Pathophysiology > EXAM > Pathophysiology Midterm Quiz 1: Questions and Answers (LATEST 2021 Exam) (All)
Pathophysiology Midterm Quiz 1: Questions and Answers (LATEST 2021 Exam)
Document Content and Description Below
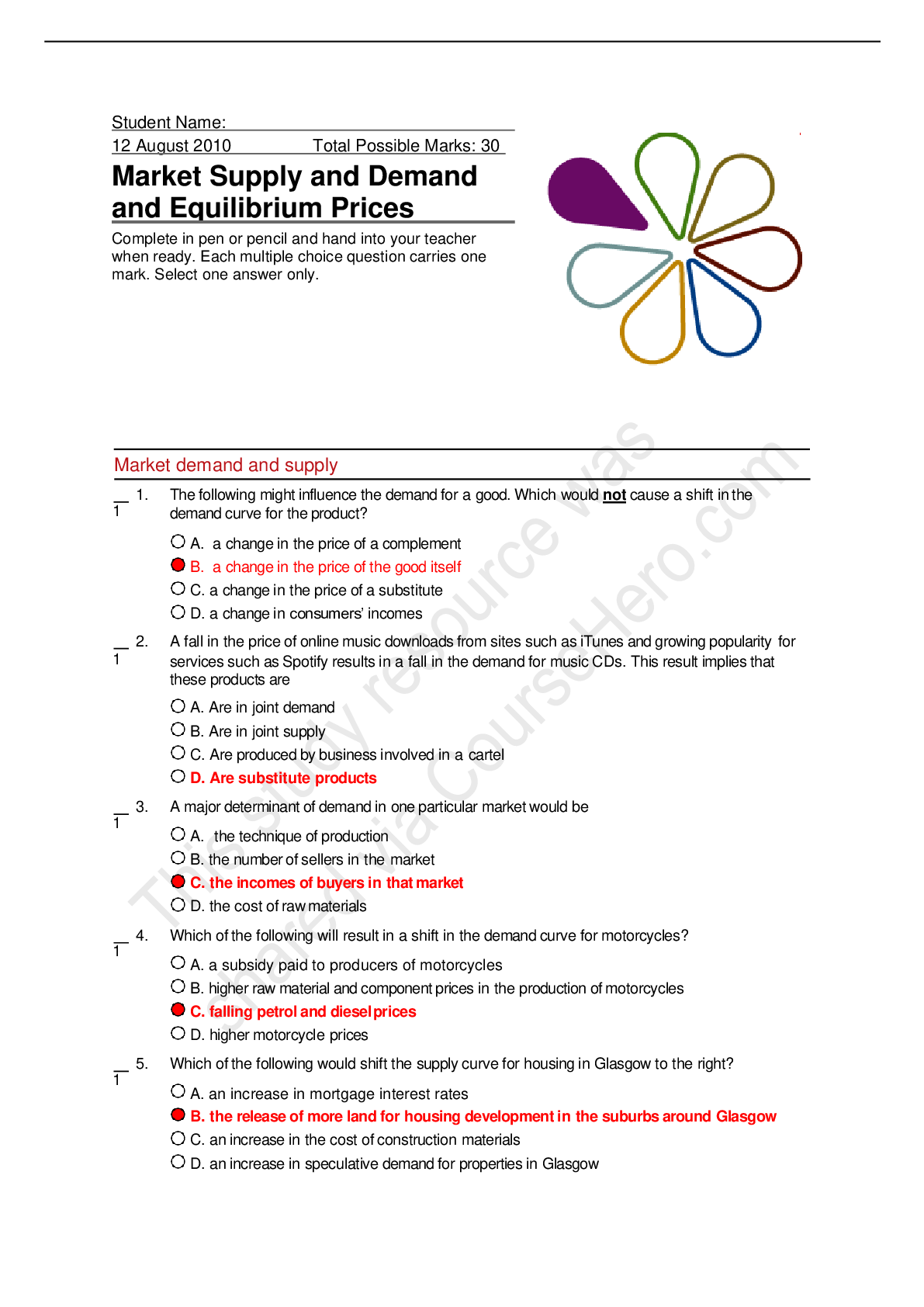
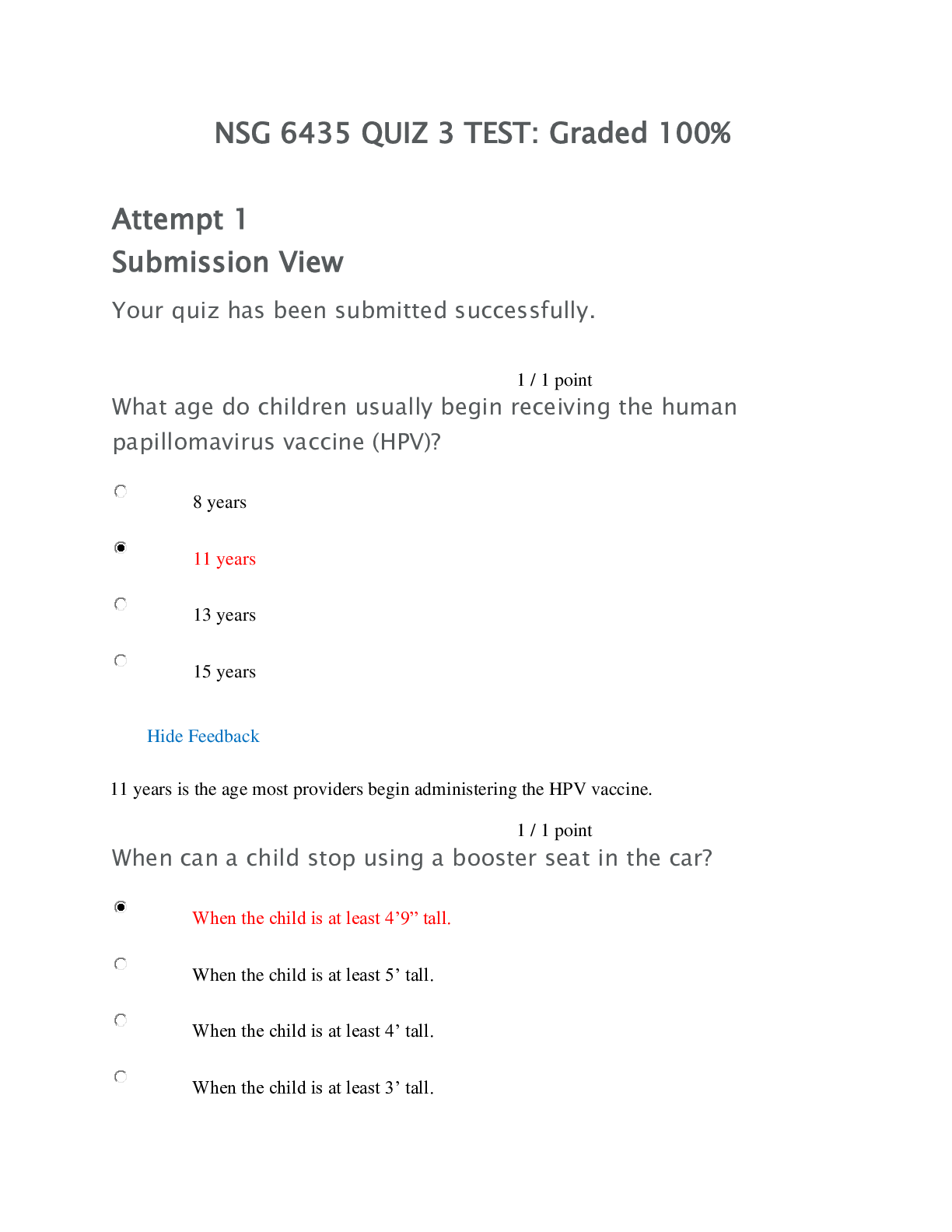
Patho Midterm Quiz 1 A change in a tissue marked by cells that vary in size and shape and show increased mitotic figures would be called: ❖ metaplasia. ❖ Atrophy. ❖ dysplasia. ❖ hyper ... trophy. A situation when there is a higher than expected number of cases of an infectious disease within a given area is called a/an: ❖ epidemic. ❖ exacerbation. ❖ morbidity. ❖ pandemic. Which of the following conditions distinguishes double blind studies used in health research? ❖ Neither the members of the control group or the experimental group nor the person administering the treatment knows who is receiving the experimental therapy. ❖ Both groups of research subjects and the person administering the treatment know who is receiving the experimental therapy. ❖ The research subjects do not know, but the person administering the treatment knows who is receiving placebo or standard therapy. ❖ Only members of the control group know they are receiving standard therapy. Which of the following can cause cell injury or death? 1. Hypoxia 2. Exposure to excessive cold 3. Excessive pressure on a tissue 4. Chemical toxins ❖ 1, 2 ❖ 2, 4 ❖ 1, 3, 4 ❖ 1, 2, 3, 4 A collection of signs and symptoms, often affecting more than one organ or system, that usually occur together in response to a certain condition is referred to as a (an): ❖ acute disease. ❖ multiorgan disorder. ❖ syndrome. ❖ manifestation. An abscess contains: ❖ serous exudate. ❖ purulent exudate. ❖ fibrinous exudate. ❖ hemorrhagic exudate. In normal capillary exchange, what is net hydrostatic pressure based on? ❖ The difference between the hydrostatic pressure within the capillary, as compared with the hydrostatic pressure of the interstitial fluid ❖ The relative osmotic pressures in the blood and the interstitial fluid ❖ The difference between the hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure within the capillary ❖ The difference between the concentrations of blood cells, plasma proteins, and dissolved substances in the blood and the interstitial fluid A burn area in which the epidermis and part of the dermis is destroyed is classified as: ❖ full-thickness. ❖ deep partial-thickness. ❖ superficial partial-thickness. ❖ first-degree. All of the following are factors that promote healing EXCEPT: ❖ good nutrition: protein, vitamins A and C. ❖ a clean, undisturbed wound. ❖ effective circulation. ❖ advanced age. Purulent exudates usually contain: ❖ small amounts of plasma protein & histamine in water. ❖ red blood cells & all types of white blood cells. ❖ numerous leukocytes, bacteria, and cell debris. ❖ large amounts of water containing a few cells. Causes of inflammation include: ❖ direct physical damage such as cuts and sprains. ❖ allergic reactions. ❖ infection. ❖ All the above Glucocorticoids are used to treat inflammation because they directly: ❖ promote the release of prostaglandins at the site. ❖ decrease capillary permeability. ❖ mobilize lymphocytes and neutrophils. ❖ prevent infection. Purulent exudates usually contain: ❖ small amounts of