Chapter 01: The History and Interviewing Process
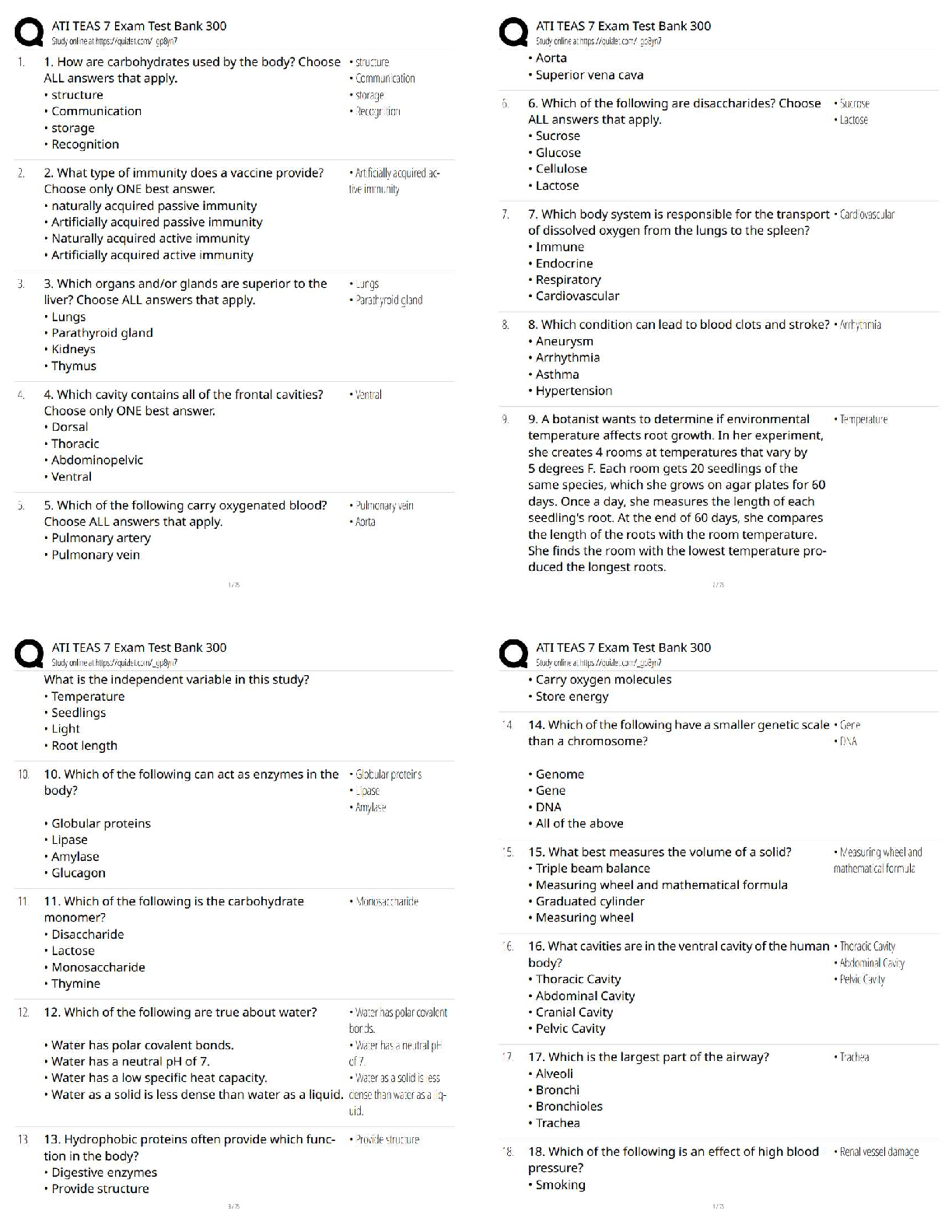
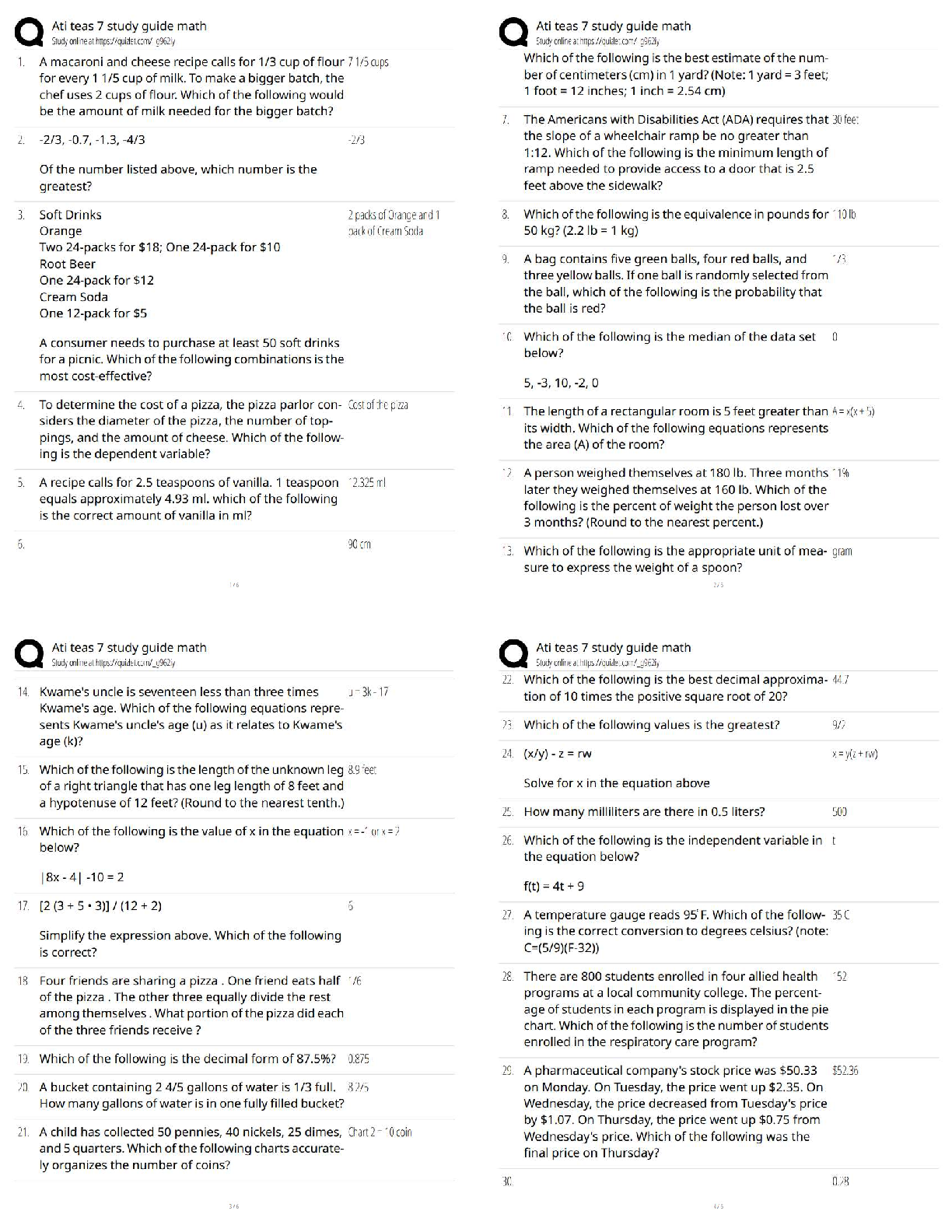
