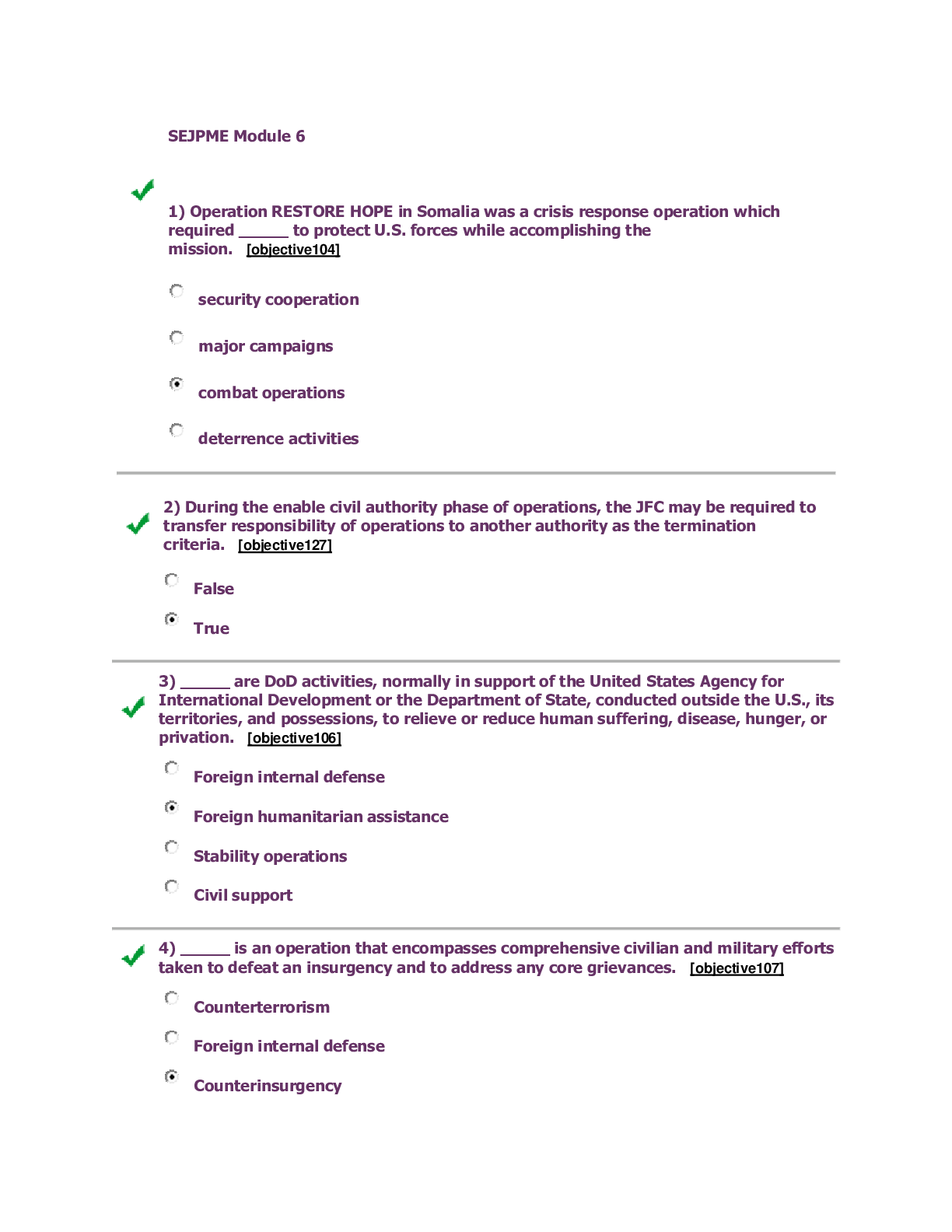
SEJPME 2 MOD 6/SEJPME II Module 6.
$ 10

NCLEX RN EXAM LATEST 865 REAL EXAM QUESTIONS AWITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS LATEST UPDATE 2024
$ 20
.png)
Sterile Processing Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

Ati pn maternal newborn proctored exam pn ati maternal newborn proctored exam complete document 1.pd
$ 18
.png)
Test Bank for Families and Professionals Trusting Partnerships in General and Special Education 8th Edition By Ann Turnbull, George Singer, Rutherford Turnbull, Grace Francis, Meghan Burke, Kathleen Kyzar
$ 19

