*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 661 Week 8 – Chronic Men’s Health Problems Questions and Answers (2020) (All)
NR 661 Week 8 – Chronic Men’s Health Problems Questions and Answers (2020)
Document Content and Description Below
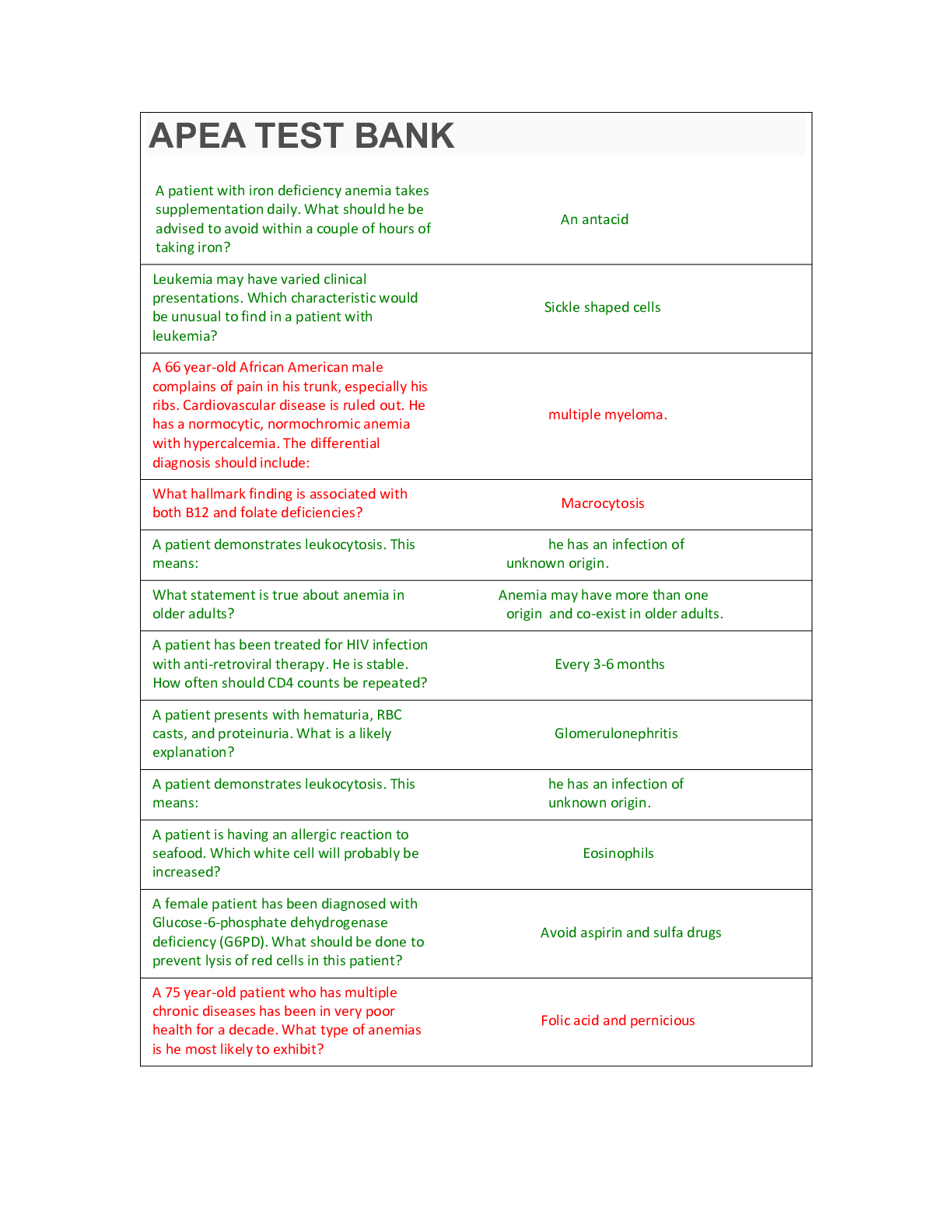
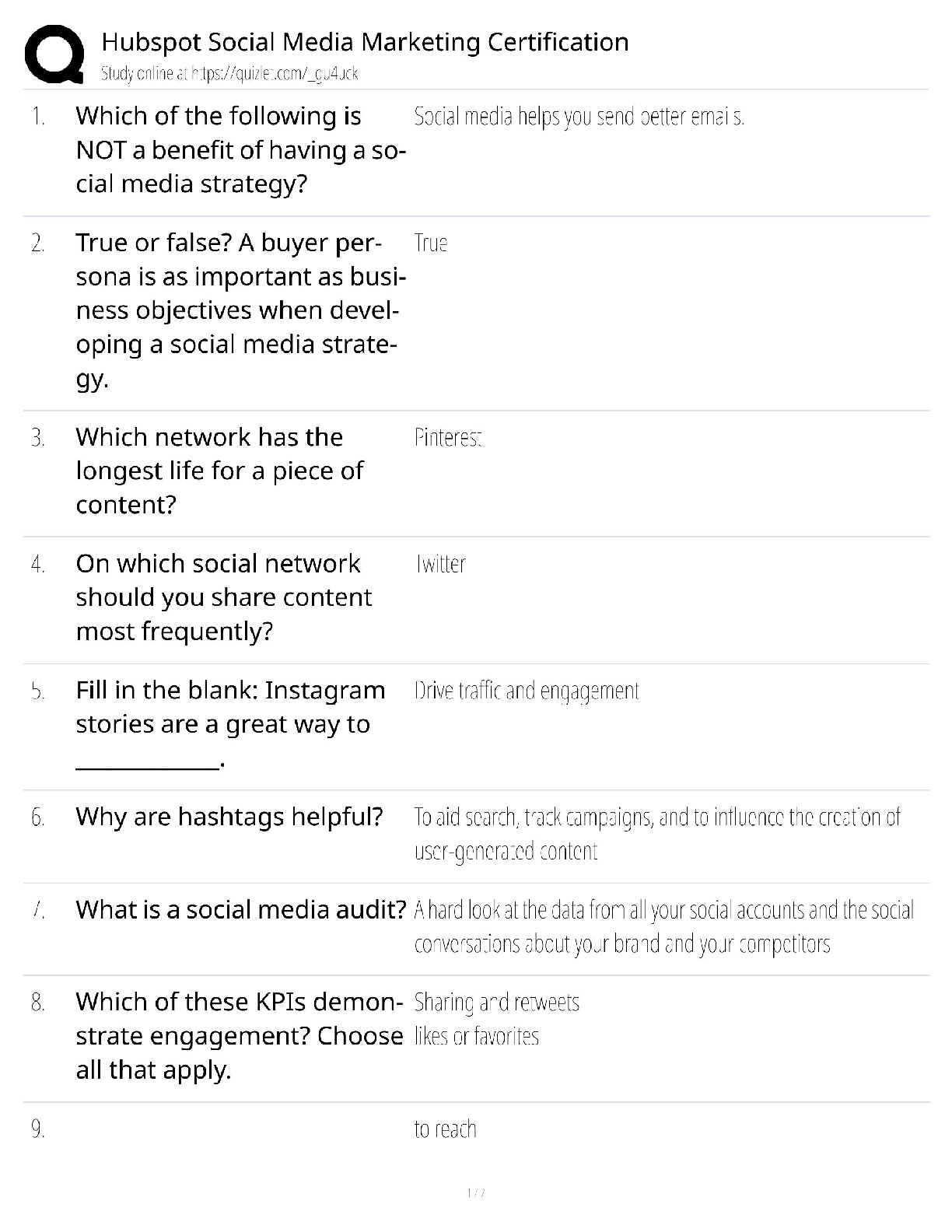
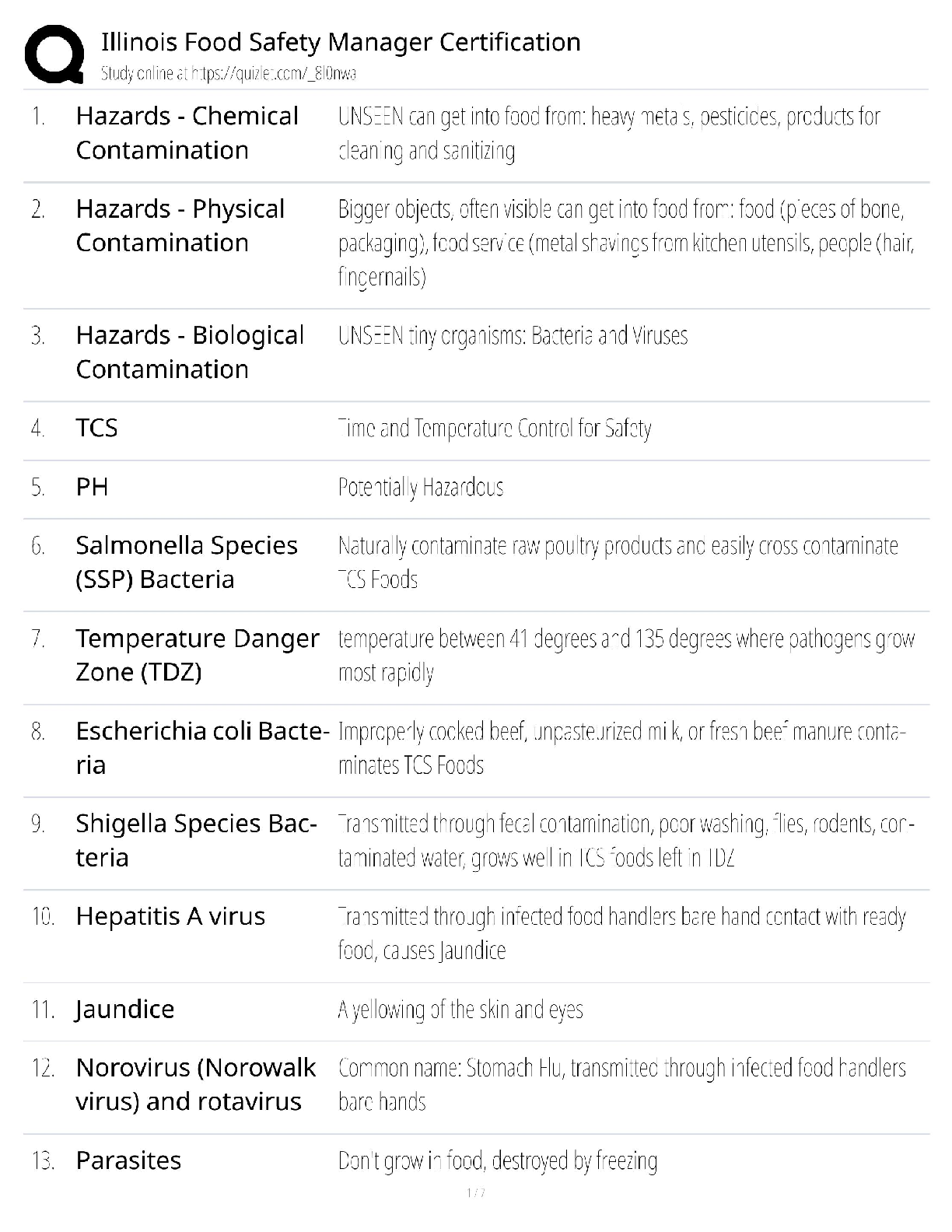
Week 8 – Chronic Men’s Health Problems Appropriate screening tests for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) include: Prostate-specific antigen testing. Urinalysis. Renal function testing. Th ... ere are no screening tests for BPH. You have just diagnosed your patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia. He has an AUA Symptom Index score of 18. You discuss starting pharmacotherapy with your patient and he states that he has heard that saw palmetto is a safe and effective wonder-drug from his herbalist friend and so he wants to treat his symptoms with saw palmetto. Your evidence-based therapeutic response would be: Encourage the patient to follow his herbalist friend’s recommendations because many phytotherapeutic agents have been proven to be effective in reducing symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Discuss with the patient that although many phytotherapeutic agents such as saw palmetto, African prune tree extract, and rye pollen are on the market, reliable research to date has not demonstrated any of them to be effective in relieving the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Advise the patient that phytotherapeutics and dietary supplements should never be considered when addressing a real medical problem. Give the patient a prescription for doxazosin 1mg by mouth every day at bedtime and tell him to “just take the medication.” A 70-year-old male reports urinary hesitancy, post-void dribbling, and a diminished urine stream. A digital rectal exam reveals an enlarged prostate gland that feels rubbery and smooth. Which tests will the primary care provider order based on these findings? Bladder scan for post-void residual PSA and bladder imaging Urinalysis and serum creatinine Urine culture and CBC with differential With respect to the prevalence and incidence of benign prostatic hyperplasia, which of the following statements is true? BPH is very uncommon though it is easy to predict who will develop the problem. BPH is very common and it is difficult to predict who will develop the problem. BPH is very uncommon and it is difficult to predict who will develop the problem. BPH is very common though it is easy to predict who will develop the problem. Which of the following statements is not true? Benign prostatic hyperplasia is generally considered to be a progressive disease. Benign prostatic hyperplasia always requires medications or surgery as treatment. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is considered to be the most common benign tumor in men. Not all men who have histologic benign prostatic hyperplasia will have symptoms. 1A patient is diagnosed with prostate cancer and diagnostic testing reveals disease that has gone past the prostatic capsule without evidence of metastasis. The patient does not wish to undergo treatment. What will the provider tell this patient? Chemotherapy is indicated to provide cure for this cancer. Monitoring PSA with regular DSE is an acceptable option. Palliative radiation therapy is necessary to improve quality of life. This level of disease requires intervention with hormonal therapy. An older male patient has a screening PSA which is 12 ng/mL. What does this value indicate? A normal result Benign prostatic hypertrophy Early prostate cancer Prostate cancer Your 50-year-old male patient comes to the clinic with a complaint of hesitancy during voiding. After completing an appropriate history and physical, you diagnose him with benign prostatic hyperplasia. His American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index Score is less than seven. Your initial treatment plan should include: Starting the patient on a low initial dose of an α-blocker Referring the patient to urology for consideration of a transurethral resection of the prostate Watchful waiting. Starting the patient on a 5α-reductase inhibitor. Goals of clinical management of benign prostate hyperplasia include: Choosing a cost-effective approach for diagnosing BPH Choosing a treatment plan that maximizes client adherence Selecting a treatment plan that returns the client to a symptom-free state in a safe and effective manner All of the above An older male patient reports urinary frequency, back pain, and nocturia. A dipstick urinalysis reveals hematuria. What will the provider do next to evaluate this condition? Order a PSA and perform a digital rectal exam Refer for a biopsy Refer the patient to a urologist Schedule a transurethral ultrasound More recent studies have indicated that ___________ and _____________ increase the risk of BPH and BPH symptom progression. Diabetes and obesity Your 60-year-old male patient has just been diagnosed by you with benign prostatic hyperplasia. He states he wants a transurethral resection of the prostate, because that’s what his brother had “and it took care of the problem right away.” You provide him with appropriate education regarding his treatment options, but he continues to insist on invasive treatment. It would be most appropriate to: Refer the patient to urology services for a consult 2Per the