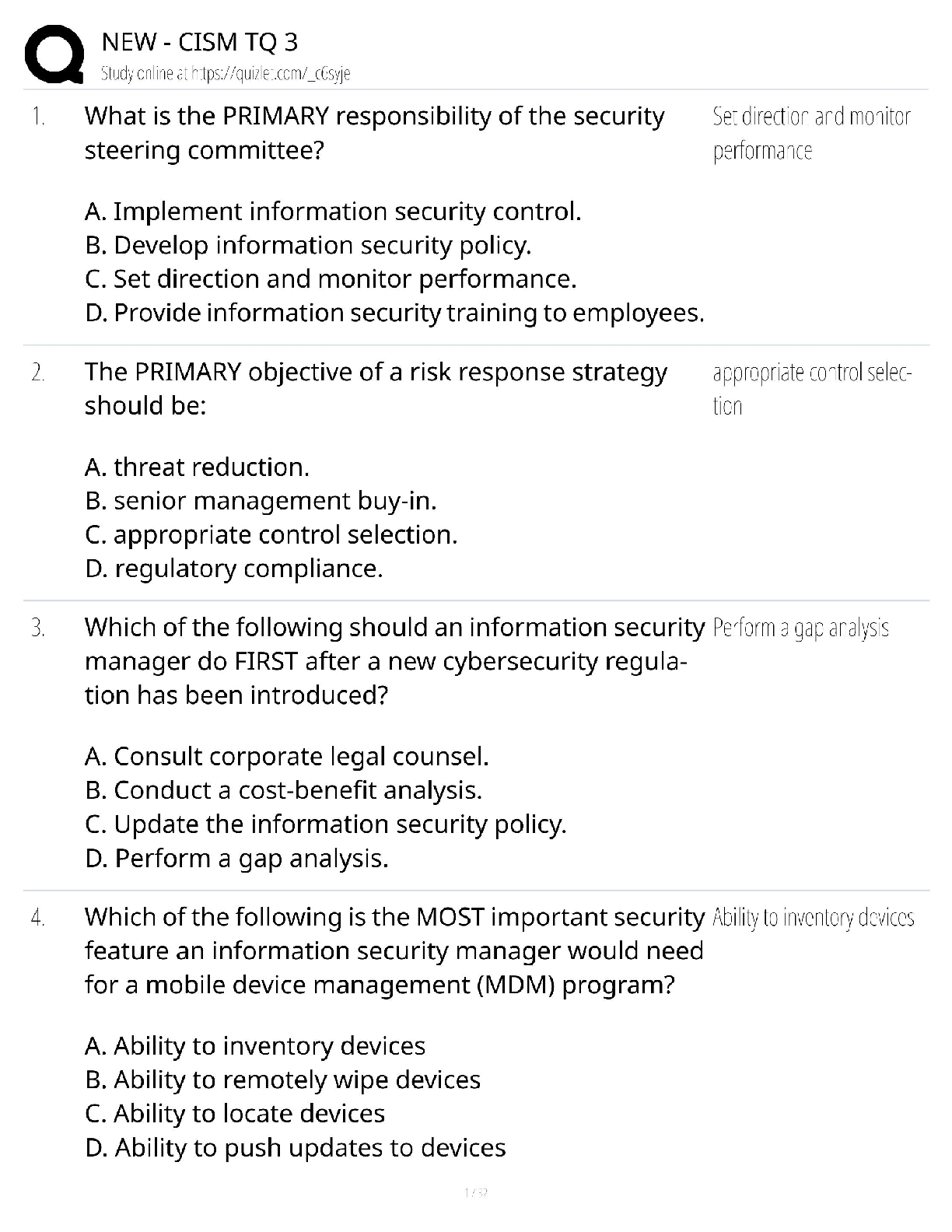
Ball: Seidel¶V GXide WR Ph\Vical E[aPiQaWiRQ, 9Wh EdiWiRQ
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which TXeVWiRQ ZRXld be cRQVideUed a ³leadiQg TXeVWiRQ?´
a. ³PleaVe deVcUibe aQ\ aVVRciaWe
...