611-PATHO EXAM 2 INTENSE Q&A- GRADED 100%
$ 18

Review - Maternal Newborn Practice B 2019
$ 12

(WGU D094) EDUC 2216 - Educational Psychology & Development - OA Review 20242025
$ 10

MED SURG III/ FINAL,100% CORRECT
$ 16

BIOD171 ESSENTIALS IN MICROBIOLOGY MODULE 3 MICROSCOPY FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 10

Chapter 15: Weight Management Nix: Williams' Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy, 15th Edition QUESTION AND ANSWERS
$ 15

Prophecy General ICU A V3 2025 Complete Prep Guide — Advanced Clinical Review, Practice Scenarios & Expert-Level Explanations
$ 8.5

ServSafe Practice Test 2023/2024
$ 9

TEST BANK For Porth's Essentials of Pathophysiology 5th Edition by Tommie L Norris All Chapters 1 - 52
$ 13.5

NSG 6001 Knowledge Check Week 2 | LATEST ANSWERS
$ 12

Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2022 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Religious Studies A (1RA0) Paper 1: Area of Study 1 - Study of Religion Option 1B: Christianity Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications
$ 7

Exam 3 Study Guide
$ 11

eBook Socio-Spatial Small Town Dynamics in South Africa,by Ronnie Donaldson
$ 29

CNDV 5350 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (1)
$ 18

HPR 205 Final Assignment Heart Disease Study Guide
$ 14

(WGU C624) CHEM 3501 - Biochemistry - FA Review 20242025
$ 10

eBook Kantian Ethics and the Attention Economy 1st Edition By Timothy Aylsworth , Clinton Castro
$ 30

NUR 4827 Leadership Roles and Management Functions in Nursing 9th Edition questions and answers 2021
$ 13

Instructor Manual With Test Bank For An Introduction to Theories of Personality 8th Edition By Matthew Olson Hergenhahn (Lecture Notes Only)
$ 25

ATI Leadership
$ 14

The International Fire Service Training Association IFSTA/FFS Essentials 3rd Edition Practice Test Bank Questions and Answers.
$ 16

eBook PDF {EPUB} Astrophysics For Dummies 1st Edition By Cynthia Phillips & Shana Priwer
$ 20