plasma protein & histamine in water. ❖ red blood cells & all types of white blood cells. ❖ numerous leukocytes, bacteria, and cell debris. ❖ large amounts of water containing a few cells. The characteristic appearance of a full-thickness burn is: ❖ painful with multiple blisters. ❖ heavy bleeding. ❖ red with some swelling. ❖ dry, firm, charred, or hard white surface. Identify the correct statement about burns: ❖ The severity of the burn depends on the temperature, duration, and extent of the burn. ❖ Young children are less likely to suffer severe burns from immersion in excessively hot water. ❖ Burns to the palms of the hands are more damaging than burns on the face. ❖ With a major burn, excessive bleeding usually causes shock. The term homeostasis refers to: ❖ the causative factors in a particular disease. ❖ maintenance of a stable internal environment. ❖ a condition that triggers an acute episode. ❖ a collection of signs and symptoms. The term disease refers to: ❖ the period of recovery and return to a normal healthy state. ❖ a deviation from the normal state of health and function. ❖ the treatment measures used to promote recovery. ❖ a basic collection of signs and symptoms. A circumstance that causes a sudden acute episode of a chronic disease to occur is termed: ❖ latent stage. ❖ predisposing factor. ❖ incidence. ❖ precipitating factor. Which of the following is the best definition of epidemiology? ❖ The science of tracking the occurrence and distribution of diseases ❖ The relative number of deaths resulting from a particular disease ❖ Identification of a specific disease through evaluation of signs and symptoms ❖ The global search for emerging diseases Which of the following would be the most likely cause of an iatrogenic disease? ❖ An inherited disorder ❖ A combination of specific etiological factors ❖ An unwanted effect of a prescribed drug ❖ Prolonged exposure to toxic chemicals in the environment Quiz 2: Which of the following hormonal imbalances causes myxedema? ❖ Increased glucocorticoids ❖ Decreased glucocorticoids ❖ Deficit of ADH ❖ Deficit of T3 and T4 The anterior pituitary gland secretes all of the following hormones EXCEPT: ❖ prolactin (PRL). ❖ glucagon. ❖ adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ❖ growth hormone (GH). Which of the following does NOT apply to inappropriate ADH syndrome? ❖ The cause is excess ADH secretion. ❖ Severe hyponatremia results. ❖ Excessive sodium is retained. ❖ Fluid retention increases. What causes loss of consciousness in a person with diabetic ketoacidosis? ❖ Toxic effects of excessive insulin ❖ Excessive glucose in the blood ❖ Metabolic acidosis ❖ Lack of glucose in brain cells Which of the following applies to diabetic macro-angiography? 1. It affects the small arteries and arterioles. 2. It is related to elevated serum lipids. 3. It leads to increased risk of myocardial infarction and peripheral vascular disease. 