Question 1
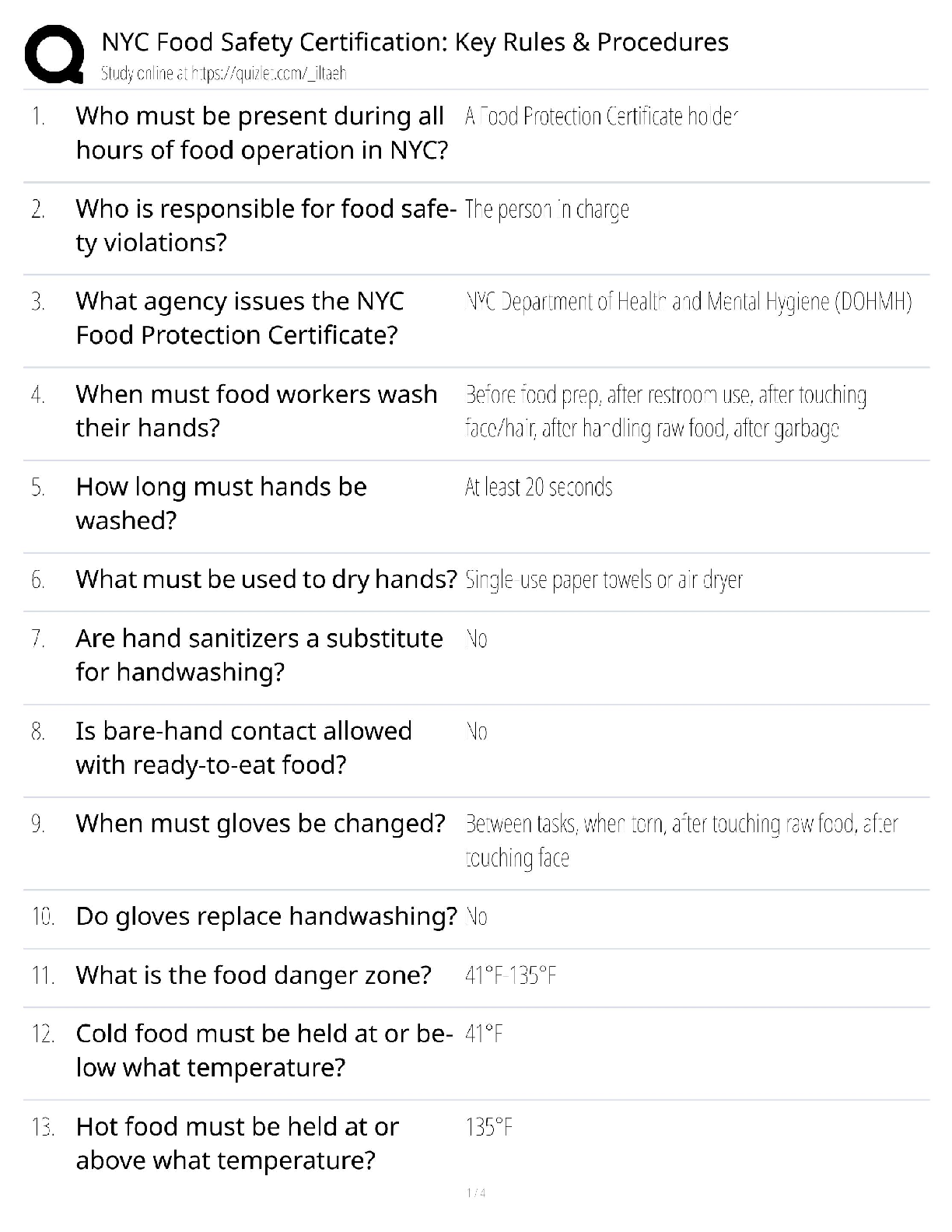
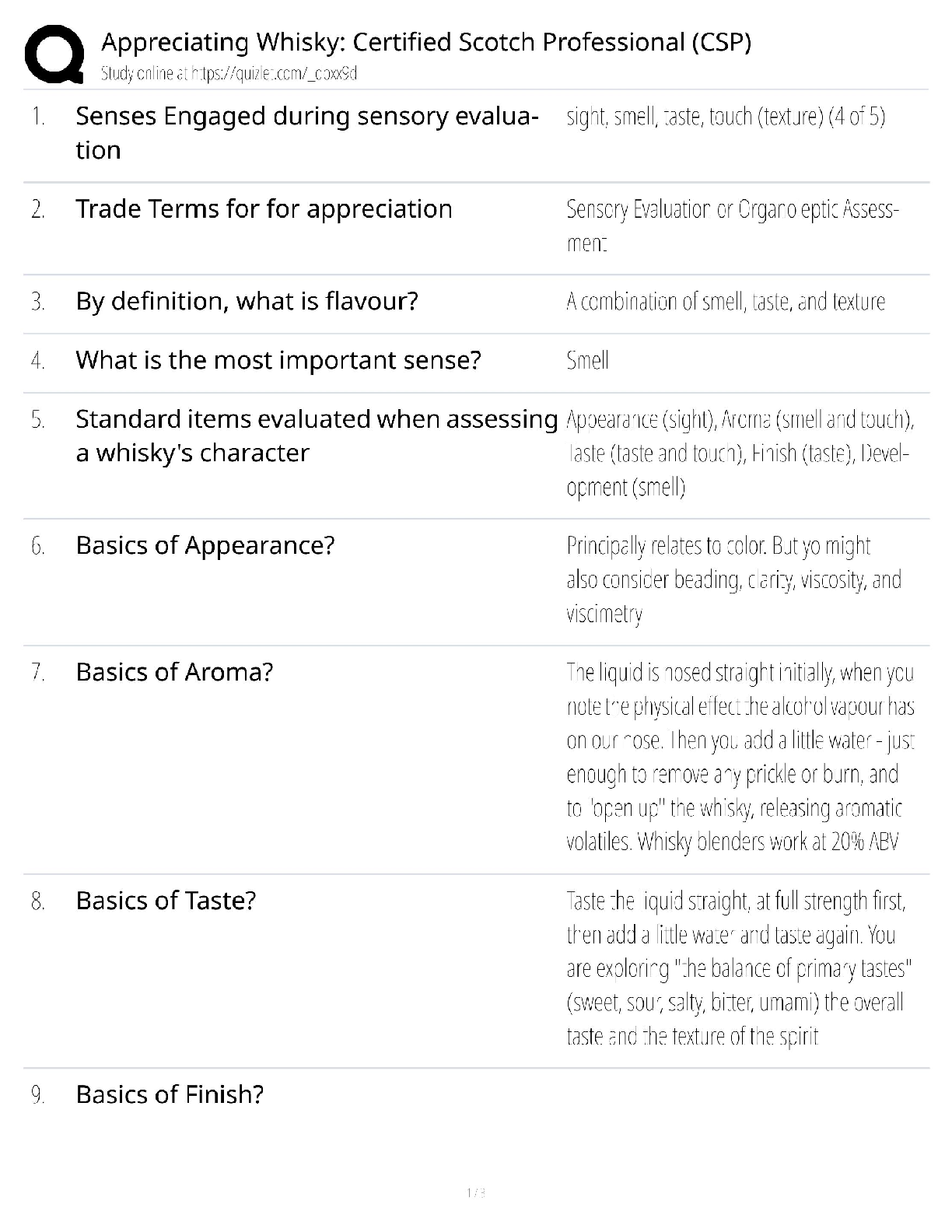
S. is a 59-year-old female who has been followed for several years for aortic
regurgitation. Serial echocardiography has demonstrated normal ventricular function,
but the patient was lost to follow-up for t
...
Question 1
S. is a 59-year-old female who has been followed for several years for aortic
regurgitation. Serial echocardiography has demonstrated normal ventricular function,
but the patient was lost to follow-up for the last 16 months and now presents
complaining of activity intolerance and weight gain. Physical examination reveals a
grade IV/VI diastolic aortic murmur and 2+ lower extremity edema to the midcalf. The
AGACNP considers which of the following as the most appropriate management
strategy?
