Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > AP BIO_ AP Biology_Winter Break MCQ HOMEWORK_ Assignment. Contains 200 of the Most Commonly Tested (All)
AP BIO_ AP Biology_Winter Break MCQ HOMEWORK_ Assignment. Contains 200 of the Most Commonly Tested MCQ and Answer key.
Document Content and Description Below
A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 1 Winter Break MCQ HOMEWORK 1 | P a g e Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select th... e one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet. 1. In mammals, an increase in the concentration of sodium in the blood triggers the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the pituitary gland. As the concentration of sodium in the blood returns to previous levels, the release of ADH from the pituitary gland is reduced. Based on the information presented, which of the following describes the most likely role of ADH in maintaining blood osmolarity?The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes the substrate that are similar in shape and structure to glucose. (A) ADH promotes an increase in the movement of sodium into the bloodstream. (B) ADH promotes an increase in the movement of water in the bloodstream. (C) ADH promotes an increase in the excretion of water from the body. (D) ADH promotes an increase in the secretion of additional ADH from the pituitary gland. 2. A cell is treated with a drug that prevents the formation of new lysosomes. The cell continues to transcribe the genes that code for the hydrolytic enzymes that are normally found in lysosomes and continues to translate the mRNAs for those proteins on membranebound ribosomes. The hydrolytic enzymes are most likely to accumulate in which of the following cellular structures? (A) Nucleus (B) Mitochondrion (C) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (D) Golgi complex. 3. The p53 protein regulates a cellular response to DNA damage. Based on the diagram above, which of the following best describes the role of p53 in the response to DNA damage? (A) Phosphorylated p53 binds to DNA and repairs the damage. (B) Phosphorylated p53 stimulates transcription of p21, and the resulting p21 protein suppresses cell division until the DNA damage is repaired. (C) Phosphorylated p53 binds cyclin-Cdk complexes, and the resulting protein complex repairs the DNA damage. (D) Phosphorylated p53 activates p21 proteins and the p21 proteins in turn repair the DNA damage.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 2 2 | P a g e 4. The diagram above illustrates feedback control as exerted by the hormone thyroxine. Following surgical removal of the thyroid gland, the level of TSH in the blood will increase. Which of the following best explains this increase? (A) Residual blood thyroxine, from prior to thyroid gland removal, will bind ot cells in the anterior pituitary, signaling more TSH secretion. (B) Thyroxine will remain bound to thyroxine receptors on various body cells, and these body cells will secrete additional hormones that stimulate the anterior pituitary to secrete TSH. (C) Thyroxine that was stored in the anterior pituitary prior to thyroid gland removal will signal more TSH secretion (D) A decrease in thyroxine levels means a loss of inhibition to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, leading to increased TSH secretion.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 3 3 | P a g e 5. The figure above shows a model of a ligand precursor being cleaved to produce an active ligand that binds to a specific receptor. Which of the following is most likely to reduce the binding of the active ligand to its receptor? (A) A change in the cytoskeletal attachment of transmembrane proteins (B) The presence of a large amount of the precursor form of the ligand (C) An increase in the ratio of the number of unsaturated to the number of saturated fatty acid tails of the membrane lipids (D) A mutation in the receptor gene that causes a substitution of a charged amino acid for a nonpolar amino acid in the ligand binding site of the receptor 6. The illustration above depicts a neuromuscular junction of a patient with an autoimmune disorder. Acetylcholine is a stimulatory neurotransmitter. Which of the following would be the most likely result of the continued presence of the antibody? (A) An increase in action potentials in the motor neuron and constant nerve pain (B) A decrease in action potentials in the muscle, causing muscle weakness and fatigue. (C) A decrease in the opening of sodium-gated channels in the muscle, causing less sodium to be released from the muscle (D) An increase in the opening of sodium-gated channels in the motor neuron because of the accumulation of acetylcholine in the junctionA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 4 4 | P a g e 7. Paramecia are unicellular protists that have contractile vacuoles to remove excess intracellular water. In an experimental investigation, paramecia were placed in salt solutions of increasing osmolarity. The rate at which the contractile vacuole contracted to pump out excess water was determined and plotted against osmolarity of the solutions, as shown in the graph. Which of the following is the correct explanation for the data? (A) At higher osmolarity, lower rates of contraction are required because more salt diffuses into the paramecia. (B) The contraction rate increases as the osmolarity decreases because the amount of water entering the paramecia by osmosis increases. (C) The contractile vacuole is less efficient in solutions of high osmolarity because of the reduced amount of ATP produced from cellular respiration. (D) In an isosmotic salt solution, there is no diffusion of water into or out of the paramecia, so the contraction rate is zero. 8. A human kidney filters about 200 liters of blood each day. Approximately two liters of liquid and nutrient waste are excreted as urine. The remaining fluid and dissolved substances are reabsorbed and continue to circulate throughout the body. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted in response to reduced plasma volume. ADH targets the collecting ducts in the kidney, stimulating the insertion of aquaporins into their plasma membranes and an increased reabsorption of water. If ADH secretion is inhibited, which of the following would initially result? (A) The number of aquaporins would increase in response to the inhibition of ADH. (B) The person would decrease oral water intake to compensate for the inhibition of ADH. (C) Blood filtration would increase to compensate for the lack of aquaporins. (D) The person would produce greater amounts of dilute urine. 9. Researchers claimed that a particular organelle originated from a free-living prokaryotic cell that was engulfed by a larger cell, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. A model showing a cell engulfing a smaller cell. Which of the following provides evidence to best support the researchers’ claim? (A) The organelle has a phospholipid membrane (B) The organelle has protein in the membrane (C) The organelle has a double membrane. (D) The organelle as an internal environments that is similar to the cytosol of the larger cell.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 5 5 | P a g e Answer question 10 and 11 based on the excerpt below. Dialysis tubing is permeable to water molecules but not to sucrose. Four dialysis tubes are half filled with 5 percent, 10 percent, 20 percent, and 40 percent sucrose solutions, respectively, and two dialysis tubes are half filled with distilled water. The dialysis tubes are all sealed at both ends, and the initial masses are determined. Five dialysis tubes are placed into beakers containing distilled water, and the sixth dialysis tube, containing distilled water, is placed into a 40 percent sucrose solution. The masses of the dialysis tubes are recorded at 30-minute intervals for 90 minutes, as shown in the table below. 10. A net movement of water into the beaker occurs in which of the following dialysis tubes? (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 11. The contents of which dialysis tube are initially isotonic to the distilled water in the beaker? (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 6 6 | P a g e 12. A researcher examining a root tip observes a plant cell with condensed sister chromatids, kinetochores with attached microtubules, and individual chromosomes that are aligned at the equatorial plate of the cell. Which of the following best describes what the next process will be in the cell? (A) Homologous chromosomes (each with two sister chromatids) will move toward opposite poles of the cell. (B) Paired chromatids will separate, and the new daughter chromosomes will move toward opposite poles of the cell. (C) The nuclear envelope will break down, and the spindle will begin to form. (D) The chromatin will decondense, and the daughter cell will enter interphase. 13. A sample of human blood was placed in a test tube containing a physiological saline solution (0.9% sodium chloride). This type of solution is often used intravenously to quickly rehydrate patients. A drop of the blood from the test tube was placed on a slide and red blood cells (RBCs) were observed under a microscope. Three possible outcomes are diagrammed below. Which of the following best predicts which diagrammed microscope view the laboratory worker would see and best explains why? (A) View 1 because RBC membranes are freely permeable to water. (B) View 2 because the RBCs use energy to allow sodium entry and to pump water out. (C) View 2 because the rate of water movement into the RBCs equals the rate of water movement out of the cells. (D) View 3 because the sodium-potassium pumps in the RBC membranes use energy to keep the sodium out but allow water to freely flow into the cells. 14. Which of the following questions will best direct an investigation of the mechanism of ATP synthase? (A) What is the source of the inorganic phosphate that is used to generate ATP from ADP? (B) Is the phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase dependent on the formation of a proton gradient? (C) Can ATP synthase use the energy released by phosphorylation of ADP to pump protons against a concentration gradient? (D) Can oxidative phosphorylation be uncoupled from the electron transport chain?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 7 7 | P a g e 15. According to the chemiosmotic theory (chemiosmotic coupling), the energy required to move protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space against a concentration gradient comes most directly from (A) Photons of red or blue light (B) The hydrolysis of ATP (C) The breakdown of high energy fatty acids in the mitochondrial matrix. (D) Electrons flowing along the electron transport chain. Answer question 16 and 17 based on the excerpt below. An experiment to measure the rate of respiration in crickets and mice at 10oC and 25oC was performed using a respirometer, an apparatus that measures changes in gas volume. Respiration was measured in mL of O2 consumed per gram of organism over several five-minute trials and the following data were obtained. 16. According to the data, the crickets at 25oC have greater oxygen consumption per gram of tissue than do the crickets at 10oC. This trend in oxygen consumption is the opposite of that in the mice. The difference in trends in oxygen consumption among crickets and mice is due to their (A) Relative size (B) Mode of nutrition (C) Mode of internal temperature regulation (D) Mode of ATP production. 17. According to the data, the mice at 10oC demonstrated greater oxygen consumption per gram of tissue than did the mice at 25oC. This is most likely explained by which of the following statements? (A) The mice at 10oC had a higher rate of ATP production than the mice at 25oC. (B) The mice at 10oC had a lower metabolic rate than the mice at 25oC. (C) The mice at 25oC weighed less than the mice at 10oC. (D) The mice at 25oC were more active than the mice at 10oC.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 8 8 | P a g e A student placed 20 tobacco seeds of the same species on moist paper towels in each of two petri dishes. Dish A was wrapped completely in an opaque cover to exclude all light. Dish B was not wrapped. The dishes were placed equidistant from a light source set to a cycle of 14 hours of light and 10 hours of dark. All other conditions were the same for both dishes. The dishes were examined after 7 days, and the opaque cover was permanently removed from dish A. Both dishes were returned to the light and examined again at 14 days. The following data were obtained. 18. According to the results of the experiment, germination of tobacco seeds during the first week is (A) Increased by exposure to light (B) Unaffected by light intensity (C) Prevented by paper towels (D) Accelerated in green-leaved seedlings. 19. A researcher proposes a model of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in which a reactant is converted to a product. The model is based on the idea that the reactant passes through a transition state within the enzyme-substrate complex before the reactant is converted to the product. Which of the following statements best helps explain how the enzyme speeds up the reaction? (A) The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes the reactant, which decreases the free-energy change of the reaction. (B) The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes the transition state, which decreases the activation energy of the reaction. (C) The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes the product, which increases the amount of energy released by the reaction. (D) The enzyme’s active site binds to and stabilizes both the reactant and the product at the same time, which increases the reaction’s equilibrium constant.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 9 9 | P a g e 20. The illustration shows the active transport of hydrogen ions through a membrane protein. Which of the following best predicts the effect of not having available to supply energy to this process? (A) H+ ions will stop moving through the protein. (B) H+ ions will move in the other direction through the protein. (C) H+ ions will continue to move through the protein in the original direction but at a slower rate. (D) H+ ions will begin to move through the phospholipid portion of the membrane in the original direction. 21. Figure 1. Shows a model of how a channel protein influences the movement of a particle across a cell’s plasma membrane. Figure 1. A section of a cell’s plasma membrane, showing a channel protein and a concentration gradient across the membrane. An investigator wants to understand whether a newly found membrane protein is involved in membrane transport of a certain particle. Which investigation will help determine whether the new membrane protein is a channel protein involved in membrane transport? (A) Add small nonpolar molecules to the extracellular space and measure the direction of particle movement of the molecules. (B) Measure the rate of extracellular fluid movement into the intracellular space. (C) Add more of the proteins to the plasma membrane and measure the rate of the particle movement. (D) Remove ATP from the intracellular space and measure the rate of the particle movement into the intracellular space. 22. The CFTR protein is made up of 1480 amino acids linked together in a chain. Some humans produce a version of the CFTR protein in which phenylalanine (an amino acid) has been deleted from position 508 of the amino acid chain. Which of the following best predicts how the amino acid deletion will affect the structure of the protein? (A) It will have no observable effect on the structure of the CFTR protein. (B) It will affect the primary structure of the CFTR protein only. (C) It will affect the secondary and tertiary structures of the CFTR protein, but the primary structure will not be affected. (D) It will affect the primary, secondary, and tertiary structures of the CFTR protein.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 10 10 | P a g e 23. The relative amount of DNA in a cell at various stages of the cell cycle is shown in Figure 1 . Figure 1. Amount of DNA per cell during different stages of the cell cycle, relative to the beginning of the G1 stage. Which of the following best describes how the amount of DNA in the cell changes during M phase? (A) The amount of DNA doubles as the DNA is replicated. (B) The amount of DNA slightly increases as a result of new organelle synthesis. (C) The amount of DNA does not change while the cell grows. (D) The amount of DNA is halved as the cell divides into two daughter cells. 24. Amylase is a protein that catalyzes the conversion of starch to simple sugars. Amylase activity in an aqueous solution can be measured by using iodine as a starch indicator. A solution containing iodine and starch will have a dark-blue color, whereas a solution containing iodine but no starch will have a light-brown color. The color change of an iodine solution from dark blue to light brown can be used to measure the rate at which starch is converted to simple sugars. A student designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental pH on amylase function. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1. Table 1. An experiment for investigating the effect of on amylase function Which of the following statements best justifies the inclusion of test tube V as a control in the experiment? (A) It will provide a measurement of amylase activity at an acidic pH. (B) It will provide a measurement of amylase activity at a basic pH. (C) It will show the color change that occurs in the absence of enzyme activity. (D) It will show the color change that occurs in the absence of the amylase protein.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 11 11 | P a g e Answer question 25 and 26 based on the excerpt below. A student studied the effects of light intensity on oxygen production in green algae. The algae were suspended in water inside a sealed glass jar, and the jar was placed into a constant-temperature, lightproof box containing a light source. A probe was inserted into the jar to record the concentration of oxygen. The probe was connected to a recording device. The setup is shown below. The student decreased the intensity of the light hourly and recorded the corresponding changes in oxygen concentration. The graph below shows the results from the recording device. 25. An increase in the rate of oxygen production by algae would be accompanied by a comparable increase in the rate of production of which of the following substances? (A) C6H12O6 (B) CO2 (C) CH4 (D) NH3 (E) H2O 26. The rate of oxygen production equaled the rate of oxygen consumption during which of the following time periods? (A) G to H (B) H to I (C) I to J (D) J to K (E) G to KA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 12 12 | P a g e 27. An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions. (A) Cytochrome (B) FADH2 (C) NAD+ (D) NADP+ (E) Oxygen (O2) 28. Coenzyme that transfers electrons from the Krebs cycle to the mitochondrial electron-transport chain at a lower energy level than that of electrons entering at the beginning of the chain (A) Cytochrome (B) FADH2 (C) NAD+ (D) NADP+ (E) Oxygen (O2) 29. Anabaena is a simple multicellular photosynthetic cyanobacterium. In the absence of fixed nitrogen, certain newly developing cells along a filament express genes that code for nitrogen-fixing enzymes and become nonphotosynthetic heterocysts. The specialization is advantageous because some nitrogen-fixing enzymes function best in the absence of oxygen. Heterocysts do not carry out photosynthesis but instead provide adjacent cells with fixed nitrogen, in exchange receiving fixed carbon and reduced energy carriers. As shown in the diagram above, when there is low fixed nitrogen in the environment, an increase in the concentration of free calcium ions and 2-oxyglutarate stimulates the expression of genes that produce two transcription factors (NtcA and HetR) that promote the expression of genes responsible for heterocyst development. HetR also causes production of a signal, PatS, that prevents adjacent cells from developing as heterocysts. Based on your understanding of the ways in which signal transmission mediates cell function, which of the following predictions is most consistent with the information given above? (A) In an environment with low fixed nitrogen, treating the Anabaena cells with a calcium-binding compound should prevent heterocyst differentiation. (B) A strain that overexpresses the patS gene should develop many more heterocysts in a low fixed nitrogen environment. (C) In an environment with abundant fixed nitrogen, free calcium levels should be high in all cells so that no heterocysts develop. (D) In environments with abundant fixed nitrogen, loss of the hetR gene should induce heterocyst development.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 13 13 | P a g e 30. Which statement best describes the effect on water transport across the cell membrane if the aquaporin in the figure ceases to function? (A) Water molecules will no longer be able to move across the cell membrane. (B) Water molecules will still be able to move across the cell membrane but at a slower rate. (C) Water molecules will only be able to enter the cell by active transport. (D) Water molecules will move across the cell membrane at a faster rate without the aquaporin regulating their flow. 31. Aquaporins are channel proteins that facilitate the transport of water across the cell membrane. One group of researchers hypothesizes that without functional aquaporins, no water will be able to enter the cell. A different group proposes an alternative hypothesis, stating that even with nonfunctional aquaporins, a small amount of water will still cross the cell membrane. An experiment is set up in which plant cells with mutated (nonfunctional) aquaporins and plant cells with normally functioning aquaporins are both placed in distilled water. Which of the following data would support the alternative hypothesis? (A) Cells with functional aquaporins exhibit low turgor pressure and are hypertonic. (B) Cells with functional aquaporins exhibit high turgor pressure and are hypotonic. (C) Cells with mutated aquaporins exhibit an absence of turgor pressure and are completely plasmolyzed. (D) Cells with mutated aquaporins exhibit moderate turgor pressure and are hypertonic. 32. A researcher claims that increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels cause increased growth rates in plants. Which of the following statements best supports the researcher’s claim? (A) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is produced by the burning of fossil fuels, which are formed from the remains of living organisms such as plants. (B) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is a byproduct of cellular respiration, which is a metabolic process that occurs in plants and other living organisms. (C) Atmospheric carbon dioxide typically enters plant leaves through stomata, which plants rely on for regulating gas exchange with the atmosphere. (D) Atmospheric carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis, which plants rely on for producing sugars and other organic compounds 33. A researcher claims that the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is essential to cellular function. Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher’s claim? (A) ADP is a small molecule that some cells release into their environment as a way of communicating with other cells. (B) ATP hydrolysis is an energy-releasing reaction that is often coupled with reactions that require an input of energy. (C) Inorganic phosphate is a substance that cells typically acquire from their environment. (D) ATP synthase is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ADP and Pi to ATP.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 14 14 | P a g e 34. ATP serves as a common energy source for organism because (A) It I s the smallest energy molecule. (B) It stores the least energy of any energy source (C) Its energy can be easily transferred to cellular work (D) It is extremely stable and can be stored in the cell for long period of time (E) It traces of ii have been found in fossils of ancient organisms dating back to the beginning of life on Earth. 35. A researcher claims that different metabolic pathways allow bacteria to use different molecules as sources of matter and energy. Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher’s claim by providing a relevant example? (A) Rhizobia bacteria form close associations with the roots of bean plants. (B) E. coli bacteria reproduce in liquid media containing either glucose or galactose. (C) The antibiotic rifampicin inhibits the growth of some bacterial strains but not of others. (D) Some viruses that infect bacteria reproduce by either the lysogenic cycle or the lytic cycle. 36. A researcher claims that some bacteria contain factors that influence the function of a particular enzyme but other bacteria do not. To test the claim experimentally, the researcher will grow two different bacterial strains in separate liquid cultures and isolate the contents of the cells in each culture. The researcher will add different combinations of cellular contents, substrate, and enzyme to test tubes containing a buffer solution adjusted to the optimal pH of the enzyme and then measure the rate of product formation. The design of the researcher’s experiment is presented in Table 1. Table 1. An experiment for investigating the influence of bacterial factors on enzyme function. Which of the following statements best justifies the inclusion of test tubes 3 and 7 in the experiment? (A) They will show whether the isolated cellular contents have enzymatic activity. (B) They will show whether environmental pH affects the function of the enzyme. (C) They will show the rate of product formation in the absence of bacterial factors. (D) They will show the rate of product formation in the absence of the substrate 37. Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria. In an experiment, bacteriophages were labeled with either radioactive phosphorus or radioactive sulfur. The labeled bacteriophages were incubated with bacteria for a brief amount of time and then removed. The infected bacteria cells were found to contain significant amounts of radioactive phosphorus but not radioactive sulfur. Based on the results of the experiment, which of the following types of molecules did the bacteriophages most likely inject into the bacteria cells? (A) Simple carbohydrate (B) Amino acid (C) DNA (D) PolypeptideA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 15 15 | P a g e Answer question 38 and 39 based on the excerpt below. A student formulated a hypothesis that water-soluble pollutants damage living organisms by increasing the permeability of cellular membranes. To test the hypothesis, the student investigated the effect of isopropanol and acetone on beet root cells. The vacuoles of beet root cells contain large amounts of betacyanin, a watersoluble pigment that is released into the extracellular environment as a result of increased membrane permeability. The student prepared identical samples of beet root tissue and incubated each sample for 15 minutes in the specific solution for that group. At the end of the incubation period, the student measured the absorbance of 460 nm light for each sample. A greater concentration of betacyanin in the solution surrounding the beet root cells results in a greater absorbance of 460 nm light. The results of the experiment are shown in the table above. 38. Based on the data from the investigation, which of the following is the best scientific question about organisms living in water that is polluted with organic solvents? (A) Do organisms without pigments have a selective advantage in polluted environments? (B) Will organisms living in polluted environments exhibit detrimental effects from an increased permeability of their cellular membranes? (C) Will organic solvents from the environment become incorporated into the cell membranes of organisms living in polluted environments? (D) Should governments place more stringent restrictions on the release of organic solvents into aquatic ecosystems?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 16 16 | P a g e 39. The illustration above is a model of a typical beet root cell. Based on the experimental results, which of the following best represents the effect of acetone on the permeability of cellular membranes?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 17 17 | P a g e Answer question 40 based on the excerpt below. In response to elevated blood glucose levels, beta (β) cells in the pancreas release insulin, a regulatory hormone. Insulin signals body cells to take up glucose from the blood, which returns blood glucose levels back to normal. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that destroys β-cells, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels. Researchers have proposed that diabetes could be treated by implanting human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) that have been induced to develop into β-cells (hESC-β). To test the proposed treatment, the researchers set up two groups of genetically identical mice and implanted the mice from one group with hESC-β cells. Several weeks after the hESC-β implant, both groups of mice were given a drug (STZ) that selectively destroys the naturally occurring mouse β-cells but does not affect the implanted hESC-β cells. Figure 1 shows a comparison of average blood glucose levels in both groups of mice. Figure 1. Average blood glucose levels in mice after STZ treatment. Error bars indicate standard deviation. In a continuation of the experiment, the researchers removed the hESC-β implant from one of the mice 16 weeks after STZ treatment. Figure 2 shows the blood glucose levels in the mouse over the duration of the experiment. Figure 2. Blood glucose levels for an individual mouse over the duration of the experiment.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 18 18 | P a g e 40. Based on the data, which of the following best represents how the mice with the implanted hESC-β cells use negative feedback to return blood glucose levels to normal if blood glucose levels increase? (A) Decreased insulin secretion by body cells → increased glucose uptake by mouse β-cells → increased insulin secretion by body cells (B) Increased insulin production by mouse β-cells → increased glucose uptake by hESC-β cells → decreased glucose metabolism by body cells (C) Increased insulin secretion by hESC-β cells → increased glucose uptake by body cells → decreased insulin secretion by hESC-β cells (D) Increased metabolism of glucose by hESC-β cells → differentiation of hESC-β cell into body cells → increased glucose production by body cells 41. Diapause is the interruption of an organism’s life cycle in response to environmental cues. The soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is capable of entering adult reproductive diapause (ARD) when food is scarce. In C. elegans, individuals normally become reproductively mature 2 days after hatching and remain fertile for 18 days. They reproduce either by self-fertilization or by mating with another individual. In an investigation, researchers examined the survival and reproductive success without food for 0-30 days. Upon s of C. elegans following different times in ARD. In the first experiment, groups of C. elegans were held in ARD reintroduction of food, average brood sizes (average number of offspring per adult) were determined following either self-fertilization or mating with a well-fed male. The results are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Mean brood sizes ± SEg after different times in ARD. Individual C. elegans were held in ARD and subsequently allowed to reproduce either via self-fertilization (unshaded bars) or by mating with well-fed males (shaded bars). In a second experiment, individuals were held in ARD without food for 0-30 days and monitored for average survival times following reintroduction of food (Figure 2).A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 19 19 | P a g e Figure 2. Mean survival ± SEg following different times in ARD. Individual C. elegans were held in ARD and subsequently given access to food, whereupon their survival times were determined. 41. Based on the experimental results, which of the following is the best evolutionary explanation for the occurrence of ARD in C. elegans ? (A) The ability to enter ARD provides a strong selective advantage because reproduction can occur despite periods of food scarcity. (B) Acquiring the genes for ARD gives individuals a selective advantage because they produce more offspring than do individuals who cannot enter ARD. (C) Individuals who can enter ARD are selected for in the population because they live longer than do individuals who cannot enter ARD. (D) Individuals who can enter ARD have high fitness because they can reproduce even when food is scarce. Answer question 42 based on the excerpt below. Excess intracellular iron is toxic to cells (iron-induced toxicity). Ferritin is an intracellular iron storage protein that binds excess iron. The presence of ferritin can protect cells from iron-induced toxicity. In an experiment to investigate the effects of dietary iron intake on ferritin synthesis, rats were given food containing different amounts of iron. Subsequently, the levels of ferritin protein in the liver were measured. The results are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Effects of dietary iron on ferritin levels in rat liver.