4. It frequently causes damage to the kidneys. ❖ 1, 3 ❖ 1, 4 ❖ 2, 3 ❖ 2, 4 Which of the following is an effect of Addison’s disease? ❖ Elevated blood glucose levels ❖ High blood pressure ❖ Low serum potassium levels ❖ Poor stress response How do many oral hypoglycemic drugs act? ❖ To replace insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) ❖ To transport glucose into body cells ❖ To prevent gluconeogenesis ❖ To stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin Goiters may be caused by: ❖ hypothyroid conditions only. ❖ either hypothyroid or hyperthyroid conditions. ❖ hyperthyroid conditions only. ❖ fungal infections such as candidiasis. Differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes include which of the following? ❖ Type 1 diabetes weight gain is common, and type 2 weight loss often occurs. ❖ Type 1 diabetes leads to fewer complications than does type 2 diabetes. ❖ Type 1 diabetes may be controlled by adjusting dietary intake and exercise, but type 2 diabetes requires insulin replacement. ❖ Type 1 diabetes occurs more frequently in children and adolescents, and type 2 diabetes occurs more often in adults. Which of the following applies to acromegaly? ❖ It occurs in infants and children. ❖ It causes excessive longitudinal bone growth. ❖ It results from excessive secretion of growth hormone (GH). ❖ It does not change soft tissue growth. All these tissues use glucose without the aid of insulin EXCEPT: ❖ liver. ❖ digestive system. ❖ exercising skeletal muscle. ❖ brain. Metabolic syndrome is marked by: ❖ abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism. ❖ periodic hypotension. ❖ deficit of glucagon. ❖ early onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus. What is the most common cause of type 1 diabetes mellitus? ❖ Increased glucose production in the liver ❖ Destruction of pancreatic cells by an autoimmune reaction ❖ Increased resistance of body cells to insulin action ❖ Chronic obesity What causes loss of consciousness in a person with diabetic ketoacidosis? ❖ Toxic effects of excessive insulin ❖ Excessive glucose in the blood ❖ Metabolic acidosis ❖ Lack of glucose in brain cells Which of the following results from a deficit of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? ❖ Inappropriate ADH syndrome ❖ Gigantism ❖ Diabetes insipidus ❖ Myxedema The anterior pituitary gland secretes all of the following hormones EXCEPT: ❖ prolactin (PRL). ❖ glucagon. ❖ adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ❖ growth hormone (GH). Catabolic effects of Cushing’s syndrome include: ❖ osteoporosis. ❖ hypertension. ❖ increased erythrocyte production. ❖ moon face and buffalo hump. Early signs of hyperglycemia include polyphagia, which means: ❖ thirst. ❖ increased urine output. ❖ hunger. ❖ glucose in the urine. A type of diabetes that may develop during pregnancy and disappear after delivery is called: ❖ temporary maternal diabetes. ❖ fetal diabetes. ❖ acute developmental diabetes. ❖ gestational diabetes. Which of the following hormonal imbalances causes Addison’s disease? ❖ Increased glucocorticoids ❖ Decreased glucocorticoids ❖ Deficit of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) ❖ Deficit of T3 and T4 Quiz 3: Malignant brain tumors: ❖ metastasize quickly to all parts of the body. ❖ spread first to lungs and bone. ❖ spread to other parts of CNS. ❖ do not metastasize anywhere at any time. Which of the following is a characteristic of a benign tumor? ❖ It is unencapsulated and invasive. ❖ It consists of undifferentiated cells. ❖ It exerts systemic effects. ❖ Cells appear relatively normal. The most critical adverse effects of chemotherapy and radiation therapy are: ❖ thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. ❖ headache