A. Serial echocardiography every 6 months B. Begin a calcium channel antagonist
C. Begin an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor D. Surgical consultation
and intervention
Question 2
An ascending thoracic aneurysm of > 5.5 cm is universally considered an indication for
surgical repair, given the poor outcomes with sudden rupture. Regardless of the
aneurysm’s size, all of the following are additional indications for immediate operation
except:
A. Comorbid Marfan’s syndrome B. Enlargement of > 1 cm since diagnosis
C. Crushing chest pain D. History of giant cell arteritis
Question 3
Jasmine is a 31-year-old female who presents with neck pain. She has a long history of
injection drug use and admits to injecting opiates into her neck. Physical examination
reveals diffuse tracking and scarring. Today Jasmine has a distinct inability to turn her
neck without pain, throat pain, and a temperature of 102.1°F. She appears ill and has
foul breath. In order to evaluate for a deep neck space infection, the AGACNP orders:
A. Anteroposterior neck radiography B. CT scan of the neck C. White blood cell
(WBC) differential D. Aspiration and culture of fluid
Question 4
Mr. Draper is a 39-year-old male recovering from an extended abdominal procedure. As
a result of a serious motor vehicle accident, he has had repair of a small bowel
perforation, splenectomy, and repair of a hepatic laceration. He will be on total
parenteral nutrition postoperatively. The AGACNP recognizes that the most common
complications of parenteral nutrition are a consequence of:
A. Poorly calculated solution B. Resultant diarrhea and volume contraction C. The
central venous line used for infusion D. Bowel disuse and hypomotility
Question 5
Mr. Mettenberger is being discharged following his hospitalization for reexpansion of his
second spontaneous pneumothorax this year. He has stopped smoking and does not
appear to have any overt risk factors. While doing his discharge teaching, the AGACNP
advises Mr. Mettenberger that his current risk for another pneumothorax is:
A. < 10% B. 25-50% C. 50-75% D. > 90
Question 6
One of the earliest findings for a patient in hypovolemic shock is:
A. A drop in systolic blood pressure (SBP) < 10 mm Hg for > 1 minute when sitting up
B. A change in mental status C. SaO2 of < 88% D. Hemoglobin and hematocrit
(H&H) < 9 g/dL and 27%
Question 7
Traumatic diaphragmatic hernias present in both acute and chronic forms. Patients with
a more chronic form are most likely to be present with:
A. Respiratory insufficiency B. Sepsis C. Bowel obstruction D. Anemia
Question 8
The AGACNP is managing a patient in the ICU who is being treated for a pulmonary
embolus. Initially the patient was stable, awake, alert, and oriented, but during the last
several hours the patient has become increasingly lethargic. At change of shift, the
oncoming staff nurse appreciates a profound change in the patient’s mental status from
the day before. Vital signs and hemodynamic parameters are as follows: BP 88/54 mm
Hg Pulse 110 bpm Respiratory rate 22 breaths per minute SaO2 93% on a 50% mask
Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) 1600 dynes ∙ sec/cm5 Cardiac index 1.3 L/min
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) 8 mm Hg This clinical picture is most
consistent with which shock state?
A. Hypovolemic B. Cardiogenic C. Distributive D. Obstructive
Question 9
When counseling patients to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications, the
AGACNP knows that with respect to smoking cessation, the American College of
Surgeons and National Surgical Quality Improvement Program guidelines are clear that
patients who stop smoking _____ weeks before surgery have no increased risk of
smokingrelated pulmonary complications.
A. 2 B. 4 C. 6 D. 8
Question 10
Mitch C. is a 39-year-old male who is brought to the ED by paramedics. According to the
report of a neighbor, Mitch was distraught over a breakup with his fiancée and
attempted to commit suicide by mixing some chemicals from under his kitchen sink and
drinking them; afterward he changed his mind and knocked on his neighbor’s door
asking for help. Mitch is awake but stuporous, and the neighbor has no idea what he
drank. Visual inspection of his mouth and oropharynx reveals some edema and
erythema. He is coughing and has large amounts of pooling saliva. Mitch is not capable
of answering questions but he appears in pain. Endoscopy reveals full thickness
mucosal injury with mucosal sloughing, ulceration, and exudate. The AGACNP knows
that the appropriate course of treatment must include:
A.At least 6 hours of observation in the emergency department B. Periodic
esophagram C. Aggressive fluid resuscitation D.Esophagogastrectomy
Question 11
Jared V. is a 35-year-old male who presents for evaluation of a dry cough. He reports
feeling well overall but notices that he gets out of breath more easily than he used to
when playing soccer. A review of systems yields results that are essentially benign,
although the patient does admit to an unusual rash on his legs. Physical examination
reveals scattered erythematous nodules on both shins. There is no drainage, discomfort,
or itch. Additionally, diffuse, mildly enlarged lymph nodes are appreciated bilaterally.
Results of a comprehensive metabolic panel and complete blood count are within
normal limits. Twelve-lead ECG reveals sinus bradycardia at 58 bpm. Chest radiography
reveals bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy. The AGACNP suspects:
A.Bronchiectasis B. Pulmonary fibrosis C. Sarcoidosis D.Lung carcinoma
Question 12
Mrs. Miller is a 44-year-old female who is on postoperative day 1 following a total
abdominal hysterectomy. Her urine output overnight was approximately 200 mL. The
appropriate response for the AGACNP would be to order:
A.A urinalysis and culture B. 1 liter of NSS over 8 hours C. Encourage increased
mobility D.Liberalize salt in the diet
Question 13
All of the following are risk factors for spontaneous pneumothorax except:
A.Connective tissue disease B. Scuba diving C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD) D.Central line insertion
[Show More]