing
Bacterial sinusitis:
Bells palsy: S&S, treatment, pain management-
Cardiovascular disorders
• Chapter 10, “Heart Disease” (pp. 328-446)
• Chapter 11, “Systemic Hypertension” (pp. 447-478)
• Chapter 12, “Blood Vessel & Lymphatic Disorders” (pp. 479-506)
• Chapter 28, “Lipid Disorders” (pp. 1269-1277)
ACS protocol: low risk vs high risk mi
Metabolic syndrome- (three or more of the following )
Contraindications to thrombolytic therapy in stroke and MIs
MONA, what is it an when is it used?
Duke criteria for infective endocarditis, presentation and treatment-
Major Diagnostic Criteria
Minor Diagnostic Criteria
Heart murmurs: physical exams, grades of murmurs-
Systolic murmurs
[Show More]


, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)