Discussion:
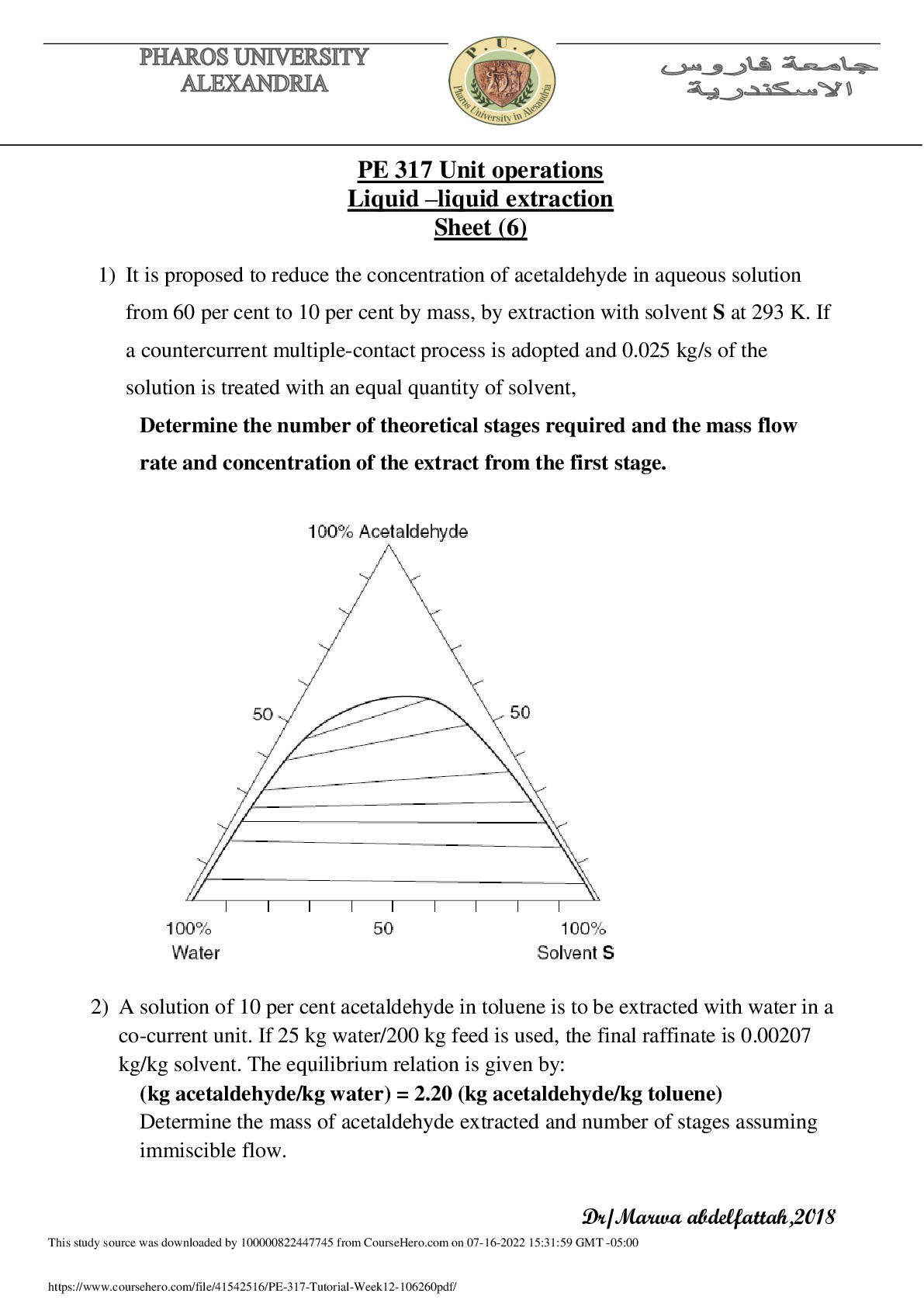
Polarity is an example of a physical property of compounds. Polarity affects solubility of
molecules. This indicates that polar solutes will dissolve better and faster in polar solvents and
likewise for
...
Discussion:
Polarity is an example of a physical property of compounds. Polarity affects solubility of
molecules. This indicates that polar solutes will dissolve better and faster in polar solvents and
likewise for nonpolar molecules. In the lab experiment, this idea was further observed with the
use of two organic compounds, malonic acid and biphenyl. In the part A of the lab, malonic acid
was determined to be soluble with water and methanol. According to the Lewis structure of
malonic acid, the molecule is polar. This means that there is a net dipole due to the differences in
electronegativity of the atoms within the molecule. Malonic acid was soluble in water and
methanol because the two solvents were also polar molecules. In the experiment, it was observed
that the acid dissolved faster in water than in methanol because water was more polar. However,
malonic acid was insoluble in hexane. This was due to the solvent being a nonpolar molecule.
The second compound, biphenyl, was a nonpolar molecule according to its Lewis structure.
From the lab experiment, it was discovered that biphenyl was insoluble in water and methanol,
while it was soluble in hexane. Biphenyl was insoluble in water and methanol because of the
differences in their polarity. The nonpolar solute did not dissolve in both of the polar solvents.
