*NURSING > EXAM > NR 508 week one quiz (GRADED A) Questions and Answer solutions | Chamberlain College of Nursing (All)
NR 508 week one quiz (GRADED A) Questions and Answer solutions | Chamberlain College of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
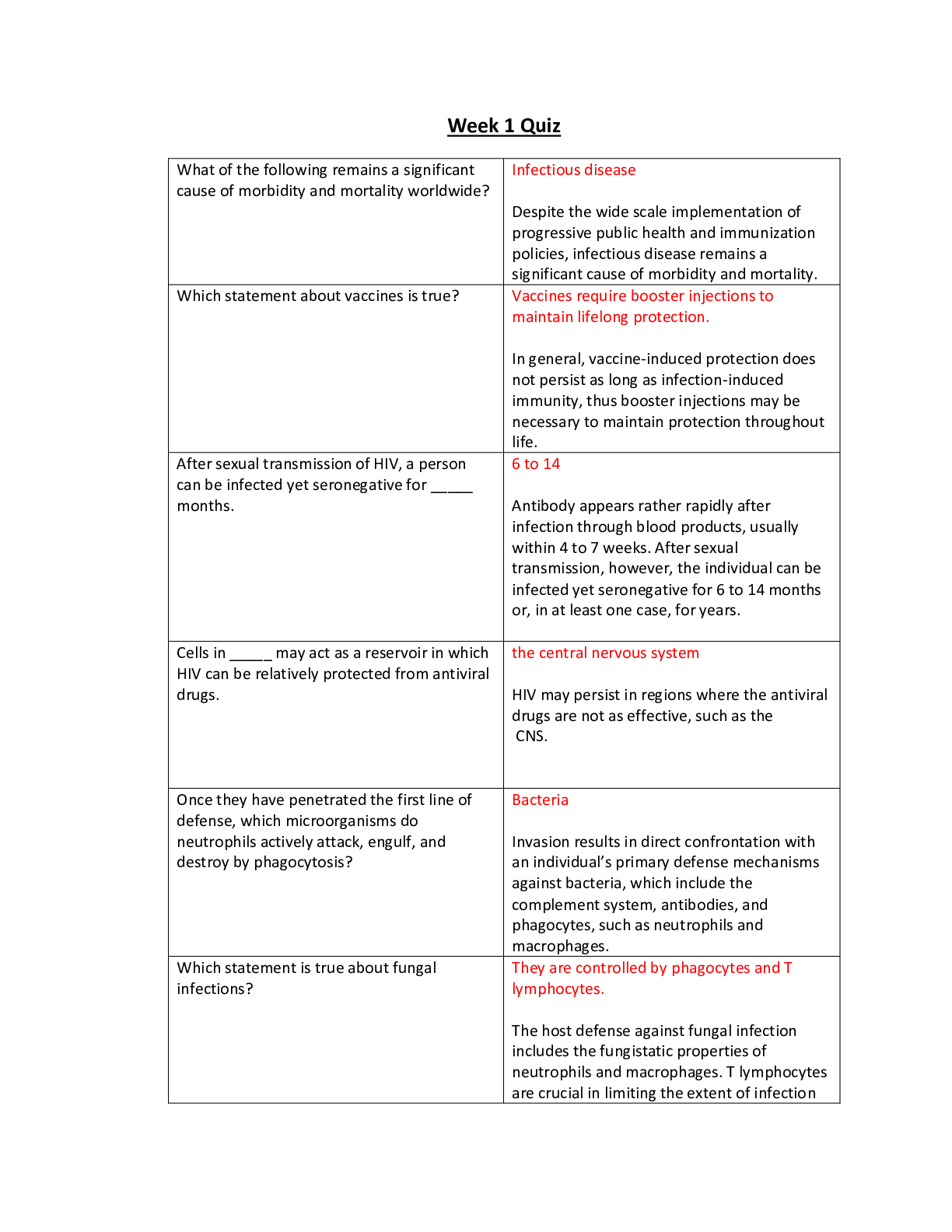
1. Question : Osteopenia is diagnosed in a 55-year-old woman who has not had a period in 15 months. She has a positive family history of breast cancer. The primary care NP should recommend: ... Student Answer: testosterone therapy. estrogen-only therapy. nonhormonal drugs for osteoporosis. estrogen-progesterone therapy for 1 to 2 years. Instructor Explanation: Although estrogen slows the progression of osteoporosis, it also increases the risk of breast cancer when initiated early in menopause. This woman should receive a nonhormonal treatment for osteoporosis and may receive HT in 5 years if menopausal symptoms persist. Testosterone therapy, estrogen-only therapy, and estrogen-progesterone therapy are not indicated. Question 2 . Question : A patient takes a cardiac medication that has a very narrow therapeutic range. The primary care NP learns that the particular brand the patient is taking is no longer covered by the patient’s medical plan. The NP knows that the bioavailability of the drug varies from brand to brand. The NP should: Student Answer: contact the insurance provider to explain why this particular formulation is necessary. change the patient’s medication to a different drug class that doesn’t have these bioavailability variations. accept the situation and monitor the patient closely for drug effects with each prescription refill. ask the pharmaceutical company that makes the drug for Instructor Explanation: samples so that the patient does not incur out-of-pocket expense. In this case, the NP should advocate for the desired drug because changing the drug can have life-threatening consequences. If this fails, other options may have to be explored. Question 3 . Question : A patient brings written information about a medication to a primary care NP about a new drug called Prism and wants to know if the NP will prescribe it. The NP notes that the information is from an internet site called “Prism.com.” The NP should tell this patient that: Student Answer: this information is probably from a drug advertisement website. this is factual, evidence-based material with accurate information. the information is from a nonprofit group that will not profit from drug sales. internet information is unreliable because anyone can post Instructor Explanation: information there. Commercial internet sites are identifiable by “com” at the end of their web address. Many provide reliable information, but others may be more interested in selling something. Nonprofit groups use “org” at the end of their web addresses. Internet information is reliable as long as the internet user is aware of how things are posted and by whom. Question 4 . Question : A primary care NP is reviewing written information about a newly prescribed medication with a patient. To evaluate this patient’s understanding of the information, the NP should ask the patient to: Student Answer: read the information aloud. describe how the medication will be taken. write down questions about the medication. tell the NP if the information is unclear. Instructor Explanation: To evaluate a patient’s understanding, the NP should ask the patient to describe in his or her own words what is taught. Asking a patient to read aloud is sometimes used to assess literacy. Patients who are not literate may not be able to write down questions and, because of shame, may not tell the NP that the written information is unclear. Question 5 . Question : A patient is diagnosed with lupus and reports occasional use of herbal supplements. The primary care NP should caution this patient to avoid: Student Answer: ginseng. echinacea. ginkgo biloba. St. John’s wort. Instructor Explanation: Patients with lupus who take echinacea may experience an increase in symptoms, even if the patient is taking immunosuppressants. Question 6 . Question : A patient who has chronic pain and who takes oxycodone (Percodan) calls the clinic to ask for a refill of the medication. The primary care NP notes that the medication refill is not due for 2 weeks. The patient tells the NP that the refill is needed because he is going out of town. The