Medical Conditions: Priority Postpartum Client (RN QSEN - Safety, Active Learning Template - Basic Concept, RM MNRN 10.0 Chap 9)
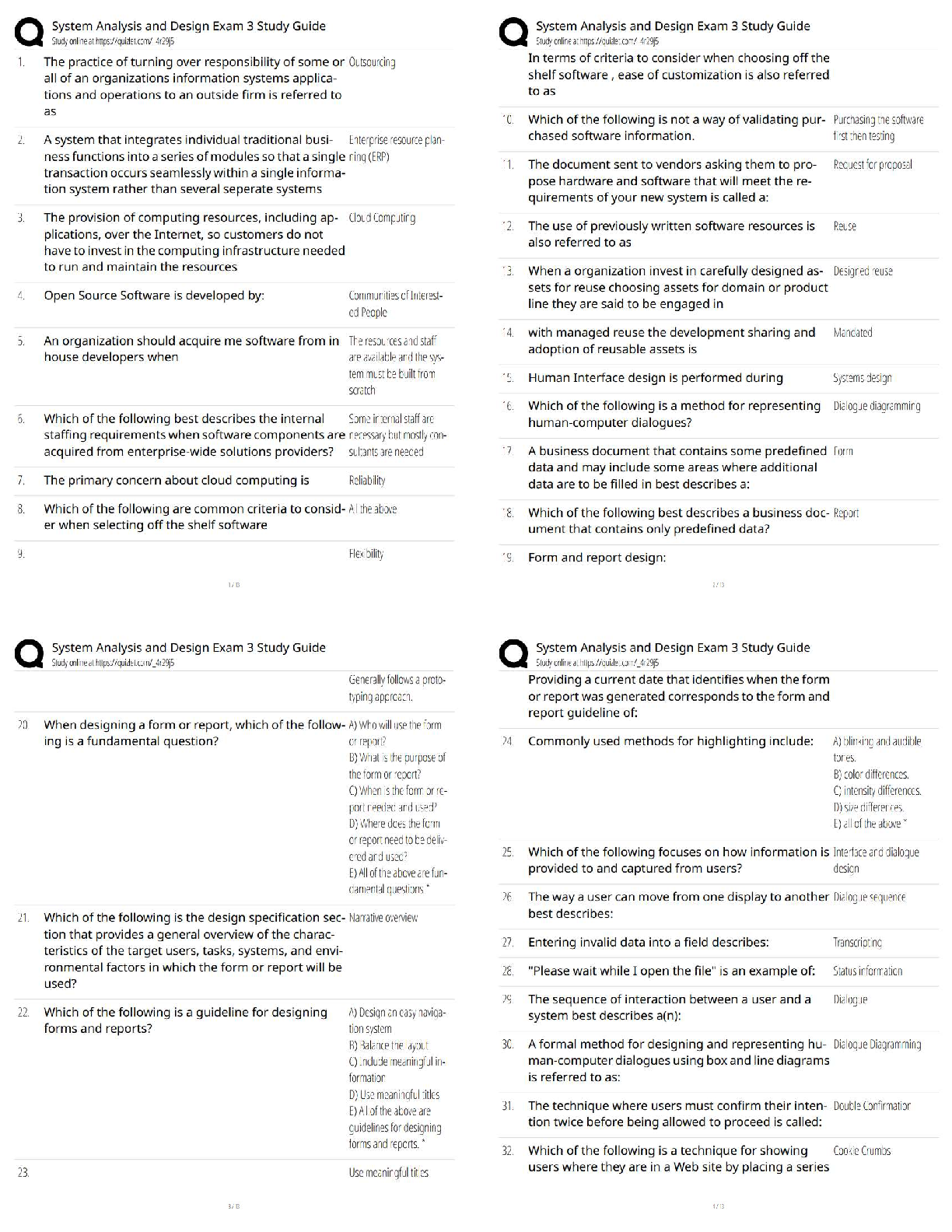
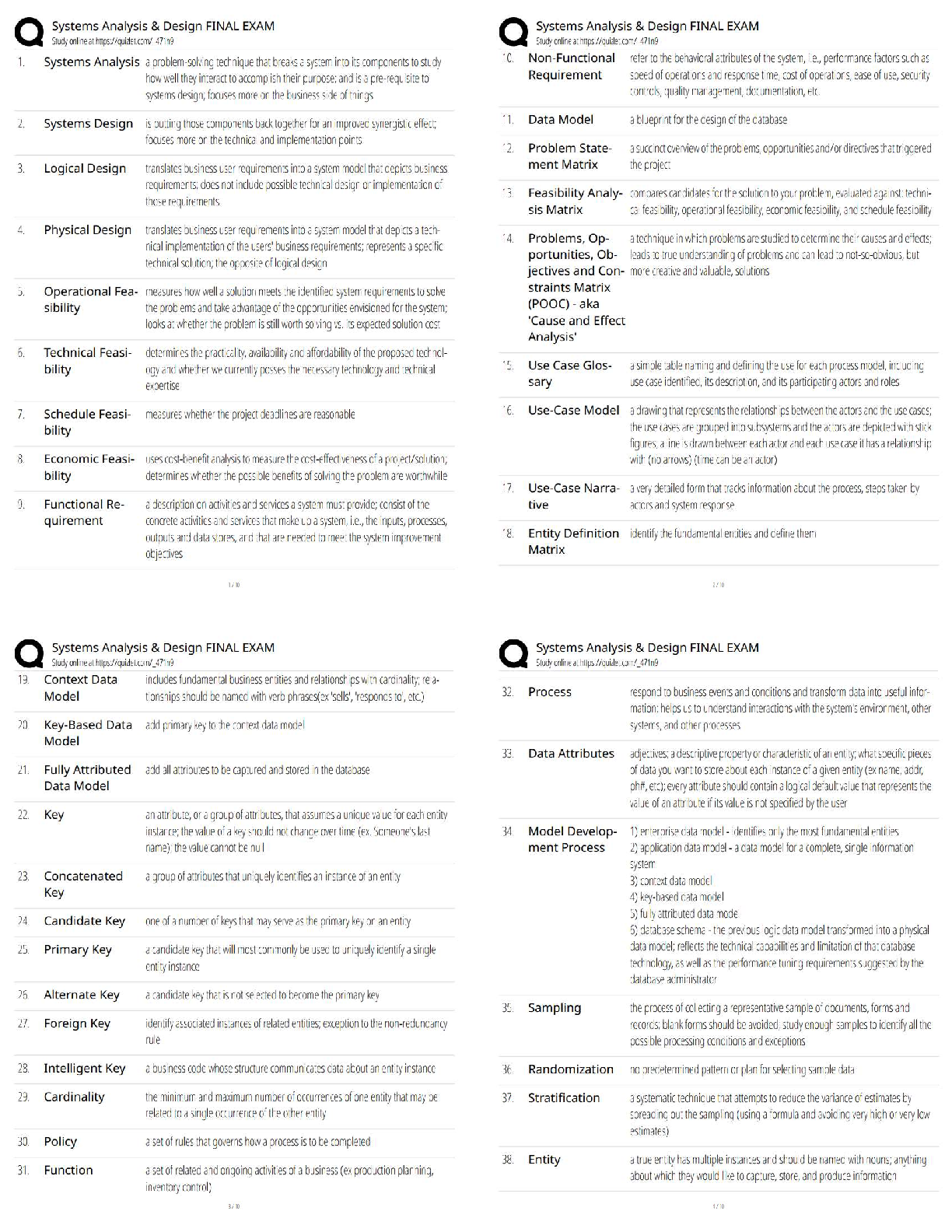
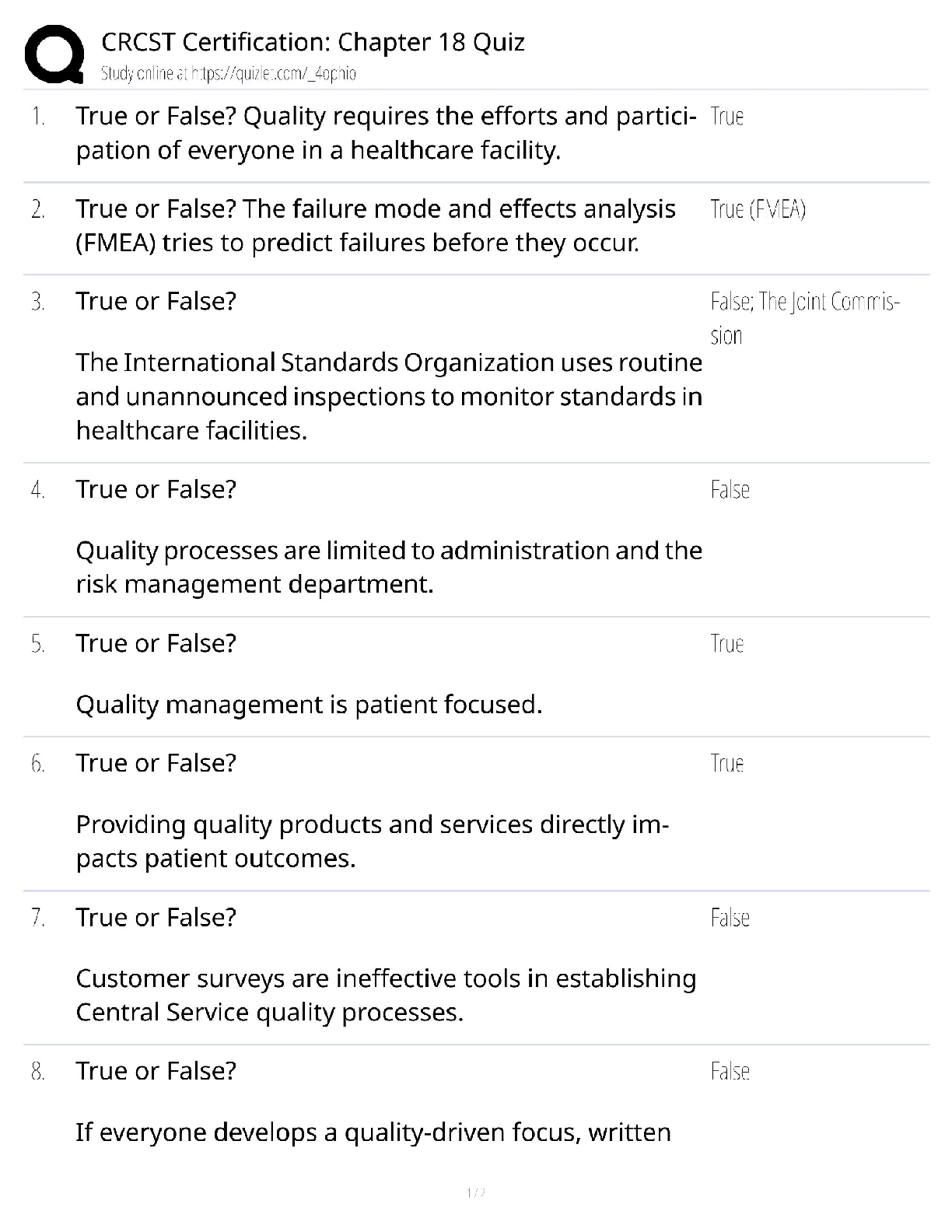
• -monitor vitals • -provide education on pregnancy medical condition and what it means
...
Medical Conditions: Priority Postpartum Client (RN QSEN - Safety, Active Learning Template - Basic Concept, RM MNRN 10.0 Chap 9)
• -monitor vitals • -provide education on pregnancy medical condition and what it means now that pt is postpartum • -do all necessary lab tests to see if labs have returned to normal • -provide medications if needed • -maintain patient comfort • -provide medications to baby if needed
Infections: Caring for a Newborn Whose Mother Has HIV (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM MN RN 10.0 Chp 8)
