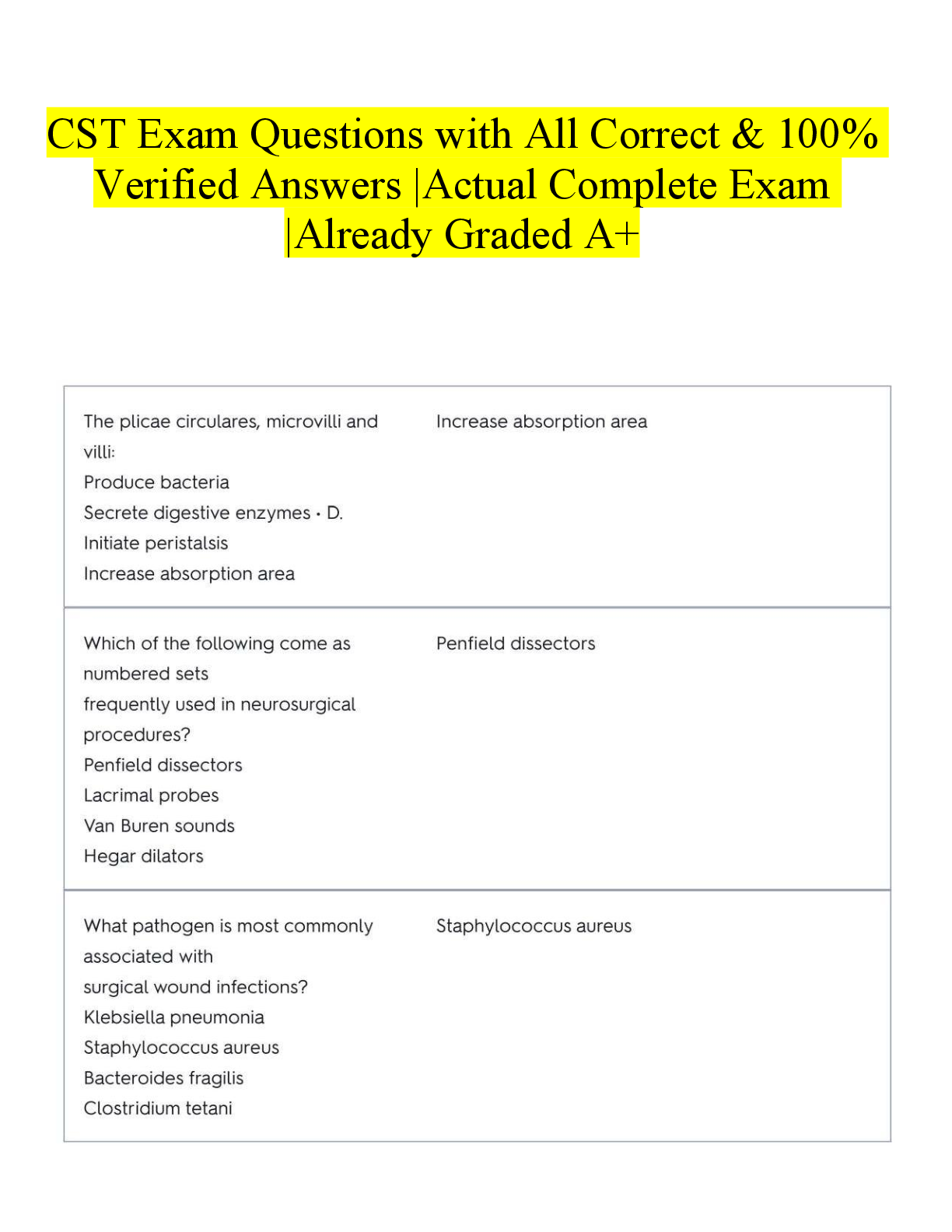
*NURSING > EXAM > NR 511 Final practice questions WITH DETAILED KEY ANSWERS HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW (Chamberlain College (All)
NR 511 Final practice questions WITH DETAILED KEY ANSWERS HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW (Chamberlain College of Nursing)VERY HELPFUL DURING REVISION
Document Content and Description Below
Final Exam Practice Questions Question 1. Matthew, age 52, is a chef who just severed 2 of his fingers with a meat cutter. You would recommend that he: 1. Wrap the severed fingers tightly in a dry ... towel for transport to the emergency department with him. 2. Leave the severed fingers at the scene because fingers cannot be reattached. 3. Immediately freeze the severed fingers for reattachment in the near future. 4. Wrap the fingers in a clean, damp cloth; seal them in a plastic bag; and place the bag in an ice water bath. Rationales Option 1: Severed fingers should be wrapped in a clean, damp cloth; sealed in a plastic bag; and placed in an ice water bath. Option 2: Severed fingers can be reattached after 1 to 2 days—or more—if properly stored. Option 3: Severed fingers should be wrapped in a clean, damp cloth; sealed in a plastic bag; and placed in an ice water bath, not frozen or kept at body temperature. Option 4: If a client has severed his fingers, the fingers should be wrapped in a clean, damp cloth; sealed in a plastic bag; placed in an ice water bath; and transported to the emergency room along with the client. The valgus stress test, varus stress test, Lachman test, and thumb sign are all considered standard tests to check the integrity of the ligaments of the knee. Which test would the nurse practitioner choose to assess the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), which is the most commonly involved structure in severe knee injury? 1. Valgus stress test. 2. Varus stress test. 3. Lachman test. 4. Thumb sign. Rationales Option 1: The valgus stress test assesses stability of the medial collateral ligament (MCL). Option 2: The varus stress test assesses stability of the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Option 3: The Lachman test assesses the ACL. Option 4: The thumb sign assesses the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). Lillian, age 70, was told that she has osteoporosis. When she asks you what this is, you respond that osteoporosis: 1. Develops when loss of bone occurs more rapidly than new bone growth. 2. Is a degenerative joint disease characterized by loss of cartilage in certain joints. 3. Is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects multiple joints.4. Is a bone disorder that has to do with inadequate mineralization of the bones. Rationales Option 1: Osteoporosis develops when bone resorption occurs more rapidly than bone deposition. Option 2: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by degeneration and loss of articular cartilage in synovial joints. Option 3: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder characterized by persistent synovitis of multiple joints. Option 4: Osteomalacia is a metabolic bone disorder characterized by inadequate mineralization of the bone matrix, often caused by vitamin D deficiency. Mike, age 42, a golf pro, has had chronic back pain for many years. His workup reveals that it is not the result of a degenerative disk problem. His back “goes out” about twice per year, and he is out of work for about a week each time. Which of the following should the nurse practitioner advise him to do? 1. Consider changing careers to something less physical. 2. Begin a planned exercise program to strengthen back muscles. 3. Make an appointment with a neurosurgeon for a surgical consultation. 