Chapter 01: The History and Interviewing Process
Ball: Seidel¶V GXide WR Ph\Vical E[aPiQaWiRQ, 9Wh EdiWiRQ
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which TXeVWiRQ ZRXld be cRQVideUed a ³leadiQg TXeVWiRQ?´
a. ³PleaVe deVcUibe aQ\ aVVRciaWed V\mSWRmV ZiWh \RXU headacheV?´
b. ³YRX dRQ¶W geW headacheV RfWeQ, dR \RX?´
c. ³WhaW acWiYiWieV affecW Whe VeYeUiW\ Rf \RXU headacheV?´
d. ³WhaW WimeV Rf Whe da\ aUe \RXU headacheV Whe mRVW VeYeUe?´
e. ³WhaW ZRUUieV \RX mRVW abRXW \RXU headache?´
ANS: B
ThiV TXeVWiRQ ZRXld limiW Whe iQfRUmaWiRQ iQ Whe SaWieQW¶V aQVZeU. The RWheU chRiceV allRZ Whe
patient more discretion about the extent of an answer.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
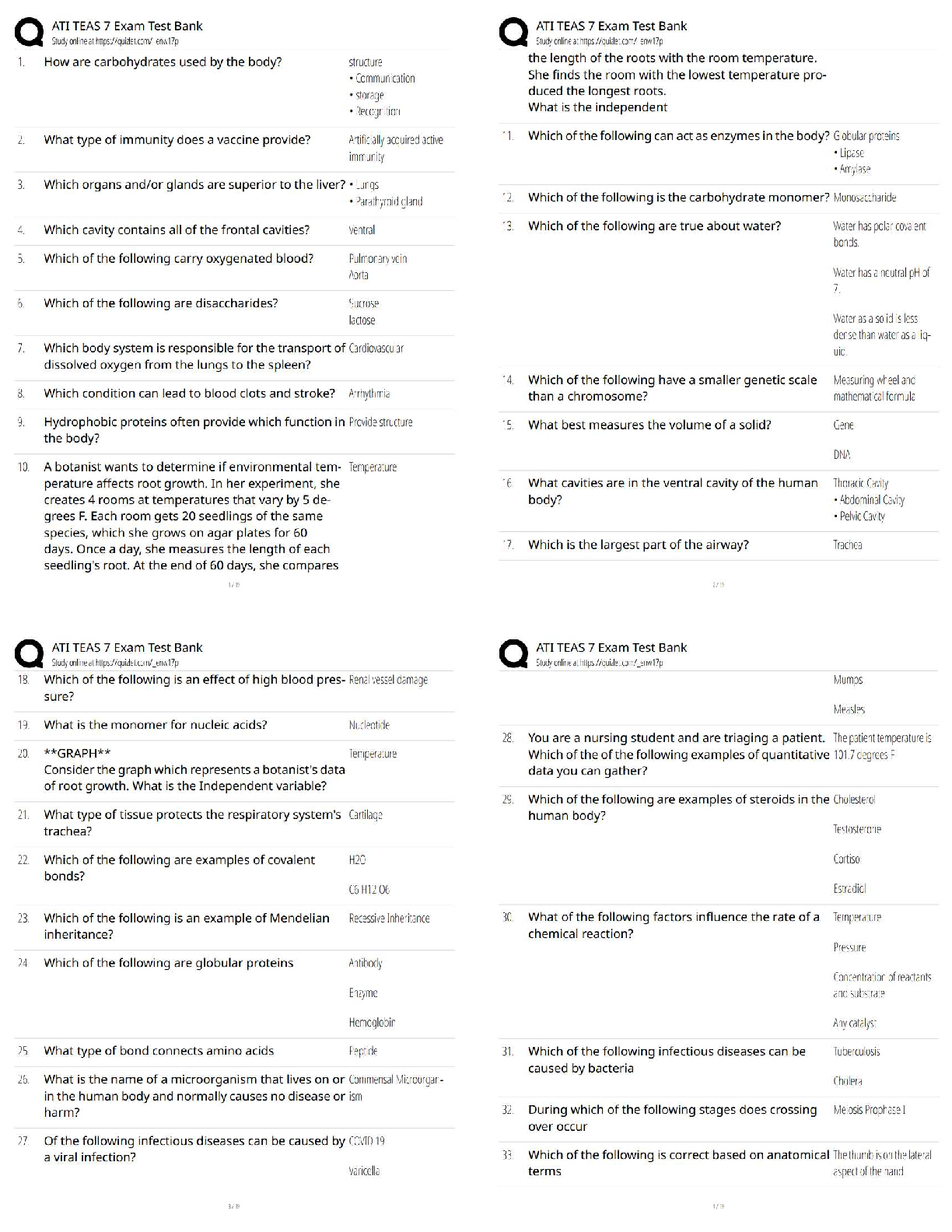
2. Which action would best promote accurate translations as well as confidentiality when the
caUegiYeU dReV QRW VSeak Whe SaWieQW¶V laQgXage?
a. Ask a person unfamiliar with the patient to translate.
b. Have a friend of the patient translate.
c. Ask simple leading questions that the patient may understand.
d. Use a neighbor as translator.
e. Involve the family with the translation.
