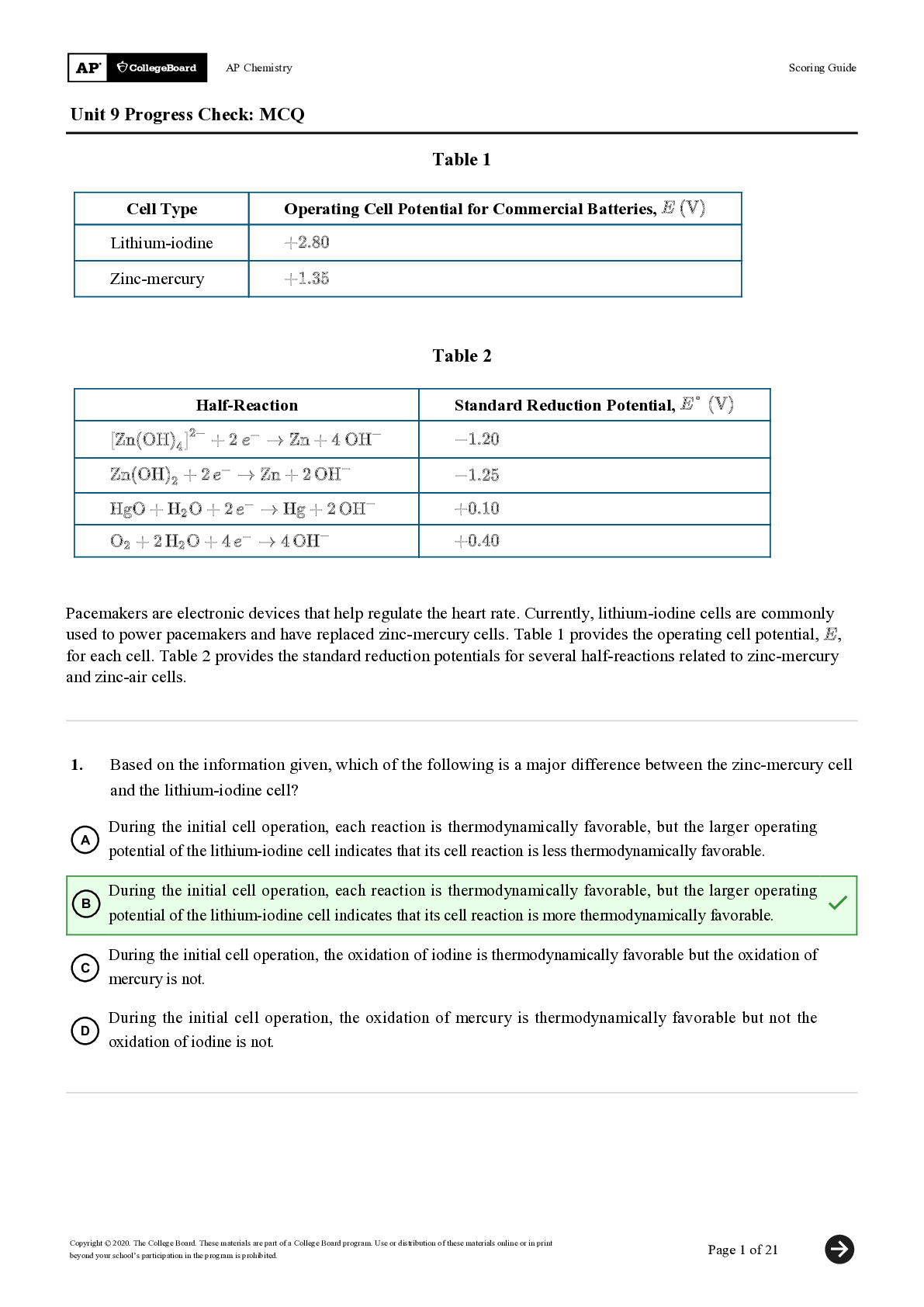
Engineering > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > George Washington University<ECE 3820<unit_6_ps1_airways_and_alveolar_gas_exchange_answer_key-REVIEW (All)
George Washington University<ECE 3820<unit_6_ps1_airways_and_alveolar_gas_exchange_answer_key-REVIEWED BY EXPERTS-ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
PROBLEM SET 6.1: AIRWAY RESISTANCE AND ALVEOLAR GAS EXCHANGE ANSW ER KEY 1. The density of Hg is 13.6 g cm3 and the acceleration due to gravity is 981 cm s-2. Convert the pressure exerted by a colu... mn of Hg 1 mm high to Pascals, N m-2. If the atmospheric pressure on top of a 3000 m peak is 527 mm Hg, what is it in Pascals? The pressure exerted by a column of Hg is its gravitational force divided by its area. For a column of Hg 1 mm high with a cross-sectional area A, the gravitational force on the column downward is F = m x g where g is the acceleration due to gravity = 981 cm s-2. The mass of the column of Hg is just its density times the volume. Thus m = DV = D x A x h, where D = 13.6 g cm-3 is the density, A is the area and h is the height, which is 1 m m in this case. The pressure is P = F/A = (m x g) / A = (D x A x h x g)/A = D x g x h So the pressure of a 1 mm colum n of Hg is P = 13.6 g cm-3 x 981 cm s-2 x 0.1 cm = 1334.2 g cm s-2 cm-2 = 1334.2 dyne cm-2 The unit of dyne in the cgs system is not part of ISI; It is converted to N (kg m s-2) by multiplying by 10-5 N dyne-1 ; converting from cm-2 to m-2 requires multiplying by 104 cm2 m-2 ; This gives P = 133.4 N m-2 = 133.4 Pa As the equivalent measure of 1 mm Hg: 1 mm Hg = 133.4 Pa If atmospheric pressure at the top of a 3000 m peak is 527 mm Hg, then this is equivalent to 527 mm Hg x 133.4 N m -2 mm Hg-1 = 70302 N m-2 = 70302 Pa 2. A. The typical diameter of an alveolus is about 0.3 mm . If there are 300 x 106 alveoli in the lungs calculate the approximate area for gas exchange, assuming that the alveoli are spheres. The surface area of a single alveolus given that it approximates a sphere and its diameter is 0.3 mm = 0.3 x 10-3 m, is A = 4 x B x r2 = 4 x B x [0.15 x 10-3 m]2 = 2.82 x 10-7 m2 The total area is the area per alveolus times the number of alveoli, which is 300 x 106; thus the total area is Total Area = 2.82 x 10-7 m -2 x 300 x 106 = 84.8 m2 [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 07, 2021
Number of pages
11
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 07, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
80








.png)

.png)


.png)



.png)


.png)




