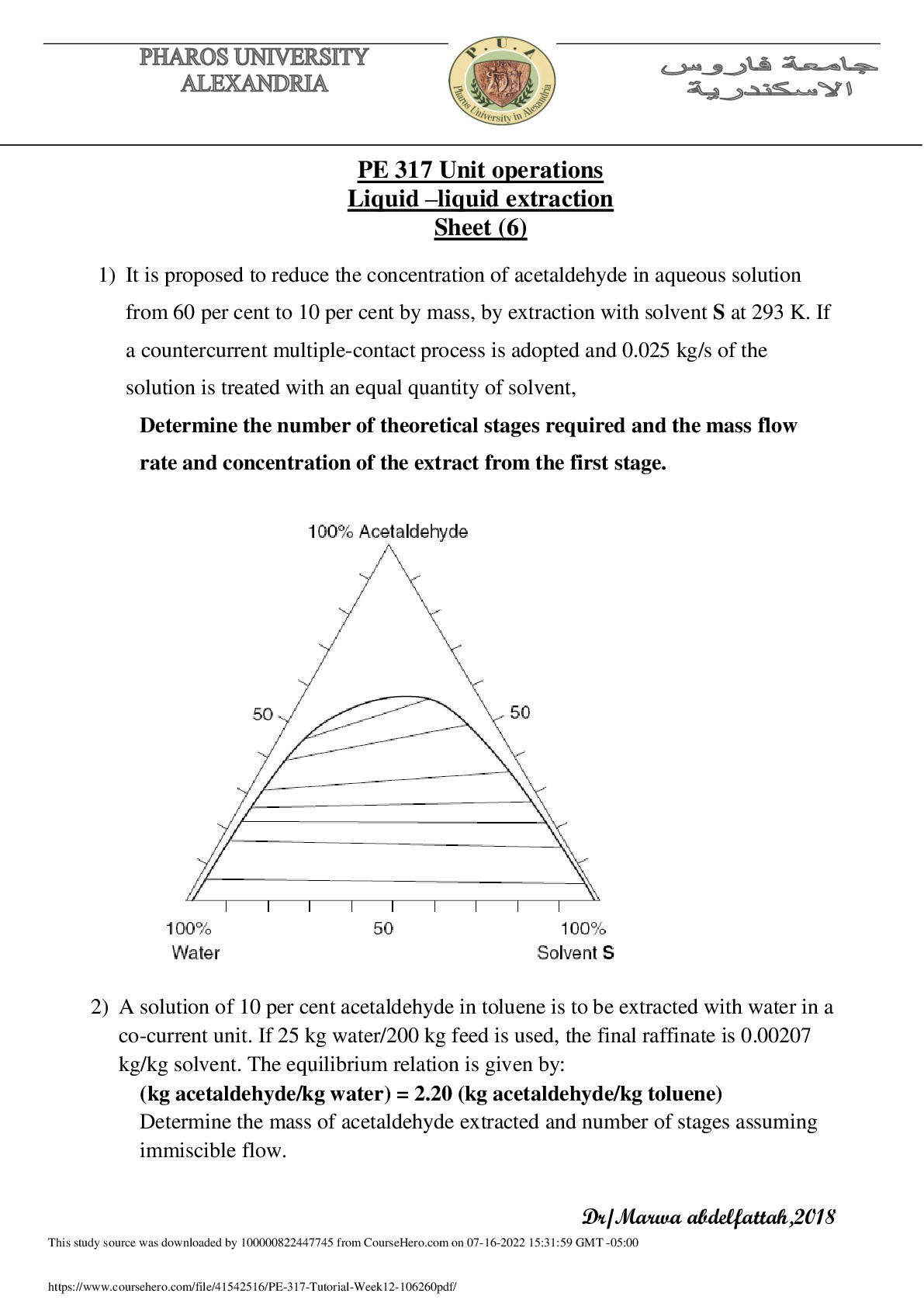
Experimental:
In part A of the experiment approximately 350 mL of water was heated to 50 °C in a 600 mL
beaker which served as a water bath for the reaction. 2.01g of Salicylic acid and 5 mL acetic anhydride
were then
...
Experimental:
In part A of the experiment approximately 350 mL of water was heated to 50 °C in a 600 mL
beaker which served as a water bath for the reaction. 2.01g of Salicylic acid and 5 mL acetic anhydride
were then mixed in a 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask followed by 5 drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. The
flask was swirled until the salicylic acid dissolved. The flask was then placed in the hot water bath at
about 53 °C by partially submerging the flask in the water using a clamp and a retort stand for 10
minutes. The flask was cooled to room temperature. The inside of the flask was then scratched to act as
a seed for the crystals to form and were then placed in the ice bath for about 10 minutes. No crystals
formed right away so a small amount of aspirin was added to speed up the reaction and then the
mixture was heated and cooled a second time. Once crystal formation was complete (after about 45
minutes), 50 mL cold distilled water was added to the crystals. The solution was mixed and then placed
into the ice bath again for approximately 15 minutes. The product was then collected by vacuum
filtration using a Buchner funnel. A small amount of cold water was used to transfer the crystals from the
flask to the funnel and to moisten the filter paper. The crystals were then transferred to a watch glass
and dried under the heat lamp for about 10 minutes. The final dry crude product was then weighed and
recorded. A small amount was set aside to then measure the melting point of the sample.
In part B, the product from part A was added to 3 ml of ethyl acetate in a 50 mL beaker and
heated the on a hot plate until crystals dissolved. The solution was then left to cool to room
temperature. The inside of the beaker was scratched to initialize crystallization and then placed in the ice
bath for about 15 minutes. Vacuum filtration was used once again to separate the crystals from the
solution. They were then transferred to a watch glass and placed under a heat lamp for 10 minutes to
allow for complete drying. The pure product was weighed and the melting point of acetylsalicylic acid
was measured. The waste was disposed of properly into the labeled containers
[Show More]
.png)


.png)