Liberty University - EDCO 735/EDCO735 Week 2 Quiz
Document Content and Description Below
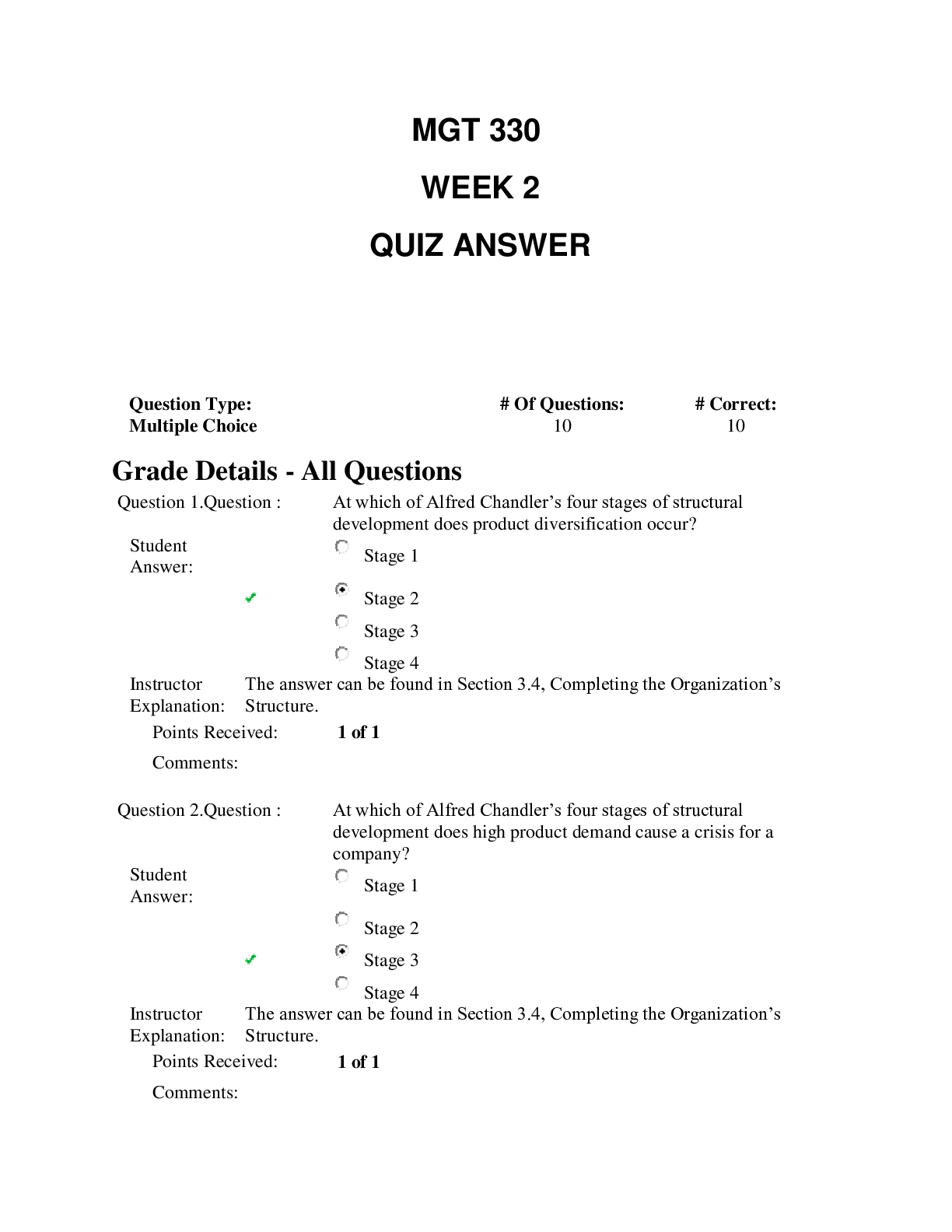
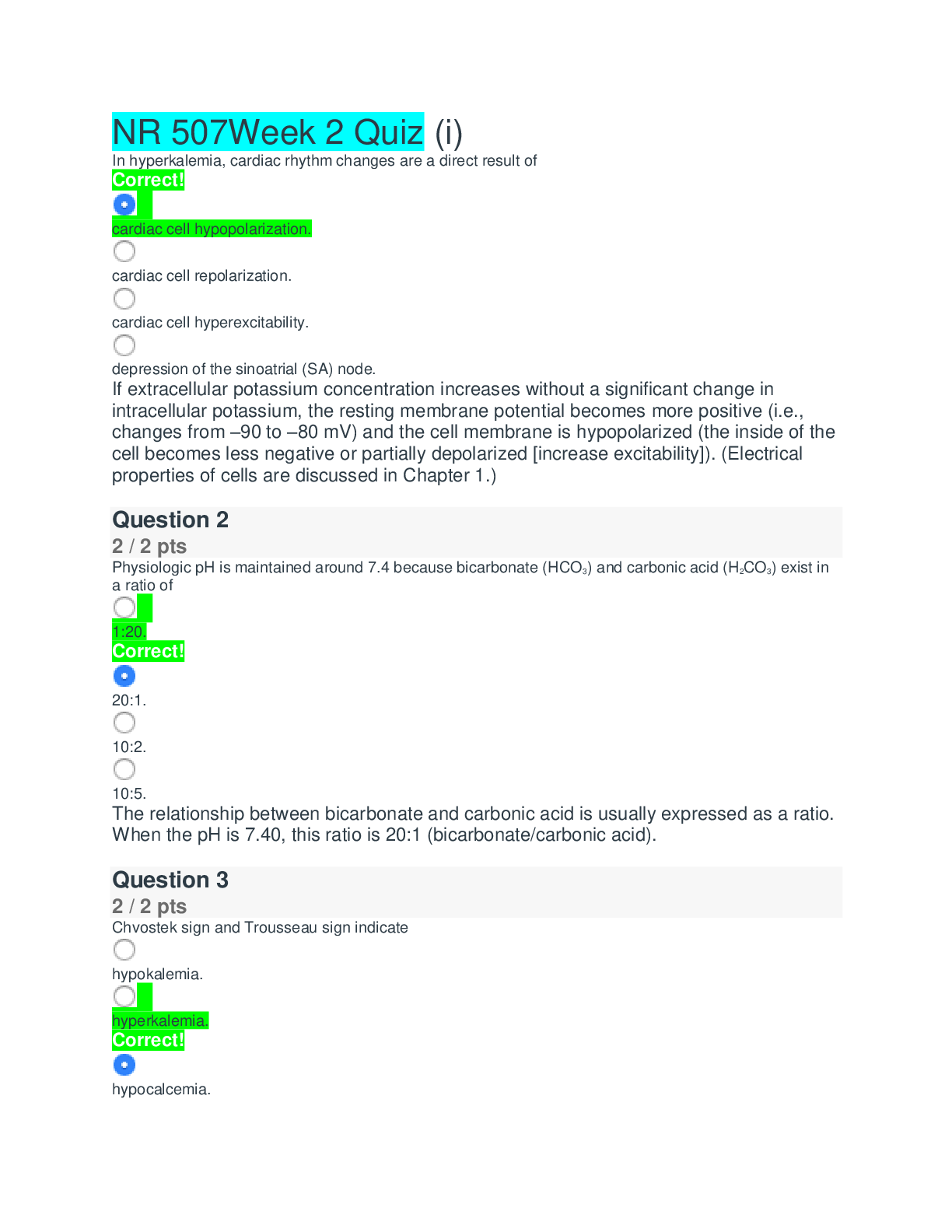
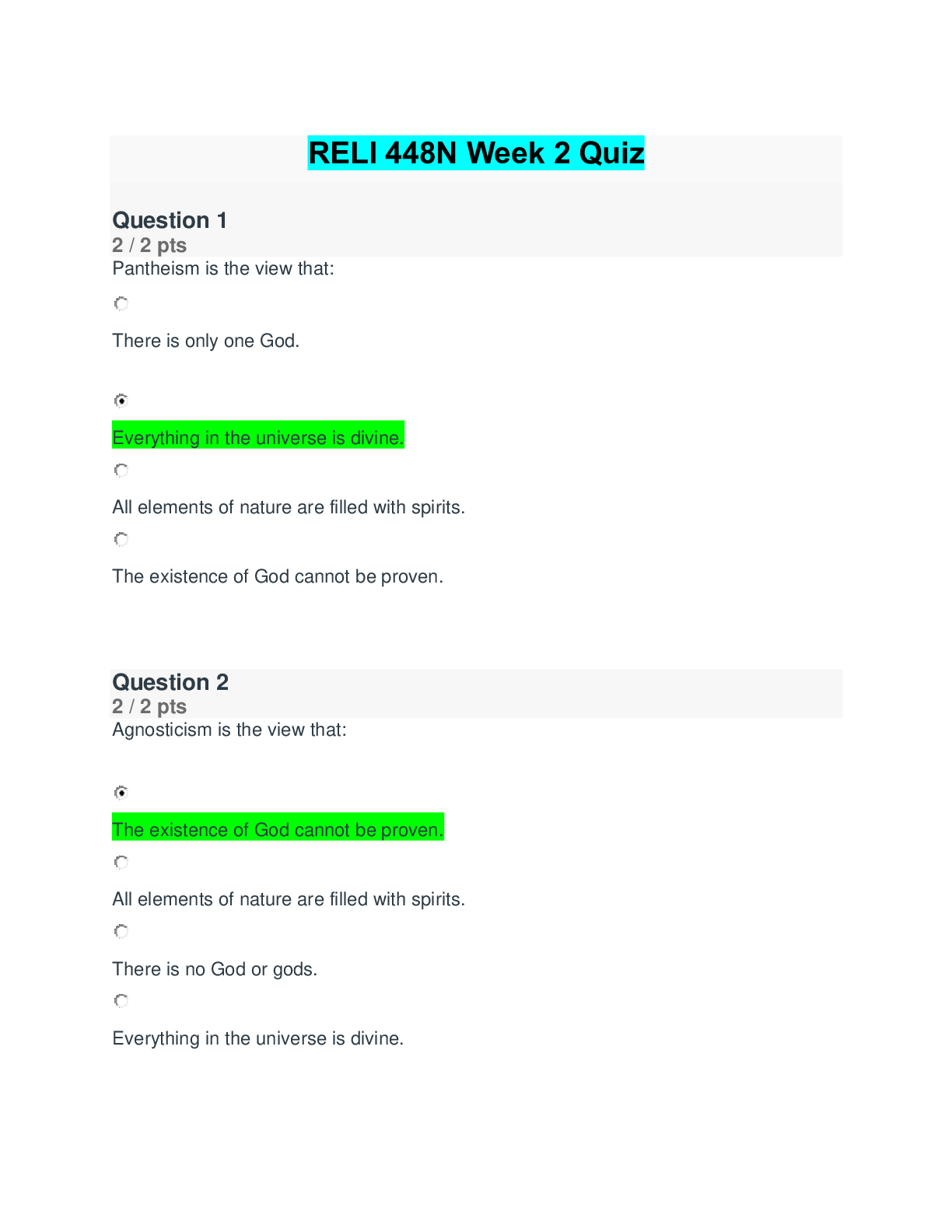
Liberty University - EDCO 735/EDCO735 Week 2 Quiz A two-tailed outlier for the t distribution must have a t score equivalent to the: highest 5% or lowest 5% of the t distribution only the highest 5... % of the t distribution only the lowest 5% of the t distribution highest 2.5% or lowest 2.5% of the t distribution In order to calculate the mean you must: multiply each score by itself take the square root of the sum have at least interval level of measurement divide by degrees of freedom Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.3 Outliers in the sample are defined by: a measure of dispersion how far any given score in the population can be expected to be from the mean how many standard deviations there score is from the mean the square root of variance The t distribution and the z distribution: are skewed have 95% confidence level have values associated with percentiles are random 1.5 Calculating the sample standard deviation always makes use of: nominal level of measurement variance convenience sample random sample Known distributions (e.g., t, z, and F) allow us: determine causal inference determine the percentile of our score or statistic give and receive scores label our means Which of the following is needed to calculate confidence interval's upper limit? population mean SS variance 2.6 Which of the following is needed to calculate confidence interval's upper limit? SEM SS each score value Sampling error: depends on sample size is large when we have a diverse population is the s is smaller the more educated the sample For every statistic (e.g., mean) a researcher calculates in her sample, she is estimating that same value in the: second sample distribution population experimental sample In order to calculate the mean you must: divide by the sample size use a representative sample have at least ratio level of measurement have a normal distribution 7.5 A one-tailed outlier for the t distribution must have a t score equivalent to the: only the lowest 