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 20 20 | P a g e Based on these and other data, researchers have developed the following model demonstrating how ferritin synthesis is regulated by iron. When iron levels are low, a repressor of translation, iron response protein (IRP), binds to an iron response element (IRE), which is a stem-loop structure near the 5’ end of ferritin mRNA. When iron levels are high, intracellular iron binds to the IRP, and the iron-IRP complex dissociates from the IRE, permitting ribosomes to proceed with the translation of ferritin mRNA. Figure 2 represents the model of the regulation of ferritin mRNA translation by iron. 42. Based on the model of ferritin synthesis presented in Figure 2, which of the following describes the role of feedback on the control of intracellular iron levels? (A) A decrease in iron levels activates the IRP. The IRP in turn activates iron transport proteins in the cell membrane, thereby returning free iron levels to normal. (B) A decrease in iron levels activates synthesis of ferritin protein. Ferritin protein in turn releases bound iron, thereby returning free iron levels to normal. (C) An increase in iron levels activates the IRP. The IRP in turn binds iron, thereby decreasing both free iron levels and ferritin synthesis. (D) An increase in iron levels activates synthesis of ferritin protein. Ferritin protein in turn binds iron, thereby decreasing both free iron levels and ferritin synthesis.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 21 21 | P a g e Answer question 43 and 44 based on the excerpt below. Researchers investigating the regulation of neurotransmitter release from presynaptic neurons proposed a model (Figure 1) in which CDK5, a protein expressed in axon terminals, inhibits the movement of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane. To test their model, the researchers used a modified version of green fluorescent protein (GFP*). In slightly alkaline conditions, GFP* exhibits a bright green fluorescence. In acidic conditions, GFP* exhibits no fluorescence. Using standard techniques, the gene encoding GFP* is easily introduced into living cells. By engineering the expression of GFP* in laboratory-cultured nerve cells, the researchers found that a bright green fluorescence was exhibited only when a presynaptic neuron was given a certain stimulus. 43. Based on the model, which of the following best explains how regulation of neurotransmitter release might increase the range of responses to a stimulus in the nervous system? (A) In the absence of any stimulus, neurons can still release neurotransmitters. (B) Different neurons in the same neural network can release different amounts of neurotransmitter. (C) In the depolarization phase of an action potential, postsynaptic neurons can adjust the amount of neurotransmitter bound to receptors on their surface. (D) In the recovery phase following a stimulus, enzymes can be mobilized to degrade molecules present in the synaptic vesicles. 44. Previous experiments indicate that CDK5 is active only when attached to a protein called p35. Which of the following best predicts how p35 might play a role in regulating neuron function? (A) Elevated intracellular levels of p35 result in increased synaptic activity. (B) Degradation of p35 results in increased synaptic activity. (C) Reabsorption of p35 from the synaptic cleft results in increased synaptic activity. (D) Attachment of p35 to synaptic vesicles results in increased synaptic activity.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 22 22 | P a g e 45. Cancer can result from a variety of different mutational events. Which of the following is LEAST likely to result in the initiation of a cancerous tumor? (A) receptor mutation results in activation of a cell-division pathway in the absence of the appropriate ligand. (B) A mutation results in the loss of the ability to produce a tumor-suppressor protein. (C) A defect in a cell-cycle checkpoint prevents a cell from entering the S phase. (D) At the anaphase checkpoint, separation of chromatids occurs without all centromeres being attached to kinetochore microtubules from both poles. 46. A researcher claims that only a portion of the light energy captured by green plants is available for growth and repair. Which of the following observations best helps justify the researcher’s claim? (A) Light-capturing pigment molecules in green plants absorb red, blue, and violet light but reflect green light. (B) The energy of a photon of light is proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength. (C) As light energy is converted to chemical energy by metabolic processes, some of the energy is lost as heat. (D) Captured energy is stored in the molecular bonds of organic molecules, including simple sugars and starch. 47. The carbohydrates glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula but different structural formulas (C6H12O6), as represented in the figure. Which of the following statements about glucose, galactose, and fructose is most likely true? (A) The carbohydrates have the same properties because they have the same number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. (B) The carbohydrates have the same properties because they each have a single carbon-oxygen double bond. (C) The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different arrangements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. (D) The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different numbers of carbon-carbon bonds. 48. Carbohydrate-synthesizing reactions of photosynthesis directly require (A) Light (B) Products of the light reactions (C) Darkness (D) Oxygen and water (E) Chlorophyll and carbon dioxide.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 23 23 | P a g e 49. Researchers performed an experiment to determine the effect of certain genetic mutations on mitosis in tropical fruit fly embryos. They determined the percentage of cells in each of four phases of mitosis as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Percent of cells in phases of mitosis Which of the following patterns is shown by the data? (A) Mutant 1 cells are more similar to mutant 3 cells than to wild-type cells. (B) In wild-type cells, the percent of cells in anaphase is twice the amount of those in telophase. (C) In mutant 3 cells, more time is spent in prophase/prometaphase than in the later stages of mitosis. (D) The percent of mutant 2 cells in anaphase is higher than that of mutant 1 cells. 50. What is the expected percent change in the DNA content of a typical eukaryotic cell as it progresses through the cell cycle from the start of the G1 phase to the end of the G2 phase? (A) -100% (B) -50% (C) +50% (D) +100% 51. Plant cell walls are composed of cellulose, while fungal cell walls are composed of chitin. A group of scientists hypothesize that this difference means the cell wall has largely different functions in plant cells and fungal cells. Alternatively, another group of scientists hypothesize that despite their biochemical differences, plant and fungal cell walls serve similar functions. Which of the following observations would best support the alternative hypothesis described above? (A) Plant cell walls are found just outside the plasma membrane, while fungal cell walls are found just beneath the plasma membrane. (B) In both plant cells and fungal cells, the cell wall surrounds the outside of the cell membrane. (C) Some plant cells have secondary cell walls that confer additional rigidity, while fungal cells do not. (D) Photosynthesis occurs in plant cells, but it does not occur in fungal cells.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 24 24 | P a g e 52. Cholesterol is an important component of animal cell membranes. Cholesterol molecules are often delivered to body cells by the blood, which transports the molecules in the form of cholesterol-protein complexes. The complexes must be moved into the body cells before the cholesterol molecules can be incorporated into the phospholipid bilayers of cell membranes. Based on the information presented, which of the following is the most likely explanation for a buildup of cholesterol molecules in the blood of an animal? (A) The animal’s body cells are defective in exocytosis. (B) The animal’s body cells are defective in endocytosis. (C) The animal’s body cells are defective in cholesterol synthesis. (D) The animal’s body cells are defective in phospholipid synthesis. 53. TABLE 1. PHOTOPIGMENTS IN CYANOBACTERIA Cyanobacteria contain a variety of pigment molecules, as shown in Table 1. As a result, the color of cyanobacteria cultures can vary significantly based on the relative amount of each pigment produced. A researcher placed a culture of cyanobacteria under green lights. Within a few weeks, the appearance of the cyanobacteria changed from green to red. The researcher claimed the color change in the culture was the result of an adaptation allowing greater photosynthesis. Which of the following provides the best reasoning to justify the researcher’s claim? (A) In green light, more chlorophyll a molecules are produced, reflecting more light to other cyanobacteria to be used for photosynthesis. (B) In green light, more phycoerythrin molecules are produced, allowing more green light to be absorbed, thus increasing photosynthesis. (C) In green light, cyanobacteria that have more phycocyanin molecules are less likely to survive and reproduce. (D) In green light, cyanobacteria that have more allophycocyanin molecules are more likely to survive and reproduce.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 25 25 | P a g e 54. Figure 1 shows the number of chromosomes observed in an actively dividing human cell at each stage of cell division. Figure 1. Number of chromosomes in a human cell at different stages of cell division Which of the following presents a correct interpretation of the changes in chromosome number depicted in Figure 1 ? (A) DNA replication occurs between metaphase and anaphase, doubling the number of chromosomes. Between telophase and cytokinesis, the cell divides in two, with each cell receiving half of the replicated chromosomes. (B) New chromosomes formed during prophase are doubled during anaphase and are recombined before cytokinesis. (C) Chromosomes enter metaphase containing two chromatids attached by a centromere. During anaphase, the chromatids are separated, each becoming a chromosome. Cytokinesis distributes the chromosomes into two separate cells. (D) At anaphase a cell contains two identical copies of each chromosome, but following telophase, one of the copies is broken down into nucleotides. 55. Which molecule below contains hydrolytic enzymes associated with the intracellular digestion of macromolecules? (A) Centriole (B) Lysosome (C) Nucleolus (D) Peroxisome (E) Ribosome.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 26 26 | P a g e 56. Water is constantly diffusing into the cytosol of freshwater single-celled organisms. In order to maintain the proper solute concentrations in the cytosol, contractile vacuoles pump out the excess water. An experimenter placed single-celled organisms into various saline concentrations and recorded the ATP used by the contractile vacuole. The data are shown in the graph. Of the following, which additional investigation can be used to determine when the cells are in an isotonic solution? (A) Decreasing the salinity of the environment a little at a time until the ATP usage reaches a maximum (B) Decreasing the salinity of the environment a little at a time until ATP usage reaches a minimum (C) Increasing the salinity of the environment a little at a time until ATP usage reaches a maximum (D) Increasing the salinity of the environment a little at a time until the ATP usage reaches a minimum 57. A researcher designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental temperature on the function of an enzyme. For each trial included in the experiment, the researcher will add the enzyme and its substrate to an aqueous buffer solution and then measure the amount of product formed over 20 minutes. Which of the following must remain the same for all trials of this experiment? (A) The initial concentration of the substrate (B) The final concentration of the product (C) The three-dimensional structure of the enzyme (D) The temperature of the aqueous buffer solution 58. Cortisol is a hormone produced in response to stress, including starvation, in humans. Which of the following is most likely an immediate effect of a starvation-induced increase in cortisol secretion? (A) Increased activation of the immune system (B) Increased urine production by the kidneys (C) Increased bone and collagen formation (D) Increased mobilization of fatty acids from fat cells. 59. Researchers compared similar proteins from related organisms in different habitats. They found that the proteins from organisms living in harsh environments had a greater number of cysteine amino acids than did proteinsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 27 27 | P a g e from organisms not living in harsh environments. The structure of cysteine is shown. Bonds can form between the sulfur atom of different cysteine amino acids ( S-S bonds). Figure 1. Chemical structure of cysteine Which of the following best describes the effect of a greater number of cysteine amino acids on the stability of the proteins? (A) The change has no effect on the stability of the protein because only one type of amino acid is involved. (B) The change leads to increased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins. (C) The change leads to decreased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins. (D) The change leads to increased protein stability only when the added cysteine amino acids are next to other cysteine amino acids in the primary structure. 60. Damaged tissue releases chemicals that activate platelets and stimulate the formation of blood clots. Which of the following predictions about the activity of platelets best describes a positive feedback mechanism? (A) Activated platelets release chemicals that inhibit blood clot formation. (B) Activated platelets release signaling molecules that inhibit cell division in damaged tissue. (C) Activated platelets constrict the blood vessels, stopping blood flow. (D) Activated platelets release chemicals that activate more platelets. 61. Figure 1 represents a nucleic acid fragment that is made up of four nucleotides linked together in a chain. Figure 1. Nucleic acid fragment. Which of the following characteristics of Figure 1 best shows that the fragment is RNA and not DNA? (A) The 5’ to 3’ orientation of the nucleotide chain (B) The identity of each nitrogenous base (C) The charges on the phosphate groups (D) The type of bond linking the nucleotides togetherA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 28 28 | P a g e 62. DNA replication occurs (A) During the S phase of the cell cycle (B) As the nuclear envelope breaks down in early mitosis (C) During mitosis but not during meiosis (D) In animal cells but not in plant cells. (E) Only in cells destined to become gametes. 63. During mitosis, which of the following normally occurs? (A) Homologous chromosomes pair (B) Replicated chromosomes line up on the equatorial plate (C) Tetrads form. (D) Unreplicated chromosomes become oriented in the center of the cell. (E) Maternal and paternal chromatids pair. 64. During respiration, most ATP is formed as a direct result of the net movement of (A) Potassium against a concentration gradient (B) Protons down a concentration gradient (C) Electrons against a concentration gradient (D) Electrons through a channel (E) Sodium ions into the cell 65. Which of the following statements best supports the claim that certain organelles within eukaryotic cells evolved from free-living prokaryotic cells? (A) The cytoplasm of both eukaryotes and prokaryotes is surrounded by a plasma membrane. (B) Eukaryotes and prokaryotes both contain ribosomes, but the ribosomes of eukaryotes are more complex in structure than those of prokaryotes. (C) Eukaryotes exchange segments of internal membranes between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, but prokaryotes have no such internal membranes. (D) Some organelles contain their own DNA that is more similar to prokaryotic DNA in structure and function than to the eukaryotic DNA found in the cell's nucleus. 66. Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme? (A) The free energy of the reactants is greater than the free energy of the products. (B) The equilibrium constant of the reaction is much greater than 1. (C) The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme. (D) The concentration of the enzyme inside living cells is greater than the concentration of substrate. 67. Epinephrine is a protein hormone found in many animals. Epinephrine stimulates a signaling pathway that results in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver cells. Which of the following describes the initial steps in the process whereby epinephrine stimulates glycogen breakdown? (A) Epinephrine binds to a cell-surface receptor; the activated receptor stimulates production of the second messenger, cAMP. (B) Epinephrine binds to a cell-surface receptor; the activated receptor catalyzes the conversion of glycogen to glucose. (C) Epinephrine diffuses through the plasma membrane; the hormone dimerizes in the cytosol. (D) Epinephrine is taken into the cell by endocytosis; glycogen is converted to glucose in the endocytotic vesicle.