*NURSING > EXAM > Canadian Practical Nurse Registration Examination (CPNRE) Test Bank Exams Questions with Explained A (All)
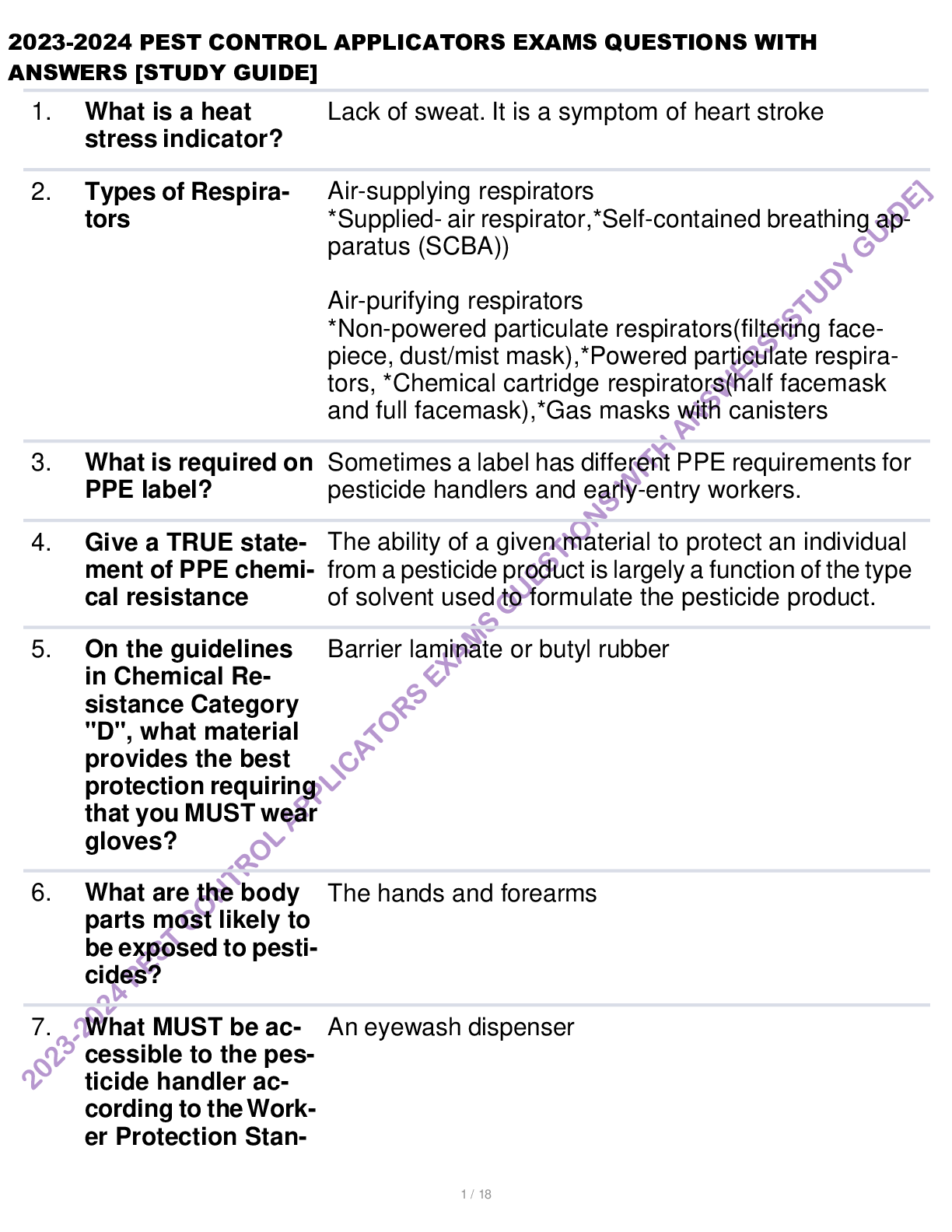
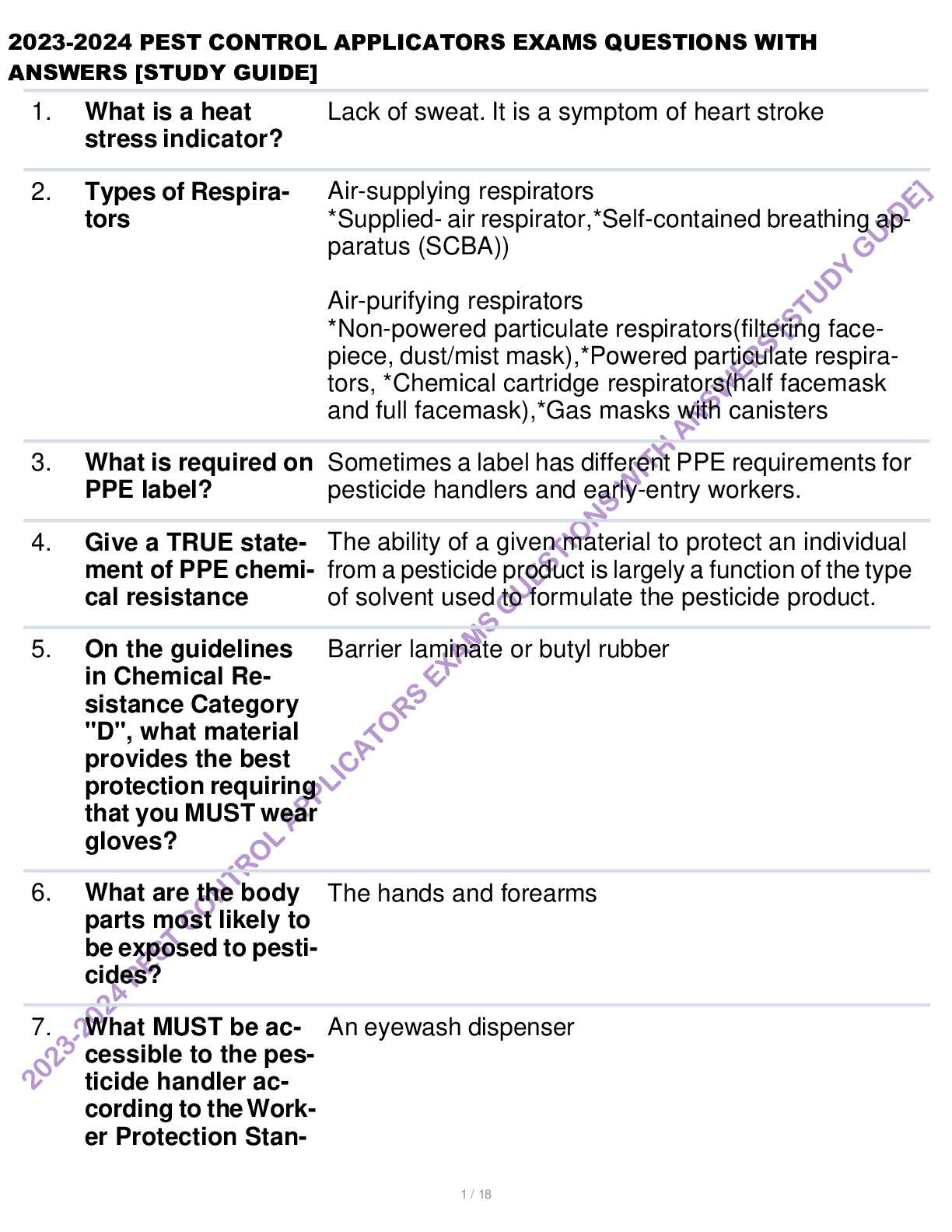
Canadian Practical Nurse Registration Examination (CPNRE) Test Bank Exams Questions with Explained Answers
Document Content and Description Below
Canadian Practical Nurse Registration Examination (CPNRE) Test Bank Exams Questions with Explained Answers-The nurse is administering heparin via the subcutaneous route. Which intervention should the ... nurse implement? a. Prepare the medication using a 25-gauge, ½ inch needle b. After injecting the needle, aspirate and observe for blood c. After removing the needle, massage the area gently d. Administer the medication in the client's "love handles"-Prepare the medication using a 25-gauge, ½ inch needle Knowledge: The nurse should NOT aspirate for blood when administering heparin because this can damage surrounding tissue and cause bruising. The nurse should not massage after injecting heparin because this may cause bruising or bleeding. Heparin is administered in the abdomen at least 2 inches from umbilicus-best practice. The nurse is administering morning medications on a medical floor. Which medication should the nurse administer first? a. Regular insulin sliding scale to an elderly client diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes mellitus b. Methylprednisolone, a glucocorticoid, to a client diagnosed with lupus erythematosus c. Morphine, a narcotic analgesic, to a client diagnosed with AIDS d. Lasix, a diuretic, to a client with hypertension-a. Regular insulin sliding scale to an elderly client diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes mellitus b. Methylprednisolone, a glucocorticoid, to a client diagnosed with lupus erythematosus (can be administered within the 30-minute acceptable time frame) c. Morphine, a narcotic analgesic, to a client diagnosed with AIDS -pain medication is a priority, but it can be administered after the sliding scale d. Lasix, a diuretic, to a client with hypertension- can be administered within the 30-minute acceptable time frame Regular insulin is administered prior to meals; therefore, this medication should be administered. Critical Thinking Which data would indicate that the antibiotic therapy has been successful for a client diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia? a. The client's hematocrit is within normal range b. The client is expectorating thick green sputum c. The client's lung sounds are clear to ausculatation d. The client has complaints of pleuritic chest pain.