Biology > STUDY GUIDE > Nonessential amino acids can be created by the liver or (11) Matching complete and incomplete protei (All)
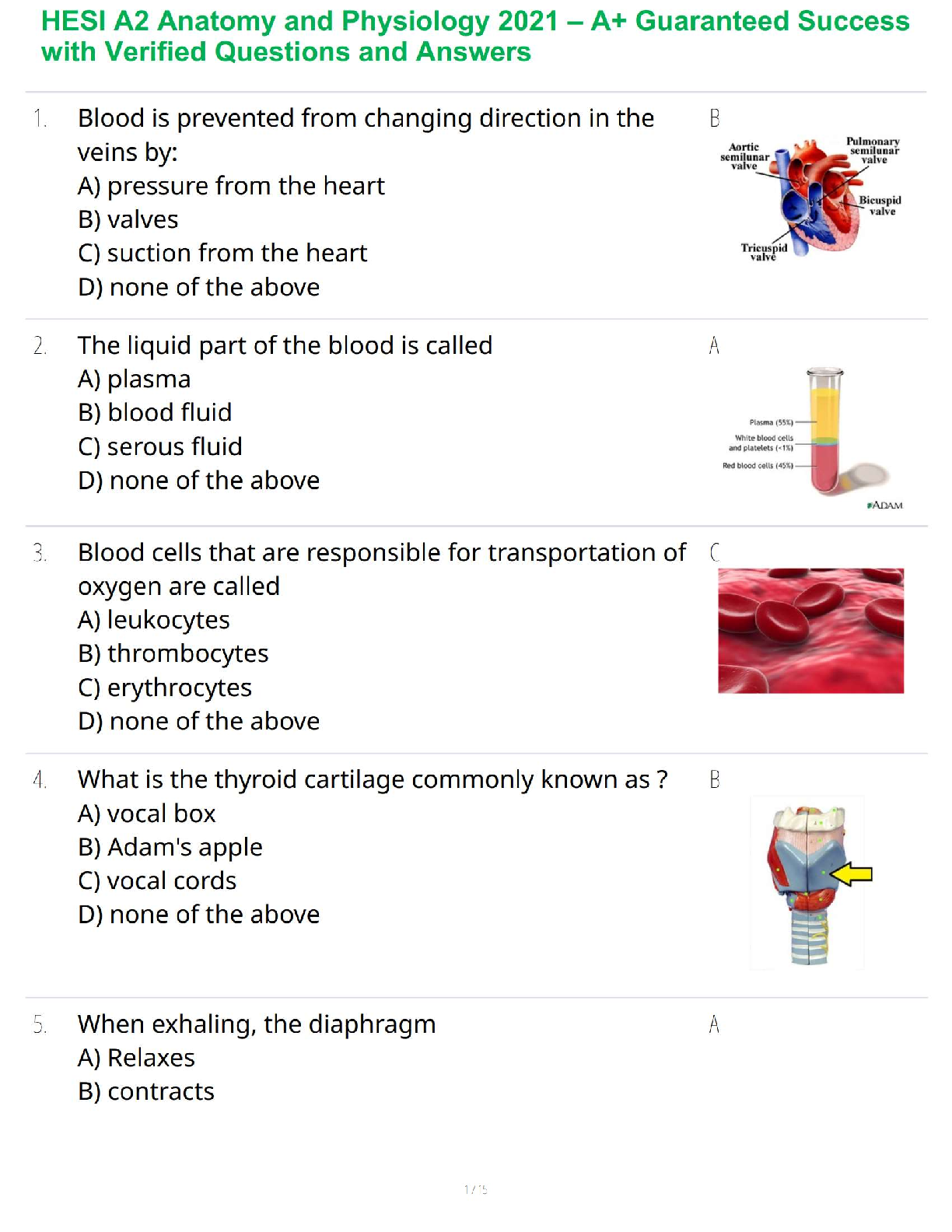
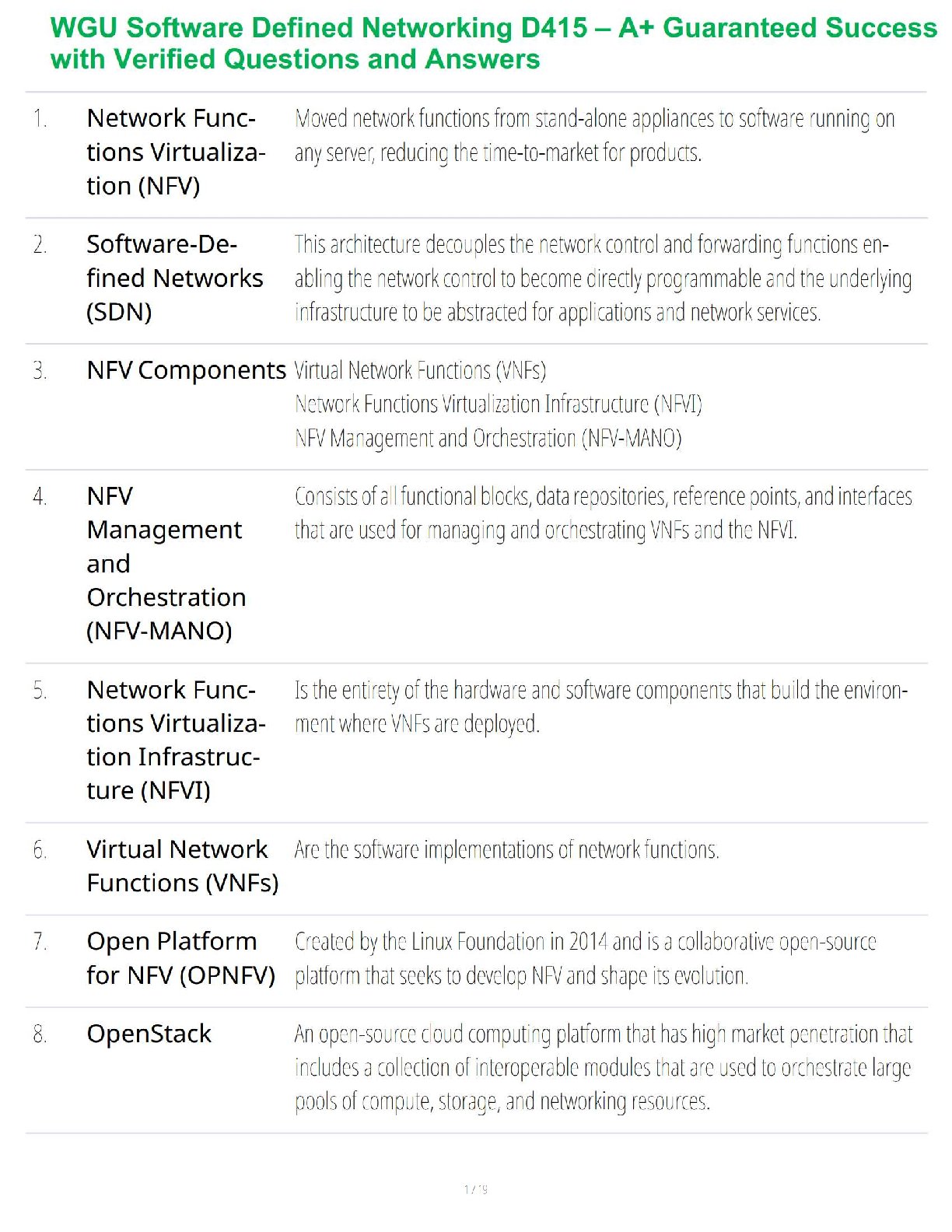
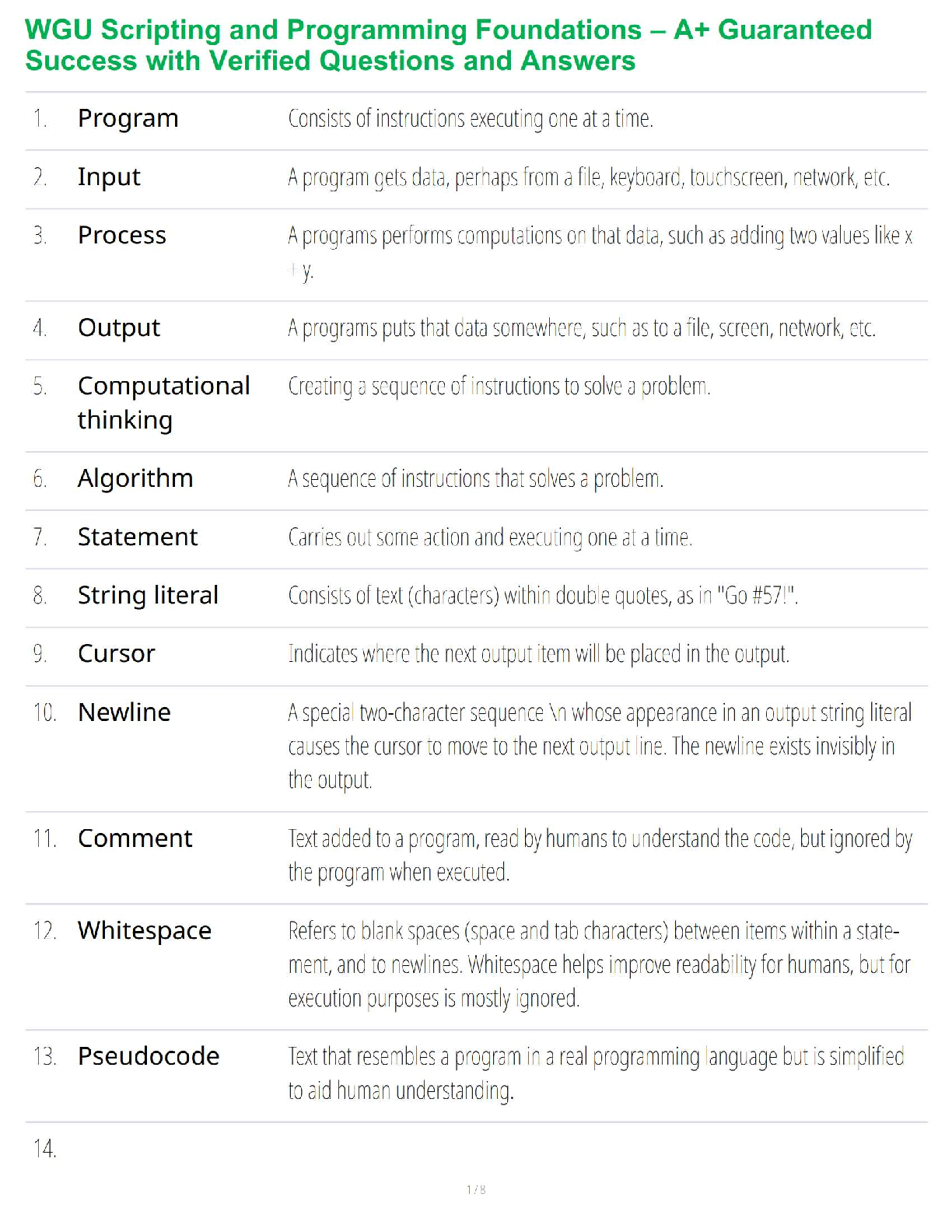
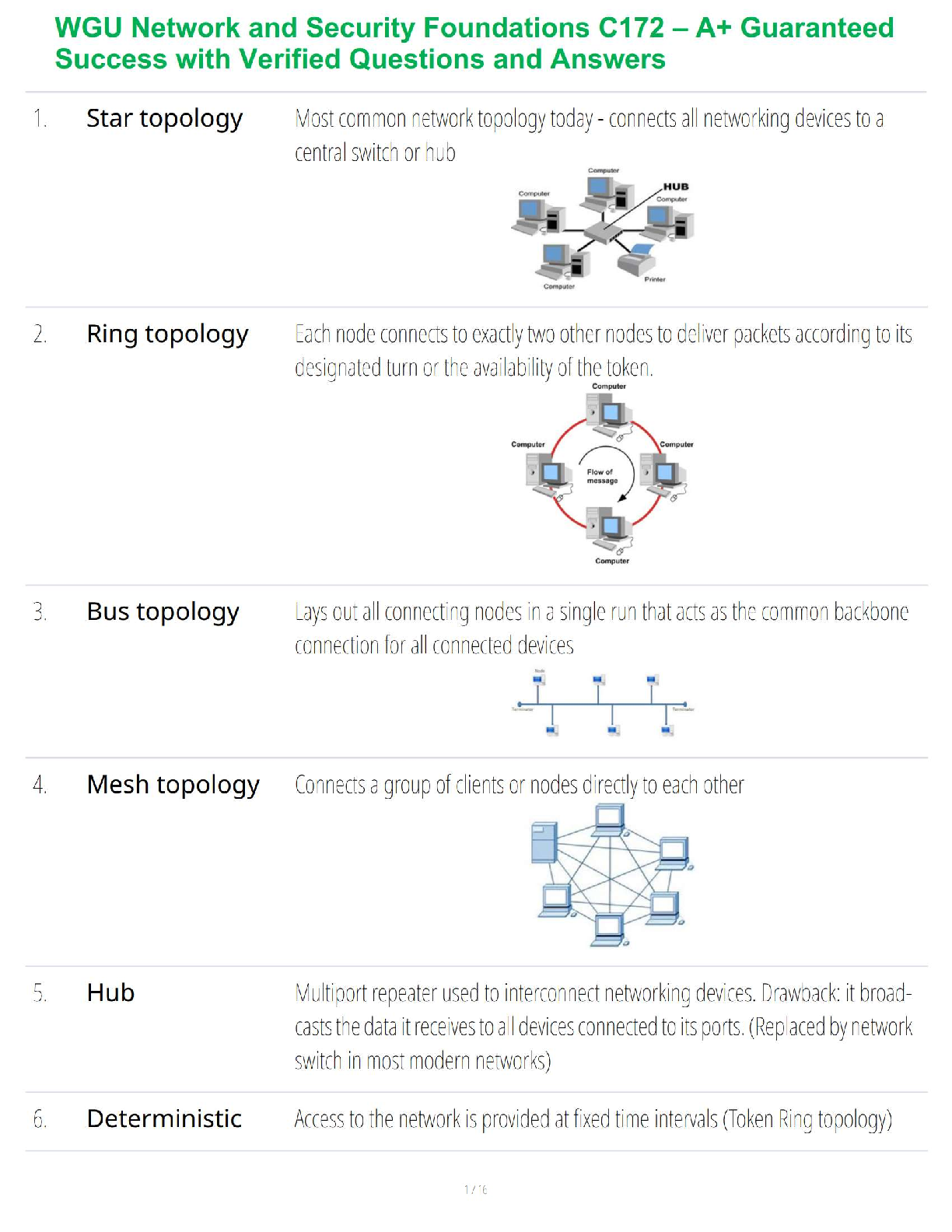
Nonessential amino acids can be created by the liver or (11) Matching complete and incomplete proteins
Document Content and Description Below
• What is the major function of triglyceride in food and physiologically in the body? Food functions: Triglycerides ➢ Triglycerides provide food functions of energy, palatability, safety, food pr ... ocessing, and source of nutrients. ➢ Source of energy ➢ Palatability: fat makes food smell and taste good ➢ Satiety and satiation: fat helps prevent hunger between meals. Fat slow down digestion because of the hormones released in response to its presence in the GI tract, causing us to feel full and satisfied->satiety. Satiation occurs during, not after eating. Satiation tends to increase our desire to eat more fatty food, not less. ➢ Food processing: emulsifier- a substance that works by being soluble in water and fat at the same time. Lecithin, a phospholipid, has an extensive role as an emulsifier ➢ Nutrient source ✓ Contain and transport fat-soluble vitamin A D E K ✓ Contain and transport essential fatty acids (linoleic and linolenic: essential) Physiologically functions: ➢ Stored energy ✓ Adipose tissue storage form of fat (mainly triglycerides), could produce about 3500 kcal as energy ✓ Important source of fuel during illness and food restriction, and major energy source for muscle work ➢ Organ protection ➢ Temperature regulator ➢ Insulation: a substance composed largely of fatty tissues, called myelin, cover nerve cells. This covering provided electrical insulation that allows for transmission of nerve impulses • Where does the digestion of lipids mainly occur? Digestion of lipids occurs mainly in the small intestine Fat as a Nutrient in the Body: Digestion ● Mouth ➢ Primary fat digestive process is mechanical, inasmuch as teeth masticate fatty food. ➢ Glands of the tongue produce fat-splitting enzyme (lingual lipase), released with saliva. ● Stomach ➢ Mechanical digestion continues through peristalsis. ➢ Fat-splitting enzymes such as gastric lipase hydrolyze fatty acids from triglycerides. ● Small intestine ➢ Duodenum releases hormone cholecystokinin (CCK). ● CCK action causes gallbladder to release bile into small intestine. ➢ Muscular action continues digestion. ➢ Pancreatic enzyme, lipase, breaks down triglycerides. ➢ Some fats may pass through undigested and are excreted. • What is the difference between saturated, polyunsaturated and