NP should: Student Answer: fill the prescription and document the patient’s explanation of the reason. review the patient’s chart to see if this is a one-time or repeat occurrence. call the patient’s pharmacist and report suspicion of drug- seeking behaviors. confront the patient about misuse of narcotics and refuse to fill Instructor Explanation: the prescription. When patients fill prescriptions early for drugs that have abuse potential, providers should be alert to possible abuse. The first step would be to see if this is a one-time occurrence or a pattern. Providers should do this before refilling the prescription. If this is a pattern, the pharmacist should be notified. Patients should be confronted if a problem is apparent, and practitioners should not refill the prescriptions. Question 7 . Question : The primary care NP prescribes an extended-cycle monophasic pill regimen for a young woman who reports having multiple partners. Which statement by the patient indicates she understands the regimen? Student Answer: “I have to take a pill only every 3 months.” “I should expect to have only four periods each year.” “I will need to use condoms for only 7 more days.” “This type of pill has fewer side effects than other types.” Instructor Explanation: The extended-cycle pills have fewer pill-free intervals, so women have only four periods a year. Patients take pills every day. Because this patient has multiple partners, she should continue to use condoms. This type of pill has the same side effects as other types. Question 8 . Question : The primary care NP sees a patient covered by Medicaid, writes a prescription for a medication, and is informed by the pharmacist that the medication is “off-formulary.” The NP should: Student Answer: inform the patient that an out-of-pocket expense will be necessary. write the prescription for a generic drug if it meets the patient’s needs. call the patient’s insurance provider to advocate for this particular drug. contact the pharmaceutical company to see if medication Instructor Explanation: samples are available. Medicaid often stipulates which medications are or are not covered. Unless the particular drug is absolutely necessary, the NP should substitute with an acceptable generic drug. Insisting that the patient pay out of pocket may mean that the prescription is not filled. If the drug is necessary, the NP may advocate for its use by contacting the third-party payer. Asking for drug samples is not a long-term solution for the problem. Question 9 . Question : A 55-year-old woman has not had menstrual periods for 5 years and tells the primary care nurse practitioner (NP) that she is having increasingly frequent vasomotor symptoms. She has no family history or risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) or breast cancer but is concerned about these side effects of hormone therapy (HT). The NP should: Student Answer: tell her that starting HT now may reduce her risk of breast cancer. advise a short course of HT now that may decrease her risk for CHD. tell her that HT will not help control her symptoms during postmenopause. recommend herbal supplements for her symptoms to avoid HT Instructor Explanation: side effects. The current gap hypothesis regarding breast cancer supports initiating HT 5 years or more after menopause. To decrease risk for CHD, HT should begin at the time of menopause. HT will relieve vasomotor symptoms at all stages of menopause. Herbal supplements have estrogenizing effects and carry the same risks as estrogen therapy. Question 10 . Question : A primary care NP recommends an over-the-counter medication for a patient who has acid reflux. When teaching the patient about this drug, the NP should tell the patient: Student Answer: to take the dose recommended by the manufacturer. not to worry about taking this drug with any other medications. to avoid taking other drugs that cause sedation while taking this drug. that over-the-counter acid reflux medications are generally safe Instructor Explanation: to take with other medications. Because patients often increase over-the-counter drug doses themselves, it is important to reinforce the need to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for dosing. As with any drug, interactions may occur with other medications. Antacids do not cause sedation, so patients need not be cautioned to avoid other sedating