ANS: A
WheQ \RX dR QRW VSeak Whe SaWieQW¶V laQgXage, famil\ membeUV RU fUieQdV ma\ SRVe a
communication barrier and may have issues of confidentiality; a stranger as an interpreter is
less biased.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
3. Periods of silence during the interview can serve important purposes, such as:
a. allowing the clinician to catch up on documentation.
b. giving you a clue that you should speed up the interview.
c. providing time for reflection.
d. increasing the length of the visit.
e. promoting a calm environment.
ANS: C
Silence is a useful tool during interviews for the purposes of reflection, summoning of
courage, and displaying compassion. It is usually a clue for you to go slower and not to push
too hard.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
4. Which WechQiTXe iV mRVW likel\ WR UeVXlW iQ Whe SaWieQW¶V XQdeUVWaQdiQg Rf TXeVWiRQV?
a. Use phrases that are commonly used by other patients in the area.
b. UVe Whe SaWieQW¶V RZQ WeUmV if SRVVible.
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
c. Use language that keeps the patient from being expansive in his or her answer.
d. Use proper medical and technical terminology.
e. Use the simplest language possible.
ANS: B
To ensure that your questions have been correctly understood, be clear, and explicit while
XViQg Whe SaWieQW¶V idiRm aQd leYel Rf XQdeUVWaQdiQg.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
5. A SaWieQW becRmeV UeVWleVV dXUiQg Whe hiVWRU\ aQd Va\V, ³I dRQ¶W haYe Wime fRU all of this
cRQYeUVaWiRQ. I¶Ye gRW WR geW back WR ZRUk.´ YRXU mRVW aSSURSUiaWe UeVSRQVe ZRXld be WR:
a. stop using open-ended questions and become more direct.
b. ask another open-ended question and insist on an answer.
c. ask questions about his anger and move closer to him.
d. acknowledge his anger and proceed with the history and examination.
e. ignore his displeasure and become more assertive about getting answers.
ANS: D
This is the only answer that resists the tendency for patient manipulation, pursues the
iQfRUmaWiRQ, aQd cRQfURQWV Whe SaWieQW¶V aQgeU.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
6. WheQ TXeVWiRQiQg a SaWieQW UegaUdiQg alcRhRl iQWake, Vhe WellV \RX WhaW Vhe iV ³RQl\ a VRcial
dUiQkeU.´ Which iQiWial UeVSRQVe iV aSSURSUiaWe?
a. ³I¶m glad WhaW \RX aUe a UeVSRQVible dUiQkeU.´
b. ³MaQ\ SeRSle ZhR aUe Ueall\ alcRhRlic Va\ Whe\ aUe VRcial dUiQkeUV.´
c. ³WhaW amRXQW aQd ZhaW kiQd Rf alcRhRl dR \RX dUiQk iQ a Zeek?´
d. ³If \RX RQl\ dUiQk VRciall\, \RX ZRQ¶W Qeed WR ZRUU\ abRXW alZa\V haYiQg a
deVigQaWed dUiYeU.´
e. ³DR Whe RWheU SeRSle iQ \RXU hRXVehRld cRQVXme alcRhRl?´
ANS: C
ThiV aQVZeU claUifieV Whe SaWieQW¶V RZQ WeUm ZiWhRXW aVkiQg a leadiQg TXeVWiRQ RU beiQg
judgmental.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
7. A 50-year-old man comes to the primary care clinic. He tells you he is worried because he has
had severe chest pains for the past 2 weeks. Which initial history interview question is most
appropriate?
a. ³CaQ \RX deVcUibe Whe SaiQ?´
b. ³The SaiQ dReVQ¶W UadiaWe WR \RXU aUm, dReV iW?´
c. ³HaYe \RX beeQ WUeaWed fRU aQ[ieW\ befRUe?´
d. ³DReV \RXU faWheU haYe heaUW diVeaVe?´
e. ³AUe Whe SaiQV ZRUVe afWeU \RX eaW?´
ANS: A
Initially, an open-eQded TXeVWiRQ iV a mRUe aSSURSUiaWe UeVSRQVe. ³CaQ \RX deVcUibe Whe SaiQ?´
is an open-ended question that offers clues to the chief concern.
