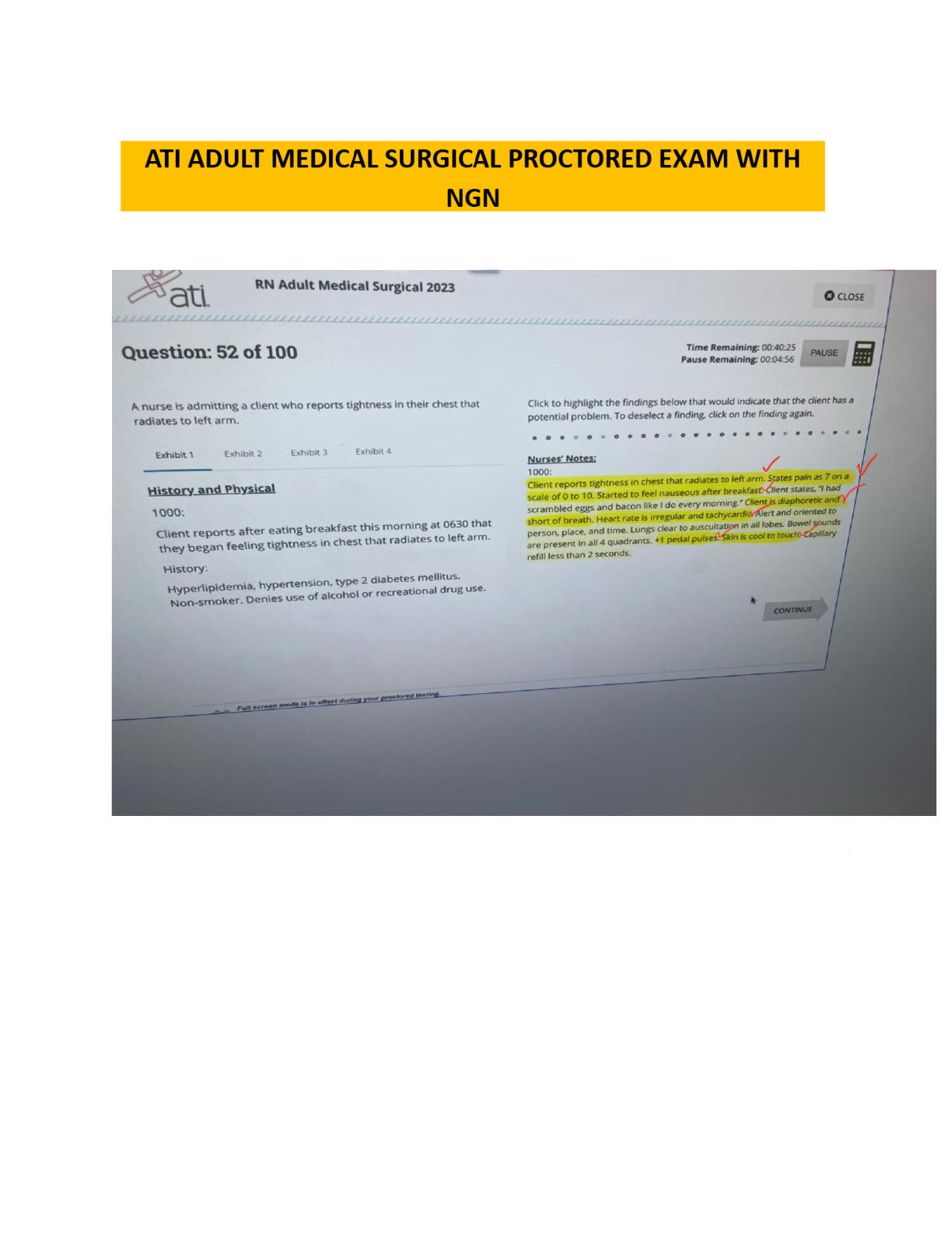
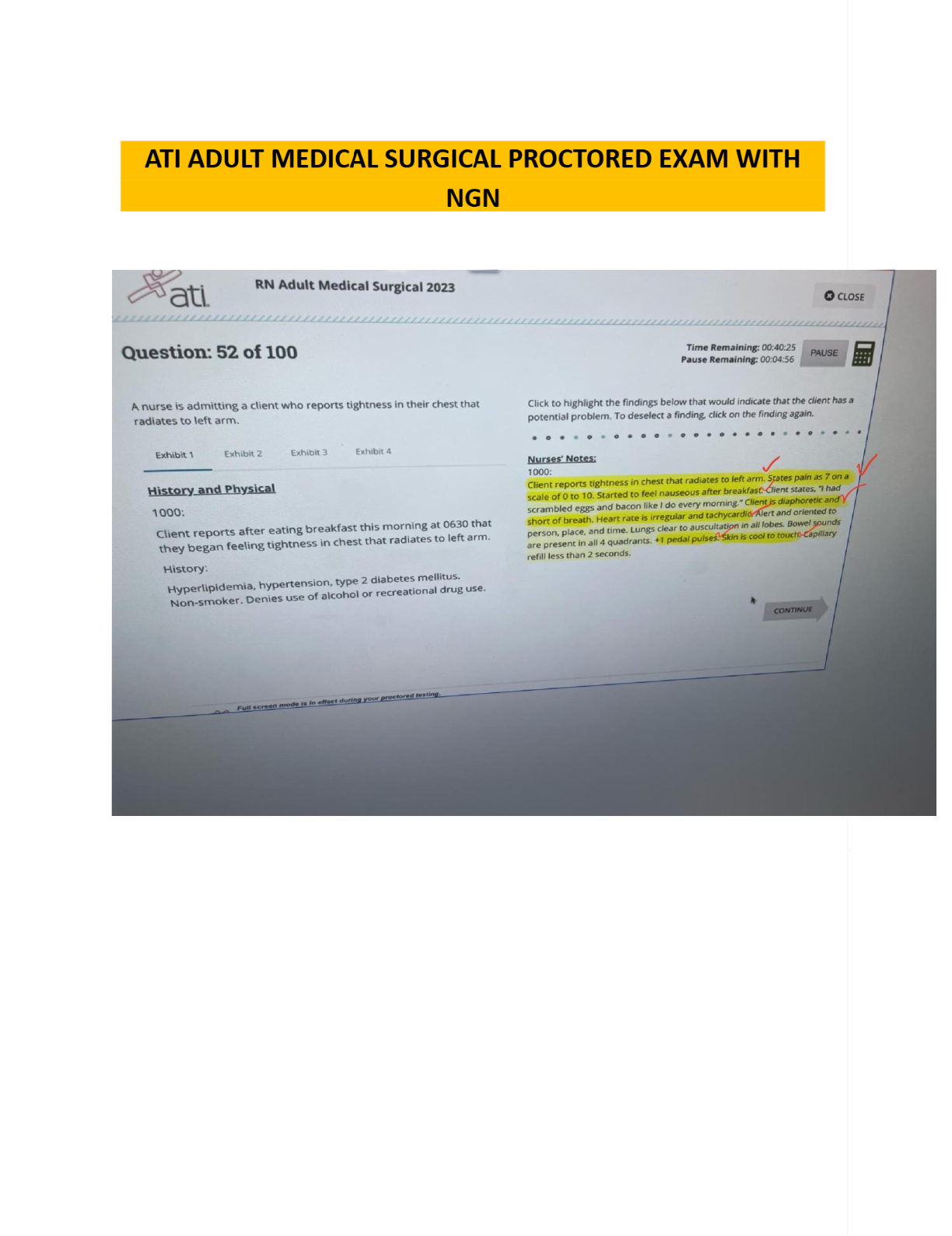
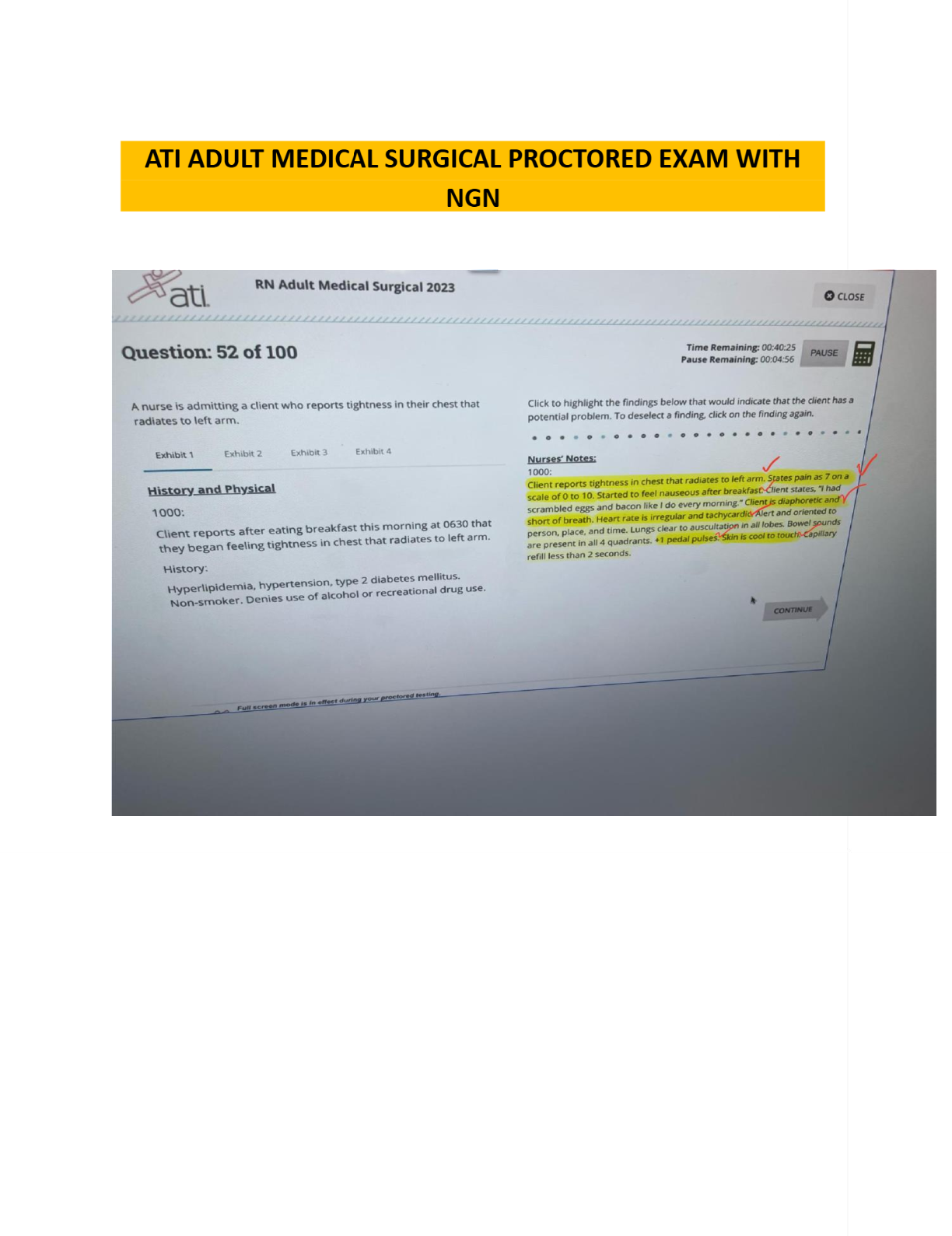
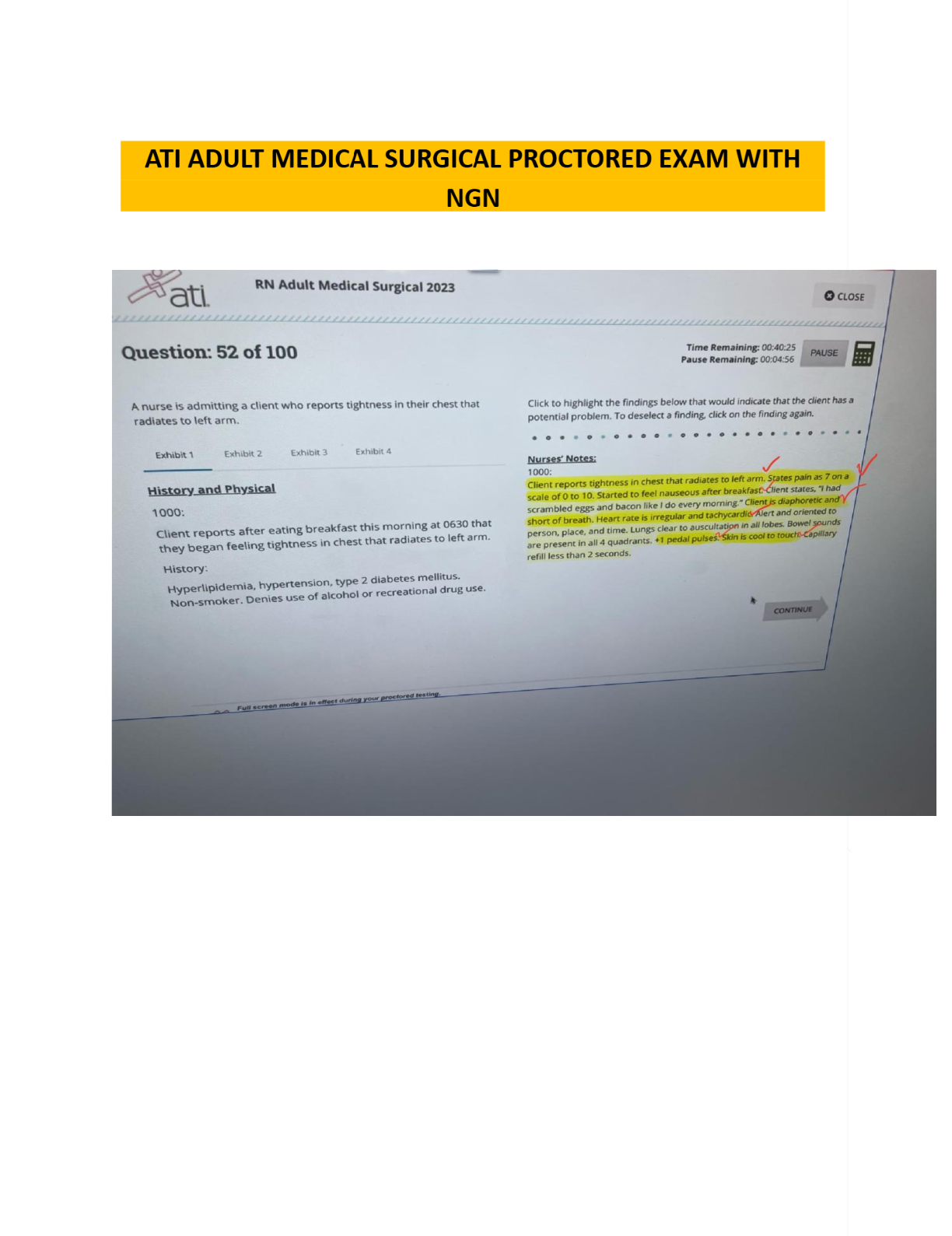
Data Mining > EXAM > MSMIT CSC550: Data Mining. Final Exam. 40 Questions and Answers. All the correct answers are indicat (All)
MSMIT CSC550: Data Mining. Final Exam. 40 Questions and Answers. All the correct answers are indicated.
Document Content and Description Below
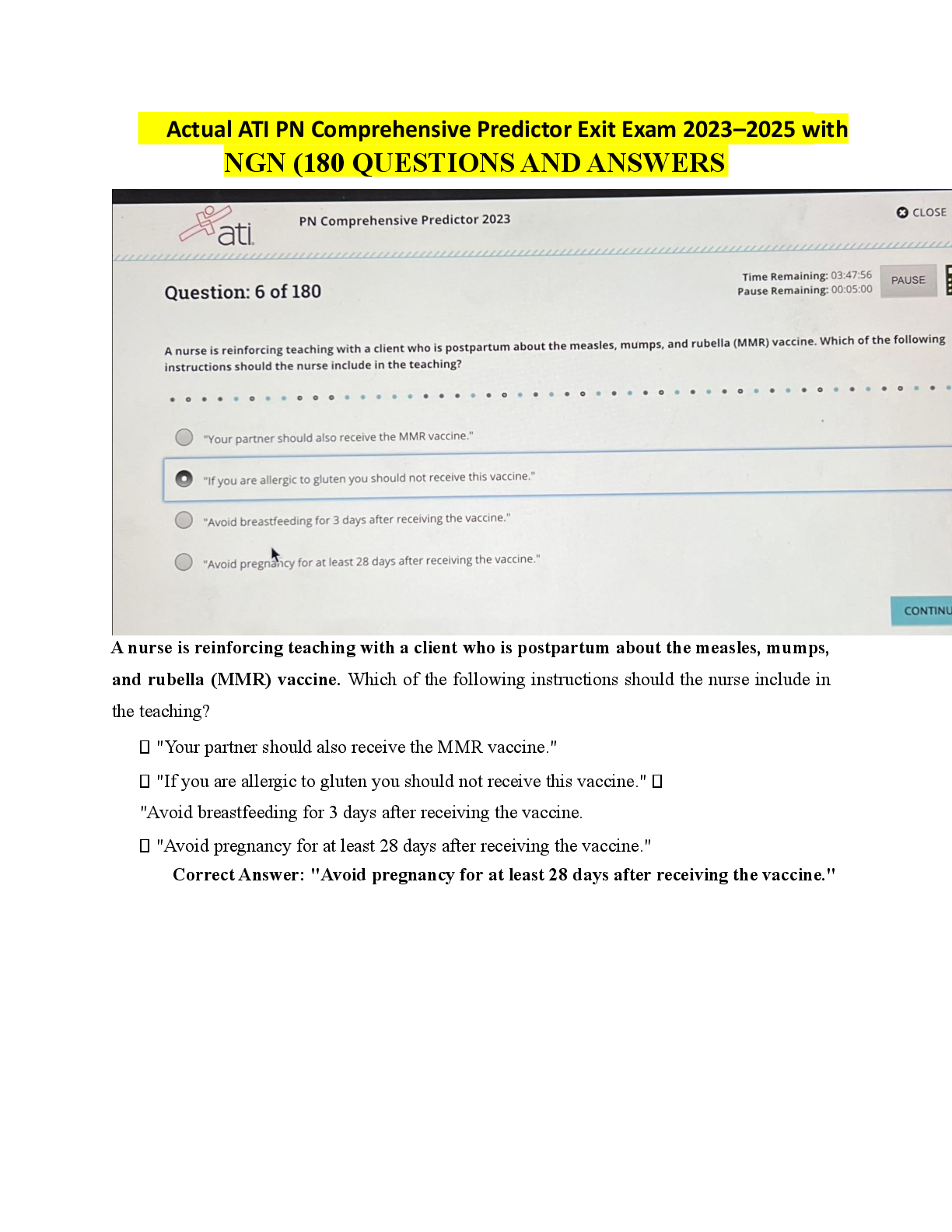
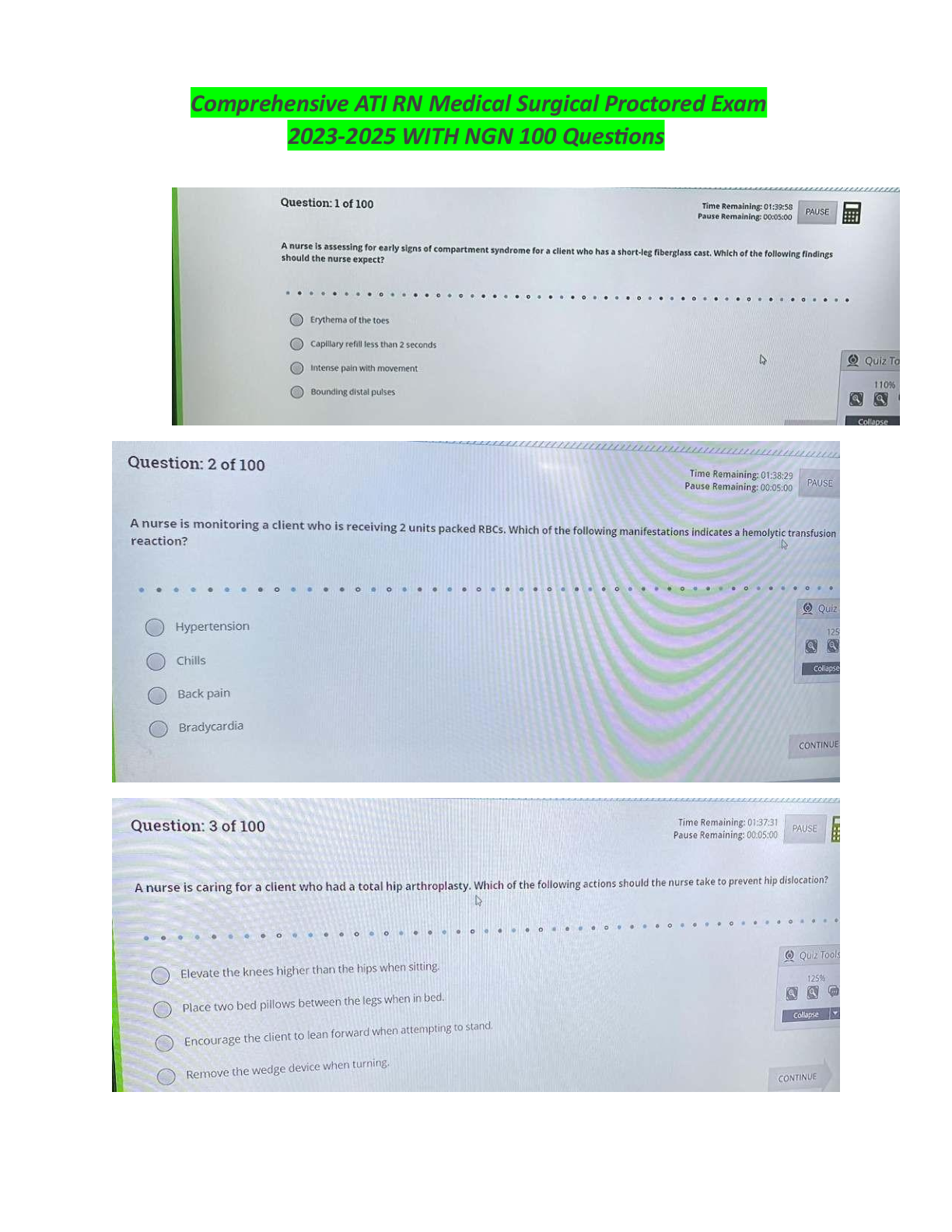
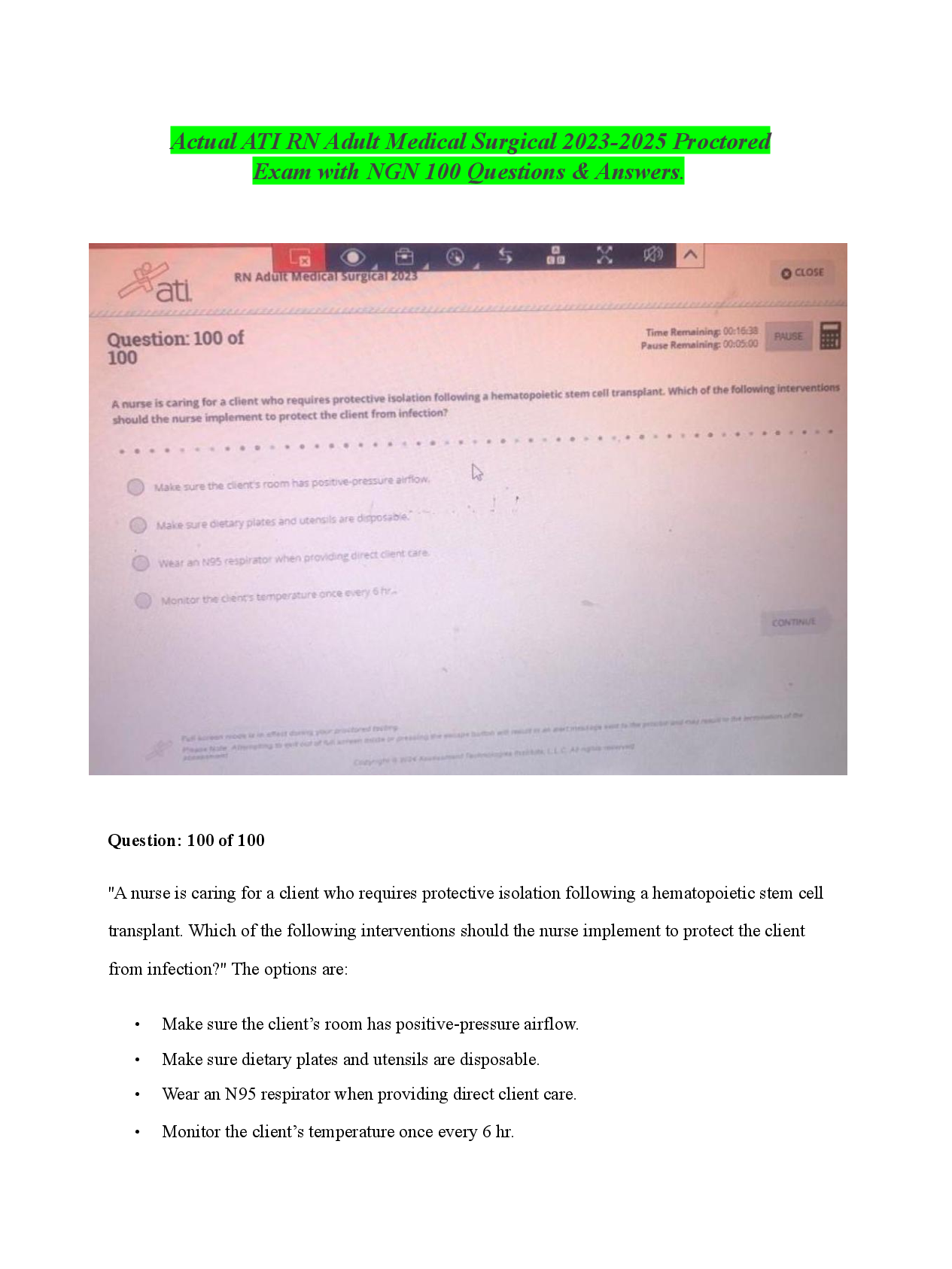
MSMIT CSC550: Data Mining. Final Exam 1. The “k” in k-nearest neighbors refers to the number of _________. A) variables that will be used by the k-NN methods B) records that will be used ... by the k-NN methods C) records in the training data D) records in the validation data 1.0/1.0 B 2. The sharp increase in the required size of the training set with the increase in the number of predictors is referred to as ________. A) overfitting to the noise B) the loss of local structure due to over smoothing C) the curse of dimensionality D) None of the above 1.0/1.0 C 3. A drawback of the k-NN method is that the _________. A) method does