unsaturated fats? What are some sources of each? Triglyceride is a compound consisting of three fatty acids and one glycerol molecule. A saturated fatty acid is contained in meats, butterfat, shortening, and vegetable oils. Additional food sources of saturated fatty acids are primarily animal, including beef, poultry, pork, lamb, luncheon meats, egg yolk, and dairy products (milk, butter, cheese); the only major plant sources are palm and coconut oils (often called tropical oils) and cocoa butter. CARBON CHAINS COMPLETELY SATURATED OR FILLED WITH HYDROGEN Monounsaturated fatty acid is in olive oil, peanuts (peanut butter and peanut oil), and canola oil. CONTAIN A CARBON CHAIN WITH ONE UNSATURATED DOUBLE BOND Polyunsaturated fatty acid is in vegetable oils (corn, safflower, wheat germ, canola, sesame, and sunflower), fish and margarine. FATTY ACID CONTAINING TWO OR MORE DOUBLE BONDS ON THE CARBON CHAIN ➢ Omega-3 fatty acids (linoleic acid), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ➢ Omega-6 fatty acids (linoleic acid) ➢ Food sources of omega-3 fatty acids and supplements ➢ Abundance of linoleic acid from consumption of large amounts of vegetable oils, such as margarine and salad dressing, and large amounts of prepared foods. Another source if linoleic acid may be form animal foods. Ex: poultry fat is predominantly saturated, also