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
8. MV. A. VWaWeV, ³M\ life iV jXVW WRR SaiQfXl. IW iVQ¶W ZRUWh iW.´ She aSSeaUV deSUeVVed. Which RQe
of the following statements is the most appropriate caregiver response?
a. ³TU\ WR WhiQk abRXW Whe gRRd WhiQgV iQ life.´
b. ³YRX VhRXldQ¶W feel WhaW Za\; lRRk aW all Whe gRRd WhiQgV iQ \RXU life.´
c. ³YRX caQ¶W meaQ ZhaW \RX¶Ue Va\iQg.´
d. ³If \RX WhiQk abRXW iW, QRWhiQg iV ZRUWh geWWiQg WhiV XSVeW abRXW.´
e. ³WhaW iQ life iV caXViQg \RX VXch SaiQ?´
ANS: E
Specific yet open-ended questions are best used when the patient has feelings of loss of
self-worth and depression. The other responses hurry the patient and offer superficial
assurance.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
9. During an interview, you have the impression that a patient may be considering suicide.
Which action is essential?
a. Immediately begin proceedings for an involuntary commitment.
b. Ask whether the patient has considered self-harm.
c. Ask whether the patient would like to visit a psychiatrist.
d. RecRUd Whe imSUeVViRQ iQ Whe SaWieQW¶V chaUW aQd UefeU Whe SaWieQW fRU
hospitalization.
e. Avoid directly confronting the patient regarding your impression.
ANS: B
If you think the patient may be considering suicide, he or she probably is. Mentioning it gives
permission to talk about it.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
10. You are collecting a history from an 11-year-old girl. Her mother is sitting next to her in the
examination room. When collecting history from older children or adolescents, they should:
a. never be interviewed alone because this may alienate the parent.
b. be mailed a questionnaire in advance to avoid the need for her to talk.
c. be given the opportunity to be interviewed without the parent at some point.
d. be allowed to direct the flow of the interview.
e. be ignored while you address all questions to the parent.
ANS: C
An older child should be given the opportunity to give information directly. This enhances the
probability that the child will follow your advice.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
11. When communicating with older children and teenagers, you should be sensitive to their:
a. SaUeQW¶V QeedV.
b. natural urge to communicate.
c. need for verbal instructions.
d. typical reluctance to talk.
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
e. desire for adult companionship.
ANS: D
Adolescents are usually reluctant to talk; therefore, the provider should clearly communicate a
respect for their confidentiality.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
12. When you suspect that your 81-year-old patient has short-term memory loss because he
cannot remember what he had for breakfast, you should:
a. order a neurology consult.
b. stop all of his medications.
c. continue to press the patient for appropriate answers.
d. validate the concern with his family or caregivers.
e. dismiss the finding as a normal age-related change.
ANS: D
When older adults experience memory loss for recent events, consult other family members to
clarify discrepancies or to fill in the gaps.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
13. To what extent should the patient with a physical disability or emotional disorder be involved
in providing health history information to the health professional?
a. All information should be obtained from family members.
b. All information should be collected from past records while the patient is in
another room.
c. The patient should be involved only when you sense that he or she may feel
ignored.
d. The patient should be fully involved to the limit of his or her ability.
e. The patient should be present during information collection but should not be
addressed directly.
ANS: D
Patients with disabilities may not give an effective history, but they must be respected, and the
history must be obtained from them to the greatest extent possible. Family members may help
provide a more complete history but not at the exclusion of the patient.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
14. When taking a history, you should:
a. ask patients to give you any information they can recall about their health.
b. VWaUW Whe iQWeUYieZ ZiWh Whe SaWieQW¶V famil\ hiVWRU\.
c. use a chronologic and sequential framework.
d. use a holistic and eclectic structure.
e. start the interview with the social history.
ANS: C
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
To give structure to the present problem or chief concern, the provider should proceed in a
chronologic and sequential framework. Asking patients to give you any information they can
recall about their health and using a holistic and eclectic structure do not provide for structure.