not support prediction B) method can be used to classify only two classes C) relationship between the dependent variable and the predictor variables must be linear D) required size of the training set increases exponentially with the number of predictors 1.0/1.0 D 4. The method k-nearest neighbors can be used for _________. A) classification only B) prediction only C) both classification and prediction D) neither classifiation nor prediction 1.0/1.0 C 5. In k-NN which of the following statements describes characteristics of low values of k? A) They provide more smoothing, more noise, and capture local structure in the data. B) They provide more smoothing, less noise, but may miss local structure. C) They capture local structure in the data, but also may include noise. D) They capture local structure in data, less smoothing, and less noise. 1.0/1.0 C 6. In a k-NN classification model where k is equal to the number of records in the training data, which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The classification rule is equivalent to the naïve (majority) rule. B) None of the information of the predictor variables will affect the classifications. C) The resulting k-NN model will be of no value to the data miner. D) None of the above. 0.0/1.0 D 7. In k-NN which of the following statements describes characteristics of high values of k? A) They provide more smoothing, more noise, and capture local structure in the data. B) They provide more smoothing, less noise, but may miss local structure. C) They capture local structure in the data, but also may include noise. D) They capture local structure in data, less smoothing, and less noise. 1.0/1.0 B 8. In k-NN for prediction ________. A) cannot be done B) can be done with the use of majority voting to determine class C) can be done with the use of weighted averages with weights decreasing as distance increases D) can be done when the outcome variable is categorical 1.0/1.0 C 9. The most commonly used “nearness” criterion used in k-NN is _________. A) Euclidean distance B) ordinary least squares C) the minimax principle of decision making D) data smoothing 1.0/1.0 A 10. To equalize the scales that the various predictors may have, predictors should be ________ prior to using the k-NN method. A) partitioned B) smoothed C) standardized D) verified 1.0/1.0 C 11. Which of the following statements