Anatomy and Physiology - A&P 1 > Quiz > Portage Learning BIOD 151 Module 2: Problem Set: Essential Human Anatomy & Physiology I w/Lab - Burt (All)
Portage Learning BIOD 151 Module 2: Problem Set: Essential Human Anatomy & Physiology I w/Lab - Burtt - 2025E| Answered 100% correct.
Document Content and Description Below
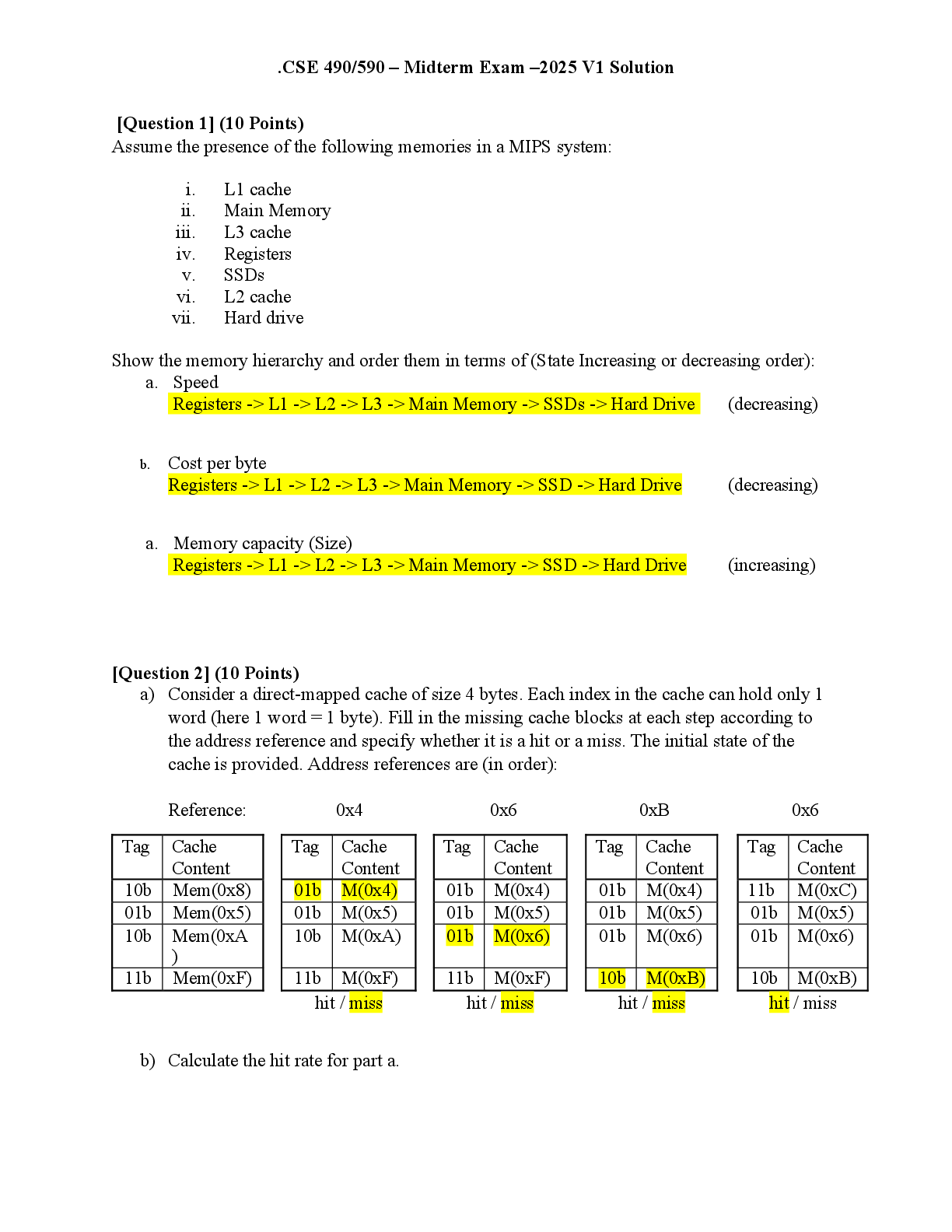
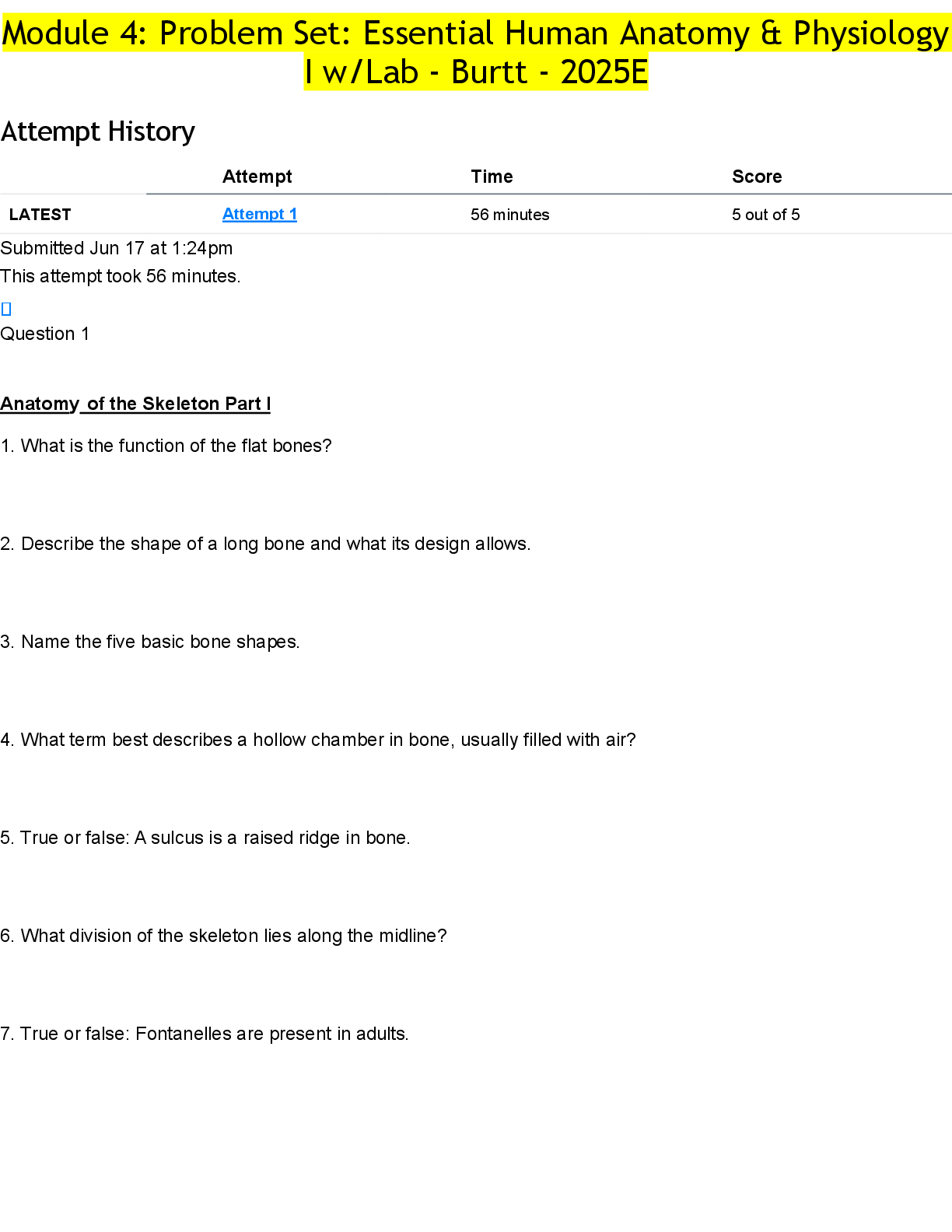
Mo dule 2: Problem Set Due No due date Points 5 Questions 8 Time Limit None Instructions Please be familiar with all bold face words in the module. In addition, below are some review q... uestions that will be helpful. This is not an exhaustive list of review questions. It is a general list of possible topics which could be on the exam. Question 1 0 / 0 pts General Anatomy 1. What are the three main functions of the respiratory system (anatomical organization)? 2. What are the three parts of the pharynx? (Review figure to label locations) 3. Identify the hard palate vs. the soft palate 4. True or false: the rings that cover the trachea are a complete circle. 1. The anatomical organization of the respiratory system allows the respiratory system to perform three main functions: 1) Air conduction, 2) Air filtration, and 3) Exchange of Gases. (also called respiration) 2. Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, laryngopharynx 3. SEE FIGURES in module 4. False: the cartilaginous rings of the trachea do not meet on the posterior side Question 2 0 / 0 pts General Anatomy 5. Label the following figures: Anterior View of the lungs: Label A- Label TBhi- Label C- Label D- Label E- Posterior view of the larynx (“voice box”): Label A- Label B- Label C- Label D- Label E- Label F- Label G- 5. SEE FIGURES in module Question 3 6. What important steps need to happen during the swallowing process to prevent aspiration? 7. Why does the soft palate elevate during swallowing? 8. What is the glottis? 9. What is aspiration? 10. True or False? The left lung has three lobes. 11. Name two functions of the pleura. 