contains some PUFAs, including linoleic acid. ➢ Linolenic acid is associated with fish consumption. Main omega 3 fatty acid is in fish. Good source provide more omega 3 fatty acids: tuna, salmon, bluefish, halibut, sardines, and rainbow trout • What are the functions of phospholipids and cholesterol? Lecithin is the main phospholipid. Lecithin is a constituent of lipoproteins-carriers or transporters of lipids- including fats and cholesterol in the body. Functions of phospholipids a. Cell membrane structure b. Lecithin: main phospholipid, part of lipoproteins • What are the functions of sterols? Functions of sterols a. Precursors to bile, vitamin D, sex hormones, cells in brain and central nervous system i. Cholesterol: part of cell membranes, nerve tissue, and hormones. When exposed to ultraviolet light, a cholesterol substance in out skin can be converted to vitamin D by the kidney and liver. ii. Liver: synthesizes cholesterol to produce bile, the emulsifying substance necessary to absorb dietary lipids • What are some examples of foods high in cholesterol? Egg yolks, organ meats (liver and kidney) • Identify three types of lipids and list sources of each. Triglycerides, Phospholipids, and Sterols • What is the function of the linolenic and linoleic essential fatty acids? Are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Cant be made by the body and must be consumed in the diet Making compounds such as prostaglandins, that regulate many body functions including BP, blood clotting through platelet aggregation, gastric acid secretions, and muscle secretions • Identify some sources of Omega-3 fatty acids. Linolenic acid: (Flaxseed, flax oil, pumpkin seed, walnut oil, green leafy vegetables, walnuts, canola oil. EPA and DHA (Fish) • From a nursing perspective, explain why digestion, absorption, and transportation of lipids in the body is so important. • What are three different types of lipoproteins and their functions? VLDL: deliver TGs to body cells LDL: deliver cholesterol to all body cells HDL: pick up cholesterol form the body cells and take it back to the liver = reverse cholesterol transport. Potential to help reverse heart disease • What are the potential health concerns related to excessive dietary fat intake? Health concerns of dietary fat intake fall into several categories: appropriate energy intake, reduced intake of other nutrients because of excessive dietary fat consumption, and the relationship between dietary fat intake and dietary related disorders. TYPE 2 DM, HTN, CVD, CERTAIN ANCERS , [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 18, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 18, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
78