Meanwhile, biphenyl was soluble in hexane because the solvent was also a nonpolar molecule.
Solubility can also be synonymous to miscibility. Miscibility specifically refer to the mixing of
liquids and to be completely dissolve with one another to create a homogenous solution. In the
lab, water and ethanol were determined to be miscible with each other, while water and diethyl
ether were miscible with each other. This also relates to the polarity of the molecules. Water is a
polar liquid; therefore, it was miscible in ethanol, also a polar liquid. Water was immiscible with
diethyl ether and created two layers of liquid because it was a nonpolar liquid.
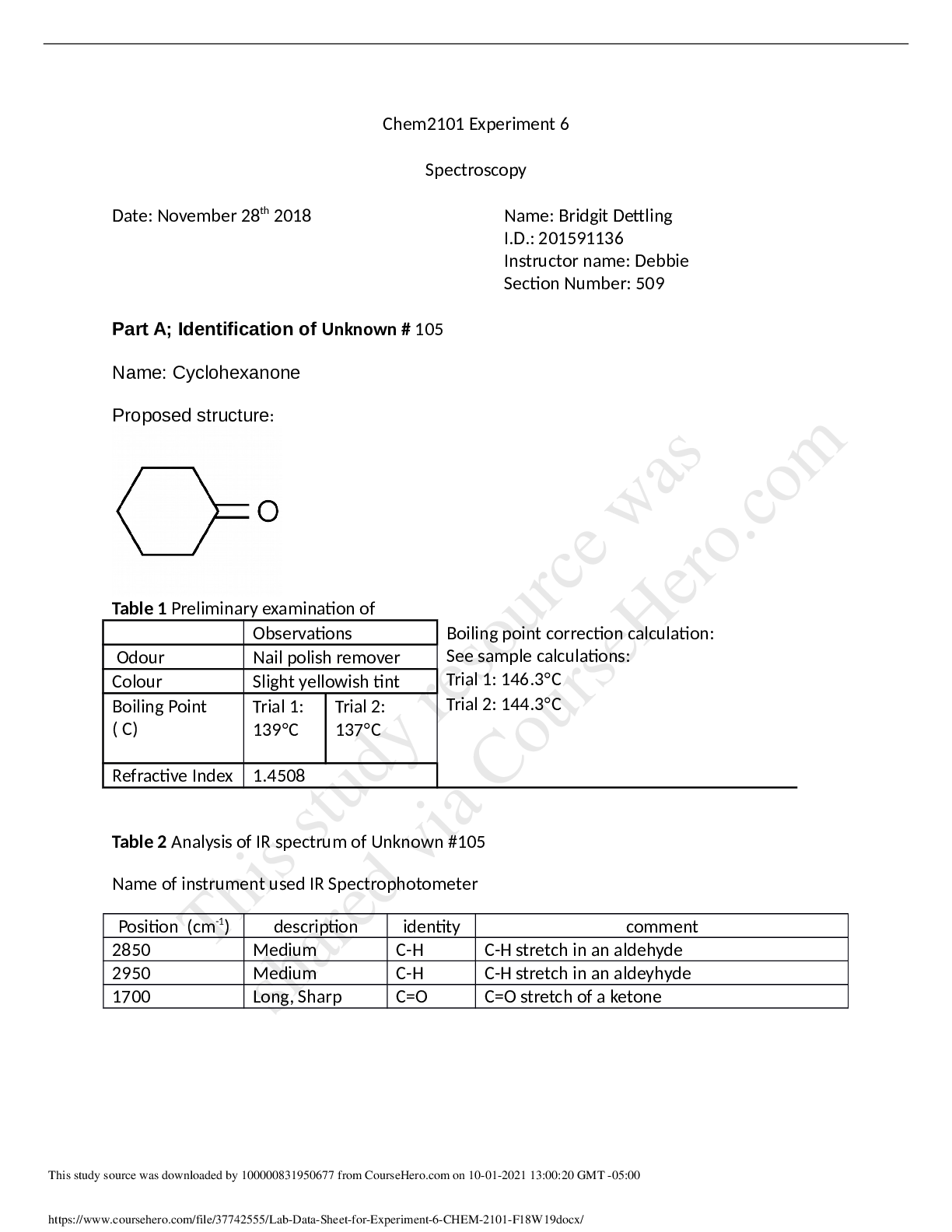
Boiling point and melting point are also examples of physical properties of molecules;
Boiling point and melting point determines which molecules will have less rigid structures and
have stronger intermolecular forces. The purpose of Part B of the lab experiment was to
determine the boiling point of an unknown liquid sample. The chosen unknown liquid sample
was determined to have a boiling point of approximately 84oC. The unknown liquid sample was
colourless and had a pungent odour. From these physical properties, the unknown sample D was
determined to be 2-propanol. Meanwhile, the purpose of part C of the lab experiment was to
determine the melting point of an unknown solid. In the experiment, the unknown sample began
melting at a temperature of 95oC and then reached 96oC, in which all the solid sample had
melted. The unknown solid sample was slightly yellow in colour. It had a crystalline appearance
[Show More]



.png)

.png)