NR 302FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
$ 7.5
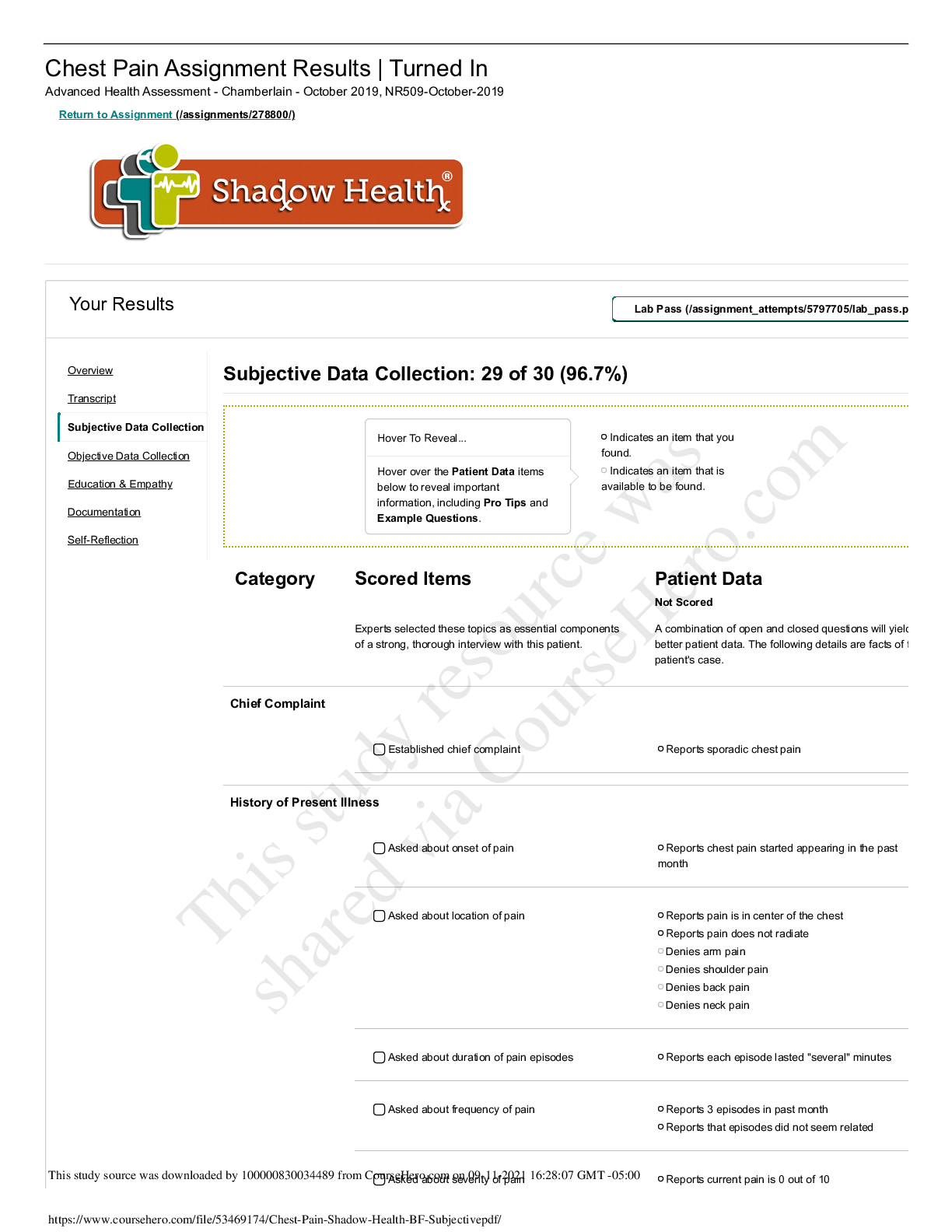
Focused Exam: Chest Pain Results | Turned In Advanced Health Assessment - Chamberlain, NR509-April-2018
$ 6

AVIA 245 final exam questions and answers, 100% complete [top rated]
$ 8

(WGU C483)BUS 2301 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 14

(WGU D196) ACCT 2020 PRINCIPLES OF FINANCIAL & MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 14

SHRM CP - 2022 | 50 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 10

Test Bank for 21st Century Astronomy: The Solar System Seventh Edition by Stacy Palen & George Blumenthal - Complete, Elaborated and Latest Test Bank. ALL Chapters (1-24) Included and Updated
$ 38

SOCI 111 QUIZ 2
$ 14
.png)
Pearson Edexcel GCE In Business (9BS0) Paper 2: Business activities, decisions and strategy
$ 10

Emory University BUS 320 Sample final
$ 7

ATI Adult Health Final Study Guide
$ 13

MKT 435 Week 1 Impact of Consumer Behavior on Marketing Strategy Paper, complete solution & rated A+ by student like you.
$ 8

Human Resource Management Functions, Applications, Skill Development 2e Robert Lussier, John Hendon (Test Bank)
$ 20

Nursing_knowledge_Assessment_Practice_Exam RN Exit Exam Questions and Answers
$ 10

eBook Grasshopper, Visual Scripting for Rhinoceros 3D (Volume 1) 1st Edition By David Bachman
$ 29

ChemicalChanges gizmo
$ 8

MEDSURG EXAM 3 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 10

ServSafe practice Test answers
$ 9.5
Atomic Structure High Demand Questions. HIGHLY EXAMINABLE QUESTION PAPER.. RATED A+
$ 12
.png)
> GCE Biology A H420/01: Biological processes Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for Autumn 2021
$ 10

BUS 311 Week 5, Final Paper|Final Paper Proposal: ACME Fireworks (complete solution)
$ 10

