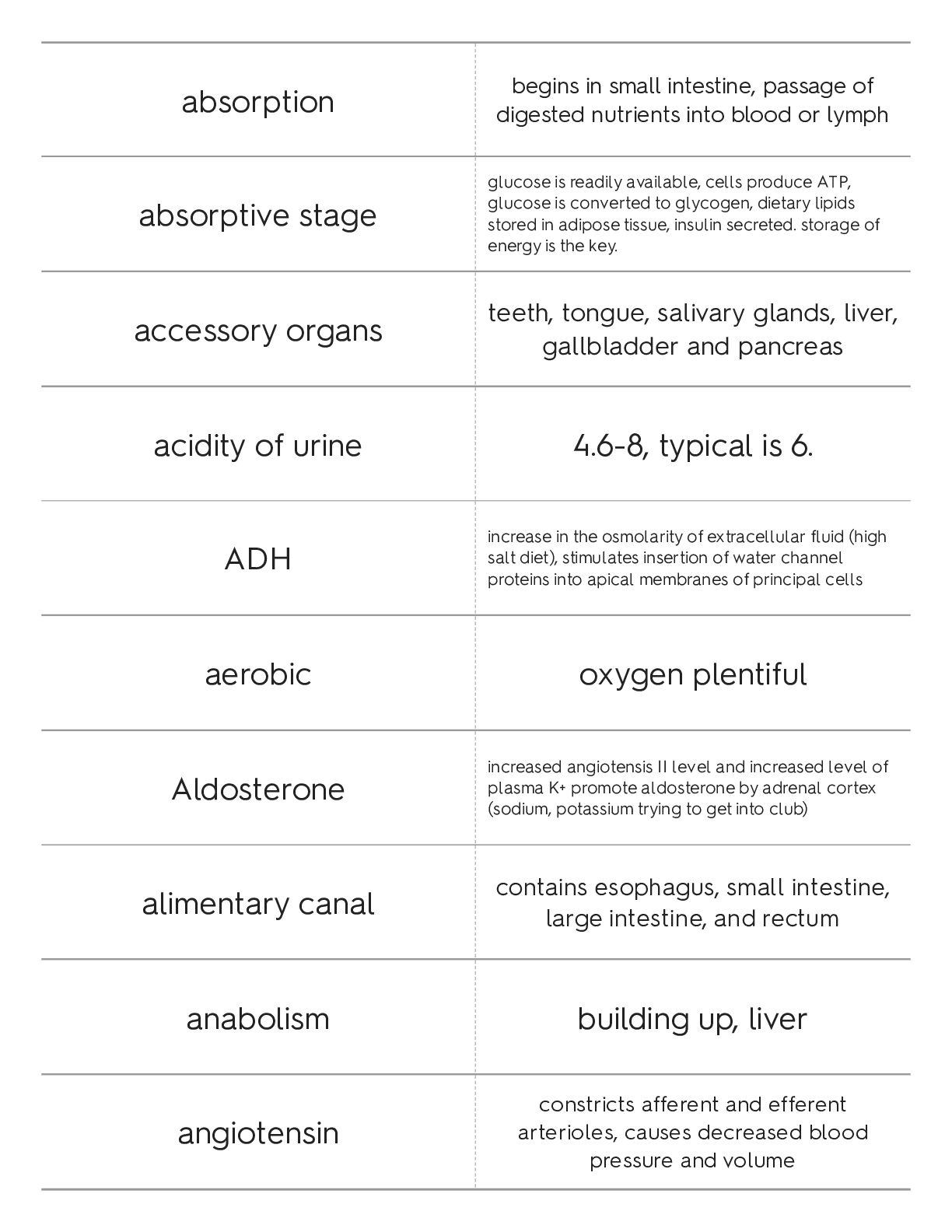
absorption
begins in small intestine, passage of
digested nutrients into blood or lymph
absorptive stage
glucose is readily available, cells produce ATP,
glucose is converted to glycogen, dietary lipids
stored in a
...
absorption
begins in small intestine, passage of
digested nutrients into blood or lymph
absorptive stage
glucose is readily available, cells produce ATP,
glucose is converted to glycogen, dietary lipids
stored in adipose tissue, insulin secreted. storage of
energy is the key.
accessory organs
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver,
gallbladder and pancreas
acidity of urine 4.6-8, typical is 6.
ADH
increase in the osmolarity of extracellular fluid (high
salt diet), stimulates insertion of water channel
proteins into apical membranes of principal cells
aerobic oxygen plentiful
Aldosterone
increased angiotensis II level and increased level of
plasma K+ promote aldosterone by adrenal cortex
(sodium, potassium trying to get into club)
alimentary canal
contains esophagus, small intestine,
large intestine, and rectum
anabolism building up, liver
angiotensin
constricts afferent and efferent
arterioles, causes decreased blood
pressure and volume
ANP
stretching of atria of heart stimulates ANP secretion,
blood volume increases (suppressed reabsorption of
Na+ and water in proximal tubule)
autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic: increase digestive activity
sympathetic: decrease certain digestive
activities
beriberi
loss of appetite and overall lassitude, digestive
irregularities, and a feeling of numbness and
weakness in the limbs and extremities
bicuspids/premolars crush, mash and grind food
bladder can hold up to 700-800 mL.
BMR
measure of how much thyroxine the thyroid
gland is producing, measured with body in
quiet, resting and fasting state.
bowman's capsule visceral and parietal layers,
brunner's glands
secrete alkaline mucus,
found in the duodenum.
Calorie equal to 1000 calories
calorie
amount of heat energy required to raise
temperature of 1 gram of water from
140C to 150C.
canine teeth tearing/slashing food
carbohydrates
monosaccharides, digestion
occurs in the mouth
catabolism
breaking down, mouth
stomach and duodenum
celiac disease
ingestion of gluten injures
small intestine
Cellular Respiration
oxidation of glucose to produce
ATP (4 sets are involved)
chemical digestion
water added to break chemical
bonds, fats carbs and proteins
Chemoiosmosis
movement of H+ across mitochondrial
membrane down electrochemical
gradient
chief cells
secretes pepsinogen, and
gastric lipase.
cholecystokinin
stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice rich
in digestive enzymes causes ejection of bile
from gallbladder and opening of sphincter
chylomicrons
transport dietary lipids in
blood to fats
chyme
the pulpy acidic fluid that passes from the
stomach to the small intestine, consisting of
gastric juices and partly digested food.
cirrhosis
causes portal hypertension, rupture due to increased
fluid, the fluid moves to peritoneal cavity, and
decreased absorption of nutrients in small intestine
color of urine
typically yellow-amber but varies
according to recent diet and
concentration of urine
cortical neprons
80-85% of nephrons, short loops of
henle extend only into outer region of
medulla
countercurrent multiplication
he process of using energy to generate an osmotic
gradient that enables you to reabsorb water from the
tubular fluid and produce concentrated urine.
deglutition swallowing
density of normal urine 0.001 to 0.035
dialysis hemo and peritoneal,
duodenum
breakdown of food in small
intestine
electrolytes
absorbed into blood, absorbed by
the large intestine.
Electron Transport Chain
mitochondria, series of electron carriers,
oxygen is final electron acceptor,
produces H2O +28 ATP, heat.
Energy transfer
phosphate group added to ADP
along with energy to form ATP
enteric nervous
system/local mechanism
respond to changes in pH or chemical
stimuli, has submucosal and myenteric
plexus
enteroendocrine cell
also known as g cells,
secrete gastrin
enterokinase trypsinogen, trypsin
enuresis involuntary urination
esophagus
propulsion, moves food into
stomach
[Show More]











.png)
.png)