• -Provide counseling prior to and after testing • -Refer client for a mental health consultation, legal assistance, and financial resources • -administer antiviral prophylaxis, triple-drug antiviral, or highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) as prescribed • -encourage vaccination against hepatitis B, pneumococcal infection, Haemophilius influenzae type B and viral influenza • -Infant should be bathed after birth before remaining with mother
Infections: Prophylaxis Treatment for a Newborn Whose Mother is HBsAgPositive Mothers (RN QSEN - Safety, Active Learning Template - Basic Concept, RM MN RN 10.0 Chp 8)
• -information for immunization • --infants get their first dose as infants • --completes over a period of 6 months (at birth, 1 month, and 6 months) • --given as an injection • --usually 0.5ml for a newborn dosage • --know how many mLs you need to draw up • --know how to do dosage calculations based on information given in the question • --it is recommended to be administered to all newborns • --informed consent must be obtained • -info about immune globulin
• --know how to do dosage calculations based on info given in the question • --for moms who are infected with hep B, the hep B immunoglobulin and the hep B vaccine is given within 12 hours of birth • --vaccine is then given at 1 month, 2 months, and 12 months
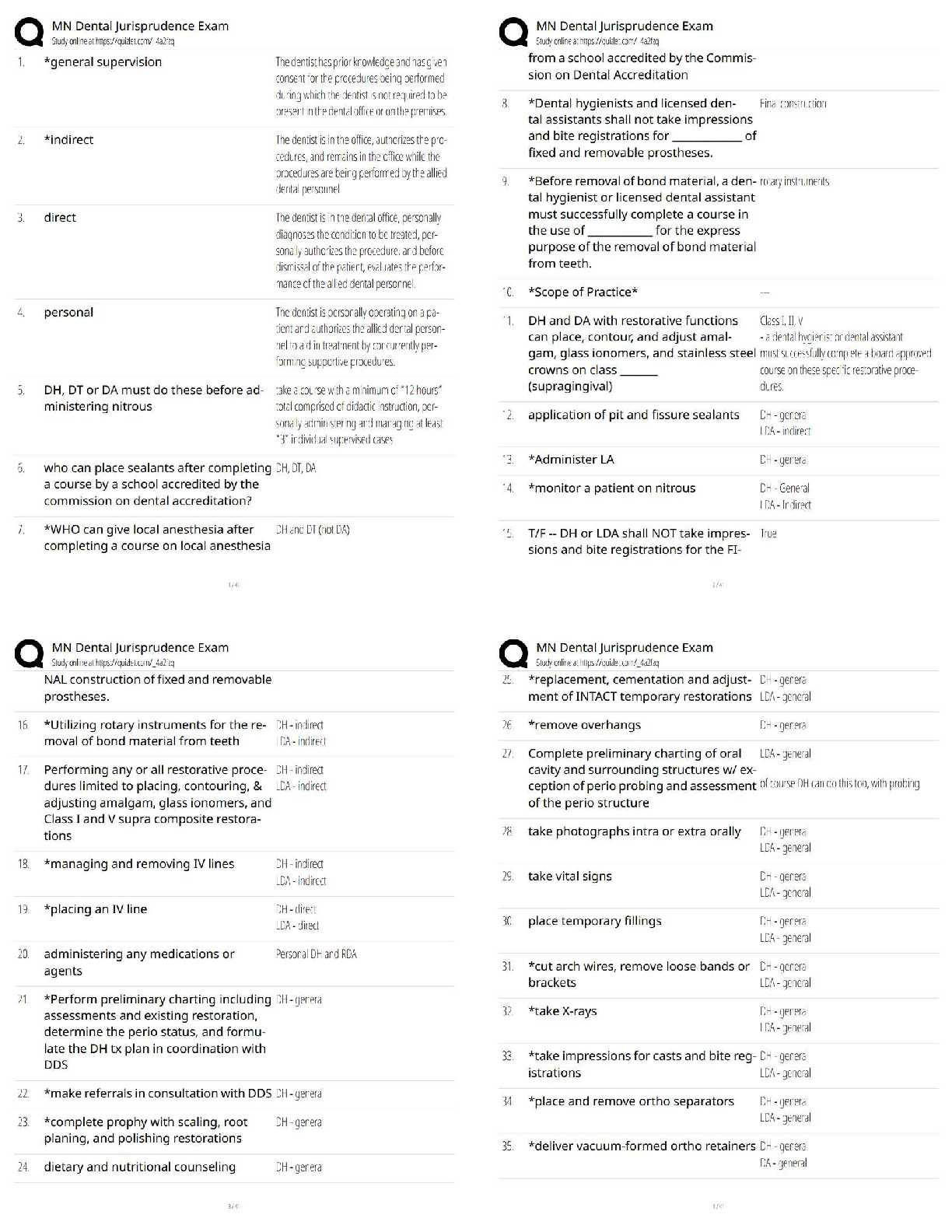
1
Not from ATI Can’t FIND
• The first hepatitis B vaccine is given at the birth facility to infants of uninfected mothers as well as to those whose mothers are positive for hepatitis B. Hepatitis B immune globulin is also given to infants of infected mothers.
• The hepatitis B vaccine should be administered with a 25-gauge, 5/8-inch needle. Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all infants. If the infant is born to an infected mother who is a chronic carrier, hepatitis vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin should be administered within 12 hours of birth. Hepatitis B vaccine should be given in the vastus lateralis muscle. Hepatitis B vaccine can be given at birth.
Assessment of Fetal Well-Being: Contraindications for a Contraction Stress Test (Active Learning Template – Diagnostic Procedure, RM MN RN 10.0 Chp 6)
• -contraindications for oxytocin stimulation • -can be difficult to stop and could lead to preterm labor! • -only used this method when nipple stimulation fails
• -contradictions are placenta previa, bass previa, preterm labor, multiple gestation, previous classic incision from a cesarean birth, and reduced cervical competence
[Show More]




.png)







.png)