ATI SCIENCE :DIGESTIVE SYSTEM REVIEW
$ 13
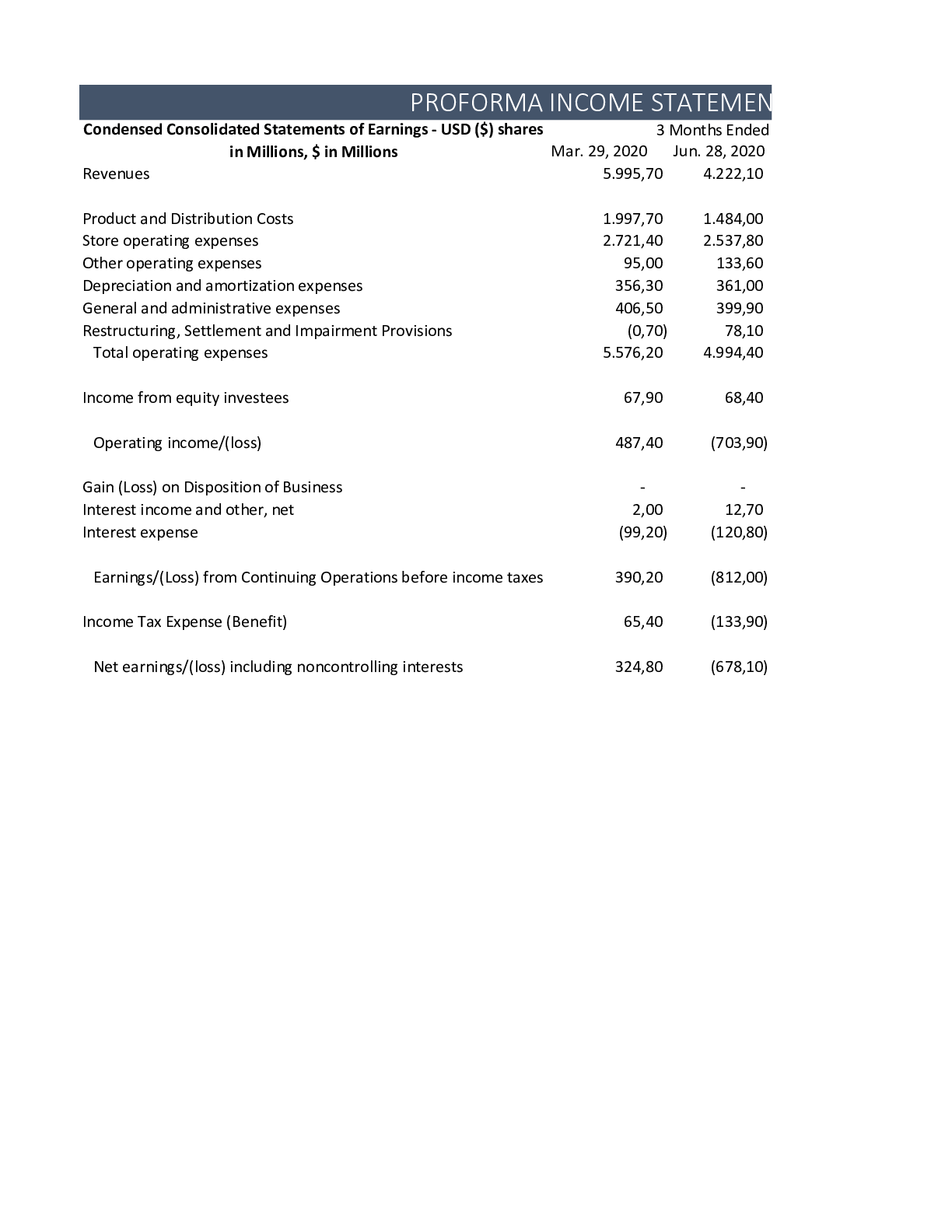
BUS 629 Week 1 Assignment Financial Forecasting
$ 15

Case Study Analysis: Best Bibs and Tucker
$ 18

Monroe College > nursing > SOAP Note UTI.complete and graded A
$ 8

MCB 3020 - Exam One(Study Guide)_LATEST,100% CORRECT
$ 16

NR 446 Chapter 9: Time Management
$ 10

NHA CCMA Study Guide/ NHA certification Study Guide for CCMA 2022
$ 9.5

HESI EXAM TEST BANK ( LATEST 2024 / 2025 ) ACTUAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 100% CORRECT
$ 15

Test Bank For Paralegal Today The Legal Team at Work 8th Edition By Roger LeRoy Miller, Mary Meinzinger
$ 30