warnings of the Food and Drug Administration, it is important to insure that your patient’s ophthalmologist is aware that your patient is taking an α1–blocker because the medication puts the patient at risk for: Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome There is a clear correlation between the development of BPH and getting prostatic cancer. False The size of the prostate, as determined during the digital rectal exam, can be expected to correlate with the severity of the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. False A male patient reports nocturia and daytime urinary frequency and urgency without changes in the force of the urine stream. What is the likely cause of this? Bladder outlet obstruction Lower urinary tract symptoms Prostate cancer Urinary tract infection A 70-year-old male reports urinary hesitancy, post-void dribbling, and a diminished urine stream. A digital rectal exam reveals an enlarged prostate gland that feels rubbery and smooth. Which tests will the primary care provider order based on these findings? Bladder scan for post-void residual PSA and bladder imaging Urinalysis and serum creatinine Urine culture and CBC with differential A patient has been taking terazosin daily at bedtime to treat BPH and reports persistent daytime dizziness. What will the provider do? Prescribe finasteride instead of terazosin Recommend taking the medication in the morning Suggest using herbal preparations Switch the prescription to doxazosin 3You have just diagnosed your patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia. He has an AUA Symptom Index score of 18. You discuss starting pharmacotherapy with your patient and he states that he has heard that saw palmetto is a safe and effective wonder-drug from his herbalist friend and so he wants to treat his symptoms with saw palmetto. Your evidence-based therapeutic response would be: Discuss with the patient that although many phytotherapeutic agents such as saw palmetto, African prune tree extract, and rye pollen are on the market, reliable research to date has not demonstrated any of them to be effective in relieving the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Advise the patient that phytotherapeutics and dietary supplements should never be considered when addressing a real medical problem. Encourage the patient to follow his herbalist friend’s recommendations because many phytotherapeutic agents have been proven to be effective in reducing symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Give the patient a prescription for doxazosin 1mg by mouth every day at bedtime and tell him to “just take the medication.” Your 50-year-old male patient comes to the clinic with a complaint of hesitancy during