-a. The client’s hematocrit is within normal range- does not indicate client response b. The client is expectorating thick green sputum- symptom of pneumonia c. The client’s lung sounds are clear to ausculatation d. The client has complaints of pleuritic chest pain.— symptom of pneumonia The symptoms of pneumonia includes crackles and wheezes, rhonchi in the lung fields. Clear lungs indicate an improvement in the pneumonia and that the medication is effective. Application The nurse is administering Humalog at 0730 to a client diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes. Which intervention should the nurse implement? a. Ensure the client eats at least 90% of the lunch tray b. Do not administer unless the breakfast tray is in the client's room c. Check the client's blood glucose level 1 hour after receiving the insulin d. Have 50% dextrose in water at the bedside for emergency use.-a. Ensure the client eats at least 90% of the lunch tray—insulin will not be working 4-5 hours after being administered b. Do not administer unless the breakfast tray is in the client’s room c. Check the client’s blood glucose level 1 hour after receiving the insulin—glucose level should be checked prior to administering d. Have 50% dextrose in water at the bedside for emergency use.—this is administered when a client is unconscious secondary to hypoglycemia, and should not be kept at the bedside. Orange juice or some form of simple glucose can be kept at the bedside. Application: The insulin peaks in 15-20 minutes after being administered; therefore, the meal should be at the bedside prior to administering this medication The client has a severe anaphylactic reaction to insect bites. What priority discharge intervention should the nurse discuss with the client? a. Wear an insect repellent on exposed skin b. Keep prescribed antihistamines on their person c. Keep an EpiPen in the refrigerator at all times d. Wear a MedicAlert identification bracelet-a. Wear an insect repellent on exposed skin —appropriate intervention, but if the client has an insect bite, the repellent will not prevent anaphylaxis, therefore, not priority intervention b. Keep prescribed antihistamines on their person —used with anaphylaxis, but it takes at least 30 minutes to work, therefore not a priority medication c. Keep an EpiPen in