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 29 29 | P a g e Answer question 68 and 69 based on the excerpt below. The epinephrine signaling pathway plays a role in regulating glucose homeostasis in muscle cells. The signaling pathway is activated by the binding of epinephrine to the beta-2 adrenergic receptor. A simplified model of the epinephrine signaling pathway is represented in Figure 1. 68. Based on Figure 1, which of the following statements best describes the epinephrine signaling pathway? (A) It involves the opening and closing of ion channels. (B) It involves enzymes activating other enzymes. (C) It involves changes in the expression of target genes. (D) It involves protons moving down a concentration gradient. 69. Which of the following outcomes will most likely result from the irreversible binding of to the G protein? (A) The intracellular concentration of glycogen will increase (B) The intracellular concentration of activated protein kinase A will increase (C) The intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP will increase (D) The intracellular concentration of glucose-1-phosphate will increase.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 30 30 | P a g e 70. Figure 1 is a proposed model of the feedback system controlling erythrocyte (red blood cell) production. Figure 1. Model of erythrocyte production control Air is less dense at very high elevations, so less oxygen is available than in the denser air at sea level. Based on the model in Figure 1, if a person travels from sea level to a high elevation location, which of the following correctly predicts the response to the decreased blood oxygen level? (A) More erythropoietin will be secreted from the kidneys, decreasing production of erythrocytes. (B) More erythropoietin will be secreted from the kidneys, increasing production of erythrocytes. (C) Less erythropoietin will be secreted from the kidneys, decreasing production of erythrocytes. (D) Less erythropoietin will be secreted from the kidneys, increasing production f erythrocytes. 71. Ethylene causes fruits to ripen. In a signaling pathway, receptors activate transcription factors, which ultimately leads to ripening. Which of the following best supports the claim that ethylene initiates the signal transduction pathway that leads to ripening of fruit? (A) Ethylene is a simple gaseous molecule, which makes it easily detected by receptors. (B) Fruit will ripen in closed containers without exposure to air. (C) Ethylene synthesis is under both positive and negative feedback regulation. (D) Loss-of-function mutations in ethylene receptors result in changes to the ripening process. 72. Which of the following organelle evolved from a photoautotrophic prokaryote?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 31 31 | P a g e 73. The molecular structures of linoleic acid and palmitic acid, two naturally occurring substances, are shown in the figure. Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature? (A) Linoleic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together. (B) Linoleic acid, because the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds prevents the molecules from packing closely together. (C) Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together. (D) Palmitic acid, because the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds prevents the molecules from packing closely together. 74. Organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum have membranes that compartmentalize reactions and other metabolic processes. To function properly, the organelles must move substances across their membranes. Which of the following statements describes a feature shared by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum that increases the efficiency of their basic functions? (A) They have rigid, nonfluid membranes. (B) They have highly folded membranes. (C) They have membranes composed of many carbohydrates. (D) They have double membranes, with one membrane enclosed within the other. 75. From the initial conditions and results described, which of the following is a logical conclusion? (A) The initial concentration of glucose in the bag is higher than the initial concentration of starch in the bag. (B) The pores of the bag are larger than the glucose molecules but smaller than the starch molecules. (C) The bag is not selectively permeable (D) A net movement of water into the beaker has occurred. (E) The molarity of the solution in the bag and the molarity of the solution in the surrounding beaker are the same.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 32 32 | P a g e 76. If, instead of the bag, a potato slice were placed in the beaker of distilled water, which of the following would be true of the potato slice? (A) It would gain mass. (B) It would neither gain nor lose mass. (C) It would absorb solutes from the surrounding liquid. (D) It would lose water until water potential inside the cells is equal to zero. (E) The cells of the potato would increase their metabolic activity 77. Which of the following best describes the condition expected after 24 hours? (A) The bag will contain more water than it did in the original condition. (B) The contents of the bag will have the same osmotic concentration as the surrounding solution. (C) Water potential in the bag will be greater than water potential in the surrounding solution. (D) Starch molecules will continue to pass through the bag. (E) A glucose test on the solution in the bag will be negative. 78. Gelatin is a protein that is derived from collagen which is found in the bones, skin, and connective tissue of animals. To investigate the ability of various enzymes to digest gelatin, a group of students set up an assay involving camera film. Camera film contains gelatin and appears black when exposed to light but turns clear as the gelatin gets broken down. The students incubated pieces of exposed camera film in test tubes, each containing one of three different enzyme solutions (trypsin, lipase, or amylase) as indicated in Figure 1. The students recorded the time it took for the enzymes to digest the gelatin in each test tube, turning the film from black to clear. Figure 1. Diagram of experimental setup. Which of the following would be the most appropriate control for this experiment? (A) A test tube containing no camera film (B) A test tube containing only a piece of exposed camera film (C) A test tube containing a piece of exposed camera film submerged in water (D) A test tube containing a piece of exposed camera film and all three enzyme solutionsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 33 33 | P a g e 79. All eukaryotic cells contain at least one Golgi complex, typically located in the cytoplasm and near the endoplasmic reticulum. Which of the following best describes a process that occurs within the Golgi complex? (A) Enzymatic modification of newly synthesized integral membrane proteins (B) Synthesis of cytosolic proteins based on the nucleotide sequences of mRNAs (C) Degradation of proteins by hydrolytic enzymes contained within the complex (D) Synthesis of various types of lipids 80. Glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta is a protein kinase that has been implicated in many types of cancer. Depending on the cell type, the gene for glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta (GSK3B) can act either as an oncogene or as a tumor suppressor. Which of the following best predicts how GSK3B mutations can lead to the development of cancer? (A) Cells with inactive GSK3B fail to trigger apoptosis. (B) Cells with inactive GSK3B fail to proceed past the G2/M checkpoint. (C) Cells with overactive GSK3B are more likely to repair DNA damage. (D) Cells with overactive GSK3B have longer cell cycles. 81. The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which is an important step in glycolysis. The reaction involves the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to glucose. Either a glucose molecule or a water molecule can fit in the active site of hexokinase. The presence of a water molecule in hexokinase’s active site would result in the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP instead of the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of hexokinase? (A) Both glucose and water are polar molecules that form favorable interactions with charged and polar amino acid side chains in hexokinase’s active site. (B) Both glucose and water have oxygen atoms that can form covalent bonds with the phosphorus atoms of phosphate groups. (C) Glucose is an energy-rich organic molecule that can be broken down by glycolysis to produce ATP, whereas water is an inorganic molecule. (D) Glucose has the right shape and charge to cause hexokinase to undergo a structural change needed for catalysis, whereas water does not. 82. Water and ammonia interact to form hydrogen bonds, as represented in the figure. Which statement best helps explain the formation of the hydrogen bond represented in the figure? (A) The oxygen has a partial positive charge, and the nitrogen has a partial negative charge. (B) The nitrogen has a partial negative charge, and the hydrogen attached to the oxygen has a partial positive charge. (C) The hydrogen attached to the oxygen has a partial negative charge, and the nitrogen also has a partial negative charge. (D) The nitrogen has a partial positive charge, and the hydrogen attached to the oxygen also has a partial positive charge.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 34 34 | P a g e 83. If an individual with diabetes consumes food that is high in simple carbohydrates, blood-sugar levels can rise above normal levels. Which of the following questions would provide the best direction for a researcher who wanted to study the impact of abnormally high blood-sugar levels on cellular homeostasis in diabetics? (A) Are cells in diabetics larger in size than those in nondiabetics? (B) Do the cells in diabetics have more potassium ion channels in the cell membrane than the cells in nondiabetics do? (C) Does water move from cells into blood vessels more rapidly in diabetics than in nondiabetics when blood-sugar levels are higher than normal? (D) Do the cells of diabetics use simple sugars as an energy source? 84. If ATP breakdown (hydrolysis) is inhibited, which of the following types of movement across cell membranes is also inhibited? (A) Movement of oxygen into a cell (B) Movement of water through aquaporins (C) Passage of a solute against its concentration gradient (D) Facilitated diffusion of a permeable substance 85. If chemical signals in the cytoplasm control the progression of a cell to the M phase of the cell cycle, then fusion of a cell in G1 with a cell in early M phase would most likely result in the (A) A replication of chromosomes only in the G1 cell (B) exiting of both cells from the cell cycle and into the G0 phase (C) condensation of chromatin in preparation of nuclear division in both cells (D) transfer of organelles from the G1 cell to the cell in the M phase Answer question 86 to 88 based on the excerpt below. To study the actions of the enzyme catalase on hydrogen peroxide, students performed the following experiment. Catalase was extracted from potatoes by blending raw potatoes in a blender with cold distilled water. The filtrate was stored on ice. The following hydrogen peroxide solutions were made: 1 percent, 5 percent, 10 percent, and 15 percent. Filter paper disks were soaked in the catalase filtrate and dropped into beakers containing the various solutions. The activity of the enzyme was measured by the amount of time it took for the disks to float to the surface of the solution on the bubbles produced by the reaction. The following data were obtained. 86. If the potato solution was boiled for 10 minutes and cooled for 10 minutes before being tested, the average time for the disks to float to the surface of the hydrogen peroxide solution would be (A) less than 1 seconds (B) 5 seconds (C) 10 seconds (D) 30 seconds (E) more than 30 secondsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 35 35 | P a g e 87. Which of the following best describes why ice was used during this experiment? (A) To increase the activity of the enzyme (B) To retard the breakdown of the catalase (C) To purge the solution of excess air trapped during blending (D) To slow the catalase molecules to increase the probability of contact with the hydrogen peroxide molecules (E) To increase the size of the active site on the enzyme. 88. Which of the following best describes why the disks rose to the surface faster in the more concentrated hydrogen peroxide solutions? (A) There was more enzyme present in the more concentrated solutions. (B) A greater amount of heat was generated in the more concentrated solutions. (C) The more concentrated solutions lowered the activation energy of the reaction. (D) The higher substrate concentrations in the more concentrated solutions speeded the reaction. (E) The density of the water was lower in the more concentrated solutions. 89. In an experiment, a scientist isolates mitochondria from living cells and suspends them in two different buffered solutions. One solution is maintained at pH 4, while the other solution is maintained at pH 9. The scientist finds that mitochondria in the solution at pH 4 continue to produce ATP but those in the pH 9 solution do not. The results of the experiment can be used as evidence in support of which of the following scientific claims about mitochondrial activity? (A) Mitochondria in a cell-free environment are unable to convert thermal energy into ATP (B) The electron transport chain pumps electrons from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix (C) ATP production in mitochondria requires a hydrogen ion gradient that favors movement of protons into the mitochondrial matrix (D) ATP synthase molecules change their orientation in relation to the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane. Answer question 90 and 91 based on the excerpt below: In the first step of an experiment, rat liver cells were exposed for 5 minutes to amino acids labeled with a radioactive isotope. The cells were then washed to stop any further incorporation of radioactive amino acids. The cells were sampled periodically thereafter, and the radioactivity of a certain protein (protein X) was measured in various cell components, as shown below.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 36 36 | P a g e 90. In graphing the data from this experiment, the sampling time would be shown on the x-axis because (A) Cell components were shown on the y-axis (B) Radioactivity level shows the most variation (C) Time values are always located on the horizontal axis (D) All quantitative values are represented on the x-axis 91. Which of the following correctly shows the order in which protein X moves through the cell? (A) Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus lysosome (B) Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus nucleus cytoplasm lysosome (C) Extracellular space mitochondria cytoplasm (D) Golgi apparatus cytoplasm lysosomes (E) Cytoplasm mitochondria extracellular space. 92. In most freshwater fish, nitrogenous waste is primarily excreted as ammonia, which is highly soluble in water and is toxic at low concentrations. In terrestrial mammals, ammonia is converted to urea before it is excreted. Urea is also highly soluble in water but is less toxic than ammonia at low concentrations. Which of the following best explains why freshwater fish do not convert ammonia to urea for excretion? (A) The metabolic pathways of fish do not normally involve nitrogen consumption. (B) The dilution of ammonia by direct excretion into freshwater conserves energy. (C) Ammonia is concentrated in tissues, where it is stored prior to excretion. (D) The nitrogen in ammonia is recycled for use in protein and nucleotide synthesis. 93. Changing the shape or morphology of the mitochondrial inner membrane can change the efficiency of mitochondrial function. Which of the following outcomes will most likely result from a change in the shape of the mitochondrial inner membrane from a highly folded surface to a smooth, flat surface? (A) Mitochondria will become more efficient because the inner mitochondrial membrane will become more permeable to ions. (B) Mitochondria will become more efficient because the total volume of the mitochondria will increase. (C) Mitochondria will become less efficient because the inner mitochondrial membrane will become less permeable to large molecules. (D) Mitochondria will become less efficient because the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membranes will decrease. 94. Intact cells of two unknown cell types were placed into solutions with different concentrations of NaCl. Type I cells swelled and burst in the solution with the lowest concentration of NaCl. Type II cells swelled but did not burst in the solution with the lowest concentration of NaCl. Which of the following descriptions of cell type I and cell type II are most consistent with the data?