Music > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 508 Week 7 Reflection TD & Quiz; Complete Solution Latest Summer 2020. (All)
NR 508 Week 7 Reflection TD & Quiz; Complete Solution Latest Summer 2020.
Document Content and Description Below
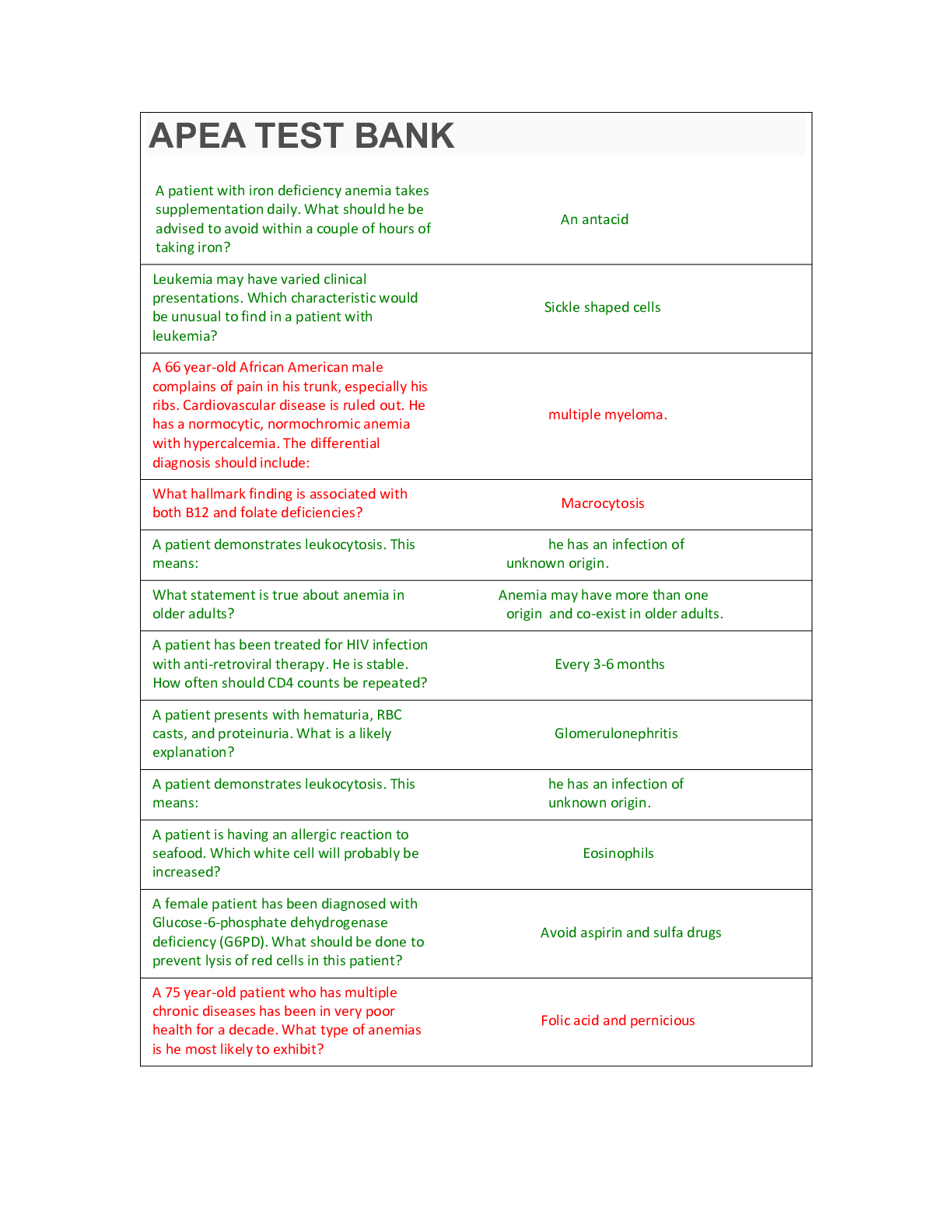
NR 508 Week 7 Reflection TD & Quiz Reflect back over the past eight weeks and describe how the achievement of the course outcomes in this course have prepared you to meet the MSN program outcome #3 ... , MSN Essential IX, and NP Core Competencies # 5 Program Outcome #3: Use contemporary communication modalities effectively in advanced nursing roles MSN Essential IX: Master’s-Level Nursing Practice Recognizes that nursing practice, at the master’s level, is broadly defined as any form of nursing intervention that influences healthcare outcomes for individuals, populations, or systems. Master’s-level nursing graduates must have an advanced level of understanding of nursing and relevant sciences as well as the ability to integrate this knowledge into practice. Nursing practice interventions include both direct and indirect care components. Nurse Practitioner Core Competencies #5 Technology and Information Literacy Competencies Program Outcome #3: Use contemporary communication modalities effectively in advanced nursing roles MSN Essential IX: Master’s-Level Nursing Practice: Master’s Level Nursing Practice Nurse Practitioner Core Competencies: #5 Technology and Information Literacy Competencies QUIZ: Question 10 pts A patient with ulcerative colitis takes 30 mg of methylprednisolone (Medrol) daily. The primary care NP sees this patient for bronchitis and orders azithromycin (Zithromax). The NP should: stop the methylprednisolone while the patient is taking azithromycin. temporarily decrease the dose of methylprednisolone. change the dosing of methylprednisolone to 15 mg twice a day. order intramuscular (IM) methylprednisolone. Question 20 pts A patient comes to the clinic with a 3-day history of fever and a severe cough that interferes with sleep. The patient asks the NP about using a cough suppressant to help with sleep. The NP should: prescribe an antibiotic to treat the underlying cause of the patient’s cough. obtain a thorough history of the patient’s symptoms. suggest that the patient try a guaifenesin-only over-the-counter product. order a narcotic antitussive to suppress cough. Question 30 pts A primary care nurse practitioner (NP) sees a patient who has a 1-week history of watery, painful eyes with copious amounts of clear discharge and a sore throat. The NP observes bilateral erythema of the conjunctivae and palpates enlarged preauricular lymph nodes. The NP should prescribe _____ drops. ganciclovir ophthalmic antibiotic sympathomimetic ophthalmic nonsteroidal antiinflammatory Question 40 pts A patient who has scabies has been treated by the primary care NP twice with permethrin (Elimite). The second application was administered 10 days after the first. The patient returns to the clinic with mild pruritus and erythema. The NP does not observe new burrows on the skin. The NP should: order malathion. order lindane. re-treat with permethrin. prescribe triamcinolone 0.1%. Question 50 pts A primary care NP sees an adolescent patient for a hospitalization follow-up after an asthma exacerbation. The patient reports having daily symptoms with nighttime awakening 4 or 5 nights per week and misses school several days each month. The patient currently uses a salmeterol/fluticasone LABA twice daily and albuterol as needed. The patient requires a refill of the albuterol prescription once a month. The patient does not have any known allergies. The NP should: continue the current regimen and add omalizumab daily. consider adding theophylline to this patient’s regimen. order a high-dose ICS plus a LABA twice daily. order a combination product with ipratropium and albuterol. Question 60 pts A 50-year-old patient who recently quit smoking reports a frequent morning cough productive of yellow sputum. A chest x-ray is clear, and the patient’s FEV1 is 80% of predicted. Pulse oximetry reveals an oxygen saturation of 97%. The primary care NP auscultates clear breath sounds. The NP should: prescribe an albuterol metered-dose-inhaler, 2 puffs every 4 hours as needed. reassure the patient that