the refrigerator at all times —keeping medication in the refrigerator does not allow it to be available to the client at all times. d. Wear a MedicAlert identification bracelet Application: Bracelet indicates the client is at risk for an anaphylactic reaction; therefore, this is the priority intervention. The client's mother contacts the clinic regarding medication administration stating, "My daughter cannot swallow this capsule. It's too large." Investigation reveals that the medication is a capsule marked SR. The nurse should instruct the mother to: a. Open the capsule and mix the medication with apple sauce b. Crush the medication and administer it with a glass of liquid c. Call the pharmacist and request a change to a different medication d. Stop the medication and inform the physician-d. Stop the medication and inform the physician Application: SR means sustained released. These medications cannot be altered. In answers A and B, crushing or opening the capsule is not allowed. The best response would be to inform the prescriber (the doctor) immediately The client calls the nursing station and requests pain medication. When the nurse enters the room with the narcotic medication, the nurse finds the client laughing and talking with visitors. Which action should the nurse administer first? a. Administer the client's prescribed pain medication b. Assess the client's perception of pain on a 1-10 scale c. Wait until the visitors leave to administer any medication d. Check the MAR to see if there is a nonnarcotic medication ordered-a. Administer the client’s prescribed pain medication —should not administer pain medication until after assessing the client’s pain b. Assess the client’s perception of pain on a 1-10 scale c. Wait until the visitors leave to administer any medication —should assess client whether the client has visitors or not d. Check the MAR to see if there is a nonnarcotic medication ordered —nurse should assess the client’s pain first Application: first action is to always assess the client in pain to determine if client is having a complication that requires medical intervention rather than PRN medication. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 week ago
Preview 1 out of 204 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$17.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 21, 2025
Number of pages
204
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 21, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
4