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 37 37 | P a g e 95. A tissue culture of vertebrate muscle was provided with a constant excess supply of glucose under anaerobic conditions starting at time zero and the amounts of pyruvic acid and ATP produced were measured. The solid line in the graph above represents the pyruvic acid produced in moles per liter per minute. ATP levels were also found to be highest at points A and C, lowest at B and D. A second culture was set up under the same conditions, except that substance X was added, and the results are indicated by the dotted line. It is most reasonable to hypothesize that, in the breakdown of glucose, substance X is (A) An activator (B) An inhibitor (C) A substrate (D) A coenzyme (E) A cofactor. 96. In chloroplast, ATP is synthesized from ADP plus inorganic phosphate (Pi) in a reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase molecules that are embedded in the thylakoid membrane. Which of the following statements provides evidence to support the claim that no ATP will be synthesized in the absence of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane? (A) Blocking electron flow from one carrier to the next in the electron transport chains blocks formation of a proton gradient in the thylakoid. (B) Increasing the proton concentration difference across the thylakoid membrane is not associated with a parallel increase in the rate of ATP synthesis (C) No ATP is synthesized when channel proteins that allow the free passage of protons are inserted into the thylakoid membrane. (D) No ATP is synthesized while the Calvin cycle is synthesizing carbohydrates and using ATP and NADPH at a high rate. 97. Liver cells manufacture glycoproteins, while adipose cells store fat. Which of the following subcellular structures is likely to be more prominent in liver cells than in adipose cells? (A) Nucleus (B) Golgi apparatus (C) Cytoskeleton (D) Plasma membrane.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 38 38 | P a g e 98. The figure shows a process by which a cell might absorb food from its surrounding environment and break it down for use as a source of energy and matter. The process involves lysosomes, which are membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes. Activation of the hydrolytic enzymes requires an acidic pH, and lysosomes maintain an internal acidic pH by using ion pumps. Which of the following outcomes will most likely result from a loss of ion pump function in the cell’s lysosomes? (A) The internal pH of the lysosomes will decrease, which will prevent the activation of hydrolytic enzymes and interfere with the intracellular digestion of food. (B) The internal pH of the lysosomes will increase, which will prevent the activation of hydrolytic enzymes and interfere with the intracellular digestion of food. (C) The internal pH of the lysosomes will decrease, which will activate hydrolytic enzymes and enhance the intracellular digestion of food. (D) The internal pH of the lysosomes will increase, which will activate hydrolytic enzymes and enhance the intracellular digestion of food. 99. Which of the following claims is scientifically accurate and consistent with an observation that a decrease in lysosome production within a cell leads to a decline in mitochondrial activity? (A) A lack of lysosomes will cause a decrease in the synthesis of enzymes necessary for cellular respiration. (B) Fewer lysosomes will be available to break down macromolecules to provide the necessary nutrients for cellular respiration. (C) Fewer lysosomes will be available to store materials required for the functioning of the mitochondria. (D) Lysosomes will not be available to modify proteins so that they are targeted to the mitochondria.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 39 39 | P a g e 100. A cell’s membrane potential is maintained by the movement of ions into and out of the cell. A model showing the influence of membrane proteins on the movement of sodium (Na+ ) and potassium (K+) ions across the plasma membrane is presented in Figure 1. Figure 1. Section of a cell’s plasma membrane, showing ion concentrations and membrane proteins. Based on the model presented in Figure 1, which of the following outcomes will most likely result from a loss of protein X function? (A) The membrane potential will be disrupted by an increase in Na+ concentration inside the cell. (B) The membrane potential will be disrupted by an increase in K+ concentration inside the cell. (C) The membrane potential will be maintained by the Na+-K+ pump moving more K+ ions into the cell. (D) The membrane potential will be maintained by the diffusion of Na+ ions into the cell. 101. Many human cells can be stimulated to divide by hormonelike growth factors that bind to receptor proteins (R) on the plasma membrane and trigger an internal signal-transduction cascade. In many cases, however, the process of contact inhibition prevents mitosis when cells are in direct contact with one another. Contact inhibition occurs when proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) interact, causing them to change shape so that the growth-factor signaling proteins that normally associate with CAMs are replaced by another protein, called M. Both pathways are depicted in the figures below.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 40 40 | P a g e Which of the following statements accurately uses the information presented to support the hypothesis that interruption of M function in a single body cell can result in cancer? (A) Protein 3 will be prevented from interacting with CAMs, causing the cell cycle to stop permanently. (B) The ras protein will remain bound to DNA, blocking expression of genes required for mitosis. (C) Growth-factor signaling can trigger mitosis in cells that are in direct contact with other cells. (D) The receptor proteins of body cells will no longer bind to growth-factor proteins. 102. The figure shows a model of the exchange of matter between the organisms that live together in an aquarium. The model includes matter exchange between plants, fish, and bacteria. The bacteria are represented as rodshaped organisms living in the gravel at the bottom of the aquarium. Which of the following statements best describes how molecules released by the fish become nutrients for the plants? (A) The carbon dioxide molecules released by the fish are converted by the bacteria to oxygen atoms, which are used by the plants to make water molecules. (B) The oxygen molecules released by the fish are converted by the bacteria to ammonia molecules, which are used by the plants to make lipids and fatty acids. (C) The nitrites released by the fish are converted by the bacteria to carbon dioxide molecules, which are used by the plants to make carbohydrates. (D) The ammonia molecules released by the fish are converted by the bacteria to nitrates, which are used by the plants to make proteins and nucleic acids. 103. Membrane-bound organelles have been an important component in the evolution of complex, multicellular organisms. Which of the following best summarizes an advantage of eukaryotic cells having internal membranes? (A) Eukaryotic cells are able to reproduce faster because of the presence of organelles. (B) Some organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, are similar to prokaryotic cells in structure. (C) Organelles isolate specific reactions, increasing metabolic efficiency. (D) Compartmentalization leads to a higher mutation rate in DNA, which leads to more new species.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 41 41 | P a g e 104. Vertebrate immune responses involve communication over short and long distances. Which of the following statements best helps explain how cell surface proteins, such as MHC proteins and T cell receptors, mediate cell communication over short distances? (A) The proteins receive electrical signals from nerve cells. (B) The proteins leave the cell and travel in the bloodstream to other cells. (C) The proteins interact directly with proteins on the surfaces of other cells. (D) The proteins bind to molecules secreted by cells located in other parts of the body. 105. The endosymbiont theory proposes a model for the evolution of mitochondria. According to the model, an ancestral eukaryote engulfed a small, free-living prokaryotic organism. The engulfed prokaryote then formed an endosymbiotic relationship with the eukaryotic host. Which of the following observations best supports the model? (A) Prokaryotes and eukaryotes acquire nutrients from the surrounding environment. (B) Organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum have membranes composed of phospholipids. (C) Mitochondria and some prokaryotes share similar metabolic reactions that produce ATP. (D) Eukaryotes evolved after prokaryotes and have more complex structures. 106. Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membranes to large molecules? (A) ATP production will increase because of an increase in the rate at which proteins diffuse out of mitochondria. (B) ATP production will increase because of an increase in the mixing of mitochondrial and cytosolic substances. (C) ATP production will decrease because of an increase in the occurrence of uncontrolled chemical reactions. (D) ATP production will decrease because of an increase in the surface area of the mitochondrial membranes. 107. Muscle cells have high ATP demands. Which of the following is a scientific claim about how the structure of the mitochondria in muscle cells should be different than it is in other cells because of the high energy demands of mitochondria? (A) The inner membrane of the mitochondria in muscle cells should have more folds to increase the surface area, allowing more ATP to be synthesized. (B) The inner membrane of the mitochondria in muscle cells should be more permeable to large enzymes, allowing the same reactions to occur in both compartments of the mitochondria. (C) The outer membrane of the mitochondria in muscle cells should be thicker, allowing more rapid diffusion of molecules into the mitochondria. (D) The outer membrane of the mitochondria of muscle cells should have more folds, increasing the surface area for faster diffusion of molecules from the cytoplasm. 108. Most cells that have become transformed into cancer cells have which of the following characteristics when compared to normal, healthy cells? (A) Shorter cell cycle (B) More carefully regulated rates of cell division (C) Lower rates of mitosis (D) Higher rates of protein translation (E) Identical DNAA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 42 42 | P a g e 109. In addition to the pigments commonly associated with photosynthesis, a certain photosynthetic species contains two additional pigment types. Which of the following best supports the claim that this species is better adapted to environmental changes than other photosynthetic species are? (A) The increased pigment concentration better facilitates energy production within the cells of the species. (B) The pigment combination allows the organism to absorb heat as well as light, making better use of available energy. (C) The additional pigments allow the species to outcompete other species for the wavelengths of light commonly used in photosynthesis. (D) The additional pigments allow the species containing them to harvest energy from wavelengths of light that the other photosynthetic species cannot use. 110. Muscle contraction depends on ATP hydrolysis. During periods of intense exercise, muscle cells rely on the ATP supplied by three metabolic pathways: glycolysis, mitochondrial respiration, and the phosphagen system. Figure 1 shows the rates at which the three metabolic pathways produce ATP following the start of an intense period of exercise. Figure 1. ATP production by three metabolic pathways following the start of an intense period of exercise Which of the following correctly uses the data to justify the claim that the phosphagen system is an immediate, shortterm source of ATP for muscle cells? (A) ATP production by the phosphagen system increases and decreases rapidly following the start of the exercise period. (B) ATP production by the phosphagen system increases gradually and continuously throughout the entire exercise period. (C) The ATP produced by the phosphagen system contains more energy per molecule than does the produced by the other pathways. (D) ATP hydrolysis in muscle cells occurs immediately after the start of the exercise period but stops before the end of the exercise period.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 43 43 | P a g e 111. Figure 1 shows a model of a signal transduction cascade, initiated by the binding of a ligand to the transmembrane receptor protein A. Figure 1. Model of a signal transduction cascade incorporating protein A A DNA mutation changes the shape of the extracellular domain of transmembrane receptor protein A produced by the cell. Which of the following predictions is the most likely consequence of the mutation? (A) Production of activated molecule 1 will stop, but production of activated molecules 2 and 3 will continue. (B) The molecule that normally binds to protein A will no longer attach, deactivating the cellular response. (C) The molecule that normally binds to protein A will not enter the cell, thus no cellular response will occur. (D) Since protein A is embedded in the membrane, the mutation will be silent and not affect the cellular response. 112. Cancer cells behave differently than normal body cells. For example, they ignore signals that tell them to stop dividing. Which of the following conditions will most likely cause a normal body cell to become a cancer cell? (A) The environment already contains cancer cells. (B) The environment has an abundance of nutrients. (C) The environment lacks signals that would otherwise tell the cell to stop dividing. (D) The environment contains mutagens that induce mutations that affect cell-cycle regulator proteins. 113. A team of biologists develop a new drug, and one team member hypothesizes that the drug is incapable of freely passing across the plasma membrane and requires the help of membrane proteins to enter cells. Alternatively, another biologist on the team hypothesizes that the drug can diffuse passively across the plasma membrane like O2 and CO2 can. Which of the following, if true about the drug, best supports the alternative hypothesis that the new drug will exhibit simple diffusion across plasma membranes? (A) The drug is a small nonpolar molecule. (B) The drug is a small charged molecule. (C) The drug is a large polar molecule. (D) The drug is a large charged moleculeA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 44 44 | P a g e 114. Notch is a receptor protein displayed on the surface of certain cells in developing fruit fly embryos. Notch’s ligand is a membrane-bound protein called Delta that is displayed on the surface of adjacent cells. When Notch is activated by its ligand, the intracellular tail of the Notch protein becomes separated from the rest of the protein. This allows the intracellular tail to move to the cell’s nucleus and alter the expression of specific genes. Which of the following statements best explains Delta’s role in regulating cell communication through the Notch signaling pathway? (A) Delta transmits a chemical signal to all the cells of a developing embryo. (B) Delta allows the cells of a developing embryo to communicate without making direct contact. (C) Delta restricts cell communication to short distances within a developing embryo. (D) Delta determines which cells in a developing embryo express the gene that encodes the Notch protein 115. Which of the following conclusions is most clearly supported by the representations of nucleic acid #1 and nucleic acid #2? (A) Nucleic acid #1 contains only purines, whereas nucleic acid #2 contains only pyrimidines. (B) Nucleic acid #1 contains the sugar ribose, whereas nucleic acid #2 contains the sugar deoxyribose. (C) Nucleic acid #1 contains positively charged phosphate groups, whereas nucleic acid #2 does not. (D) Nucleic acid #1 contains adenine-thymine base pairs, whereas nucleic acid #2 does not.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 45 45 | P a g e 116. Students conducted a controlled experiment to investigate whether sawdust provides enough nutrients to support plant growth. The students separated ten nearly identical sunflower seedlings into two groups. They grew the seedlings in the first group in potting soil and the seedlings in the second group in sawdust composed mostly of cellulose. After twenty days, the students recorded observations about the seedlings in each group. The students’ observations are presented in the table. The observed differences between the groups most likely resulted from differences in the ability of the seedlings to produce which of the following monomers? 