medications. Question 11 . Question : A patient will begin taking two drugs that are both protein-bound. The primary care NP should: Student Answer: prescribe increased doses of both drugs. monitor drug levels, actions, and side effects. teach the patient to increase intake of protein. stagger the doses of drugs to be given 1 hour apart. Instructor Explanation: Protein-bound drugs bind to albumin, and serum albumin levels may affect how drugs are distributed. The provider should monitor drug levels, actions, and side effects and change dosing accordingly. Increasing the dose of both drugs is not recommended unless monitoring indicates. Increasing dietary protein does not affect this. Staggering the drugs will not affect this. Question 12 . Question : The primary care NP has referred a child who has significant gastrointestinal reflux disease to a specialist for consideration for a fundoplication and gastrostomy tube placement. The child’s weight is 80% of what is recommended for age, and a recent swallow study revealed significant risk for aspiration. The child’s parents do not want the procedure. The NP should: Student Answer: compromise with the parents and order a nasogastric tube for feedings. initiate a discussion with the parents about the potential outcomes of each possible action. refer the family to a case manager who can help guide the parents to the best decision. understand that the child’s parents have a right to make choices Instructor Explanation: that override those of the medical team. In general, the goal of a health care decision maker is to choose an action that is most likely to deliver the outcomes the patient wants. Initiating a discussion about outcomes helps parents decide based on end results. A nasogastric tube is not the best choice for the child, and compromising without first exploring options is incorrect. As part of the therapeutic relationship, the NP should be involved with patients’ decisions. Although patients and families have the right to make decisions, the NP has an obligation to ensure that the decisions are informed decisions. Question 13 . Question : A primary care NP is developing a clinical practice guideline for management of a patient population in a midsized suburban hospital. The NP should: Student Answer: use an existing guideline from a leading research hospital. follow the guideline provided by a third-party payer to help ensure reimbursement. review expert opinion and experimental, anecdotal, correlational study data. write the guideline to adhere to long-standing practice protocols Instructor Explanation: already in use. Clinical guidelines should be written using all available evidence as well as expert opinion. Existing guidelines from a different type of hospital may not be based on data generalizable to this population. Third-party payer guidelines are usually weighted toward decreased costs. Long-standing protocols often do not take into account current knowledge and research. Question 14 . Question : The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) writes a prescription for an antibiotic using an electronic drug prescription system. The pharmacist will fill this prescription when: Student Answer: the electronic prescription is received. the patient brings a written copy of the prescription. a copy of the written prescription is faxed to the pharmacy. the pharmacist accesses the patient’s electronic record to verify. Instructor Explanation: E-sign effectively voids requirements that prescriptions be written on paper or printed as a hard copy. Some scheduled drugs still require written copies. Faxed copies of this drug would be allowed but are not necessary for the pharmacist to fill the prescription. The patient’s electronic medical record stands as evidence of the need for a prescription of a drug but is not needed for the pharmacist to fill the prescription. Question 15 . Question : A primary care NP is preparing to prescribe a drug and notes that the drug has nonlinear kinetics. The NP should: Student Answer: monitor frequently for desired and adverse effects. administer a much higher initial dose as a loading dose. monitor creatinine clearance at baseline and periodically. administer the drug via a route that avoids the first-pass effect. Instructor Explanation: Drugs with nonlinear kinetics are not eliminated based on dose or concentration of the drug, and these drugs have a