CHAPTER 1 (2 left to answer)
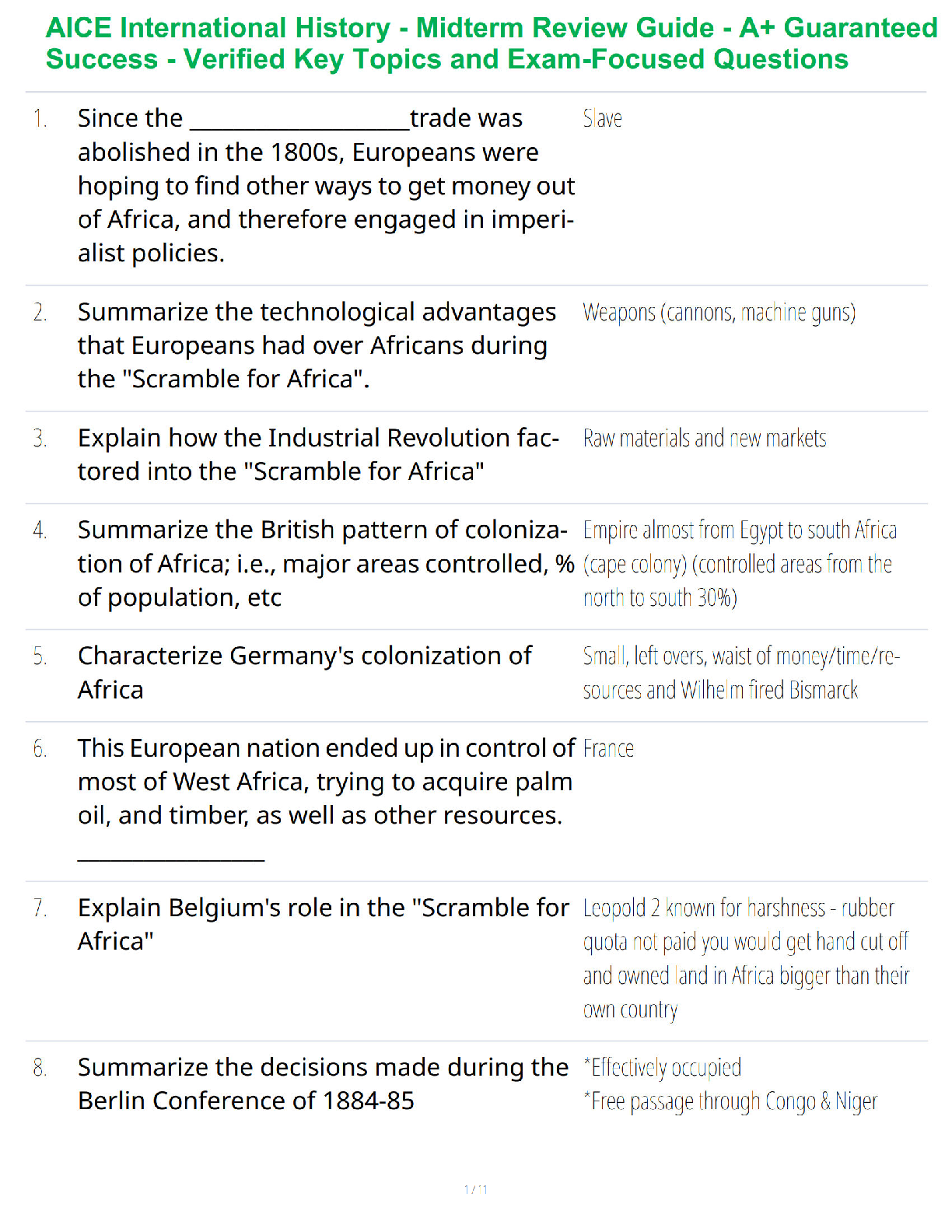
How many calories are provided by protein, carbohydrates, fat and alcohol?
Protein/Carbs: 4 kcal/gram
Fat: 9 kcal/gram
Alcohol: 7 kcal/gram
What does “nutrient density” mean? Nutrient de
...
CHAPTER 1 (2 left to answer)
How many calories are provided by protein, carbohydrates, fat and alcohol?
Protein/Carbs: 4 kcal/gram
Fat: 9 kcal/gram
Alcohol: 7 kcal/gram
What does “nutrient density” mean? Nutrient density assigns the value to a food
on the basis of a comparison of its nutrient content with the kcal the food contains.
The more nutrients and the fewer kcal a food provides, the higher its nutrient
density.
Know the basics of the six categories of nutrients.
The six categories of Nutrients; Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids (fats), Vitamins,
Minerals, Water. (**Pages 9-10 on the book goes into a lot of detail about each
one***)
CHAPTER 2 (1 left to answer)
What are the five food groups of MyPlate?
Veggies: 2 1⁄2 cups
Fruits: 2 cups
Grains: 6 oz.
Protein: 5 1⁄2 oz.
Dairy: 3 cups
What is “fortification”? Enrichment of nutrients
What nutrients are required on a food label?
Calories, calories from fat, total fat, saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol,
sodium, total carbohydrates, dietary fiber, sugars, protein, Vitamin A, Vitamin
C, Calcium & Iron
Know how to read a food label (Page 30-32, page 32 shows an actual label**) The
Daily Values is a system for food labeling composed of two sets of reference values:
daily intakes (RDIs) and daily reference values. The percent of Daily Values
information (%DV), based on a 2000 kcal diet, is intended to show consumers how
much of a day’s ideal intake of a particular nutrient they are eating. DVs for selected
nutrients and food components based on a 2500-calorie diet are also given at the
bottom of the label.
CHAPTER 3
In what order does food pass through the G.I. tract?
The mouth the esophagus the stomach small intestine large intestine
Know chemical versus mechanical digestion.
Mechanical Digestion: Chewing, peristalsis, segmentation, action of
sphincter muscles
Chemical Digestion: Actual breakdown of substances from the production
and/or storage of gastric and digestive secretions.
Know the physiological function of the stomach, small intestine, pancreas,
liver, gallbladder, and large intestine as it relates to digestion.
Stomach: Holding food for partial digestion, producing gastric juice,
providing muscular action, secreting the intrinsic factor for Vitamin b12,
releasing gastrin, and assisting in the destruction.
Small Intestine: Absorption of nutrients. Duodenum jejunum ileum
Pancreas: Releases digestive enzymes.
Liver: Releases glycogen. Breaks down RBCs. Breaks down fats and produces
energy/bile.
Gallbladder: Stores bile
Large Intestine: Absorption of water. Consists of cecum, colon and rectum.
CHAPTER 4 (1 left to answer)
What are the three sizes of carbohydrates? Name examples of each size.
Carbohydrates are classified according to the number of saccharide units making up
their structure.
• Monosaccharides: simple carbohydrates (glucose-corn syrup, fructose-fruits,
galactose-found in milk)
• Disacchardies: simple carbohydrates (sucrose-table sugar, lactose-milk sugar,
maltose-malt sugar)
• Polysaccharides: complex carbohydrates(starches-grains, legumes, and root
vegetables, Fiber-whole grains, fruits, and veggies!)
What is the normal blood glucose range? 70-100
What is the function of insulin? Bring down blood sugar.
What are the health benefits of a high fiber diet? Prevents obesity, formation of
diverticula, prevents cancer, prevents heart disease
[Show More]