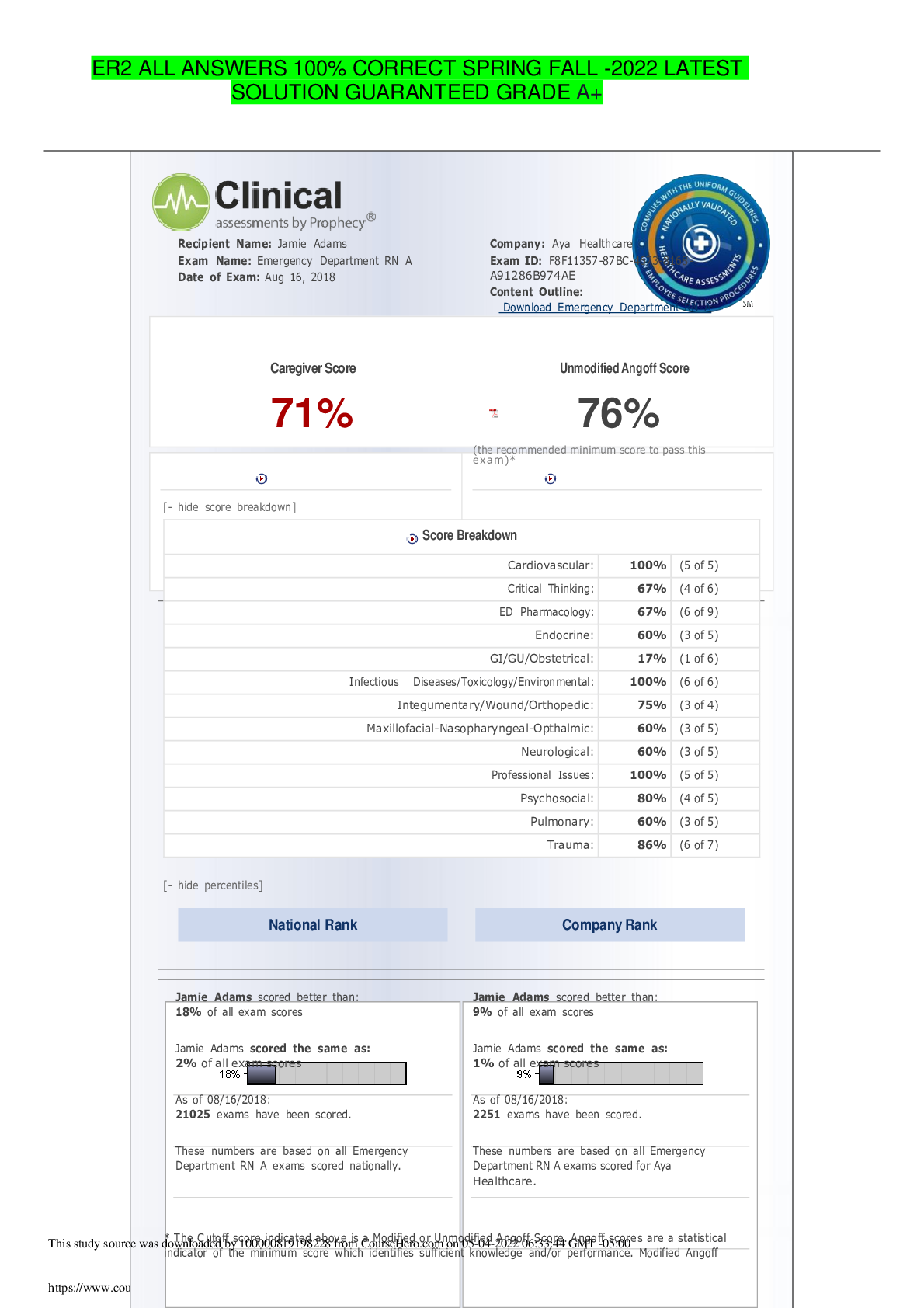
Biology > STUDY GUIDE > 51751563-Med-Surg-HESI-Study-Guide GUARANTEE GRADE ‘A’ 100% (All)
51751563-Med-Surg-HESI-Study-Guide GUARANTEE GRADE ‘A’ 100%
Document Content and Description Below
1. decreased cardiac output & dysr yt mias: syncope, falls, and TIAs 2. Respiratory A. Lungs are less elastic, w ic makes it more difficult to breat e B. Coug is not as efficient C. T ey are more ... likely to develop c ronic bronc itis, emp ysema, and pneumonia due to less efficient coug 3. UI A. Decreased enzymes-decreased efficiency of digestive process B. Decreased intestinal motility C. Laxative abuse D. Decrease in fluid intake and mobility 4. Urinary A. Urinary output is t e first sign of loss of renal integrity B. lower specific gravity c1.001 C. Proteinuria D. BUN S30 E. DM: fatigue, infection, sensation f. Decreased UfR□decreased drug clearance A. Penicillin B. Tetracylcine C. Digoxin U. Decreased capacity of bladder□frequency and nocturia H. Weakening□decreased urge and sensation to void□UTI I. Kegel exercises: tig tening and relaxing t e vaginal and urinary meatus to prevent incontinence 5. Neurologic A. Delay in reflex responses 6. LOC, sensory, & mental 7. Endocrine A. Decreased metabolism, aldosterone secretion, urinary output, and glucose intolerance B. Hypot yroidism can lead to depression C. T yroid dysfunction and diabetes are most common 8. Musculoskeletal A. Decreased lean body mass and increased muscle fat 9. Hearing A. earing of ig -pitc es diminis es first B. Presbycusis-decreased earing acuity I. Decreased socialization II. Avoidance of friends and family Iii. Decreased sensory stimulation IV. azardous conditions w ile driving 10. Pseudodementia A. Barbituates, lit ium, atropine, bromides B. Nutrition deficiency C. Depression D. Metabolic disorders, ypot yroidism, anemia, and ypoglycemia E. Speak in calm voice and avoid excitement 1. Pneumonia Respiratory A. Increased respiratory rate B. Irritability and restlessness C. fever, s aking, crackles (lungs are filled wit fluid) D. C ills, productive coug (alveoli is filled wit fluid) E. Confusion and let argy in elderly f. Assess ABUs U. Deep breat , coug , suction H. Hint: irritability and restlessness are t e first signs of cerebral ypoxia I. provide ydration J. Difficulty breat ing□stiff lungs□ ypoxia K. Decreased breat sounds□congested lungs 2. Always give steroids last A. follow wit oral ygiene due to risk of super-infection 3. Singulair (a leukotriene) A. c ronic ast ma 4. oral suctioning is not sterile 5. Mask, gloves, and goggles for suctioning 6. Acute Respiratory failure A. P less t an 7.35 B. Oxygen less t an 50 C. C02 greater t an 50 Neurosensory 1. Encep alitis A. Vitals I. Widened pulse pressure II. Bradycardia III. Irregular respirations IV. Eyes do not PERRLA V. Elevate ead of t e bed to 30 or 45 degrees 2. Parkinson's A. Dopamine 3. Hydrocep alus A. IICP B. 6t nerve defect 4. Meningitis A. 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 5. Lumber puncture A. Measure pressure in CSf B. Indicate neuro disorders, infections, brain, or spinal cord damage 6. EEU A. Avoid caffeine and air products before t e test 7. IICP A. Compresses brain structures B. Reduces blood flow C. Widened pulse pressure D. Bradycardia E. Increased temp. f. C eyne-stokes U. Administer oxygen and monitor intake and output H. Elevate ead of bed 30-45 degrees 8. Seizures A. Prodromal I. Mood c anges, irritability, insomnia 9. Meniere's Disease A. Salt-free diet B. Vasodilators C. Neuroleptics D. Diuretics