*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > ATI med surg post assessment, Latest 2020 Complete Solution Help; Bishop State Community College (All)
ATI med surg post assessment, Latest 2020 Complete Solution Help; Bishop State Community College
Document Content and Description Below
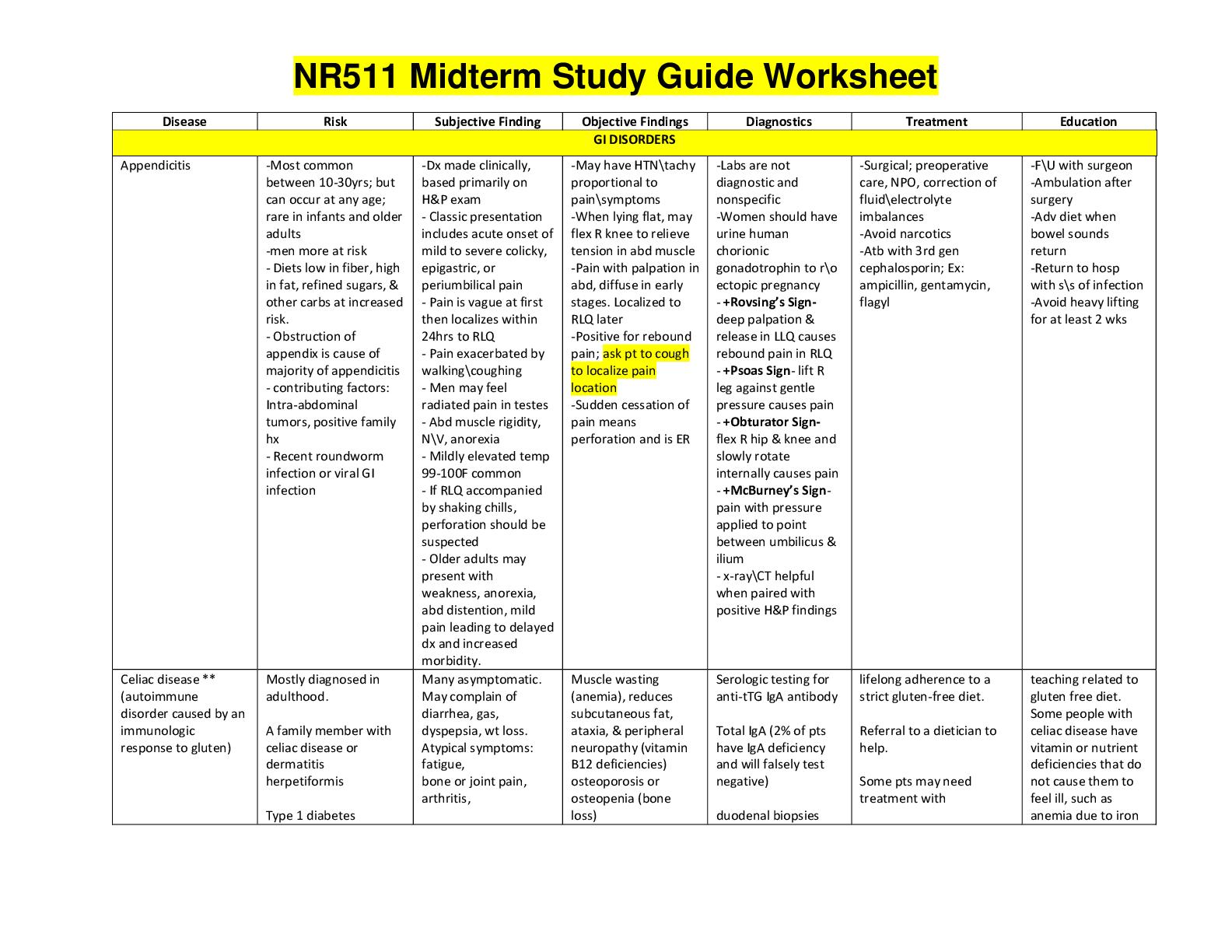
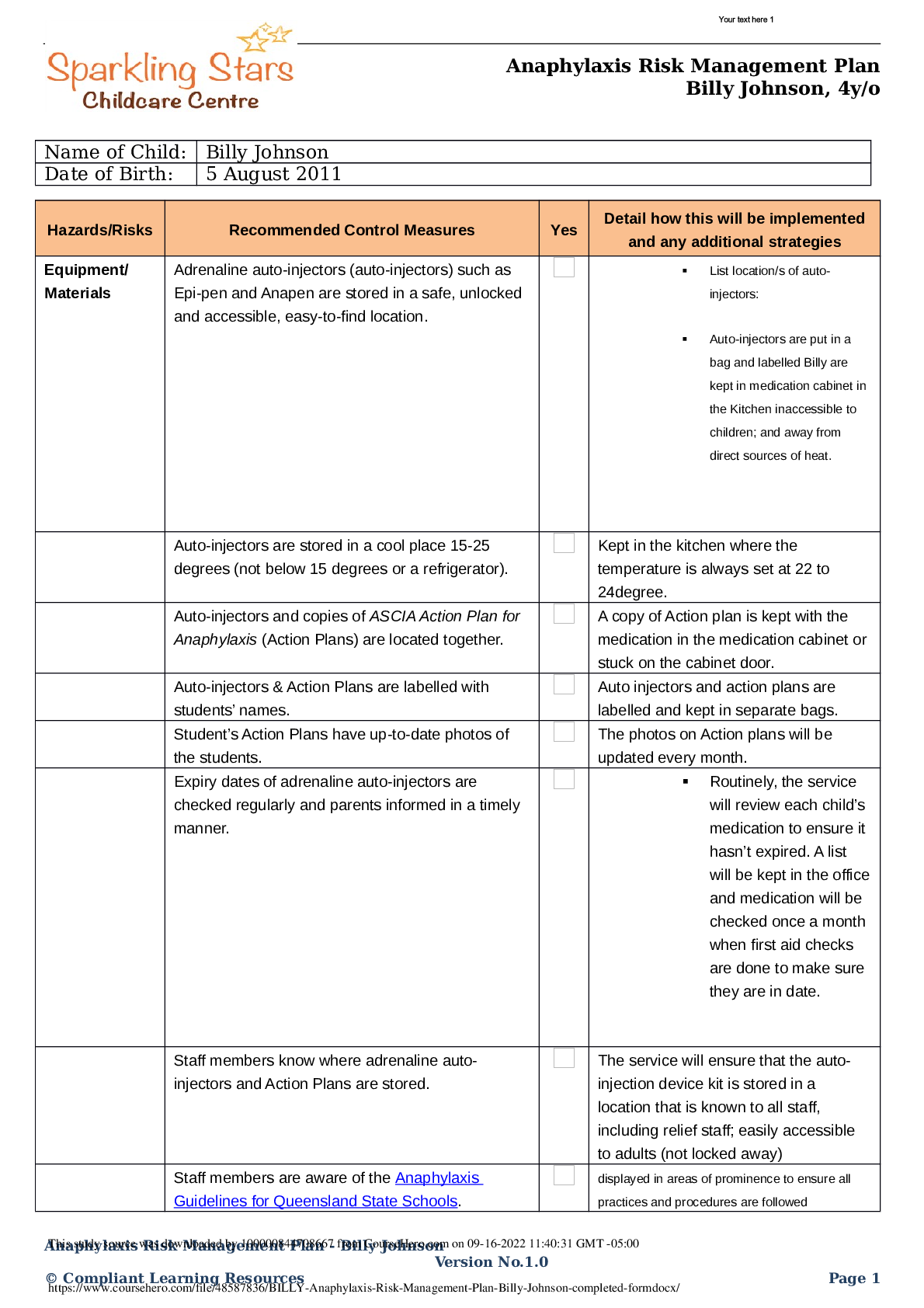
ATI med surg post assessment. Hematologic Diagnostic Procedures: Bone Marrow Biopsy (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 39, Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure) Bone biopsy takes a small sample of bone ... marrow removed by needle aspiration for cytological (histological) examination Performed with local anesthesia or conscious sedation. Used to diagnose blood disorders (anemia, thrombocytopenia) or diseases of bone marrow (leukemia, infection) or stage lymphoma or other forms of cancer. Teaching: teach client to report excessive bleeding and evidence of infection to provider Teach client to check the biopsy site daily, keep the dressing clean, dry, and intact If sutures in place, have client return in 7 days to have them removed Esophageal Disorders: Dietary Selections for a Client Who Has a Hiatal Hernia (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RN QSEN - Patient-centered Care, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 48) Avoid eating immediately prior to going to bed Avoid foods and beverages that decrease LES pressure (fatty and fried foods, chocolate, coffee, peppermint, spicy foods, tomatoes, citrus fruits, and alcohol) Musculoskeletal Trauma: Teaching Strategies to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (RN QSEN - Safety , RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 71, Active Learning Template - Basic Concept) Avoid repetitive flexion of wrist Perform ROM Have item under wrists while using computer to prevent prolonged flexion Elevate hand above level of heart Renal Calculi: Priority Intervention for a Client Who Has Renal Calculi (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 61) Report laboratory and diagnostic findings to the provider Strain all urine to check for passage of the calculus and save the calculus for laboratory analysis Encourage client to increase oral intake to 3L/day unless contraindicated Encourage ambulation to promote passage of the calculus Administer IV fluids as prescribed Urinary Elimination: Identifying Type of Urinary Incontinence (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM FUND 9.0 Ch 44) Stress: loss of small amounts of urine from increased abdominal pressure without bladder muscle contraction with laughing, sneezing or lifting Urge: inability to stop urine flow long enough to reach the bathroom due to an overactive detrusor muscle with increased bladder pressure Overflow: urinary retention from bladder overdistention and frequent loss of small amounts of urine due to obstruction of the urinary outlet or an impaired detrusor muscle Reflex: involuntary loss of a moderate amount of urine usually without warning due to hyperreflexia of the detrusor muscle, usually from spinal cord dysfunction Functional: loss of urine due to factors that interfere with responding to the need to urinate, such as [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 14, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 14, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
97





















.png)