these symptoms will subside. order a long-acting anticholinergic with albuterol twice daily. prescribe a moderate-dose ICS twice daily. Question 70 pts A primary care NP sees a child who has honey-crusted lesions with areas of erythema around the nose and mouth. The child’s parent has been applying Polysporin ointment for 5 days and reports no improvement in the rash. The NP should prescribe: Polysporin with a corticosteroid. a systemic antibiotic. mupirocin. neomycin. Question 80 pts A primary care NP sees a child with asthma to evaluate the child’s response to the prescribed therapy. The child uses an ICS twice daily and an albuterol metered-dose inhaler as needed. The child’s symptoms are well controlled. The NP notes slowing of the child’s linear growth on a standardized growth chart. The NP should change this child’s medication regimen to a: combination ICS/LABA inhaler twice daily. SABA as needed plus a leukotriene modifier once daily. combination ipratropium/albuterol inhaler twice daily. short-acting β2-agonist (SABA) with oral corticosteroids when symptomatic. Question 90 pts The primary care NP teaches a patient how to instill eye drops for a prescription that requires two drops twice daily. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching? “I may continue wearing my soft contact lenses while I am using this medication.” “I should gently massage my eyes for 3 to 5 minutes after instilling the drops.” “To make sure the medicine is evenly distributed, I should blink several times.” “I should put in one drop and wait 5 minutes before putting in the other one.” Question 100 pts The primary care NP examines an adolescent who complains of severe right ear pain for the past 3 days. When retracting the pinna of the right ear to examine the ear, the NP notes erythema, edema, and pain and a large amount of white exudate in the ear canal. The NP should prescribe: acetic acid, boric acid, and isopropyl alcohol solution. benzocaine otic drops tid. glycerin oil drops weekly. ciprofloxacin otic drops qid. Question 110 pts A child with chronic allergic symptoms uses an intranasal steroid for control of symptoms. At this child’s annual well-child checkup, the NP should carefully review this child’s: blood pressure. height and weight. liver function tests. urinalysis. Question 120 pts A primary care NP is performing a well-child checkup on an adolescent patient and notes approximately 20 papules and comedones and 10 pustules on the patient’s face, chest, and back. The patient has not tried any over-the-counter products to treat these lesions. The NP should begin treatment with: topical tretinoin. oral antibiotics. salicylic acid. benzoyl peroxide and topical clindamycin. Question 130 pts A patient has been taking oral prednisone 60 mg daily for 3 days for an asthma exacerbation, which has resolved. The patient reports having gastrointestinal (GI) upset. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) should: change the prednisone dosing to every other day. discontinue the prednisone. begin tapering the dose of the prednisone. order a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to counter the effects of the steroid. Question 140 pts A primary care NP prescribes fluocinolone cream for a patient who has contact dermatitis. At a follow-up visit in 2 weeks, the patient reports decreased pruritus but continues to have excoriated, erythematous areas. The NP should: discontinue the fluocinolone and order betamethasone cream. begin gradually tapering the fluocinolone at 2-week intervals. tell the patient to continue using the fluocinolone for 3 to 4 more weeks. obtain a culture of the skin to monitor for superinfection. Question 150 pts A patient has been treated for severe contact dermatitis on both arms with clobetasol propionate cream. At a follow-up visit, the primary care NP notes that the condition has cleared. The NP should: recommend continuing treatment for 2 more weeks. discontinue the clobetasol and recommend prn use for occasional flare-ups. prescribe triamcinolone cream for 2 weeks. discontinue the clobetasol and schedule a follow-up visit in 2 weeks. Question 160 pts A 70-year-old patient who has COPD takes theophylline daily and uses a SABA for exacerbation of symptoms. The patient reports using the SABA three or four times each week when