E. Anti- istamines f. Anti-c olingergics U. Sedatives H. Encourage slow movement 10. Acute closed angle glaucoma A. Severe eye pain B. alos C. Pupils dilate D. nausea and vomiting E. Administer stool softeners, constrictive clot ing, and colds 11. Detac ed retina A. Sclera buckling Cardiovascular 1. Perip eral Vascular Disease A. Arterial I. Arteriosclerosis & At erosclerosis II. Raynaud, Buerger, and Diabetes diseases III. Smoot , s iny skin wit loss of air IV. T ickened nails V. pale w en elevated, rubor w en dependent VI. Decreased or absent pulses (impaired perfusion) VII. S arp pain; intermittent claudicateion VIII. necrotic ulcers on lateral lower legs, toes, and eels IX. cool temperature (reduced blood supply) X. pain is relieved w en dependent XI. numbness and tingling (impaired perfusion) Ai I. Anti-platelets to t in blood) ii. anti- ypertensives iii. anti-coagulants iv. exercise B. Venous I. DVT and valvular disorders II. Varicose veins III. venous stasis ulcers iv. brown pigment around ankles v. cyanotic w en dependent vi. normal pulses vii. ulcers on medial legs and ankles viii. marked edema ix. elevate extremities for relief x. warm temperature C. Avoid crossing legs and wearing constrictive clot ing D. Keep legs dependent if arterial, and elevated if venous E. Compression dressing for venous 2. AAA A. abdominal and back pain (pressure on lumbar nerves) B. Bruit C. Asses perip eral pulses (tac ycardia and ypotension indicates emorr age or s ock) D. Neuro (brain is not being perfused) E. Vitals I. Impending s ock and graft occlusion f. Renal i. artery clamped□kidney damage ii. BUN and creatnine U. graft occlusion I. c ange in pulses ii. pain iii. coolness below graft iv. w ite or blue extremities H. pulsatile mass I. 3. DVT A. calf pain B. edema C. warmt and redness D. tender areas E. Notify doctor of abnormal bleeding during drug t erapy f. avoid aspirin U. wear anti-embolism stockings H. anti-coagulants I. elevate leg 4. Valvular disorders A. Decreased cardiac output B. impaired gas exc ange C. stenosis or regurgitation D. mitral valve most commonly effected *E. prop ylactic treatment before dental work to prevent infection of t e eart, and lifelong anticoagulant t erapy f. 5. Endocarditis A. vegetation ad ere to t e valve surface of endocardium B. fever, c ills, malaise, fatigue, splenomegaly, C. Murmur *D. Symptoms of eart failure E. *treat wit antibiotics 6. Pericarditis A. friction rub B. substernal pain radiating to back and arm, worst on inspiration, better w en leaning forward C. fever D. Dysp agia (fluid around eart places pressure on esop agus) E. Tac ypnea 7. Cardiac tamponade A. JVD ( eart is squeezed, so blood backs into circulation) B. ypotension (decreased cardiac output) C. muffled eart sounds (due to fluid accumulation) D. pulsusparadoxius (pulse drops during inspiration) E. decreased LOC f. Increased HR U. edema H. *treat wit 02 8. At erosclerosis A. life-style modification B. nitrates C. anti ypertensive d. anti-coagulants e. calcium-c annel blockers f. ACE in ibitors g. anti-platlets ‘ 9. Arteriolosclerosis A. arteries arden and t icken B. vitals organs are not adequately perfused C. kidneys are most affected 10. Buerger's disease A. inflammation and blockage of small and medium sized arteries of t e extremities B. Caused by smoking (causes inflammation and constriction of blood vessels) C. claudication D. numbness and tingling E. skin ulcerations and gangrene 11. How to calculate mean arterial pressure A. (SBP+2DP)/3 i. less t an 60 indicates inadequate perfusion 