117. Oxygen consumption can be used as a measure of metabolic rate because oxygen is (A) necessary for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation (B) necessary to replenish glycogen levels (C) necessary for fermentation to take place (D) required by all living organisms (E) required to break down the ethanol that is produced in musclesA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 46 46 | P a g e 118. Which of the following statements best explains the processes of passive and active transport? (A) Passive transport is the net movement of substances down a concentration gradient that requires metabolic energy. Active transport is the movement of substances up a concentration gradient that does not require energy. (B) Passive transport is the net movement of substances down a concentration gradient that does not require metabolic energy. Active transport is the movement of substances up a concentration gradient that requires energy. (C) Passive transport is the net movement of substances up a concentration gradient that requires metabolic energy. Active transport is the movement of substances down a concentration gradient that does not require metabolic energy. (D) Passive transport is the net movement of substances up a concentration gradient that does not require metabolic energy. Active transport is the movement of substances down a concentration gradient that requires energy. Answer question 119 and 120 based on the excerpt below. Figure 1 represents a common process that occurs in organisms. Figure 1. Structural formula for a common biological reaction 119. Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown in Figure 1? (A) The linking of amino acids with an ionic bond as an initial step in the protein synthesis process (B) The formation of a more complex carbohydrate with the covalent bonding of two simple sugars (C) The hydrolysis of amino acids with the breaking of covalent bonds with the release of water (D) The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction 120. Which of the following best describes the formation of the bond shown in Figure 1 ? (A) An ionic bond is formed between a carbon atom of one amino acid and the nitrogen atom of the other amino acid. (B) An ionic bond is formed when the negative charge of an OH group is balanced by the positive charge of a hydrogen ion. (C) A covalent bond is formed between a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom along with the formation of H2O. (D) A covalent bond is formed that replaces the hydrogen bond between the OH group and the H atom.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 47 47 | P a g e 121. The enzyme peroxidase is found in many organisms. It catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. The rate of peroxidase activity at different pH values was assessed by students in the lab. The students’ results are shown in graph 1. Graph 1. Effect of pH on peroxidase activity If the experiment is repeated at pH 11, the observed activity level of the enzyme will most likely be (A) the same as the level at pH 7 (B) lower than the level at pH 9 (C) greater than the level at pH 9 (D) between the levels observed at pH 5 and pH7. 122. Which of the following best describes the numbered areas in the figure below? (A) Areas 1 and 3 are polar, since the membrane molecules are aligned with water molecules. (B) Area 2 is polar, since water has been excluded from this area of the membrane. (C) Areas 1 and 3 are hydrophilic, since membrane molecules formed covalent bonds with water. (D) Area 2 is nonpolar, since hydrogen bonds between the adjacent lipids hold the membrane together.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 48 48 | P a g e 123. A scientist claims that Elysia chlorotica, a species of sea slug, is capable of photosynthesis. Which of the following observations provides the best evidence to support the claim? (A) Elysia chlorotica will die if not exposed to light. (B) Elysia chlorotica grows when exposed to light in the absence of other food sources. (C) Elysia chlorotica grows faster when exposed to light than when placed in the dark. (D) Elysia chlorotica grows in the dark when food sources are available. 124. Researchers propose a model to explain variation in phytoplankton cell sizes in a marine environment. They base their model on the idea that smaller cells absorb nutrients more efficiently. The researchers predict that the mean diameter of phytoplankton cells will change by 50 micrometers for every 5-kilometer increase in distance from the shore because of a gradual decrease in nutrient availability. To test their model, the researchers determine that the phytoplankton cells found closest to shore have a mean diameter of 900 micrometers. Based on the model, what will be the mean diameter of the phytoplankton cells that are found 25 kilometers from shore? (A) 650 micrometers (B) 875 micrometers (C) 925 micrometers (D) 1150 micrometers 125. In an experiment, cells were isolated from an aquatic plant and suspended in pond water, a sucrose sugar solution, or distilled water. All of the cells were then viewed under a microscope. Compared with the cell in the pond water, the cell in the sugar solution appeared shriveled, and the cell in the distilled water appeared inflated. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1. Figure 1. The results of an experiment using aquatic plant cells Which of the following statements best explains the observations represented in Figure 1 ? (A) There was a net movement of sucrose out of the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of sucrose into the cell suspended in the distilled water. (B) There was a net movement of sucrose into the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of sucrose out of the cell suspended in the distilled water. (C) There was a net movement of water out of the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of water into the cell suspended in the distilled water. (D) There was a net movement of water into the cell suspended in the sugar solution and a net movement of water out of the cell suspended in the distilled water.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 49 49 | P a g e 126. In flowering plants, plasmodesmata are narrow channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells. An explanation of how plant cells communicate across cell walls will most likely refer to the diffusion through plasmodesmata of which of the following? (A) Membrane-bound organelles (B) Condensed, duplicated chromosomes (C) Branched polysaccharides (D) Small, water-soluble molecules 127. Which of the following best describes the structures of carbohydrates? (A) They only occur as disaccharides. (B) They occur as monomers, chains of monomers, and branched structures. (C) They only occur as long and branched structures. (D) They occur as chains of monomers that hydrogen bond with complementary chains of monomers. 128. Which of the following process is found in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration? (A) Glycolysis (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) (D) Light dependent reactions of photosynthesis (E) Chemiosmosis. 129. Process in which carbon from carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic molecules. (A) Glycolysis (B) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) (C) Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions of photosynthesis) (D) Light dependent reactions of photosynthesis (E) Chemiosmosis. 130. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common? (A) A membrane-bound nucleus (B) A cell wall made of cellulose (C) Ribosomes (D) Flagella or cilia that contain microtubules (E) Linear chromosomes made of DNA and protein.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 50 50 | P a g e 131. Polypeptides are continuously being formed and degraded. One of these processes is shown. Figure 1. Polypeptide reaction Which statement is the most accurate description of the reaction shown in Figure 1? (A) It represents monomers linked by dehydration synthesis. (B) It represents a polypeptide chain that folds to form the tertiary structure. (C) It represents a polypeptide chain that is denatured into the primary structure. (D) It represents a polypeptide chain that is broken down through a hydrolysis reaction. 132. The transport of a substance across a plasma membrane of a specific organelle requires energy. The rate at which the transport takes place also depends on temperature. A scientist isolated the specific organelle and then used the following treatments to determine the conditions that will result in the maximal transport. All treatments contained the extracted organelle and were maintained at 25oC. The data from this experiment indicate that maximal rate of transport of protein X at 25oC occurs at an ATP concentration of 1.0 ??/??. Figure 1. The four concentrations used in the experiment Which procedure should be done next to gather data needed to meet the scientist’s objective? (A) Incubate samples with the same four ATP concentrations at 30oC. (B) Incubate samples containing 5.0 ??/?? of ATP at four temperatures other than 25oC. (C) Incubate samples containing 1.0 ??/?? of ATP at four temperatures other than 25oC. (D) Incubate samples containing 1.0 ??/?? of ATP at 25oC and determine the rate of transport for four other proteinsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 51 51 | P a g e 133. Cells contain smaller components called organelles that are necessary for a cell’s survival. Organelle functions have often been compared to components of larger systems. Which of the following functional differences between the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is explained by the structural differences between them? (A) Rough ER breaks down toxic substances, and smooth ER only transports them out of the cell. (B) Rough ER can synthesize and package lipids for export, and smooth ER cannot. (C) Rough ER can produce ATP, and smooth ER cannot. (D) Rough ER can synthesize and package proteins for export, and smooth ER cannot. 134. The sequences for two short fragments of DNA are shown above. Which of the following is one way in which these two segments would differ? (A) Segment 1 would not code for mRNA because both strands have T, a base not found in RNA. (B) Segment 1 would be more soluble in water than segment 2 because it has more phosphate groups. (C) Segment 1 would become denatured at a lower temperature than would segment 2 because A-T base pairs have two hydrogen bonds whereas G-C base pairs have three. (D) Segment 1 must be from a prokaryote because it has predominantly A-T base pairs. 135. Simple cuboidal epithelial cells line the ducts of certain human exocrine glands. Various materials are transported into or out of the cells by diffusion. (The formula for the surface area of a cube is 6 X S2, and the formula for the volume of a cube is S3, where S = the length of a side of the cube.) Which of the following cube-shaped cells would be most efficient in removing waste by diffusion?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 52 52 | P a g e 136. A student claims that the Y chromosome contains the sex-determining region gene, known as the SRY gene, which causes male fetuses to develop testes. Which of the following provides correct information about cell signaling that supports the claim? (A) The SRY gene produces a protein that binds to specific regions of DNA in certain tissues, which affects the development of these tissues. (B) The SRY gene produces a protein that deletes portions of the X chromosome in males so that male characteristics can develop. (C) The SRY gene produces an RNA segment that is exported from specific cells and targets the developing gonads. (D) The SRY gene is found only in tissues of the developing gonads 137. Steroid hormones, such as testosterone, pass through the plasma membrane and bind to an intracellular protein, as shown in the diagram below. The hormone-receptor complex then enters the nucleus, where it interacts with DNA to promote transcription of a specific gene. Based on the information presented, which of the following will also occur in response to steroid signaling? (A) Histone protein synthesis will increase because histones maintain the DNA in an optimal conformation for chromosome assembly. (B) Ribosome production will increase because ribosomes are specific for the mRNA with which they bind during translation. (C) DNA replication will increase as a result of the binding of the hormone-receptor complex to the DNA. (D) Production of a specific mRNA will increase as a result of the binding of the hormone-receptor complex to the DNA.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 53 53 | P a g e Both myoglobin and hemoglobin are proteins that bind reversibly with molecular oxygen. The graph below shows the oxygen-binding saturation of each protein at different concentrations of oxygen. 138. Strenuous exercise lowers the blood pH, causing the curves for both hemoglobin and myoglobin to shift to the right. This shift results in (A) an unloading of O2 at higher partial pressures (B) an increase in the number of O2-binding sites (C) the capture of more O2 by hemoglobin (D) the capture of more O2 by myoglobin 139. Students in a class measured the mass of various living organisms. They then kept the organisms in the dark for 24 hours before remeasuring them. None of the organisms were provided with nutrients during the 24- hour period. The data are as follows. Which of the following is the best explanation for the pattern of change in mass of the organisms over time? (A) Water loss due to evaporation (B) Cellular respiration (C) The law of conservation of matter (D) Growth and reproduction.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 54 54 | P a g e 140. A spherical bacterial cell has a radius of 3 ??. The human egg cell has a radius of 100 ??. Which statement correctly indicates the cell that is able to more efficiently exchange materials with the external environment and provides a correct explanation? (A) The egg cell, because it has the smallest surface-to-volume ratio. (B) The egg cell, because it has the largest surface-to-volume ratio. (C) The bacterial cell, because it has the smallest surface-to-volume ratio. (D) The bacterial cell, because it has the largest surface-to-volume ratio. 141. Figure 1 is a diagram of water molecules at the air-water interface at the surface of a pond. Figure 1. Alignment of water molecules at air-water interface Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an airwater interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface? (A) Covalent bonds between water molecules and the air above provide cohesion, which causes tiny bubbles to form under the feet of the insect. (B) Ionic bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide an electric charge, which attracts the feet of the insect, keeping it on the surface. (C) Polar covalent bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide adhesion, which supports the weight of the insect. (D) Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect 142. Which of the following molecule is synthesized at the ribosome? (A) Protein (B) Carbohydrates (C) Nucleic acids (D) Lipids (E) SteroidsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 55 55 | P a g e 143. Two different models of a living cell are represented in the figure. Of the two cells represented in the figure, which would likely be more efficient at exchanging substances with the surrounding environment? (A) Cell A, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio. (B) Cell A, because it has the smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio. (C) Cell B, because it has the larger surface-area-to-volume ratio. (D) Cell B, because it has the smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio. 144. A researcher claims that increasing the environmental temperature by10oC will double the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. To test the claim, the researcher designs an experiment that uses a particular enzyme isolated from plants. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1. For each test tube in the experiment, the researcher will measure the rate of product formation. Which of the following statements best helps justify the inclusion of test tube 5 as a control in the experiment? (A) It will provide a measurement of product formation in the absence of the substrate. (B) It will provide a measurement of product formation in the presence of a denatured enzyme. (C) It will show the effect of doubling the amount of substrate on the rate of product formation. (D) It will show the effect of increased enzyme activity on the rate of product formation.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 56 56 | P a g e 145. The carbon 'that makes up organic molecules in plants is derived directly from (A) Combustion of fuels (B) Carbon fixed in photosynthesis (C) Carbon dioxide produced in respiration (D) Coal mines 146. The chemical reaction for photosynthesis is If the input water is labeled with a radioactive isotope of oxygen, 18O, then the oxygen gas released as the reaction proceeds is also labeled with 18O. Which of the following is the most likely explanation? (A) During the light reactions of photosynthesis, water is split, the hydrogen atoms combine with the CO2, and oxygen gas is released. (B) During the light reactions of photosynthesis, water is split, removing electrons and protons, and oxygen gas is released. (C) During the Calvin cycle, water is split, regenerating NADPH from NADP+, and oxygen gas is released. (D) During the Calvin cycle, water is split, the hydrogen atoms are added to intermediates of sugar synthesis, and oxygen gas is released. 