is true about the naïve Bayes method? A) It can be used with numeric data only. B) It is an unsupervised method. C) It is a model driven approach to data mining. D) None of the above 1.0/1.0 D 12. The naïve Bayes method can be used for _________. A) classification only B) prediction only C) both classification and prediction D) neither classifiation and prediction 1.0/1.0 A 13. The main weakness of the full (exact) Bayesian classifier is _________. A) the requirement that the predictors must be independent of each other B) the very large validation set that will be needed when there are many predictors C) that all the records in the validation set must be used in the computation D) that the cutoff probability must be set at 0.5 1.0/1.0 B 14. The naïve Bayes method differs from the full (exact) Bayesian classifier in that the ________. A) naïve Bayes method uses only part of the records in the dataset while the full (exact) Bayesian classifier uses all the records in the dataset B) full (exact) Bayesian classifier uses only part of the records in the data set while the naïve Bayes method uses all the records in the dataset C) There are none significant differences between the two methods. D) None of the above. 1.0/1.0 B 15. The naïve Bayes method can be used with which of the following types of data. A) Categorical only B) Numeric only C) Both categorical and numeric D) Normalized 1.0/1.0 A 16. Which of the following are advantages of the naïve Bayes method? A) It handles purely categorical data well. B) It works well with very large datasets. C) It's conceptually simple and computationally efficient D) All of the above. 1.0/1.0 D 17. The method that uses only records from the validation dataset that are identical matches on the predictors to the record to be classified is known as the _________ method. A) k-NN B) naïve Bayes classifier C) full (exact) Bayesian classifier D) multiple regression 1.0/1.0 C 18. Suppose you have a validation dataset and you want to use the naïve Bayes method to classify a new record. But one of the key predictors is numeric. What should you do? A) Drop the numeric predictor and use the naïve Bayes method on the other predictors. B) Select another method, since the naïve Bayes method cannot be used in this case. C) Convert the numeric variable into a categorical variable by binning, and then use the naïve Bayes method in the usual way. D) Use the full (exact) Bayesian classifier instead. 