5% of the t distribution highest 5% or lowest 5% of the t distribution only the highest 5% of the t distribution highest 2.5% or lowest 2.5% of the t distribution Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.13 4.4 When different sets of data of the same size are randomly chosen from a population, the resulting variation in values is called: standard deviation sampling error confidence interval magnitude of error 3.5 In order to calculate variance you must do all of the following except for: multiply the difference between each score and the mean by itself Response Feedback: divide the sum of squared deviations by the sample size ?? compute the mean subtract the mean from each score Warner - Sections 2.4 - 2.6 3.4 degrees of freedom is the square root of variance is calculated by subtracting one from the sample size is calculated by dividing the SS by the mean is calculated by dividing the SS by the sample size In order to calculate variance you must: divide the sum of squared deviations by n divide the sum of squared deviations by df take the square-root of the sum of squared deviations divide the sum of scores by df Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.4-2.6 In study of a new treatment for depression, a researcher compares the new treatment on a group of patients with major depression with a second group that are treated with the standard treatment as usual. How many theoretical populations is the researcher estimating depression for? one two none three Response Feedback: It is important to note that before treatment each group in an experimental study is equivalent. After treatment, however, each group that is treated uniquely represents a different theoretical population. We estimate error because: Response Feedback: it helps understand the relationship between our sample and the population our population is hypothetical it effects the standard deviation its conventional to do so Warner - Section 2.11 - 2.14 6.5 How do researchers report information about the size of sampling error? using a confidence interval Response Feedback: magnitude of the difference random sample standard error Warner - 2.8-2.14 The difference between the population mean and the sample mean that arise just by chance represents the: magnitude of the difference sampling error ?? 