4. Start on a daily low-dose narcotic to take away the pain. Rationales Option 1: Suggesting a career change should be considered only in cases of disability or inability to safely continue one’s current employment. Option 2: In this case, Mike may benefit from a regular planned exercise program to strengthen his back muscles and attempt to reduce the probability of future episodes of back pain. Option 3: Surgery is recommended only for clients with low back pain caused by degenerative disk disorders, and then only when severe neurologic involvement has occurred. Surgery benefits only approximately 1% of people with low back problems. Option 4: Narcotic pain medications are not considered first-line treatment for mechanical back pain. Course Topic: Musculoskeletal Problems Concept(s): 21820Cognitive Level: Analysis [Analyzing] Janine, age 69, has class III rheumatoid arthritis. According to the American Rheumatism Association, which of the following describes her ability to function? 1. Adequate for normal activities despite a handicap of discomfort or limited motion of one or more joints. 2. Largely or wholly incapacitated, bedridden, or confined to a wheelchair, permitting little or no self-care. 3. Completely able to carry out all usual duties without handicap. 4. Adequate to perform only a few or none of the duties of usual occupation or self-care. Rationales Option 1:Class II refers to the client whose function is adequate for normal activities despite a handicap of discomfort or limited motion of one or more joints. Option 2: Class IV refers to the client who is largely or wholly incapacitated, bedridden, or confined to a wheelchair, permitting little or no self-care. Option 3: Class I refers to the client who can carry out all usual duties without handicap. Option 4: The American Rheumatism Association has established functional classes I to IV to describe a client’s ability to accomplish activities of daily living. Because Janine is class III, her function would be adequate to perform only a few or none of the duties of usual occupation or self-care. For an adult patient with a knee injury, the nurse practitioner orders a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) to be taken on a routine basis for the next 2 weeks. Patient teaching should include which of the following? 1. “You may take this medication on an empty stomach as long as you eat within two to three hours of taking it.” 2. “If one pill does not seem to help, you can double the dose for subsequent doses.” 3. “If you notice nausea, vomiting, or black or bloody stools, take the next dose with a glass of milk or a full meal.” 4. “If you have additional pain, an occasional acetaminophen (Tylenol) is permitted in between the usual doses of the NSAID.” Rationales Option 1: When teaching clients about NSAIDs, tell them not to take these drugs on an empty stomach but to take them with food or milk. Option 2: Clients should be taught to never take more than the prescribed dose of an NSAID due to the likelihood of increasing the chances of gastrointestinal (GI) and kidney damage. Option 3: When teaching clients about NSAIDs, tell them to stop the medication and call immediately if they notice any nausea, vomiting, coffee-grounds emesis, black stools, or blood in the stool. Option 4: If the client is having additional pain, acetaminophen (Tylenol) may be taken in conjunction with an NSAID because it is not an NSAID and will not potentiate gastric bleeding. Sean, a factory line worker, has osteoarthritis (OA) of the right hand. According to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), the guidelines for pharmacologic treatment include: 1. Acetaminophen, tramadol, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections. 2. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), tramadol, and articular corticosteroid injections. 3. Acetaminophen, topical capsaicin, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). 