Solutions Manual For Aircraft Propulsion 1st Edition By Saeed Farokhi
$ 30
.png)
Milestone Chapter 33 Assessment of the Cardiovascular System (Concepts for Interprofessional Collaborative Care College Test Bank)
$ 12

LATEST EXTRA ATI COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM.docx.
$ 19.5

(WGU C233) HRM 3100 EMPLOYEMENT LAW FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 11

Maternal Health
$ 35.5
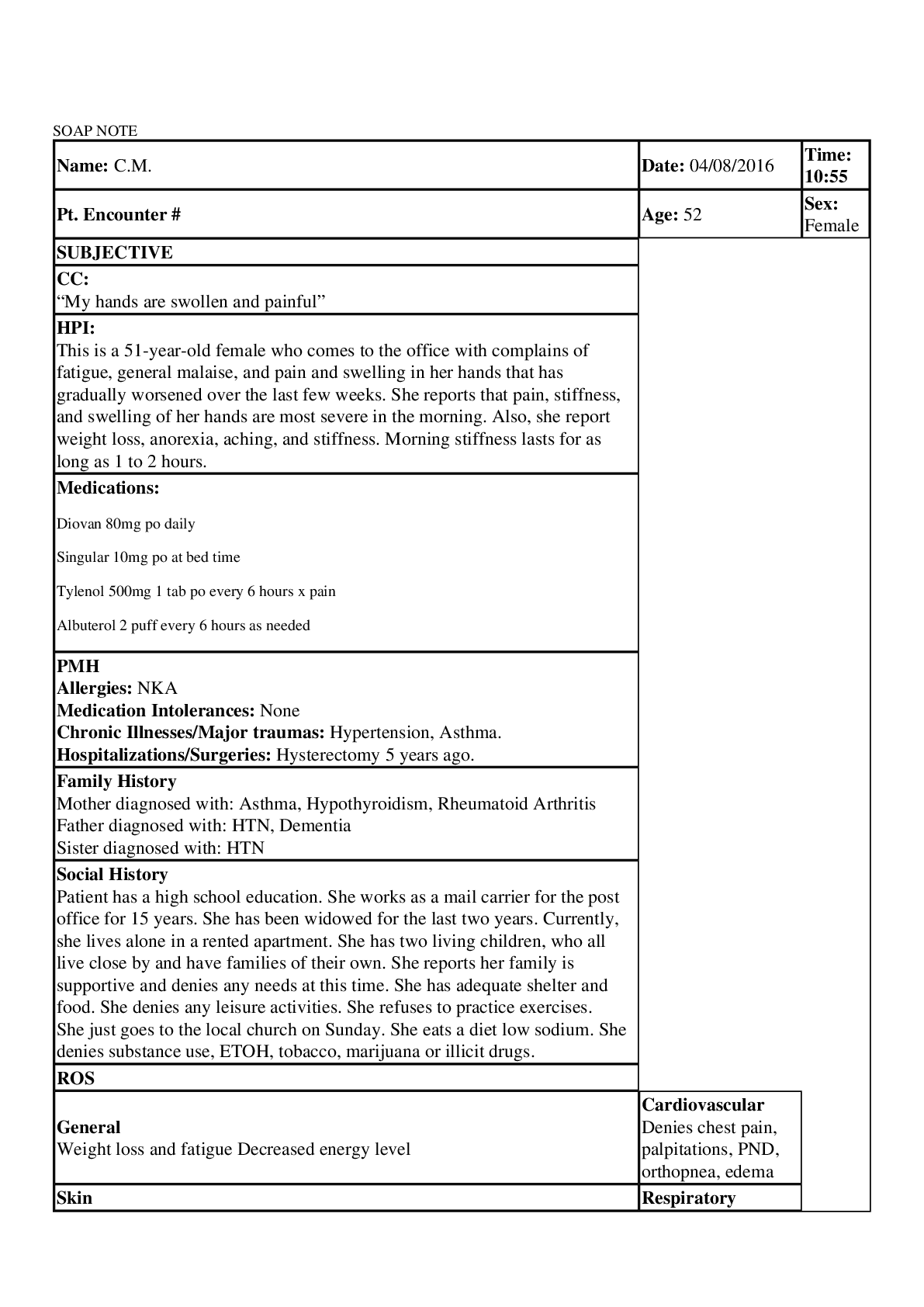
SOAP NOTE Rheumatoid Arthritis
$ 10