6 standard error prediction error Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.10 In a study of a new drug intended to reduce anxiety, a researcher has a low dose group, a medium dose group, and a placebo control group. How many theoretical populations are represented in this study? thre e one two four Sampling error refers to: about how much we should expect an individual score in our sample to be from the population mean about how much we should expect our sample mean to be from the population mean the amount of error in our measurement how representative our sample is Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.8 - 2.14 The t distribution and the z distribution are: symmetric al leptokurti c random biased Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.8 - 2.14 3.6 All of the following calculations are necessary for calculating s except for: t critical variance mean sum of squared deviations 1.6 s is all of the following except: is a measure of dispersion is the square root of variance tells us about how far any given score in the population can be expected to be from the mean is biased Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.4 - 2.6 The formula for a confidence interval's upper limit is: s + [tcritical × SEM] s - [tcritical × SEM] M - [tcritical × SEM] M + [tcritical × SEM] In words, what is the formula for the SEM? the standard deviation multiplied by the square root of the sample size the sample mean multiplied by the square root of the sample size the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size the sample mean divided by the square root of the sample size The distribution of depression scores in the theoretical population is NOT: Gaussian platykurtic symmetric al bell- shaped Response Feedback: The distribution of a quantitative variable in a theoretical population is always assumed to be normal. 8.4 Which of the following is NOT one of the steps for calculating a confidence interval? determine df calculate the F ratio determine tcritical calculate the SEM What information do you need to find tcritical for a 95% CI? df M SE M s 6.6 The variations of the t distribution are especially noticeable when: the population is normal the sample is biased sample sizes are small the sample is normal Response Feedback: Warren - Section 2.13 As N increases, the standard error of the mean: varies randomly increases remains constant decreases 2.5 A two-tailed outlier for the Z distribution must have a Z score equivalent to the: only the lowest 5% of the z distribution only the highest 5% of the z distribution highest 5% or lowest 5% of the z distribution highest 2.5% or lowest 2.5% of the z distribution 2.4 The theoretical population is: the population that a particular statistic estimates only matters when a convenience sample is used the population where both groups are drawn equivalent to the population of the world The standard error of the mean is conceptually similar to: causal inference the standard deviation variance sum of squared deviations Response Feedback: Warner - 2.11 9.6 The t distribution and the z distribution are all of the following all of the time except: platykurtic discovered or developed by statisticians have values associated with percentiles symmetrical Sum of squared deviations: can never be negative has no lower limit is divided by the sample size to calculate variance can never be zero Variance: is calculated by dividing the SS by the sample size is biased when calculated by df is a measure of dispersion tells us about how far any given score in the population can be expected to be from the mean 7.4 df are used because: samples underestimate population variance sample distributions are skewed samples underestimate SS samples provide the point estimate The t distribution and the z distribution are all of the following all of the time except: map to percentiles discovered or developed by statisticians normal symmetrical The larger the sample size: the more sampling error the less random our sample the less sampling error the more outliers influence our distribution 6.4 z and t distributions are known because: statisticians developed\discovered them they measure variance Karl Pearson developed them they have always been What is the formula for the df of a CI? M - 1 s - 1 