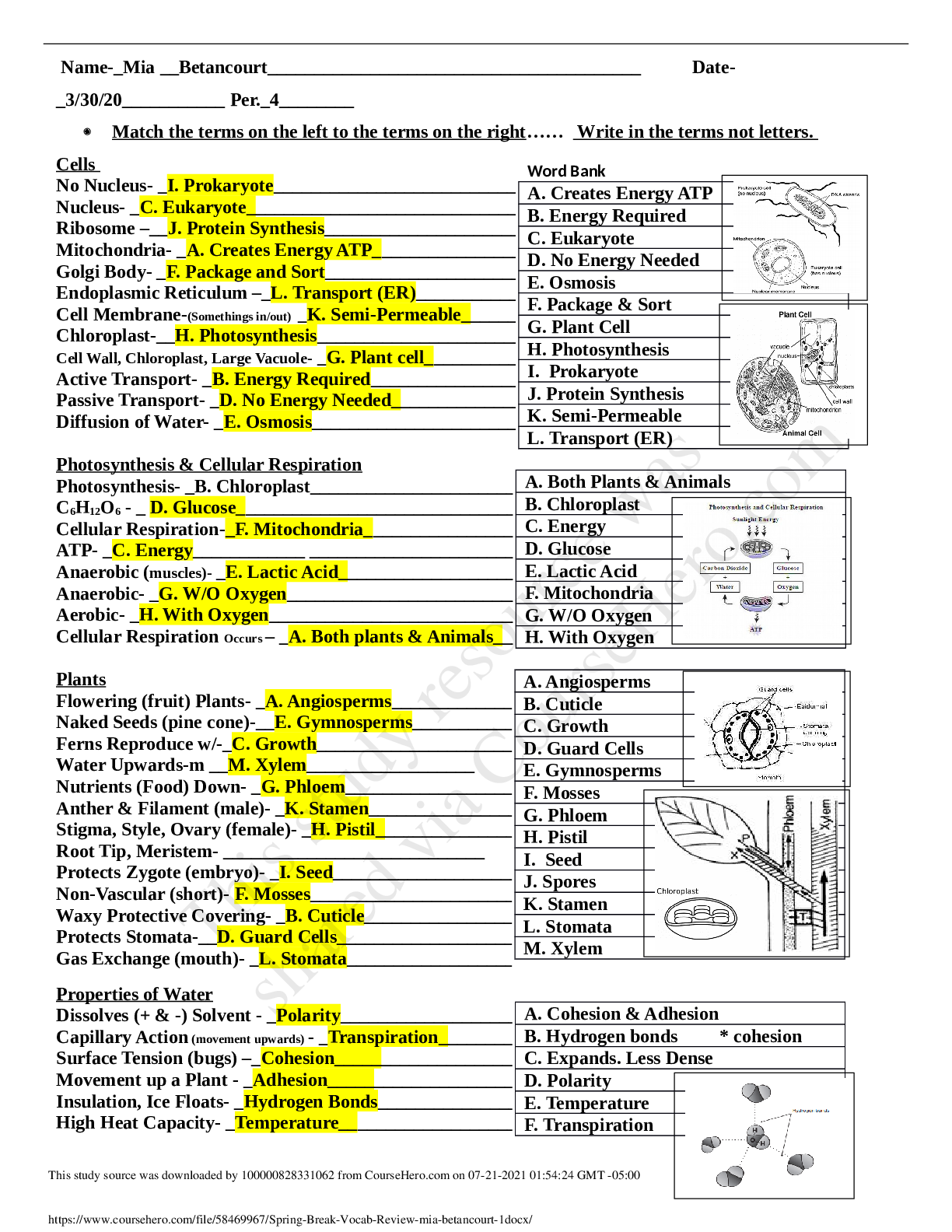
Form of necrosis a/w TB? Caseous
Most common cause of cellular injury? Hypoxia
Acid- pH 7.45
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation is the
mechanism by which energy produced f
...
Form of necrosis a/w TB? Caseous
Most common cause of cellular injury? Hypoxia
Acid- pH <7.35 Base- pH >7.45
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation is the
mechanism by which energy produced from carbs fats, and proteins is transferred to ATP.
Hypotonic solution causes cellular swelling- D5W (dextrose in water), D5 1/2NS (5% dextrose
and 0.45%NS), 1/2NS (0.45%NS), D5 1/4NS( 5% dextrose and 0.2%NS), 1/4NS (0.2%NS)
Hypertonic solution causes cellular shrinkage- 3%NS “ocean water”
Isotonic solution- LR, NS, D5NS
Heat exhaustion- hemoconcentration from water and salt loss
Water moves between the ICF and ECF compartments by osmosis. Water moves between the
plasma and interstitial fluid by osmosis and hydrostatic pressure, which can occur across the
capillary membrane.
Hypokalemia- potassium <3.5 can be caused by reduced K+ intake, increased ICF to ECF K+
concentration, loss of K+, increased aldosterone secretion and increased renal secretion. S/S:
decreased neuromuscular excitability, skeletal muscle weakness, smooth muscle atony, cardiac
dysrhythmias.
Greatest carrier to push K+ back into the cell? Insulin
Hypernatremia- Na+ > 147, can be caused by sodium gain or water loss. Movement of H20
from ICF to ECF. S/S: dehydration, convulsions, pulmonary edema, hypotension, tachycardia.
TX: Isotonic salt-free fluids
Hyponatremia- Na+ < 135, can be caused by Na+ deficits leading to plasma hypoosmolality
and cellular swelling. S/S: lethargy, HA, confusion, apprehension, seizures, and coma. TX: fluid
restriction, NaCl tablets
Physical barriers? Skin, Ex: epithelial cells
Mechanical barrier? Mucous membrane
Biochemical barrier? Epithelial surfaces. Ex: mucus, sweat, saliva, tears, earwax
Vascular injury is an acute inflammation that includes, vasodilation, increased capillary
permeability, and WBC adherence to inner vessel walls and their migration through vessel walls.
S/S/: redness, heat, swelling, and pain
[Show More]










.png)