Exam 3 Review MUSCULOSKELETAL
CT SCAN:
o Invasiveo Check consent o Renal function!!! o Increase fluids o Ask patient for Allergies!!!! o Monitor Bun and Creatinine
-
MRI:
o NOT indicated for: PACEMA
...
Exam 3 Review MUSCULOSKELETAL
CT SCAN:
o Invasiveo Check consent o Renal function!!! o Increase fluids o Ask patient for Allergies!!!! o Monitor Bun and Creatinine
-
MRI:
o NOT indicated for: PACEMAKER PATIENT, any metal in body, HIP
REPLACEMENT PATIENT, MECHANICAL VALVES PATIENTS o Noisy
o Takes 30 to 90 minutes o Weight the patient o Prosthetic Heart valve
-
Arthroscopy/Athrocentesis
-
- When you give a patient a dye, tell them to drink a lot of fluids for 1-2 days, encourage fluids!
- Ask about allergies to the dye
- Visualizes the joint, it might have swelling (arthroscopy- visualization of the joints to diagnose joint disorders)
- The fluid should be straw-colored, not red !!!!!(athrocentesis- joint aspiration)
- Assess and document the findings
- For Arthroscopy – compression dressing to control swelling - Apply ice and elevate to reduce swelling
Bone Densitometry
- How do you care for the patient? NPO?
o Not NPO, but cannot take calcium supplements the day of the test 24 hours before the exam
- This test measures the bone density
for osteoporosis
- DXA BMD
A DEXA scan is a special type of X-ray that measures bone mineral density (BMD). DEXA stands for "dual energy X-ray absorptiometry". This type of scan is also often known as DXA, or "dual X-ray absorptiometry". It's also sometimes referred to as a bone density scan or a bone densitometry scan.
DEXA scans are often used to diagnose osteoporosis (when the bones become weak and fragile, and are more likely to break).
They can also be used to assess the risk of osteoporosis developing in women aged over 50 and in men over 60.
As well as being quick and painless, a DEXA scan is more effective than normal X-rays in identifying low bone mineral density.
Bone Scan
- The nurse asks the patient about any allergies to the radioisotope, pregnancy
- Tell the patient to drink plenty of fluids to excrete the dye
- The patient must empty the bladder!!! Before the test because it interferes with visualization of the pelvic bones
Cast, splint, or brace:
o As the nurse, perform a neurovascular assessment, ask them to move the fingers and toes, depending on where the cast is
o Bivalve: the patient can’t move, the doctor will cut the cast straight down (when the cast is on too tight) to relieve pressure!!! o Splints are for short term use, braces are for longer-term use
o A cast is used to immobilize a part of the body, if the skin itches, apply ice, but do not put anything inside the cast!
o Cast= If blood, circle- date, time, initials
-
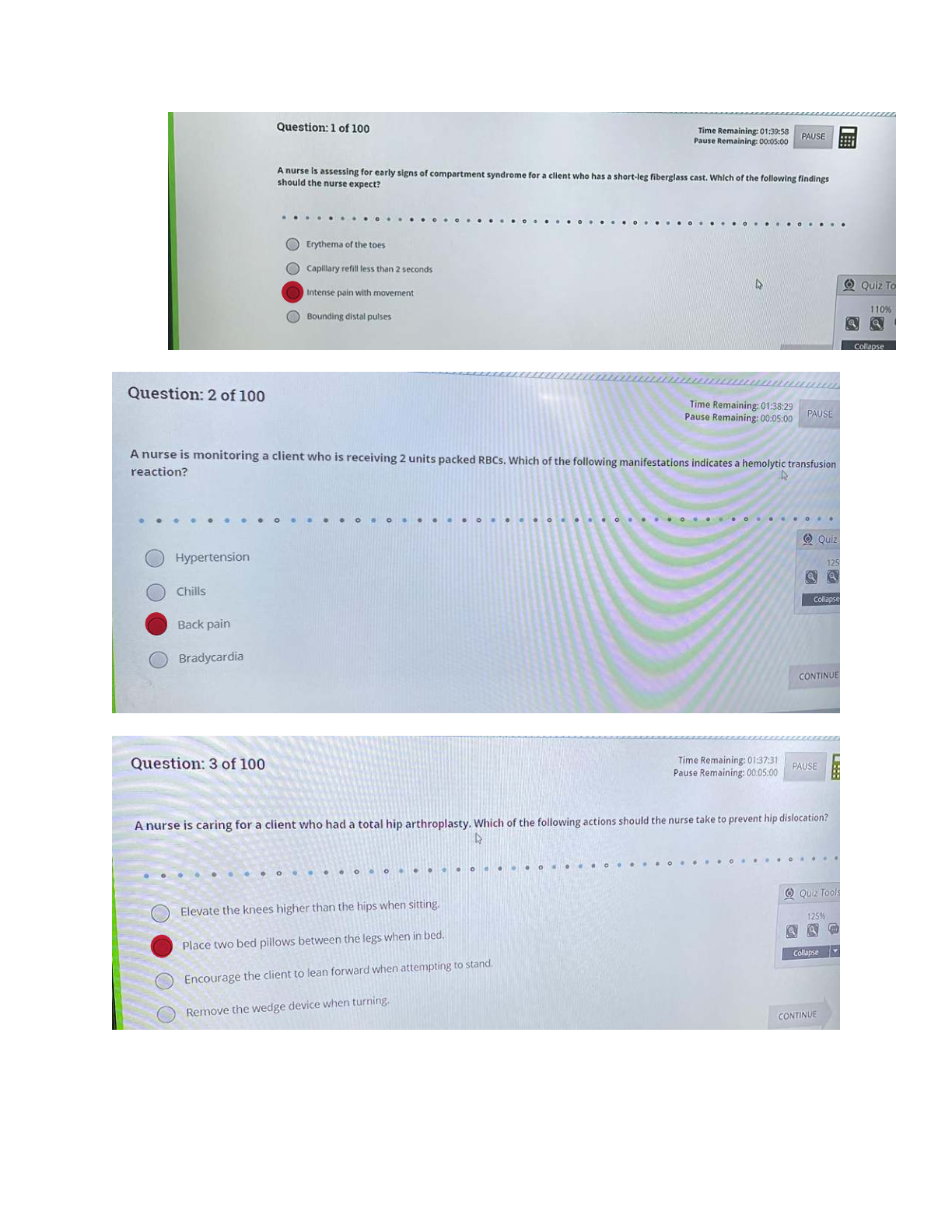
Compartment Syndrome:!!!!!
o Blood vessels get compressed o Use a doppler to assess for pulses (edema) o Maintain extremities at heart level
o Skin is pale and the peripheral pulse is weak or gone, hallmark: pain with Passive ROM
o Cut cast in half BIVALVE
o Pressure not relieved & circulation not restored, fasciotomy (cut skin) o 5 P’s Pain-Pallor-Pulselessness- Paresthesia-Paralysis
[Show More]