147. The diagram below shows energy changes in a specific chemical reaction with and without the addition of an enzyme to the reaction. Which of the following questions can best be answered by the diagram? (A) Does the addition of an enzyme reduce the activation energy required for a reaction? (B) Does the addition of an enzyme result in the formation of covalent bonds? (C) Does the addition of an enzyme produce a greater amount of products? (D) Does the addition of an enzyme change the pathway for the reaction?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 57 57 | P a g e 148. The endocrine system incorporates feedback mechanisms that maintain homeostasis. Which of the following demonstrates negative feedback by the endocrine system? (A) During labor, the fetus exerts pressure on the uterine wall, inducing the production of oxytocin, which stimulates uterine wall contraction. The contractions cause the fetus to further push on the wall, increasing the production of oxytocin. (B) After a meal, blood glucose levels become elevated, stimulating beta cells of the pancreas to release insulin into the blood. Excess glucose is then converted to glycogen in the liver, reducing blood glucose levels. (C) At high elevation, atmospheric oxygen is more scarce. In response to signals that oxygen is low, the brain decreases an individual’s rate of respiration to compensate for the difference. (D) A transcription factor binds to the regulatory region of a gene, blocking the binding of another transcription factor required for expression. 149. The energy required to run the Calvin cycle reactions of photosynthesis comes from which two substances produced during the light-dependent reactions? (A) ATP and NADPH (B) ADP and PO4 (C) H+ and PO2 (D) O2 and CO2 (E) H2O and CO2 150. The following questions refer to the following information and graph. The data presented in the figure below are measurements of the rate of oxygen consumption at differing body masses in a species of fish. Each point represents measurements from a different fish. Measurements were taken at different temperatures. (○= 10°C,●= 15°C, □= 20°C, ■= 25°C.) The fact that each line on the graph rises from left to right means that (A) higher temperatures produce higher rates of metabolism (B) there were more large fish in the samples taken at high temperatures (C) larger fish consume more oxygen than smaller fish at all four temperatures (D) when measurements are taken for larger fish late in the day, observed values are higher (E) larger fish prefer to live at higher temperatures than do smaller fishA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 58 58 | P a g e 151. The figure below illustrates a eukaryotic cell. Which of the following best describes how the three structures indicated by the arrows work together? (A) To synthesize lipids and modify toxic substances in order to render them harmless (B) To synthesize and isolate proteins for secretion or for use in the cell (C) To catabolize nutrients and produce ATP for intracellular energy storage (D) To synthesize all ribosomal proteins 152. Based on the model of eukaryotic cell cycle regulation shown in the figure, which of the following best describes the effect of a drug that blocks the production of the mitotic cyclin? (A) The cell cycle would proceed uncontrollably, and the cell would become cancerous. (B) The G1 cyclin would functionally replace mitotic cyclin, and the cell would continue dividing normally. (C) DNA synthesis would be prevented, and the cell would stop dividing. (D) The cell would be prevented from entering mitosis, and the cell would stop dividing.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 59 59 | P a g e 153. The manner in which several different ions and molecules move through a cell membrane is shown in the diagram above. For each ion or molecule, the relative concentration on each side of the membrane is indicated. Which of the following accurately describes one of the movements taking place? (A) Glucose is transported into the cell by active transport. (B) Na+ is transported into the cell by active transport. (C) The movement of glucose through the membrane requires ATP hydrolysis. (D) Na+ transport out of the cell requires ATP hydrolysis. 154. The model shown in the figure represents the role of two hormones, calcitonin and parathyroid hormone (PTH), in maintaining normal blood calcium levels in humans. If a dietary change results in an increase in blood calcium concentration above normal levels, which of the following is the most likely effect on calcium homeostasis? (A) Calcitonin levels will decline, thus stimulating the release of PTH. (B) Calcitonin levels will rise, thus promoting the deposit of calcium into bones. (C) PTH levels will decline, thus stimulating the loss of calcium from bones. (D) PTH levels will increase, thus preventing the release of calcitoninA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 60 60 | P a g e 155. Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6- bisphosphate during glycolysis, as represented in Figure 1. PFK can be allosterically inhibited by ATP at high concentrations. Which of the following is the benefit of regulating glycolysis by the concentration of ATP? (A) Glycolysis proceeds when the intracellular concentration of ATP is low, which provides ATP to drive cellular reactions. (B) Glycolysis proceeds when the intracellular concentration of ATP is high and the cell stores ATP for future use. (C) Glycolysis is inhibited when the intracellular concentration of ATP is low because PFK requires ATP as a substrate for the reaction it catalyzes. (D) Glycolysis is inhibited when the intracellular concentration of ATP is high because ATP will compete with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate for binding to the active site on the enzyme. 156. The graph above shows changes in glucagon and insulin secretions at different concentrations of blood glucose. Which of the following feedback mechanisms is best supported by the data? (A) A falling glucagon level causes a rise in the insulin level, which maintains equal amounts of both hormones in the blood. (B) A high glucagon level causes a rise in the insulin level, which maintains high levels of both hormones in the blood. (C) A low glucose level causes the release of glucagon, which stimulates the release of more glucose from tissues, which in turn lowers the amount of glucagon being released. (D) A low glucose level causes the release of insulin, which stimulates the release of more glucose from tissues, which in turn increases the amount of insulin being released.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 61 61 | P a g e 157. The diagram above represents a typical rod-shaped bacterium. Which of the following best describes a feature shown in the diagram that is unique to archaea and bacteria? (A) The organism is surrounded by a cell wall. (B) The organism contains ribosomes. (C) The organism does not have a nuclear membrane surrounding its genetic material. (D) The organism is not capable of making or providing itself with ATP. 158. Precise regulation of specific hormone levels is required for optimal sperm production in mammals, as summarized in the figure above. Anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) are synthetic variants of testosterone that are sometimes abused by persons who desire to enhance their athletic performance or alter their physique. Assuming that AAS function in the same way as naturally occurring testosterone, it is most likely that long-term abuse of AAS would (A) stimulate FSH secretion (B) stimulate testosterone production (C) stimulate LH secretion (D) reduce sperm productionA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 62 62 | P a g e 159. The figure above shows a series of microscope images taken over time of ovalbumin production in chick oviduct cells in response to stimulation with estrogen. The ovalbumin protein was detected using a fluorescent dye as shown by the white areas in the time-lapse sequence. The microscope images indicate that ovalbumin (A) is synthesized on soluble ribosomes and packaged into lysosomes, from which it is secreted into the oviduct (B) is synthesized on ribosomes bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and then secreted directly into the oviduct (C) crosses the endoplasmic reticulum membrane as it is translated, then moves to the Golgi apparatus, then to vesicles from which it is secreted (D) crosses the Golgi apparatus membrane post-translationally, is taken up by the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum, then is packaged into secretory vesicles 160. In an experiment, the efficiency of oxygen exchange across the plasma membrane is being assessed in four artificial red blood cells. The table above lists some properties of those artificial cells. Other conditions being equal, which artificial cell is predicted to be the most efficient in exchanging oxygen with the environment by diffusion? (A) The cuboidal cell (B) The tetrahedral cell (C) The cylindrical cell (D) The spherical cellA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 63 63 | P a g e 161. The figures below illustrate the similarities between ATP synthesis in mitochondria and chloroplasts. The figures can best assist in answering which of the following questions? (A) Do electron transport chains create a gradient so that ATP synthase can generate ATP molecules? (B) What are the sources of energy that drive mitochondrial and chloroplast electron transport systems? (C) What is the optimal temperature at which ATP synthase chemically converts ADP and a phosphate group into one molecule of ATP? (D) What is the evolutionary relationship between the ATP synthase in mitochondria and the ATP synthase in chloroplasts? 162. The function of which of the following organelles directly requires oxygen? (A) Ribosome (B) Mitochondria (C) Nucleus (D) Centriole (E) Golgi apparatusA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 64 64 | P a g e 163. Which of the following scientific questions is most relevant to the model represented in the figure above? (A) Is ATP required for the transportation of sugars across the outer mitochondrial membrane? (B) Do the types of phospholipids in a membrane affect the rate at which molecules enter a cell by passive diffusion? (C) Which molecular substance is actively transported across the plasma membrane? (D) How does temperature affect the movement of molecules into lysosomes? 164. The mechanism of action of many common medications involves interfering with the normal pathways that cells use to respond to hormone signals. Which of the following best describes a drug interaction that directly interferes with a signal transduction pathway? (A) A medication causes the cell to absorb more of a particular mineral, eventually poisoning the cell. (B) A medication enters the target cell and inhibits an enzyme that normally synthesizes a second messenger. (C) A medication enters the target cell’s nucleus and acts as a mutagen. (D) A medication interrupts the transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. 165. The organelle that is a major producer of ATP and is found in both heterotrophs and autotrophs is the (A) Chloroplast (B) Nucleus (C) Ribosome (D) Golgi apparatus (E) Mitochondrion 166. The following questions refer to an experiment that is set up to determine the relative volume of O2 consumed by germinating and nongerminating (dry) pea seeds at two different temperatures. The change in volume is detected by using a respirometer over a given period of time. The data are given below. The rate of oxygen consumption in germinating pea seeds at 26ºC is (A) 0.05 mL/min (B) 0.25 mL/min (C) 0.50 mL/min (D) 0.75 mL/min (E) 1.00 mL/minA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 65 65 | P a g e 167. The salinity of a small inland lake has recently started to increase. Researchers are planning to study the lake over several decades to investigate how freshwater organisms survive significant changes in their natural habitat. Which of the following physiological mechanisms will the researchers most likely observe among the surviving organisms in the lake? (A) Prokaryotic organisms will use various mechanisms to counteract swelling of cells as a result of increased water uptake. (B) Single-celled organisms will use various mechanisms to counteract the increased flow of water from cells to the environment. (C) Eukaryotic organisms will use various mechanisms to counteract the diffusion of positively charged ions across the cell membrane. (D) Multicellular organisms will use various mechanisms to counteract the loss of cell adhesion as a result of calcium deficiencies 168. The table below provides a comparison of nitrogenous waste production in selected organisms. Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data in the table? (A) In response to the hypotonic environment in which freshwater fish live, they excrete ammonia in concentrated urine or across their gills. (B) The kidneys of reptiles and birds are highly efficient because little water is needed to excrete uric acid. (C) Birds excrete ammonia in addition to uric acid, and the ratio of the two substances is independent of whether the birds are primarily terrestrial or aquatic species. (D) The similar regulation of extracellular fluid volume and composition in all the organisms suggests conservation of kidney structure throughout evolution.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 66 66 | P a g e 169. The diagram shows a developing worm embryo at the four-cell stage. Experiments have shown that when cell 3 divides, the anterior daughter cell gives rise to muscle and gonads and the posterior daughter cell gives rise to the intestine. However, if the cells of the embryo are separated from one another early during the four-cell stage, no intestine will form. Other experiments have shown that if cell 3 and cell 4 are recombined after the initial separation, the posterior daughter cell of cell 3 will once again give rise to normal intestine. Which of the following is the most plausible explanation for these findings? (A) A cell surface protein on cell 4 signals cell 3 to induce formation of the worm’s intestine. (B) The plasma membrane of cell 4 interacts with the plasma membrane of the posterior portion of cell 3, causing invaginations that become microvilli. (C) Cell 3 passes an electrical signal to cell 4, which induces differentiation in cell 4. (D) Cell 4 transfers genetic material to cell 3, which directs the development of intestinal cells 170. Protein digestion in humans is primarily carried out by three enzymes. Pepsin is found in the stomach (pH 2), where it aids in the breakdown of large proteins into smaller peptides, while trypsin and chymotrypsin are found in the small intestine (pH 8), where they aid in the further breakdown of the proteins into amino acids and dipeptides that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Graph 1 shows the effect of pH on the activity levels of the three enzymes. Graph 1. Relative activity of pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin at pH 0 through 11 Which of the following best predicts how the structure and function of pepsin will change as it enters the small intestine? (A) Pepsin will not change in shape and will continue to break down proteins in the small intestine. (B) Pepsin will not change in shape but may not work due to the basic environment of the small intestine. (C) Pepsin will change in shape because of the basic environment of the small intestine; therefore, its enzymatic activity will decrease. (D) Pepsin will change in shape because of the presence of trypsin and chymotrypsin in the small intestine, both of which act as competitive inhibitors.