SWaUWiQg Whe iQWeUYieZ ZiWh Whe SaWieQW¶V famil\ hiVWRU\ aQd ZiWh Whe VRcial hiVWRU\ aUe iQcRUUecW
because gathering data about the chief concern is the initial step.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
15. When questioning the patient regarding his or her sexual history, which question should be
asked initially?
a. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ SaUWicXlaU Ve[Xal likeV RU diVlikeV?´
b. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ ZRUUieV RU cRQceUQV UegaUdiQg \RXU Ve[ life?´
c. ³HRZ RfWeQ dR \RX haYe iQWeUcRXUVe aQd ZiWh ZhRm?´
d. ³DR \RX haYe aQ\ UeaVRQ WR WhiQk \RX ma\ haYe beeQ e[SRVed WR a Ve[Xall\
WUaQVmiWWed iQfecWiRQ?´
e. ³WhaW Ve[Xall\ WUaQVmiWWed diVeaVeV haYe \RX had iQ Whe SaVW?´
ANS: B
When approaching questioning about a sensitive area, it is recommended that the provider
first ask open-eQded TXeVWiRQV WhaW e[SlRUe Whe SaWieQW¶V feeliQgV abRXW Whe iVVXe.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
16. Direct questioning about intimate partner violence in the home should be:
a. a routine component of history taking with female patients.
b. aYRided fRU feaU Rf RffeQdiQg Whe ZRmaQ¶V SaUWQeU.
c. conducted only in cases in which there is a history of abuse.
d. used only when the patient is obviously being victimized.
e. used only when bruises are found on physical examination.
ANS: A
The presence of intimate partner violence should be routinely queried, and the questioning
should be direct for all female patients.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
17. Mrs. G. reports an increase in her alcohol intake over the past 5 years. To screen her for
problem drinking, you would use the:
a. Miller Analogies Test.
b. PACE Assessment Instrument.
c. CAGE questionnaire.
d. Glasgow Coma Scale.
e. HITS questionnaire.
ANS: C
The CAGE questionnaire is a model for approaching a discussion of the use of alcohol.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
18. When you enter the examination room of a 3-year-Rld giUl, \RX fiQd heU ViWWiQg RQ heU faWheU¶V
lap. She turns away from you when you greet her. Initially, your best response is to:
a. screen the child for sexual abuse.
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
b. ask the child to be seated on the examination table so you can talk to her father.
c. explain to the child that you will not hurt her and that she will have to trust you.
d. ask the father to persuade the child to cooperate with you.
e. leaYe Whe child ViWWiQg iQ Whe faWheU¶V laS Zhile \RX Walk WR Whe faWheU.
ANS: E
Interaction with children must be modified according to age and in a manner that promotes
trust.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
19. Tom is a 16-year-old young man with diabetes who does not follow his diet. He enjoys his
dirt bike and seems unconcerned about any consequences of his activities. Which factor is
W\Sical Rf adRleVceQce aQd SeUWiQeQW WR TRm¶V healWh?
a. Attachment to parents
b. Tendency to give too much information
c. Low peer support needs
d. Propensity for risk taking
e. High self-esteem
ANS: D
Adolescents tend to experiment with risky behaviors that lead to a high incidence of morbidity
and mortality. Adolescents may be reluctant to provide information.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
20. Pain is difficult to assess in older adults because:
a. their histories are usually unreliable.
b. sharp pain may be felt as a dull ache.
c. they tend to exaggerate symptoms.
d. their language skills decline.
e. drugs act more rapidly with age.
ANS: B
Pain is often an unreliable symptom in older adults because they lose pain perception and
experience pain in a different manner from those in other age groups.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
21. A survey of mobility and activities of daily living (ADL) is part of a(n):
a. ethnic assessment.
b. functional assessment.
c. genetic examination.
d. social history.
e. sexual history.
ANS: B
A fXQcWiRQal aVVeVVmeQW iV aQ aVVeVVmeQW Rf a SaWieQW¶V mRbiliW\, XSSeU e[WUemiW\ mRYemeQW,
household management, activities of daily living, and instrumental activities of daily living.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
22. Constitutional symptoms in the ROS refer to:
a. height, visual acuity, and body mass index.
b. fever, chills, fatigue, and malaise.
c. hearing loss, tinnitus, and diplopia.
d. rashes, skin turgor, and temperature.
e. joint stiffness, redness, and swelling.
ANS: B
General constitutional symptoms refer to fever, chills, malaise, fatigability, night sweats, sleep
patterns, and weight (average, preferred, present, change).
