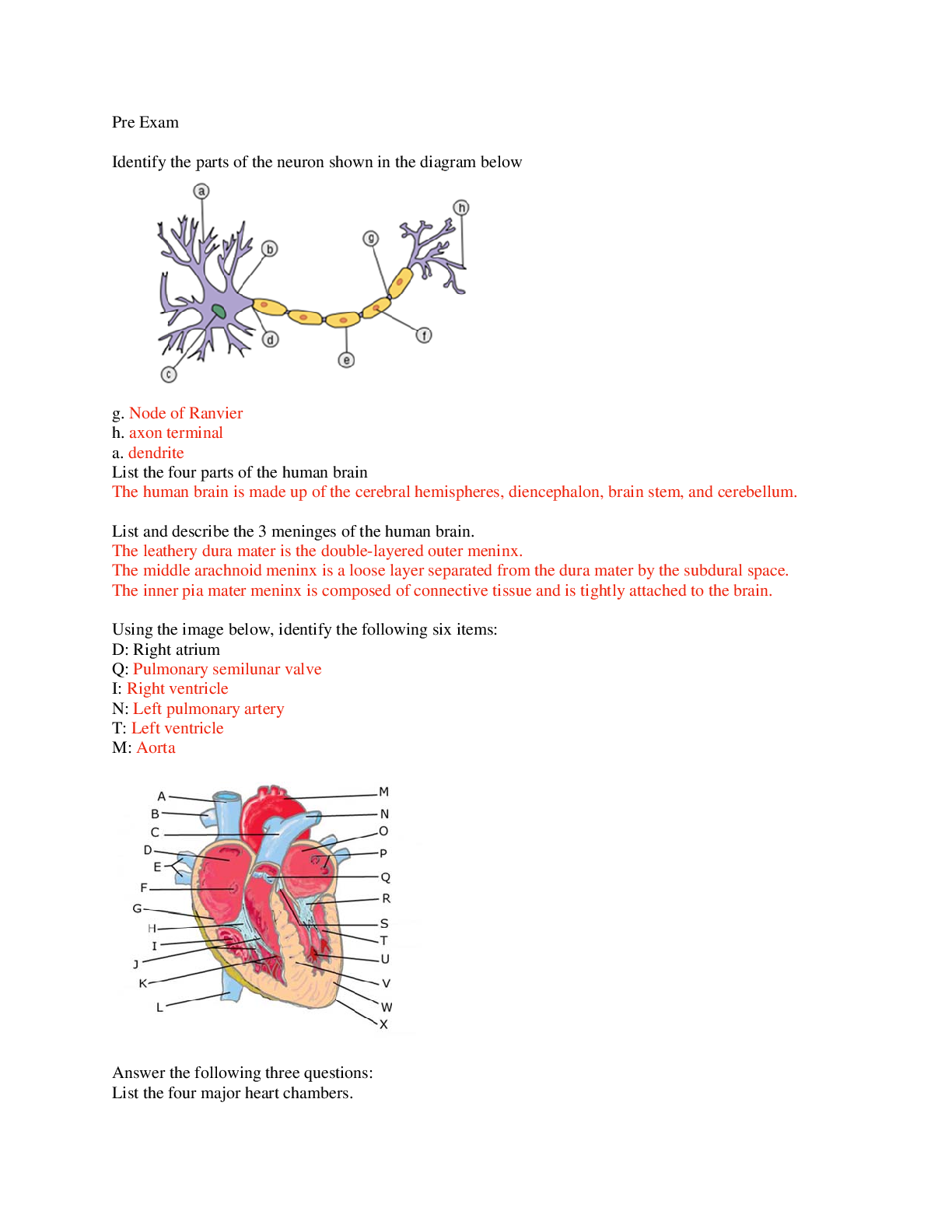
Question 1
The Brain
1. List the four parts of the human brain.
The human brain is made up of the cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum.
2. Describe the number, location and function of t
...
Question 1
The Brain
1. List the four parts of the human brain.
The human brain is made up of the cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum.
2. Describe the number, location and function of the brain ventricles.
There are four ventricles in the interior of the brain, chambers filled with cerebrospinal fluid which is produced there.
3. Label the ventricles.
See figure in module.
4. Describe the brain meninges and the layers.
The meninges are three layers of connective tissue membranes that cover and protect central nervous system organs and enclose cerebrospinal fluid. The leathery dura mater is the double-layered outer meninx. The middle arachnoid meninx is a loose layer separated from the dura mater by the subdural space. Beneath the arachnoid meninx is the subarachnoid space which contains blood vessels and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The inner pia mater meninx is a thin connective tissue tightly attached to the brain.
5. What is the function of the choroid plexus?
The choroid plexus produces cerebrospinal fluid.
6. What is the blood-brain barrier and how is it maintained?
The blood-brain barrier is a diffusion barrier which prevents most particles from entering the central nervous system tissue, keeping the brain and spinal cord separate from general blood circulation. The blood-brain barrier is formed by the relatively impermeable brain capillaries, due to the glial cells astrocytes. Maintenance of the blood-brain-barrier is important to provide a stable chemical environment for the nervous system. A stable internal environment is important to protect neurons from chemical variations which could cause uncontrollable firing of neurons.
7. Describe the cerebrum.
The cerebrum, the foremost part of the brain, is the largest part of the brain in humans comprising about 83% of total brain mass
8. What is the median longitudinal fissure?
It separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres from one another.
9. Raised ridges on the cerebrum are called____.
Gyri
10. The _______ separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
The transverse fissure
Question 2
The Brain
11. The outer portion of the cerebral hemispheres is called the ______and is highly convoluted and gray in color.
Cerebral cortex
12. Describe the functions of the lobes of the cerebrum.
The frontal lobe controls higher level executive functions such as reasoning and decision making. The frontal lobe also controls motor functions and permits control over voluntary muscle actions. The parietal lobe receives sensory information from receptors in the mouth for taste and located in the skin, such as those for touch, pressure, and pain. The occipital lobe interprets visual input. The temporal lobe has sensory areas for hearing and smelling.
13. What is the difference between a primary area and an association area in the brain?
Primary areas in each lobe receive information for one type of sensory information. Association areas act mainly to integrate more than one type of sensory information for purposeful action.
14. Label the regions of the cerebral cortex.
See figure in module.
15. List the three major parts of the brain stem.
The brain stem is made up of the mid-brain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
16. How is the medulla oblongata involved with the heart and lungs?
The medulla oblongata regulates heartbeat and breathing
17. How is the pons involved with the eyes and ears?
The pons regulates head movements in response to visual and auditory stimuli.
18. The superior and inferior colliculi are located on the posterior portion of the _____.
Midbrain
19. How is the hypothalamus involved with the entire internal environment of the body and the endocrine system in particular?
The hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, the constancy of the internal environment and controls the pituitary gland and serving as a link between the nervous and endocrine systems
20. All except what sensory impulses are channeled through the thalamus?
all sensory impulses (except those associated with the sense of smell) are channeled through the thalamus.
Question 3
The Brain
21. What is the function of the pineal body?
The pineal body secretes melatonin to control the wake-sleep cycle
22. Describe the location and structure of the cerebellum.
The cerebellum, below and at the back of the brain, is convoluted and divided into two hemispheres with deep fissures subdividing it into three lobes.
23. The major function of the cerebellum is to control what type of body function?
The cerebellum acts to coordinate body movements. The cerebellum is also involved with planning movements, maintaining balance, controlling certain eye movements, maintaining normal muscle tone and maintaining posture.
[Show More]