voiding. After completing an appropriate history and physical, you diagnose him with benign prostatic hyperplasia. His American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index Score is less than seven. Your initial treatment plan should include: Watchful waiting. Starting the patient on a 5α-reductase inhibitor. Starting the patient on a low initial dose of an α-blocker Referring the patient to urology for consideration of a transurethral resection of the prostate A 70-year-old male reports urinary hesitancy, post-void dribbling, and a diminished urine stream. A digital rectal exam reveals an enlarged prostate gland that feels rubbery and smooth. Which tests will the primary care provider order based on these findings? Urine culture and CBC with differential PSA and bladder imaging Urinalysis and serum creatinine Bladder scan for post-void residual A patient has been taking terazosin daily at bedtime to treat BPH and reports persistent daytime dizziness. What will the provider do? Recommend taking the medication in the morning Switch the prescription to doxazosin Suggest using herbal preparations Prescribe finasteride instead of terazosin A male patient reports nocturia and daytime urinary frequency and urgency without changes in the force of the urine stream. What is the likely cause of this? Urinary tract infection 4Bladder outlet obstruction Prostate cancer Lower urinary tract symptoms A patient has been taking terazosin daily at bedtime to treat BPH and reports persistent daytime dizziness. What will the provider do? Switch the prescription to doxazosin Suggest using herbal preparations Prescribe finasteride instead of terazosin Recommend taking the medication in the morning An older male patient reports urinary frequency, back pain, and nocturia. A dipstick urinalysis reveals hematuria. What will the provider do next to evaluate this condition? Refer for a biopsy Refer the patient to a urologist Order a PSA and perform a digital rectal exam Schedule a transurethral ultrasound A patient is diagnosed with prostate cancer and diagnostic testing reveals disease that has gone past the prostatic capsule without evidence of metastasis. The patient does not wish to undergo treatment. What will the provider tell this patient? Chemotherapy is indicated to provide cure for this cancer. This level of disease requires intervention with hormonal therapy. Monitoring PSA with regular DSE is an acceptable option. Palliative radiation therapy is necessary to improve quality of life. Which of the following statements is not true? Not all men who have histologic benign prostatic hyperplasia will have symptoms. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is considered to be the most common benign tumor in men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is generally considered to be a progressive disease. Benign prostatic hyperplasia always requires medications or surgery as treatment. Your 50-year-old male patient comes to the clinic with a complaint of hesitancy during voiding. After completing an appropriate history and physical, you diagnose him with benign prostatic hyperplasia. His American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index Score is less than seven. Your initial treatment plan should include: Starting the patient on a low initial dose of an α-blocker Referring the patient to urology for consideration of a transurethral resection of the prostate Starting the patient on a 5α-reductase inhibitor. Watchful waiting. 5An older male patient reports urinary frequency, back pain, and nocturia. A dipstick urinalysis reveals hematuria. What will the provider do next to evaluate this condition? Order a PSA and perform a digital rectal exam The size of the prostate, as determined during the digital rectal exam, can be expected to correlate with the severity of the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. False Appropriate screening tests for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) include: Renal function testing. There are no screening tests for BPH. Prostate-specific antigen testing. Urinalysis. A 70-year-old male reports urinary hesitancy, post-void dribbling, and a diminished urine stream. A digital rectal exam reveals an enlarged prostate gland that feels rubbery and smooth. Which tests will the primary care provider order based on these findings? Urine culture and CBC with differential Urinalysis and serum creatinine PSA and bladder imaging Bladder scan for post-void residual An older male patient reports urinary frequency, back pain, and nocturia. A dipstick urinalysis reveals hematuria. What will the provider do next to evaluate this condition? Schedule a transurethral ultrasound Refer the patient to a urologist Refer for a biopsy Order a PSA and perform a digital rectal exam A male patient reports nocturia and daytime urinary frequency and urgency without changes in the force of the urine stream. What is the likely cause of this? Lower urinary tract symptoms Bladder outlet obstruction Urinary tract infection Prostate cancer Your 50-year-old male patient comes to the clinic with a complaint of hesitancy during voiding. After completing an appropriate history and physical, you diagnose him with benign prostatic hyperplasia. His American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index Score is less than seven. Your initial treatment plan should include: Referring the patient to urology for consideration of a transurethral resection of the prostate Starting the patient on a low initial dose of an α-blocker Watchful waiting. Starting the patient on a 5α-reductase inhibitor. 