and lethargy. ❖ nausea and constipation. ❖ alopecia and weight loss. Drugs or agents that augment the natural immune response in the body to improve identification and removal of abnormal cells are called: ❖ biological response modifiers. ❖ angiogenesis stimulators. ❖ analgesic complements. ❖ targeted receptor modifiers. Select the correct pair representing a malignant tumor and its marker: ❖ colon cancer: carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) ❖ hepatic cancer: CA125, AFP ❖ prostate cancer: human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) ❖ testicular cancer: Philadelphia chromosome What is an example of a multifactorial congenital disorder? ❖ Type AB blood ❖ Down syndrome ❖ Color blindness ❖ Cleft lip and palate Down syndrome is an example of a/an: ❖ autosomal dominant disorder. ❖ multifactorial disorder. ❖ developmental defect. ❖ chromosomal disorder. Developmental disorders can result from all the following EXCEPT: ❖ exposure to radiation. ❖ mercury in foods and water. ❖ drugs and alcohol. ❖ folic acid. The most invasive prenatal screening test for fetal abnormalities is: ❖ ultrasonography. ❖ amniocentesis. ❖ X-ray. ❖ blood tests. Which of the following statements applies to Huntington’s disease? ❖ The effects are obvious at birth. ❖ There is a test for the defective gene. ❖ There is a 50% probability that the child of an affected parent will be a carrier. ❖ The child must inherit the defective gene from both parents in order to be affected. A person with sickle cell trait that is heterozygous has: ❖ an incomplete dominant gene. ❖ a multifactorial condition. ❖ co-dominant genes. ❖ X-linked dominant trait. Down syndrome is an example of a/an: ❖ autosomal dominant disorder. ❖ multifactorial disorder ❖ developmental defect. ❖ chromosomal disorder. Vomiting frequently follows a chemotherapy treatment because: ❖ the gastrointestinal tract is irritated. ❖ the chemicals stimulate the emetic center. ❖ the drugs have an unpleasant odor. ❖ A and B Identify the common dose-limiting factor for chemotherapy: ❖ Alopecia ❖ Bone marrow depression ❖ Nausea and vomiting ❖ Weight loss Which of the following does paraneoplastic syndrome refer to? ❖ The effects of substances such as hormones secreted by the tumor cells ❖ Severe weight loss and cachexia associated with advanced cancer ❖ The decreased resistance to infection resulting from malignant tumors ❖ The effects of multiple metastatic tumors The common local effects of an expanding tumor mass include: 1. obstruction of a tube or duct. 2. anemia and weight loss. 3. cell necrosis and ulceration. 4. tumor markers in the circulation. ❖ 1, 2 ❖ 1, 3 ❖ 2, 4 ❖ 3, 4 A warning sign of possible cancer would be any of the following EXCEPT: ❖ persistent, unusual bleeding. ❖ a change in bowel habits. ❖ sudden development of fever, nausea, and diarrhea. ❖ a change in shape, color, or surface of a skin lesion. The purpose of the Human Genome Project was to: ❖ map the nucleotide sequence and identify the genes on each human chromosome. ❖ study the common patterns of inheritance of single-gene disorders. ❖ manipulate the sequence of DNA in microorganisms and animals. ❖ identify spontaneous alterations in genetic material caused by teratogens. A mother is a carrier of Duchenne muscular dystrophy; the father is unaffected. They