n - 1 SEM - 1 • Question 7 All of the following calculations are necessary for calculating s except for: • Question 8 The theoretical population is: Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.10 - 2.14 • Question 5 What is the formula for the df of a CI? • Question 2 5.4 As sample size increases while all other things are constant, the confidence interval: decreases Response Feedback: Warner - Section 2.9- 2-14 • Question 3 10.5 Which of the following is NOT needed in the formula for calculating a confidence interval's lower limit? M • Question 3 The standard error is related to all of the following except: 1.4 The standard error is related to all of the following except: - causal inference 10. 4 t critical when the population is: Known 5.5 Which of the following is needed to calculate confidence interval’s lower limit? -SEm SS M Which of the following is needed to calculate confidence interval's lower limit? SEm 4.5 As N decreases we can expect the standard error of the mean to: Increases 9.4 In order to calculate the sum of squared deviations you must take the square root of the sum 4.6 In order to calculate the sum of squared deviations you must do all of the following except for: Calculate square root of variance 7.6 Outliers are defined by: where the scores or values fall on a known (t, z, F) distribution 8.6 A statistic of the sample is an estimate of: the parameter in the second sample the statistic in the second sample the parameter in the theoretical sample 10.6 The theoretical population can also be conceptualized as the: the population that a particular statistic estimates A one-tailed outlier for the Z distribution must have a Z score equivalent to the: the highest 5% of the z distribution only Which of the following is NOT needed in the formula for calculating a confidence interval's upper limit? SEm M We use a t critical when the population is: known Theoretical Variance is biased when calculated by df The mean of a sample is: the average of all scores divided by the sample size [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 09, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 09, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
276