narrow therapeutic window and must be monitored closely for desired effects and toxicity. Question 16 . Question : An important difference between physician assistants (PAs) and NPs is PAs: Student Answer: always work under physician supervision. are not required to follow drug treatment protocols. may write for all drug categories with physician co-signatures. have both inpatient and outpatient independent prescriptive Instructor Explanation: authority. PAs commonly have co-signature requirements and work under physician supervision. Question 17 . Question : A primary care NP writes a prescription for an off-label use for a drug. To help ensure compliance, the NP should: Student Answer: include information about the off-label use on the E-script. provide the patient with written instructions about how to use the medication. tell the patient to let the pharmacist know that the drug is being used for an off-label use. follow up by phone in several days to see if the patient is using Instructor Explanation: the drug appropriately. Effective communication extends beyond just the patient-provider relationship. It is important to include anyone involved in the patient’s care. The best way in this case is to include the information on the E-script so that there is a record of the off-label use and to help clarify or reinforce the provider’s instructions. Question 18 . Question : A patient reports taking antioxidant supplements to help prevent cancer. The primary care NP should: Student Answer: review healthy dietary practices with this patient. make sure that the supplements contain large doses of vitamin A. tell the patient that antioxidants are especially important for patients who smoke. tell the patient that evidence shows antioxidants to be effective Instructor Explanation: in preventing cancer. Epidemiologic evidence indicates that people who eat fruits and vegetables regularly have a decreased risk of cancer. Although retrospective studies have suggested major benefits from antioxidants, no intervention studies have determined conclusively that antioxidants prevent cancer. Large doses of vitamin A can produce a yellow hue to the skin. Antioxidants can be beneficial, but in certain populations, such as smokers, they may be harmful. Question 19 . Question : A woman comes to the clinic to talk about weight reduction. The primary care nurse practitioner (NP) calculates a body mass index (BMI) of 28. The woman’s waist measures 34 inches. The woman tells the NP that she would like to lose 20 lb for her daughter’s wedding in 6 months. The NP should: Student Answer: suggest she try over-the-counter (OTC) orlistat. consider prescribing phentermine short-term. discuss her short-term and long-term weight loss goals. give her information about physical activity and diet Instructor Explanation: modification. This woman’s BMI is in the moderate range for overweight, and her waist circumference is 34, which is not diagnostic for metabolic syndrome. Because her apparent motivation for losing weight is based on an upcoming event, the NP first should determine what her short-term and long-term weight loss goals are before initiating therapy. Orlistat is used long-term and would not be appropriate in this case. Phentermine should be used short-term and, because of serious risks, should be used only as adjunct therapy to lifestyle modifications. The initial intervention for weight loss is physical activity and diet modification. Question 20 . Question : A patient comes to the clinic and asks the primary care NP about using a newly developed formulation of the drug the patient has been taking for a year. When deciding whether or not to prescribe this formulation, the NP should: Student Answer: tell the patient that when postmarketing data is available, it will be considered. review the pharmaceutical company promotional materials about the new medication. prescribe the medication if it is less expensive than the current drug formulation. prescribe the medication if the new drug is available in an Instructor Explanation: extended-release form. About 6 to 12 months of postmarketing experience can yield information about drug efficacy and side effects, so patients should be cautioned to wait for these data. Drug company promotional materials have biased information. Most new drugs are more expensive, and costs alone should not determine drug choice. Extended-release