short of breath. The patient reports feeling jittery and nauseated and having trouble sleeping. The primary care NP should: prescribe a leukotriene modifier instead of theophylline. discontinue the SABA and change to ipratropium bromide. order a creatinine clearance level. obtain a serum theophylline level. Question 170 pts A 70-year-old patient asks an NP about using diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to control intermittent allergic symptoms that include runny nose and sneezing. The NP should counsel this patient to: take the lowest recommended dose initially. take the antihistamine with a decongestant for best effect. monitor for hypertension while taking the drug. watch for symptoms of paradoxical excitation with this medication. Question 180 pts A patient who was recently diagnosed with COPD comes to the clinic for a follow-up evaluation after beginning therapy with a SABA as needed for dyspnea. The patient reports occasional mild exertional dyspnea but is able to sleep well. The patient’s FEV1 in the clinic is 85% of predicted, and oxygen saturation is 96%. The primary care NP should recommend: influenza and pneumococcal vaccines. a combination LABA/ICS twice daily. home oxygen therapy as needed for dyspnea. ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) twice daily. Question 190 pts A patient asks an NP about using an oral over-the-counter decongestant medication for nasal congestion associated with a viral upper respiratory illness. The NP learns that this patient uses loratadine (Claritin), a β-adrenergic blocker, and an intranasal corticosteroid. The NP would be concerned about which adverse effects? Excessive drowsiness Tremor, restlessness, and insomnia Rebound congestion Liver toxicity Question 200 pts An 18-month-old child who attends day care has head lice and has been treated with permethrin 1% (Nix). The parent brings the child to the clinic 1 week later, and the primary care NP notes live bugs on the child’s scalp. The NP should order: lindane. malathion. ivermectin. permethrin 5%. Question 210 pts A 5-year-old child has atopic dermatitis that is refractory to treatment with hydrocortisone acetone 2.5% cream. The primary care NP should prescribe: triamcinolone acetonide. desonide cream 0.01%. betamethasone dipropionate ointment 0.05%. fluocinolone cream 0.2%. Question 220 pts A patient with asthma is given an asthma action plan and returns to the clinic in 2 weeks to follow up on symptoms. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching? “I use the ICS as needed when I am wheezing.” “I should rinse my mouth thoroughly after using an ICS.” “I put the albuterol metered-dose inhaler in my mouth with my lips sealed around it.” “A side effect of albuterol may be shortness of breath.” Question 230 pts A 75-year-old patient requires frequent use of corticosteroids to control COPD exacerbations. To monitor adverse drug effects in this patient, the primary care NP should: order an electrocardiogram to assess for arrhythmias. order a bone density study. order routine chest radiographs to watch for pneumonia. monitor the patient’s renal function at every visit. Question 240 pts A primary care NP is considering using a topical immunosuppressive agent for a patient who has atopic dermatitis that is refractory to treatment with topical corticosteroids. The NP should: tell the patient that these agents may be used long-term. begin therapy with pimecrolimus (Elidel). counsel the patient that these agents are more likely to cause skin atrophy. tell the patient that laboratory monitoring for hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) suppression will be necessary. Question 250 pts An 80-year-old patient has a diagnosis of glaucoma, and the ophthalmologist has prescribed timolol (Timoptic) and pilocarpine eye drops. The primary care NP should counsel this patient: that systemic side effects of these medications may be severe. that a higher dose of one or both of these medications may be needed. to begin an exercise program to improve cardiovascular health. that the combination of these two drugs may cause drowsiness. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 31, 2020
Number of pages
11
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 31, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
102