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
23. J.M. has been seen in your clinic for 5 years. She presents today with signs and symptoms of
acute sinusitis. The type of history that is warranted is a(n) _____ history.
a. complete
b. inventory
c. problem or focused
d. interim
e. family
ANS: C
If the patient is well known or if you have been seeing the patient for the same problem over
time, a focused history is appropriate.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
24. A pedigree diagram is drafted for the purpose of obtaining:
a. sexual orientation and history.
b. growth and developmental status.
c. genetic and familial health problems.
d. ethnic and cultural backgrounds.
e. the past medical history.
ANS: C
Drafting a pedigree diagram, or genogram, is a method to determine consanguinity of health
problems.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
Chapter 02: Cultural Competency
Ball: Seidel¶V GXide WR Ph\Vical E[aPiQaWiRQ, 9Wh EdiWiRQ
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Which statement is true regarding the relationship of physical characteristics and culture?
a. Physical characteristics should be used to identify members of cultural groups.
b. There is a difference between distinguishing cultural characteristics and
distinguishing physical characteristics.
c. To be a member of a specific culture, an individual must have certain identifiable
physical characteristics.
d. Gender and race are the two essential physical characteristics used to identify
cultural groups.
e. Whereas all cultural traits can be viewed as static, physical traits are dynamic.
ANS: B
Physical characteristics do not symbolize cultural groups; there is a difference between the
two, and they are considered separately. Cultures are dynamic in their evolution.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
2. A fixed image of any group that rejects its potential for originality or individuality is known
as a(n):
a. acculturation.
b. norm.
c. stereotype.
d. ethnos.
e. custom.
ANS: C
This definition describes a stereotype. A norm, on the other hand, is a standard of allowable
behavior within a group, ethnos implies the same race or nationality, and acculturation is a
pUoceVV of adopWing anoWheU cXlWXUe¶V behaYioUV. A cXVWom UefeUV Wo a habitual activity of a
group in a given situation.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
3. Your new patient is a 40-year-old Middle Eastern man with a complaint of new abdominal
pain. You are concerned about violating a cultural prohibition when you prepare to do his
rectal examination. The best tactic would be to:
a. do the examination because it is a necessary part of the physical examination.
b. ask a colleague from the same geographic area if this examination is acceptable.
c. inform the patient of the reason for the examination and ask if it is acceptable to
him.
d. refer the patient to a provider more knowledgeable about cultural differences.
e. forego the examination for fear of violating cultural norms.
ANS: C
NURSINGTB.COM
Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination 9th Edition Ball Test Bank
NURSINGTB.COM
Asking, if you are not sure, is far better than making a damaging mistake. You would not be
doing your job as a professional if you deferred the examination without a reason. It is not
necessary to refer a skill you are capable of performing.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
4. Which statement is true regarding impoverished people?
a. In the United States, socioeconomic status does not influence the delivery of health
care.
b. The morbidity and mortality rates of impoverished people are greater than those of
the middle class.
c. The morbidity and mortality rates of impoverished people are less than those of the
middle class.
d. No reliable statistics exist regarding the relationship of poverty to morbidity and
mortality.
e. The morbidity and mortality rates of impoverished people are similar to those of
the middle class.
ANS: B
Poorly educated people and people in poverty die at higher rates than those who are
advantaged; the same is true for morbidity.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
5. In terms of cultural communication differences, Americans are more likely to _____ than
other groups of patients.
a. emphasize attitudes and feelings
b. maintain eye contact
c. come quickly to the point
d. use silence comfortably
e. speak more softly than other cultures
ANS: C
In the United States, individuals are very direct in conversation and come to the point quickly.
They also tend to talk more loudly and to worry less about being overheard.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
6. Which TXeVWion haV Whe moVW poWenWial foU e[ploUing a paWienW¶V cXlWXUal beliefV UelaWed Wo a
health problem?
a. ³HoZ ofWen do \oX haYe a medical e[aminaWion?´
b. ³WhaW aUe \oXU age, Uace, and edXcaWional leYel?´
c. ³WhaW W\peV of V\mpWomV haYe \oX been haYing?´
d. ³Wh\ do \oX Whink \oX aUe haYing WheVe V\mpWomV?´
e. ³Do \oX Wake heUbal UemedieV?´
ANS: D
This open-ended question avoids stereotyping, is sensitive and respectful toward the
individual, and allows for cultural data to be exchanged.
TOP: Discipline: Behavioral Science MSC: Organ System: General
[Show More]