6Per the warnings of the Food and Drug Administration, it is important to insure that your patient’s ophthalmologist is aware that your patient is taking an α1–blocker because the medication puts the patient at risk for: Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome Retinal detachment Cataracts Macular degeneration You have just diagnosed your patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia. He has an AUA Symptom Index score of 18. You discuss starting pharmacotherapy with your patient and he states that he has heard that saw palmetto is a safe and effective wonder-drug from his herbalist friend and so he wants to treat his symptoms with saw palmetto. Your evidence-based therapeutic response would be: Give the patient a prescription for doxazosin 1mg by mouth every day at bedtime and tell him to “just take the medication.” Encourage the patient to follow his herbalist friend’s recommendations because many phytotherapeutic agents have been proven to be effective in reducing symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Discuss with the patient that although many phytotherapeutic agents such as saw palmetto, African prune tree extract, and rye pollen are on the market, reliable research to date has not demonstrated any of them to be effective in relieving the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Advise the patient that phytotherapeutics and dietary supplements should never be considered when addressing a real medical problem. Goals of clinical management of benign prostate hyperplasia include: All of the above Choosing a treatment plan that maximizes client adherence Choosing a cost-effective approach for diagnosing BPH Selecting a treatment plan that returns the client to a symptom-free state in a safe and effective manner Appropriate screening tests for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) include: Urinalysis. There are no screening tests for BPH. Renal function testing. Prostate-specific antigen testing. A 70-year-old male reports urinary hesitancy, post-void dribbling, and a diminished urine stream. A digital rectal exam reveals an enlarged prostate gland that feels rubbery and smooth. Which tests will the primary care provider order based on these findings? Bladder scan for post-void residual PSA and bladder imaging 7Urinalysis and serum creatinine Urine culture and CBC with differential 8 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 16, 2020
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 16, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
87