have one son with muscular dystrophy. Another male child is expected. The probability of the second son having muscular dystrophy is: ❖ 100% ❖ 50% ❖ 25% ❖ 0% Which of the following are common manifestations of Down syndrome?1. Congenital heart defect 2. Cleft lip and palate 3. Large protruding tongue 4. Limited intellectual development ❖ 1, 2 ❖ 1, 3 ❖ 2, 4 ❖ 1, 3, 4 Quiz 4: What is a sign of a dislocation? ❖ Crepitus ❖ Pain and tenderness ❖ Increased range of motion at a joint ❖ Deformity at a joint Ankylosis and deformity develop in rheumatoid arthritis because: ❖ skeletal muscle hypertrophies. ❖ fibrosis occurs in the joint. ❖ replacement cartilage changes alignment. ❖ ligaments and tendons shorten. The type of compound fracture in which there are multiple fracture lines and bone fragments is referred to as a/an: ❖ compression fracture. ❖ greenstick fracture. ❖ simple fracture. ❖ comminuted fracture. One factor that is responsible for increasing the mortality rate among patients suffering with necrotizing fasciitis is: ❖ a delay in initial diagnosis. ❖ lack of proper antibiotics. ❖ the appearance of additional opportunistic infections. ❖ secondary fungal infections. Why do secondary infections frequently develop in pruritic lesions? ❖ Loss of protective sebum ❖ Entry of resident flora while scratching the lesion ❖ Blockage of sebaceous glands ❖ Increased sweat production All of the following statements apply to malignant melanoma EXCEPT: ❖ The malignant cell is a melanocyte. ❖ They present as non-pruritic purplish macules. ❖ The neoplasm grows rapidly and metastasizes early. ❖ The lesion is usually dark or multicolored with an irregular border. Choose the correct match of the skin condition and its usual location. ❖ Scabies—fingers, wrists, waist ❖ Impetigo—legs, feet ❖ Pediculus humanus corporis—scalp ❖ Seborrheic keratosis—feet, hands Which of the following statements regarding acute necrotizing fasciitis is TRUE? ❖ Infection is localized in a small area of the epidermis. ❖ It is usually caused by S. aureus. ❖ Spontaneous recovery usually occurs in 48 hours. ❖ Infection rapidly causes extensive tissue necrosis and toxic shock. Therapeutic measures for osteoporosis include: ❖ non–weight-bearing exercises. ❖ dietary supplements of calcium and vitamin D. ❖ transplants of osteoblasts. ❖ avoidance of all hormones. How does the joint appear during an exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis? ❖ Relatively normal ❖ Enlarged, firm, crepitus with movement ❖ Deformed, pale, and nodular ❖ Red, warm, swollen, and tender to touch A diagnostic test that measures the electrical charge of muscle contraction and can help differentiate muscle disorders from neurological disease is a/an: ❖ electromyogram. ❖ arthroscopy. ❖ radiograph. ❖ electroencephalograph. Fluid-filled sacs composed of synovial membrane located between structures such as tendons and ligaments and act as additional cushions are called: ❖ articular capsules. ❖ bursae. ❖ synovial sacs. ❖ hyaline chambers. What is a common outcome of fibrosis, calcification, and fusion of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis? ❖ Damage to the spinal nerves and loss of function ❖ Frequent fractures of long bones ❖ Impaired heart function ❖ Rigidity, postural changes, and osteoporosis Which of the following cells produce