Business You believe that you have the necessary data management and analysis skills to carry out this task. Country level profiles are used to assist policy...
$ 7

Moraine Valley Community CollegeMDT 115Copy of Unit 4 Reading Guide (1)
$ 3

Unit 1: What Is Nursing Informatics - Entire Class's Discussion Posts
$ 8.5

Google IT Support Professional Certification / 2025 Course Review & CompTIA A+ Exam Prep
$ 19

NUR 2063 Essentials Of Pathophysiology 2023 module 02 exam (50 questions)
$ 30

AS101 Final Exam Test Bank | Modules 1-4
$ 11

ANALYZING THE MARKETING PLAN AT VISTA
$ 20

Solution Manual for Accounting Information Systems, 4th edition by Vernon J. Richardson|9781260571080|All Chapters 1-18|LATEST
$ 11

ORGSYS2.docx A2a. In the United States, coverage for medications is provided through our
$ 5

ATI TEAS 7 SCIENCE EXAM 2023 WITH ALL THE ANSWERS COMPLETE A+
$ 15

NSG 4060 Comprehensive ATI Practice B (GRADED A)
$ 11
(GCU) NRS-460 COMPLEX DISEASE MANAGEMENT FINAL EXAM GUIDE Q & A 2024
$ 13

Endethonproject__1_.docx Compensation and Benefits: EndothonTask Course Code:C236 A.
$ 10

MRL3701 ASSIGNMENT 1 SEMESTER 1 - 2022
$ 19

ETS MAJOR FIELD TEST MBA EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT SOLUTIONS 2025 GRADED A+
$ 17

ATI PN Comprehensive Predictor
$ 22

Summary Consumer Behaviour A European Outlook, 2nd Edition
$ 7

eBook All the Campus Lawyers Litigation, Regulation, and the New Era of Higher Education 1st Edition By Louis H. Guard , Joyce P. Jacobsen
$ 30

Living On One Dollar Project - Brainstorm Activity
$ 6

AQA A-level COMPUTER SCIENCE 7517/2 Paper 2 Question Paper + Mark scheme [MERGED] June 2022 *JUN227517201* IB/G/Jun22/E16 7517/2 For Examiner’s Use Question Mark 1 2
$ 7

BUS 3002 Week 3 Midterm | LATEST UPDATE
$ 15

SBB Exam 2025 Complete Study Guide — Verified Questions & Answers — Latest Update — Guaranteed Success
$ 36

BIO 344 EXAM 1 STUDY GUIDE
$ 10

FREUD’S THEORY OF PERSONALITY STRUCTURE ASSIGNMENT
$ 7

[eBook] [PDF] Drugs and the Neuroscience of Behavior An Introduction to Psychopharmacology 3rd Edition By Adam Prus
$ 30

AQA A LEVEL BUSINESS PAPER 2 BUSINESS 2 2021 QP
$ 20

ANTHEM - TOOLS FOR COMPLIANT SELLING, ANTHEM FOUNDATION-BASICS ASSESSMENT
$ 7.5

NURS 6541 Week 7 Quiz 2,100% CORRECT
$ 9

eBook A Poet’s Ashram Rabindranath Tagore’s Experimental Community in Colonial India 1st Edition By Sukalyan Chanda
$ 30

Family Violence Legal, Medical, and Social Perspectives, 9e Harvey Wallace, Cliff Roberson, Julie Globokar (Instructor manual with Test Bank)
$ 25

ATI – NCLEX PREDICTOR REMEDIATION STUDY NOTES
$ 10

2022-2023 AAPC CPC FINAL PRACCE TEST with 100 Correct Answers
$ 19

Solutions Manual For Introduction to Finance Markets, Investments, and Financial Management, 17th Edition By Ronald Melicher, Edgar Norton
$ 30

AIR CONDITIONING CERTIFICATION PRACTICE TEST EXAM SOLUTION 2022
$ 8

📄 Study Guide & Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry (9th Ed.) – Susan McMurry
$ 30
.png)
StairClimbingPowerLab
$ 7

Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward


.png)






