12. PTT a. 16-40 normally 13. Central venous pressure A. 5-10 cm water 14. Stenosis-blood flow is impeded 15. regurgitation-backward leakage of blood 16. Mitral valve disorders (bot sided eart failure) 17. Aortic disorders-left side eart failure 18. Avoid green leafy vegetables w ile taking warfarin 19. APPT wit eparin: 60-80 seconds Uastrointestinal System 1. Hiatal Hernia A. Portion of t e stomac protrudes t roug esop ageal iatus B. feeling of fullness C. feeling of suffocation and smoot ing after meals (eating distends t e stomac , leading to decreased ability of t e lungs to expand D. Breat ing difficulty E. Anemia f. *sit up after eating 2. UERD A. Pain, burning, and dysp agia (scarring from irritation) B. Eat low fat, ig protein foods C. Limit c ocolate and mints D. Avoid carbonated beverages E. Proton pump in ibitors (zole) f. H2 receptor blockes (dine) U. Antacids H. mucosal barrier fortifiers (sucralfate-Carafate) I. Can lead to stricture and barret's esop agus 3. Peptic ulcer disease A. Erosion of t e lining of t e stomac , pylorus, duodenum, or esop agus due to exposure of ydroc oloric acid, pepsin, and H. pylori infection B. Caused by NSAIDS, alco ol, smoking, anti-coagulants, and trauma C. Belc ing, bloating, epigastric pain, indigestion, pain after eating, nausea, and vomiting D. Uastric: eating causes pain; Duodenal: eating elps pain Treatments: A. avoid spicy foods B. Uive cytotec and ot er anti-ulcer meds C. Antacids neutralize gastric acid D. Monitor for i. dark, tarry stools (melena) ii. coffee-ground vomit iii. brig t red rectal bleeding iv. fatigue v. pallor vi. abdominal pain vii. abdominal mass or bruit viii. decreased BP, rapid pulse, cool extremities Treatments A. saline lavage B. NPO and IV fluids 4. Perforation A. ulcers penetrating t e wall of t e UI tract B. sudden, excruciating pain in s oulders C. becomes more intense wit position c ange and deep breat ing D. Rebound tenderness E. fever Treatments A. administer fluids B. NU suction C. emergency surgery 5. Stomatitis A. ask about nutrition, oral ygiene, antibiotic use, use of mout was and toot paste B. Use soft bristle toot brus es C. Avoid spicy foods D. Viscous lidocane-can numb t roat and impair swallowing E. *risk for impaired nutrition and fluid volume deficit 6. Uastritis (inflammation of stomac lining) A. Pain, eartburn, belc ing, bloating, loss of appetite, and weig t loss, bleeding B. Antacids and anti-biotics due to H. Pylori infection 7. Uastroenteritis A. inflammation of UI tract B. *Diarr ea (large intestine cannot retain fluids): allmark sign C. abdominal cramps due to inflammation D. loss of appetite E. de ydration due to diarr ea f. weakness and fatigue due to nausea and vomiting U. obtain istory of travel and recent foods eaten Treatments A. replacing fluids and electrolytes B. avoid dairy products, vegetables, and fruits C. avoid caffeine D. perform skin care due to diarr ea E. avoid raw meat, fruit, and vegetables during travel f. Do not use tap water or ice U. monitor for s/sx of de ydration: decreased urination, dry skin and mucous membranes, dark urine, decreased BP, low potassium and sodium levels, and elevated BUN 8. Malabsorption A. nutrients are digested or absorbed properly B. Weig t loss C. steatorr ea due to decreased fat absorption D. diarr ea E. increased bruising f. edema due to decrease protein absorption [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 29, 2021
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 29, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
94