new bone? ❖ Osteocytes ❖ Osteoblasts ❖ Osteoclasts ❖ Stem cells from the bone marrow Joints affected by osteoarthritis can sometimes affect healthy joints by: ❖ causing enzymes to be released that travel to other joints. ❖ bacteria traveling from the affected join to a healthy one through the bloodstream. ❖ inflammation and edema affecting the entire limb. ❖ the affected individuals exerting stress on the normal joint to protect the damaged one. The cause of contact dermatitis can often be identified by: ❖ using a culture and sensitivity test on the exudate. ❖ checking the frequency of the exacerbations. ❖ noting the location and size of the lesion. ❖ the type of pain associated with the lesion. What is the common signal that a recurrence of herpes simplex infection is developing? ❖ Severe pain around the mouth ❖ Malaise and fatigue ❖ Fever and severe headaches ❖ Mild tingling along the nerve or on the lips Which of the following statements regarding acute necrotizing fasciitis is TRUE? ❖ Infection is localized in a small area of the epidermis. ❖ It is usually caused by S. aureus. ❖ Spontaneous recovery usually occurs in 48 hours. ❖ Infection rapidly causes extensive tissue necrosis and toxic shock. What is a raised, thin-walled lesion containing clear fluid called? ❖ Papule ❖ Pustule ❖ Vesicle ❖ Macule Which of the following areas lacks blood vessels and nerves? ❖ Epidermis ❖ Dermis ❖ Subcutaneous tissue ❖ Fatty tissue Quiz 5: How does a depressed skull fracture cause brain damage? ❖ A bone fragment penetrates and tears brain tissue. ❖ A section of the skull is missing, leaving the brain unprotected. ❖ A section of skull bone is displaced below the level of the skull, causing pressure on the brain. ❖ Many fracture lines are present, causing instability. ❖ The contrecoup injury is the cause of brain damage. Which type of seizure commonly occurs in children? ❖ Absence ❖ Tonic-clonic ❖ Focal ❖ Complex partial What causes a herniated intervertebral disc? ❖ A tear in the nucleus pulposus ❖ A protrusion of the nucleus pulposus through the annulus fibrosus ❖ Displacement of the annulus fibrosus between the laminae ❖ Failure of the spinous processes to restrict movement of the intervertebral disc What is the pathophysiological change in Parkinson’s disease? ❖ Degeneration of motor fibers in the pyramidal tracts ❖ Excess secretion of stimulatory neurotransmitters in the CNS ❖ Degeneration of the basal nuclei with a deficit of dopamine ❖ Deficit of acetylcholine and degeneration of the motor cortex in the frontal lobe Which of the following is characteristic of generalized seizures? ❖ The localization of the seizure activity ❖ The uncontrolled discharge of neurons in both hemispheres ❖ Seizures that persist for several hours ❖ Loss of consciousness and all motor function In cases of noncommunicating hydrocephalus, why does excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulate? ❖ Absorption of CSF through the arachnoid villi is impaired. ❖ Excessive amounts of CSF are produced in the ventricles. ❖ An obstruction is present in the aqueduct of Sylvius or other channel. ❖ Flow around the spinal cord is blocked. Which statement is TRUE about tetanus infection? ❖ It is caused by a virus. ❖ Infection usually develops in deep puncture wounds. ❖ It causes flaccid skeletal muscles, impairing