forms are often more expensive. Question 21 . Question : An adolescent girl has chosen Depo-Provera as a contraceptive method and tells the primary care NP that she likes the fact that she won’t have to deal with pills or periods. The primary care NP should tell her that she: Student Answer: should consider another form of contraception after 1 year. may have irregular bleeding, especially in the first month or so. will need to take calcium and vitamin D every day while using this method. will have to take oral contraceptive pills in addition to Depo- Instructor Explanation: Provera when she takes antibiotics. Because of strong progestational effects on the endometrium, irregular bleeding or spotting is common in the early months of use. Because of concerns about the effect of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate on bone density, it is recommended that woman change to another birth control method after 2 years, not 1 year. Calcium and vitamin D supplements have not been shown to prevent bone density loss. It is not necessary to take oral contraceptive pills when taking antibiotics. Question 22 . Question : A patient receives an inhaled corticosteroid to treat asthma. The patient asks the primary care NP why the drug is given by this route instead of orally. The NP should explain that the inhaled form: Student Answer: is absorbed less quickly. has reduced bioavailability. has fewer systemic side effects. provides dosing that is easier to regulate. Instructor Explanation: An inhaled corticosteroid goes directly to the site of action and does not have to pass through gastrointestinal tract absorption or the liver to get to the lungs. It is generally well absorbed at this site, although dosing is not necessarily easier to regulate because it is not always clear how much of an inhaled drug gets into the lungs. Question 23 . Question : A patient who has breast cancer has been taking toremifene for 2 weeks. She tells her primary care NP that she thinks her tumor has grown larger. The NP should: Student Answer: schedule her for a breast ultrasound. reassure her that this is common and will subside. tell her she may need an increased dose of this medication. contact her oncologist to discuss adding another medication. Instructor Explanation: Toremifene can cause tumor flare in the first few weeks of therapy, but the tumor later regresses. An ultrasound is unnecessary at this stage. The NP does not need to notify the oncologist unless this continues to worsen. Question 24 . Question : The primary care NP is prescribing a medication for an off-label use. To help prevent a medication error, the NP should: Student Answer: write “off-label use” on the prescription and provide a rationale. call the pharmacist to explain why the instructions deviate from common use. write the alternative drug regimen on the prescription and send it to the pharmacy. tell the patient to ignore the label directions and follow the Instructor Explanation: verbal instructions given in the clinic. When prescribing a drug for an off-label use, the provider should specify this on the written prescription and should provide a rationale so that the pharmacist understands why the prescription is different from the normal use. Calling the pharmacist would not provide written documentation. Merely writing the different instructions can lead to errors if the pharmacist changes the label to conform to usual standards. The patient may forget verbal instructions and follow the usual regimen instead. Question 25 . Question : The primary care NP sees a woman who has been taking HT for menopausal symptoms for 3 years. The NP decreases the dosage, and several weeks later, the woman calls to report having several hot flashes each day. The NP should: Student Answer: increase the HT dose. discontinue HT. recommend black cohosh to alleviate symptoms. reassure her that these symptoms will diminish over time. Instructor Explanation: The Women’s Health Initiative results indicate that HT use for 3 to 5 years is safe and recommend slow weaning after women review HT with their providers at annual visits. If symptoms recur, the dose should be increased until symptoms improve. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 08, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
41



 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)






.png)




.png)