12. Be familiar with the labeling of the respiratory system diagrams. Know the upper respiratory diagram well and the diagram of the alveoli. In the lower respiratory system, know the location and names of the 5 lobes of the lungs. Question 4 Respiratory Tract Histology 6. What is the major histology type in the respiratory system? 7. What is the name of the “floor” of the epithelium in the respiratory tract? 8. Why are the cells in the respiratory epithelium called columnar cells? 9. What are the wine-glass shaped mucous-producing cells? 10. Where can stratified squamous epithelium be found in the respiratory system? 11. Describe the purpose of surfactant. 12. List and describe the two types of alveolar epithelium. 13. What is the most abundant cell found within the alveoli? Question 5 Respiratory Physiology 13. Explain the steps necessary for inhalation. 14. What is meant that “negative pressure” is created inside the lungs? 15. True or false: Exhalation is an active process. 16. What is the function of hemoglobin? 17. What muscle is largely responsible for providing movement for respiration? 18. Ultimately gas exchange occurs where? 19. Most of the carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in what form? Respiratory Physiology 22. Negative pressure is used to move air into the lungs: A negative pressure environment is created inside the lungs by the pleural space. The motion of the rib cage: the rib cage lifts superiorly and anteriorly to open and expand the lungs. The diaphragm: The diaphragm is flattened as it contracts, pulling the lungs open As the thoracic cavity expands and lung volume increases, the density of the density of the gases filling the lungs decreases Because air pressure outside of the lungs is now greater than inside (where there is negative pressure), air will naturally flow into the lungs. 23. This means that the pressure inside this space is less than that of the atmosphere, allowing air to naturally flow into the lungs. 