Name: Lucas Vale Total /65
Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
Vocabulary: dipole, dipole-dipole force, dipole-induced dipole force, electronegativity, intermolecular force, ionic bond, Lon
...
Name: Lucas Vale Total /65
Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
Vocabulary: dipole, dipole-dipole force, dipole-induced dipole force, electronegativity, intermolecular force, ionic bond, London dispersion force, molecule, nonpolar, nonpolar covalent bond, partial charges, polar, polar covalent bond, valence electron
Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
1. A big bully is having a tug-of-war with a small child. There is a ball attached to the middle of the rope.
Toward whom will the ball move? (1)The big bully
2. Two equally strong kids are having a tug-of-war. What do you expect to happen to the ball in this situation? (1) I expect the ball to not move and just stay in the middle
Gizmo Warm-up
Just like in a tug-of-war, atoms that are bonded to one another pull on the electrons they share. In the Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Gizmo, you will explore how these opposing forces relate to bond types and the forces between molecules.
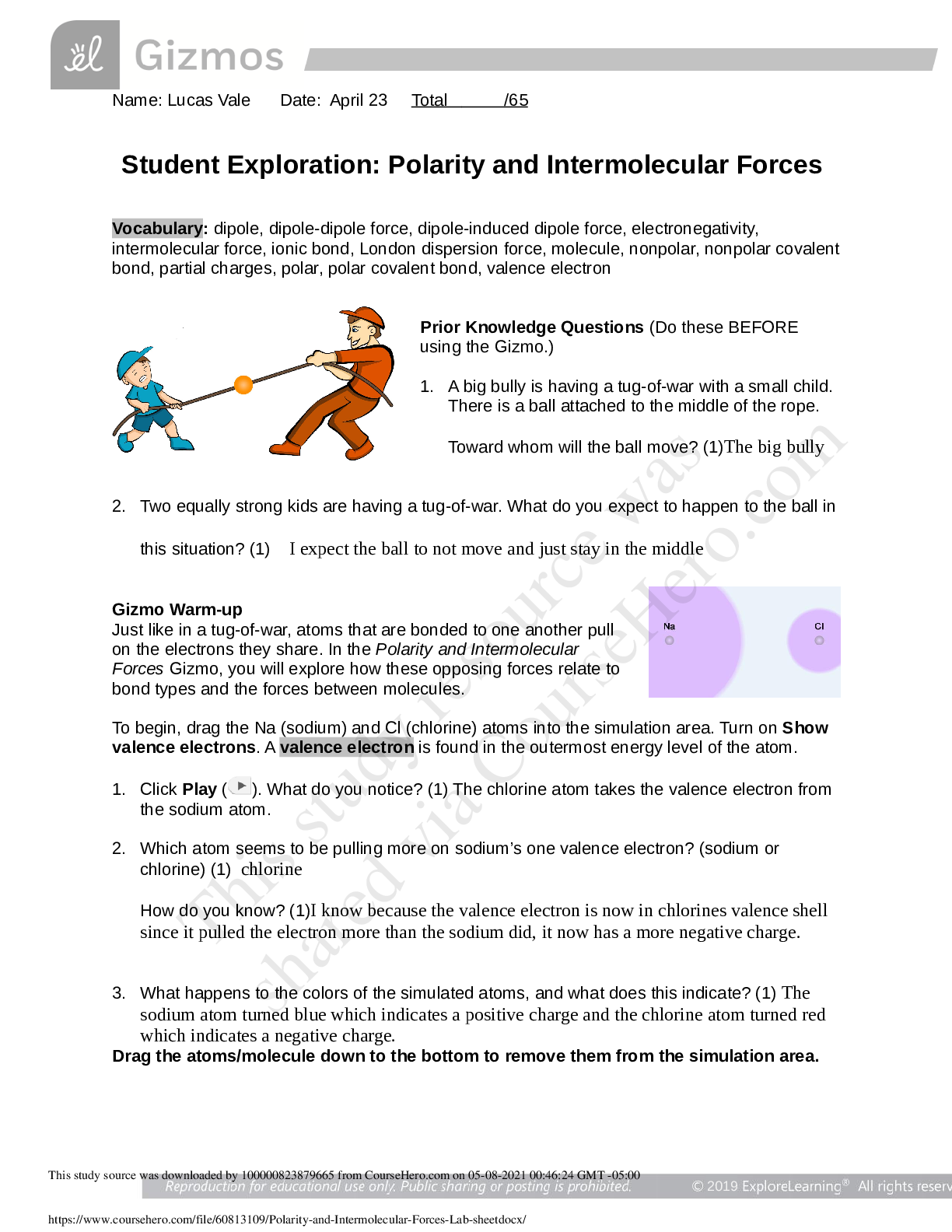
To begin, drag the Na (sodium) and Cl (chlorine) atoms into the simulation area. Turn on Show valence electrons. A valence electron is found in the outermost energy level of the atom.
1. Click Play ( ). What do you notice? (1) The chlorine atom takes the valence electron from the sodium atom.
2. Which atom seems to be pulling more on sodium’s one valence electron? (sodium or chlorine) (1) chlorine
How do you know? (1)I know because the valence electron is now in chlorines valence shell since it pulled the electron more than the sodium did, it now has a more negative charge.
3. What happens to the colors of the simulated atoms, and what does this indicate? (1) The sodium atom turned blue which indicates a positive charge and the chlorine atom turned red which indicates a negative charge.
Drag the atoms/molecule down to the bottom to remove them from the simulation area.
This study source was downloaded by 100000815948112 from CourseHero.com on 04-30-2021 00:41:04 GMT -05:00
2019
Introduction: A neutral atom has the same number of protons as electrons. Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged, while those that lose electrons become positive. A polar bond forms when shared electrons are pulled closer to one atom than another, causing the bonded atoms to become partially charged. In a nonpolar bond, electrons are shared equally.
Question: What causes bonds to be polar or nonpolar?
,....................................................................continued..........................................................................................................
[Show More]