*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Pathophysiology Adult Health 2 Exam 2 Study Guide (All)
Pathophysiology Adult Health 2 Exam 2 Study Guide
Document Content and Description Below
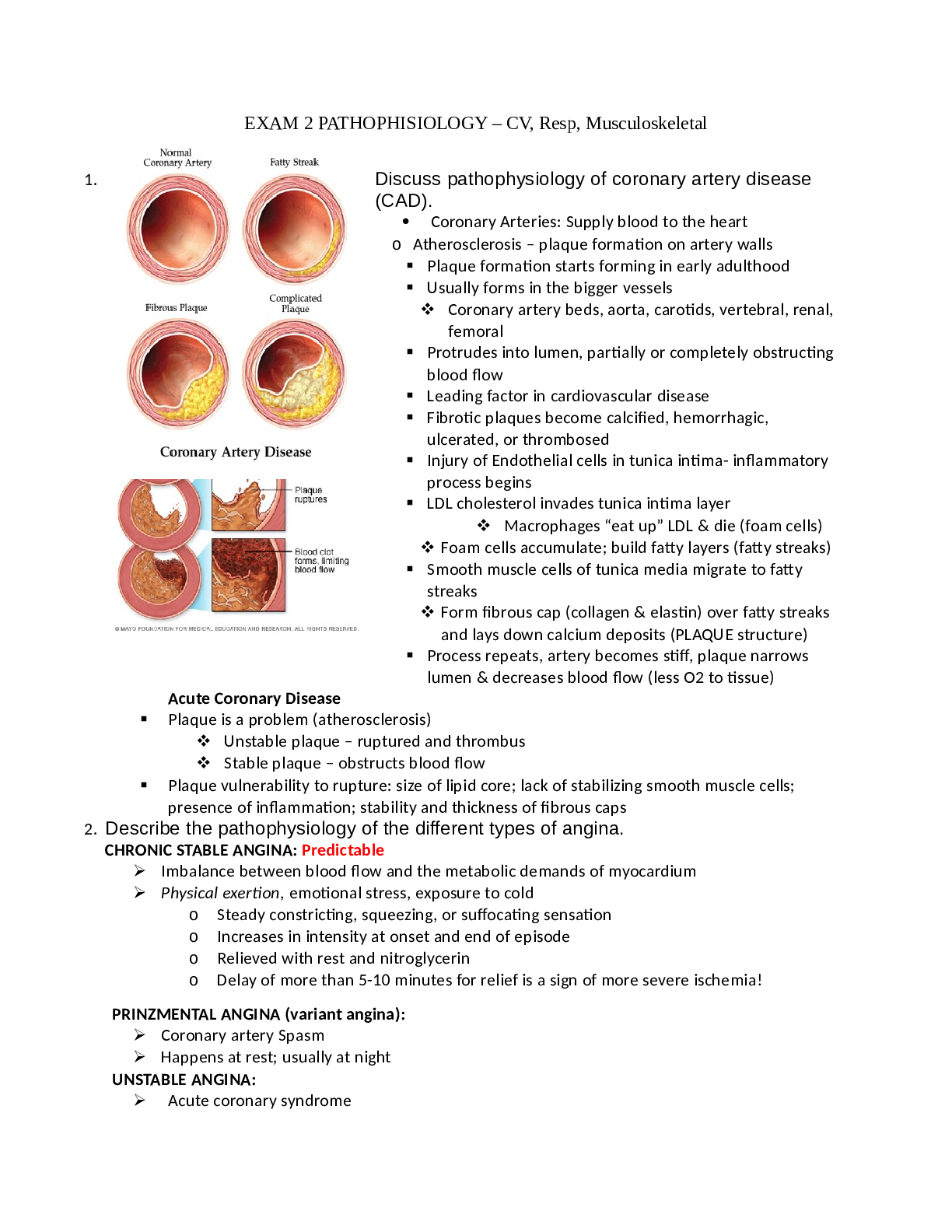
Vascular Diseases – • Inadequate oxygenation and tissue perfusion due to narrowing or occlusion of vessels • Disorders 1. Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis p. 728- 731 2. Hypertension p. ... 720-728 3. Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) p 731- 738 4. Aneurysms/Dissections p. 738-741 5. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) p. 741- 746 6. Buerger’s and Raynaud’s p. 741 7. Arteriosclerosis/Atherosclerosis 8. Arteriosclerosis ⦿ Thickening or hardening of arterial wall ⦿ Often associated with aging 9. “Loss of elasticity = Hypertension” 10. 11. Atherosclerosis - Type of arteriosclerosis involving formation of plaque within arterial wall ϫ Base of all disorders ϫ Inflammatory response ϫ Initiated by Injury o Hypertension, smoking, hyperlipidemia ϫ Fibrous plaque form over fatty deposit ϫ Narrow/obstruct vessels o Stable and unstable plaques 12. Type of arteriosclerosis 13. Plaque formation within the artery walls - Plaque formation begins in early adulthood ϫ Usually affects larger vessels: coronary artery bed, aorta, carotids, vertebral, renal, femoral ϫ Protrudes into lumen, partially or completely obstructing blood flow ϫ Leading factor in cardiovascular disease ϫ Fibrotic plaques become calcified, hemorrhagic, ulcerated, or thrombosed o Affect all layers of vessel o Progression affected by genetics, chronic diseases (diabetes), lifestyle, exercise o Stable plaques: rupture thrombus and constrict vessel causing inadequate oxygenation and perfusion to distal tissue o Unstable plaque: more severe: exposed underlying tissue causes platelet adhesion and rapid thrombus formation sudden blockage of vessel: ischemia and infarction Results in stroke/ MI/ loss of blood flow to limb. ϫ Plaques rupture: o Blood clot formation/constriction obstruct vessel lumen o Results in ischemia and infarction of tissue Strokes, MIs, arterial thrombosis… 14. For nursing care: 15. Discuss physical manifestations: o Monitor BP o Palpate pulses in all major sites of body o Assess for prolonged capillary refill o Assess for bruit 16.Homocysteine levels increase in the body when the metabolism to cysteine of methionine to cysteine is impaired. This may be due to dietary deficiencies in vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and folic acid!!! If homocysteine cannot be converted into cysteine or returned to the methionine form, levels of homocysteine in the body increase. Elevated homocysteine levels have been associated with heart attack, stroke, blood clot formation, and perhaps the development of Alzheimer's disease Most laboratories report normal homocysteine levels in the blood between 4 and 15 micromoles/liter (µmol/L). Any measurement above 15 is considered high. Any measurement below 12 is considered low. Optimal homocysteine levels are below 10 to 12. Hyperhomocysteinemia has been classified into moderate, intermediate, and severe types based on the level of homocysteine and are: Moderate (15 to 30 µmol/L) Intermediate (30 to 100 µmol/L) Severe (greater than 100 µmol/L) 17. 18. Atherosclerosis Risk Factors: 19. Nonmodifiable 20. Modifiable • Age: men > 45; women > 55 • Gender • Genetics (family history) • Ethnicity African Americans > Caucasians • Diabetes • Hyperlipidemia • Obesity • Tobacco use • Physical inactivity • Metabolic syndrome ϫ Insulin resistance fasting plasma glucose >100 ϫ Central obesity ϫ Dyslipidemia TG >150 HDL< 50 F HDL < 40 M ϫ BP > 130/85 ϫ High levels of C reactive protein ϫ Prothrombotic state (high fibrinogen level) • Glucose control 21 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 14, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 14, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
177