24. Exhalation (or expiration) passively occurs. When the rib cage is lowered and the diaphragm rises, thoracic pressure increases and therefore air moves out of the lungs where the pressure is lower. 25. Hemoglobin combines with the oxygen entering the blood to carry the oxygen in the blood system from the lungs to the cells of the tissues. 26. The diaphragm 27. Respiratory bronchioles and pulmonary alveoli 28. Bicarbonate ion Question 6 Terminology of Respiratory Physiology 29. Review all respiratory physiology measurement terms and know definitions. 30. Boyle’s law states what? 31. There are three gases in a tank. The partial pressure of the first is 120 mmHg, the pressure of the second is 320 mmHg. What is the partial pressure of the third at 1 atm? 32. This law helps explain why warming the air is beneficial to the respiratory system. 33. This is the amount of air able to be exhaled beyond normal exhalation. 34. This is the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one cycle of quiet breathing. 20. Review figure and terminology in module 21. Gas volume is inversely proportional to pressure. 22. 120 mmHg + 320 mmHg = 440 mmHg. 760 mmHg - 440 mmHg =320 mm Hg. (The answer is 320 mm Hg) **Remember that 1 atm = 760 mm Hg. 23. Charles’s Law 24. Expiratory reserve volume (typically around 1200mL) 25. Tidal volume Question 7 0 / 0 pts Lung Pathology 26. What is cystic fibrosis? 27. What is pulmonary edema? 28. Familiarize yourself with all the diseases discussed in the module. Lung Pathology 35. A serious genetic disease of excretory glands, affecting lungs and other organs; it causes production of very thick mucus that interferes with normal digestion and breathing. 36. An accumulation of fluid in the lungs 37. See module Question 8 5 / 5 pts As a reminder, the questions in this review quiz are a requirement of the course and the best way to prepare for the module exam. Did you complete all questions in their entirety and in your own words? [Show More]
Last updated: 2 weeks ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 15, 2025
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 15, 2025
Downloads
0
Views
9