Hemophilia Pedigree - Father has hemophilia, mother does not. What is the outcome for
their kids? –
His daughters would be carriers. This is x-link recessive.
Autosomal:
Dominant: - Autosomal: males and females equal
...
Hemophilia Pedigree - Father has hemophilia, mother does not. What is the outcome for
their kids? –
His daughters would be carriers. This is x-link recessive.
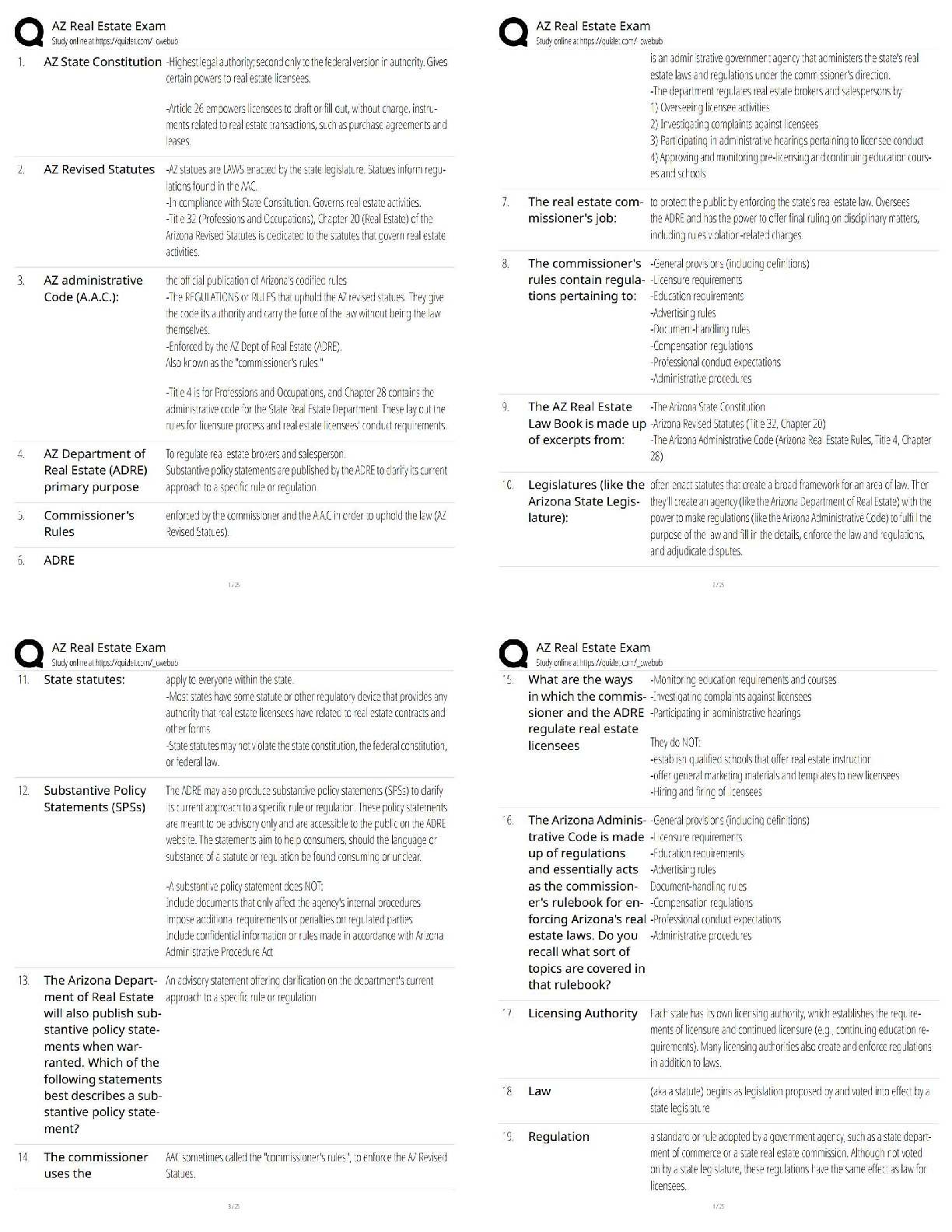
Autosomal:
Dominant: - Autosomal: males and females equally affected.
Dominant: non-carrier parents
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) –
The process of copying DNA in the lab. Uses Template DNA, Nucleotides
(dNTPS), DNA Polymerase, and DNA primers.
3 Steps of PCR –
1. Denaturation: DNA is heated to 95C to separate it.
2. Annealing: reaction is cooled to 50C; primers stick to the DNA you want to
copy and add DNA polymerase.
3. Elongation: reaction heated to 70C and DNA polymerase, adding nucleotides
building a new DNA strand.
Base Excision Repair (BER) –
How you repair a mutation. BER is used to repair damage to a base caused by
harmful molecules. You remove the base that is damaged and replace it. *BER
removes a single nucleotide*
DNA glycolsylase –
sees damaged DNA and removes it.
DNA polymeraseputs the right one back in while DNA ligase seals it.
Mismatch repair (MMR) occurs during: -
replication. DNA polymerase proofreads but sometimes a mismatch pair gets
through. MMR removes a large section of the nucleotides from the new DNA and
DNA polymerase tries again. (Ex: C-T instead of C-A)
Mismatch Repair corrects what kind of DNA damage? –
When a base is mismatched due to errors in replication. Such as G-T instead of
G-C. DNA polymerase comes by and fixes it.
What happens when DNA polymerase binds to DNA to make RNA? –
TRANSCRIPTION! DNA polymerase takes the individual nucleotides and matches
them to the parental sequences to ensure a correct pair. It must bind with RNA
primer to work.
What is needed for DNA replication? –
DNA polymerase
Nonsense Mutation –
Change in 1 nucleotide produces a STOP codon Stop= nonsense because it is no
more.
Silent Mutation –
Change in 1 nucleotide but codes for the same amino acid. Silent= the change
doesn't change the name of the protein
Missense Mutation –
Change in 1 nucleotide leads to a code for a different amino acid. Missense =
mistake was made.
What happends during RNA splicing? –
During RNA splicing introns are cut out, the remaining exons are joined together.
5'ATG AGT CTC TCT 3'
Find the DNA template strand. –
3'TAC TCA GAG AGA 5'
The DNA template strand is complimentary. So start with the opposite number,
then go L-R with the complimentary letter.
5'ATG AGT CTC TCT 3'
What is the corresonding mRNA sequence? –
5'AUG AGU CUC UCU 3'
[Show More]