4. Topical capsaicin, topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and oral NSAIDs. RationalesOption 1: Acetaminophen, oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), tramadol, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections are recommended for initial management of hip OA. Option 2: Acetaminophen, oral NSAIDs, tramadol, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections are recommended for initial management of hip OA. Option 3: The ACR conditionally recommends acetaminophen, oral NSAIDs, topical NSAIDs, tramadol, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections for OA of the knee. Option 4: Topical capsaicin, topical NSAIDs, oral NSAIDs, and tramadol are recommended by the ACR for the treatment of OA of the hand. Margaret, age 55, presents to you for evaluation of left hand and wrist pain and swelling after a slip and fall on the ice yesterday. On examination, you note tenderness at her “anatomical snuffbox.” You know this probably indicates a(n): 1. Ulnar styloid fracture. 2. Scaphoid fracture. 3. Hamate fracture. 4. Radial head fracture. Rationales Option 1: An ulnar styloid fracture would produce tenderness at the distal ulna. Option 2: There is tenderness over the “anatomical snuffbox” in a scaphoid (aka navicular) fracture, the most common injury of the carpal bones. Poor blood supply puts the scaphoid bone at risk of avascular necrosis; therefore, wrist pain and tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox, even without history of antecedent trauma, warrant a wrist x-ray. Option 3: A fracture of the hook of the hamate is an uncommon injury seen in golfers and players of racket sports that involves pain and tenderness on the ulnar side of the palm. Option 4: A radial head fracture would result in pain at the elbow joint where the radial head lies proximal to the distal humerus. Be sure not to confuse the radial head (proximal end of the radius) with the radial styloid (distal end of the radius at the wrist). Jim, age 22, a stock boy, has an acute episode of low back pain. The nurse practitioner orders a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) and should educate him in which of the following? 1. Maintaining moderate bed rest for 3 to 4 days. 2. Calling the office for narcotic medication if there is no relief with the NSAID after 24 to 48 hours. 3. Beginning lower back strengthening exercises depending on pain tolerance. 4. Wearing a Boston brace at night. Rationales Option 1:Years ago, muscle relaxants and bed rest were the treatments of choice for low back pain. Studies have now shown that resuming normal activity within the limits imposed by the pain has an effect as good as, if not better than, 2 days of bed rest. Option 2: NSAIDs, not narcotics, are generally the first-line medication treatment of low back pain and have no risk of opioid dependency. Option 3: Years ago, muscle relaxants and bed rest were the treatments of choice for low back pain. Studies have now shown that resuming normal activity within the limits imposed by the pain has an effect as good as, if not better than, 2 days of bed rest. The key here is letting pain be your guide. Exercise should begin as soon as possible after the acute injury and be directed at building endurance and stamina, with consideration given to one’s pain tolerance. Option 4: A Boston brace may be used in the treatment of scoliosis. Jessie, age 49, states she thinks she has rheumatoid arthritis. Before any diagnostic tests are ordered, the nurse practitioner completes a physical examination and makes a diagnosis of osteoarthritis rather than rheumatoid arthritis. Which clinical manifestation ruled out rheumatoid arthritis? 1. Fatigue. 2. Affected joints are swollen, cool, and bony hard on palpation. 3. Decreased range of motion. 4. Joint stiffness. Rationales Option 1: Fatigue is common to both diseases. Option 2: [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 127 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 26, 2021
Number of pages
127
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 26, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
170