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 67 67 | P a g e 171. The coagulation cascade controls blood clot formation in response to blood vessel injury. Thrombin is an enzyme that plays a key role in regulating the coagulation cascade. A simplified model of thrombin’s role in regulating the coagulation cascade is represented in Figure 1. Figure 1. A simplified model of thrombin’s role in regulating the coagulation cascade Argatroban is a competitive inhibitor of thrombin. Which of the following effects on the coagulation cascade is most likely to result from inhibiting thrombin activity with argatroban? (A) The activation of clotting factors will be blocked. (B) The rate of fibrin formation will decrease. (C) Thrombin will be converted to prothrombin. (D) The rate of blood clot formation will increase 172. Thyroxin is a hormone that increases metabolic activities within various tissue targets. Low levels of circulating thyroxin trigger the secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary. TSH secretion then stimulates thyroxin production and release by the thyroid gland. The increased level of circulating thyroxin inhibits further secretion of TSH from the anterior pituitary. Based on the information provided, which of the following can most likely be concluded about the TSH-thyroxin loop? (A) A person taking thyroxin to supplement low thyroxin secretion will produce more TSH. (B) Increased thyroxin production would cause elevated ribosomal activity in the anterior pituitary. (C) The structure of the loop would lead to elevated thyroid and tissue activity due to positive feedback. (D) The feedback mechanism would maintain relatively constant levels of thyroxin throughout tissue targets.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 68 68 | P a g e 173. Researchers determined the average amount of time that a particular type of eukaryotic cell spends in each phase of the cell cycle. The data collected by the researchers are represented in Figure 1. Figure 1. The average amount of time spent by a particular type of eukaryotic cell in each phase of the cell cycle Based on Figure 1, what percent of the time required to complete a full cycle do the cells typically spend in interphase? (A) 5% (B) 35% (C) 50% (D) 95% 174. To test the hypothesis that a particular plant synthesizes storage lipids by using glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate (G3P) from photosynthesis, a researcher plans to use radiolabeled precursors to track the molecules through the biosynthetic pathway. Which of the following radiolabeled precursors is most appropriate for the researcher to use? (A) 15N-labeled N2, because atmospheric nitrogen is fixed to amino acids by photosynthesis (B) 14C-labeled CO2, because atmospheric carbon is fixed to carbohydrates by photosynthesis (C) 35S-labeled methionine, because amino acids are incorporated into lipids during photosynthesis (D) 32P-labeled phosphate, because lipids are stored in plants as phospholipids 175. A model of the plasma membrane showing several biological molecules, including a transmembrane protein, is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Phospholipid bilayer with transmembrane protein Which statement best explains why correct protein folding is critical in the transmembrane protein shown above? (A) Interactions of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids help to anchor the protein in the membrane. (B) Interactions of the peptide bonds of the protein with the membrane will affect the rate at which substances can cross the membrane. (C) Interactions of the protein and phospholipids increase membrane fluidity. (D) Interactions of the quaternary structure of the protein will increase hydrogen bonding in the membrane and make the membrane less fluid.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 69 69 | P a g e 176. Transmission of an action potential across a synapse involves the release of neurotransmitters by the presynaptic neuron. The arrival of the action potential triggers a rise in the calcium concentration in the synaptic terminal, and the change in concentration triggers a release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Which of the following representations of the movement of calcium, sodium, and potassium ions best shows how an action potential is transmitted to the postsynaptic neuron?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 70 70 | P a g e 177. Researchers have proposed a model of the process by which a newly synthesized protein is transported to the plasma membrane and secreted into the extracellular space. The model is represented in Figure 1. Figure 1. A model of the intracellular transport of a newly synthesized secreted protein Based on the model, the newly synthesized protein is transported directly from the endoplasmic reticulum to which of the following? (A) The nucleus (B) The plasma membrane (C) The Golgi complex (D) The extracellular space 178. Trypsinogen is split by the enzyme enterokinase to form an activated molecule of the protease trypsin. Which of the following would confirm that the activation of trypsin is an example of how a positive feedback mechanism can amplify a biological process? (A) The activated trypsin enzyme can use enterokinase as a substrate. (B) The trypsin produced by the reaction is capable of splitting and activating additional trypsinogen molecules. (C) If levels of trypsin were to get too high, the trypsin molecules would inhibit the enzyme enterokinase. (D) Each mRNA molecule that codes for trypsinogen can be translated repeatedly to form many peptide moleculesA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 71 71 | P a g e 179. Cystic fibrosis is a recessively inherited disorder that results from a mutation in the gene encoding CFTR chloride ion channels located on the surface of many epithelial cells. As shown in the figure, the mutation prevents the normal movement of chloride ions from the cytosol of the cell to the extracellular fluid. As a consequence of the mutation, the mucus layer that is normally present on the surface of the cells becomes exceptionally dehydrated and viscous. An answer to which of the following questions would provide the most information about the association between the CFTR mutation and the viscous mucus? (A) Is the mucus also secreted from the cells through the CFTR proteins? (B) How does the disrupted chloride movement affect the movement of sodium ions and water by the cell? (C) How does the mutation alter the structure of the CFTR proteins? (D) What is the change in nucleotide sequence that results in the CFTR mutation? 180. Two nutrient solutions are maintained at the same pH. Actively respiring mitochondria are isolated and placed into each of the two solutions. Oxygen gas is bubbled into one solution. The other solution is depleted of available oxygen. Which of the following best explains why ATP production is greater in the tube with oxygen than in the tube without oxygen? (A) The rate of proton pumping across the inner mitochondrial membrane is lower in the sample without oxygen. (B) Electron transport is reduced in the absence of a plasma membrane. (C) In the absence of oxygen, oxidative phosphorylation produces more ATP than does fermentation. (D) In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis produces more ATP than in the absence of oxygen. 181. Two types of cholesterol transport proteins, low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), bind to cholesterol and carry it through the bloodstream. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is characterized by high cholesterol levels in the blood, which can lead to cardiovascular disease. FH is associated with a loss-of-function mutation of a gene that encodes LDL receptors in liver cells. Individuals who are heterozygous produce lower-than-normal amounts of the LDL receptors, and individuals who are homozygous for the mutant allele have no LDL receptor function. Individuals with FH can be treated with drugs that result in increased production of LDL receptors in liver cells. Which of the following best explains the observation that the drugs can effectively control blood cholesterol levels in individuals who are heterozygous but are not effective in individuals homozygous for the mutant allele? (A) The drugs repair the mutant allele by copying the wild-type allele. (B) The drugs prevent cholesterol from entering the liver cells in individuals who are heterozygous but not in individuals who are homozygous for the mutant allele. (C) Cholesterol molecules primarily bind to HDL receptors in individuals with FH. (D) There must be at least one copy of the wild-type LDL receptor allele to produce functional LDL receptors.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 72 72 | P a g e 182. Type 1 diabetes results from the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals with type 1 diabetes produce insufficient amounts of insulin, a hormone that regulates the concentration of glucose in the blood. Which of the following best explains how treatment with a drug that stimulates the production of insulin receptors on target cells will affect the insulin signaling pathway in an individual with type 1 diabetes? (A) The drug will have little or no effect on the signaling pathway because the receptors will not be activated in the absence of insulin. (B) The drug will have little or no effect on the signaling pathway because insulin receptors will not be allowed to enter the cells. (C) The drug will restore the function of the signaling pathway because insulin levels will return to normal. (D) The drug will restore the function of the signaling pathway because nonpancreatic cells will begin to produce insulin receptors. 183. Which metabolic process is common to both aerobic cellular respiration and alcoholic fermentation? (A) Krebs cycle (B) Glycolysis (C) Electron transport chain (D) Conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA (E) Production of a proton gradient. 184. Which of the following best describes an advantage that eukaryote organisms have over prokaryote organisms? (A) Prokaryotes lack a cell membrane and therefore are unable to control what enters or exits the cell. (B) Eukaryotes have a nuclear envelope separating their DNA from the rest of the cell, which increases the likelihood of advantageous mutations. (C) Eukaryotes have mitochondria and chloroplasts that contain their own genome, which allows the cells to reproduce more rapidly. (D) Eukaryotes have organelles that allow for compartmentalization of cellular processes, which increases the efficiency of those processes. 185. Which of the following best describes the function of the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD in eukaryotic cellular respiration? (A) They participate in hydrolysis reactions by accepting protons from water molecules. (B) They participate directly in the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. (C) They serve as final electron acceptors in the electron transport chain. (D) They aid vitamins such as niacin in the breakdown of glucose. (E) They accept electrons during oxidation-reduction reactionsA P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 73 73 | P a g e 186. Which of the following best describes the role of mitosis in the cell cycle? (A) Distributing replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei (B) Dividing the cytoplasm to form four gametes (C) Producing organelles and replicating chromosomes (D) Exchanging genetic material between homologous chromosomes 187. Which of the following best explains how small molecules move between adjacent cells in a plant shoot? (A) The molecules are actively transported by motor proteins along the cytoskeleton. (B) The molecules pass freely through plasmodesmata, which are cytoplasmic strands connecting two cells. (C) The molecules are swept along in the extracellular fluid by cilia projecting from cell membranes. (D) The molecules bind reversibly to receptors on the cell membranes of xylem. 188. Which of the following best represents two different signaling pathways that share a second messenger?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 74 74 | P a g e 189. Which of the following best supports the statement that mitochondria are descendants of endosymbiotic bacteria-like cells? (A) Mitochondria and bacteria possess similar ribosomes and DNA. (B) Mitochondria and bacteria possess similar nuclei. (C) Glycolysis occurs in both mitochondria and bacteria. (D) Both mitochondria and bacteria have microtubules. (E) Neither mitochondria nor bacteria possess chloroplasts. 190. Which of the following components of the cell membrane is responsible for active transport? (A) Phospholipid (B) Protein (C) Lipid (D) Phosphate (E) Cholesterol 191. Which of the following describes a metabolic consequence of a shortage of oxygen in muscle cells? (A) An increase in blood pH due to the accumulation of lactic acid (B) No ATP production due to the absence of substrate-level phosphorylation (C) A buildup of lactic acid in the muscle tissue due to fermentation (D) A decrease in the oxidation of fatty acids due to a shortage of ATP 192. Students investigated the effect of light on the carbon cycle in aquatic ecosystems by performing the controlled experiment summarized below. The students placed equal amounts of water (pH 7.0) from a large aquarium in glass beakers. The students transferred aquatic plants from the aquarium to several of the beakers, and then they placed equal numbers of the beakers in the light or the dark (Figure 1: groups I and II). Similarly, the students transferred goldfish from the same aquarium to other beakers, and then they placed equal numbers of those beakers in the light or dark (Figure 1: groups III and IV). Finally, the students placed an equal number of beakers containing water only in the light or dark (Figure 1: groups V and VI) After exposing the samples to light or dark for one hour, the students recorded the pH of the water in each beaker. Carbon dioxide dissolved in water will lower the pH of an aqueous solution. In the experiment, the students used changes in pH to monitor changes in the amount of carbon dioxide in the water. For each treatment group, the students calculated the mean pH and standard error, as documented in the table below.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 75 75 | P a g e Which of the following graphs is the most appropriate representation of the experimental results documented in the table?A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 76 76 | P a g e 193. Which of the following is a characteristic of mitochondria and chloroplasts that supports the endosymbiotic theory? (A) Both have bacteria-like polysaccharide cell walls. (B) Both can reproduce on their own outside of the cell. (C) Both contain DNA molecules. (D) Both contain endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies. (E) Both contain ribosomes that are identical to ribosomes of the eukaryotic cytoplasm. 194. Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? (A) The light-dependent reactions occur only during the day; the light-independent reactions occur only during the night. (B) The light-dependent reactions occur in the cytoplasm; the light-independent reactions occur in chloroplasts. (C) The light-dependent reactions utilize CO2 and H2O; the light-independent reactions produce CO2 and H2O. (D) The light-dependent reactions depend on the presence of both photosystems I and II; the light-independent reactions require only photosystem I. (E) The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH. 195. Which of the following is most likely to create genetic variation in a population? (A) RNA polymerase errors during transcription (B) Helicase failure to unwind DNA during DNA replication (C) DNA polymerase errors during replication (D) Misincorporation of amino acids by tRNA during translation 196. Which of the following is responsible for the cohesive property of water? (A) Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms of two adjacent water molecules (B) Covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules (C) Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule (D) Covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule (E) Hydrogen bonds between water molecules and other types of molecules 197. Which of the following is true of mitosis? (A) It is also known as cytokinesis. (B) It maintains the same chromosome number in the daughter cells as in the parent cell. (C) It is the last phase of interphase. (D) It regulates the transfer of genetic information from one daughter cell to another. (E) It moves homologous chromosomes to opposite poles.A P B I O L O G Y P a g e | 77 77 | P a g e 198. Which of the following occurs in both meiosis and mitosis? (A) Separation of homologous chromosomes (B) Reduction of chromosome number (C) Separation of sister chromatids (D) Crossing-over between homologous chromosomes (E) Production of four daughter cells 199. Which of the following organelles modifies and packages for secretion the materials produced by the ribosomes? (A) The chloroplast (B) The Golgi apparatus (C) The nucleus (D) The nucleolus (E) The mitochondrion 200. Which of the following processes is most likely to occur as a result of an animal cell receiving a signal to initiate apoptosis? (A) Ribosomes will translate mRNA to produce proteins. (B) Vesicles will release extracellular growth factors via exocytosis. (C) Lysosomes will release digestive enzymes into the cytosol. (D) Vacuoles will fuse with the cellular membrane. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 77 pages
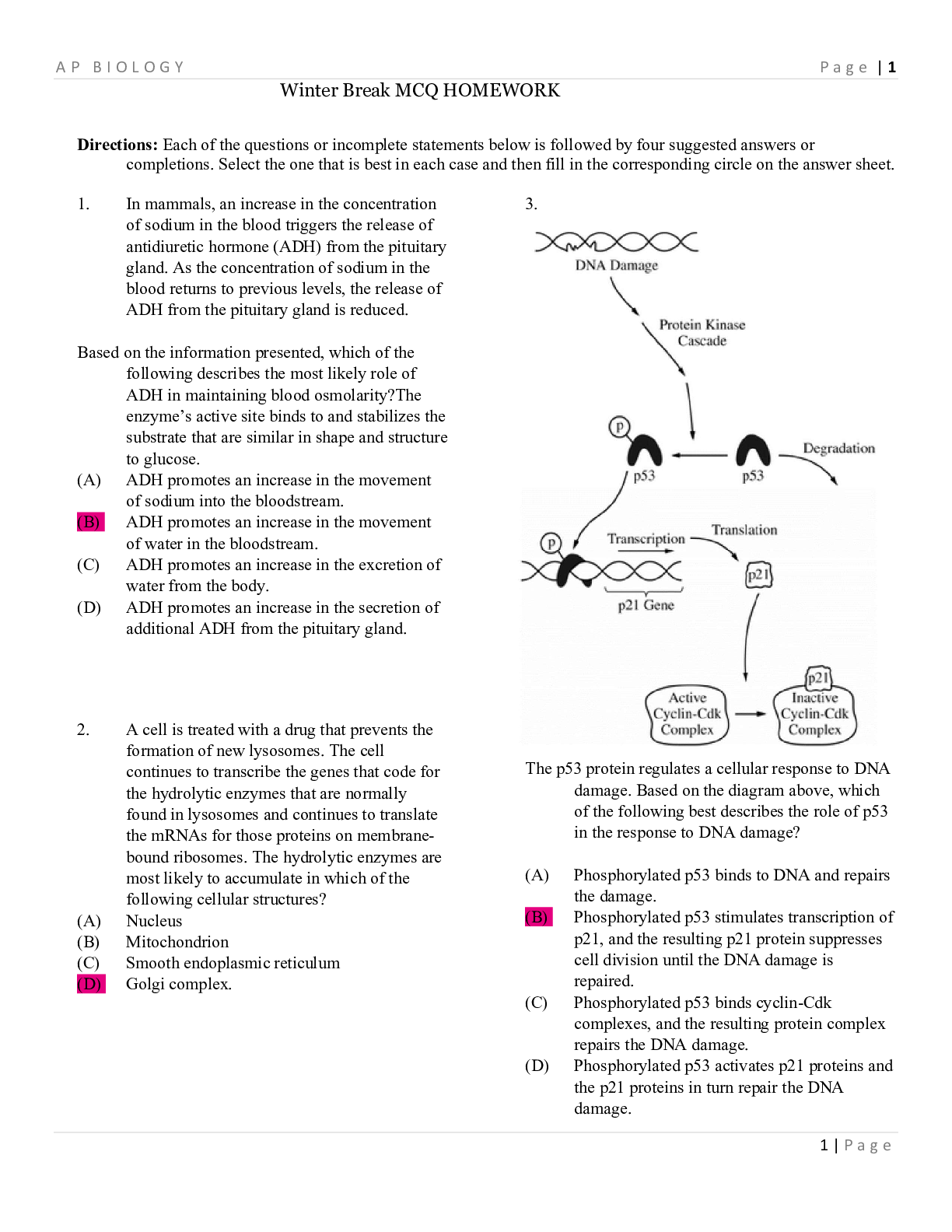
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 27, 2021
Number of pages
77
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 27, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
268
