mobility. ❖ It affects peripheral nerves initially in the legs and feet. Which of the following causes papilledema? ❖ Increased pressure of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at the optic disc ❖ Increased intraocular pressure ❖ Pressure on the oculomotor nerve ❖ Pressure on the optic chiasm Which of the following conditions is NOT part of the criteria for a declaration of “brain death”? ❖ No activity on EEG ❖ Absence of all reflexes ❖ No spontaneous respirations ❖ Presence of any head injury Typical signs of a TIA include: ❖ rapidly increasing intracranial pressure. ❖ loss of consciousness. ❖ transient muscle weakness in a hand or leg. ❖ headache, photophobia, and nuchal rigidity. Failure of the spinous processes to fuse, but without herniation of the meninges, is called: ❖ spina bifida occulta. ❖ meningocele. ❖ myelomeningocele. ❖ encephalocele. Following a spinal injury at C5, what is the expected effect during the period of spinal shock? ❖ Spastic paralysis below the level of the injury ❖ Urinary incontinence ❖ Possible periods of apnea ❖ Normal blood pressure Which of the following applies to the corticospinal tract? ❖ It is an ascending tract. ❖ The nerve fibers conduct sensory impulses. ❖ It is an extrapyramidal tract. ❖ It is a pyramidal tract for efferent impulses. Where are b1-adrenergic receptors located? ❖ Bronchiolar walls ❖ Arteriolar walls ❖ Cardiac muscle ❖ Glands of the intestinal tract In a case of bacterial meningitis, where does swelling and purulent exudate form? ❖ In the pia mater, arachnoid, and surface of the entire brain ❖ In the dura mater and epidural space ❖ At the site of the injury or entry point of the microbes ❖ Primarily around the spinal cord What is the best definition of aphasia? ❖ The inability to comprehend or express language appropriately ❖ Difficulty swallowing ❖ Loss of the visual field contralateral to the area of damage ❖ The inability to articulate words clearly In which disorders do biochemical abnormalities involving the neurotransmitters in the brain occur? 1. Bipolar disorder 2. Schizophrenia 3. Huntington’s disease 4. AIDS dementia ❖ 1, 3 ❖ 1, 4 ❖ 1, 2, 3 ❖ 2, 3, 4 Which of the following statements is TRUE about malignant brain tumors? ❖ Most brain tumors arise from malignant neurons. ❖ Primary brain tumors rarely metastasize outside the CNS. ❖ The blood-brain barrier prevents secondary brain tumors. ❖ Brainstem tumors do not manifest signs until they are quite large. Which statement does NOT apply to the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis? ❖ Demyelination of axons ❖ It affects the brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves ❖ It affects motor, sensory, and autonomic fibers ❖ Progressive random degeneration of peripheral nerves From the following, choose the two events (in correct sequence) that immediately follow the aura during a tonic-clonic event: ❖ Prodromal signs, then the clonic stage ❖ Clonic stage, then the tonic stage ❖ Loss of consciousness, then the tonic stage ❖ Loss of consciousness and cessation of respiration [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 15, 2021
Number of pages
23
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 15, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
90






 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)