1.0/1.0 C 19. When using the basic naïve Bayes method, we assign a new (unclassified) record to the class with ________. A) the highest probability for this set of predictor values B) the lowest probability for this set of predictor values C) a probability greater than 0.5 D) a probability greater than 0.5 1.0/1.0 A 20. The Naïve Bayes method can be used for the purpose(s) of ________. A) classification only B) prediction only C) both classification and prediction D) None of the above 1.0/1.0 A 21. The value that is inside the rectangle of a terminal leaf of a classification tree represents the ________. A) number of records in the training data that followed that path B) splitting point of the distribution of values of the variable C) average of the variable D) class to which a new record that followed that path will be assigned 1.0/1.0 D 22. In the recursive partitioning process, how can the problem of overfitting be managed? A) Set rules to stop tree grown before overfitting sets in. B) Prune the full-grown tree back to a level where overfitting is no longer a problem. C) Both (a) and (b). D) Neither (a) or (b). 1.0/1.0 C 23. The Gini Index ________. A) is used to measure predictive accuracy B) is used to measure impurity C) is scored on a scale of 0 to 100 D) requires that the data set be normalized before it can be used 1.0/1.0 B 24. Which of the following statements is NOT true of the value that appears inside a binary decision tree node? A) It is the value that results in the split having the minimum impurity. B) It is the midpoint of the distribution of values of the variable. C) It is a splitting point that determines which path will be followed. D) None of the above. 1.0/1.0 B 25. Which of the following is an advantage of using the “classification and regression tree” (CART) data mining method? A) It produces rules that are easy to interpret & implement. B) It does not require the assumptions of statistical models C) It does not require the assumptions of statistical models D) All of the above. 1.0/1.0 D 26. Which of the following is a disadvantage of using the “classification and regression tree” (CART) data mining method? A) The resulting trees are complex and difficult to interpret. B) The problem of overfitting is insurmountable. C) The algorithm might result in an infinite loop. D) There is no way to capture interactions between variables. 1.0/1.0 D 27. The main problem with overfitting is that it________. A) leads to low predictive accuracy of new data B) is a waste of resources C) is computationally complex D) None of the above. 1.0/1.0 A 28. Which of the following statements is true of using regression trees for prediction? A) It is used with continuous outcome variables. B) The procedure is similar to classification trees. C) The goal of the procedure is to find the split that minimizes impurity. D) All of the above. 1.0/1.0 D 29. Consider the following decision rule: IF (AGE > 50) AND (INCOME ≤ 80,000) AND (OWN_HOME = “NO”) THEN CLASS = 0. How many nodes of a decision tree must be passed through to arrive at this rule? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) It depends on how it is structured 1.0/1.0 C 30. When the recursive partitioning process is applied to the training data and is allowed to run to its end, the resulting tree ________. A) is the final solution to the problem B) has a misclassification rate of 0 C) does not have any overfitting problems D) is ready to be used on the validation data 1.0/1.0 B 31. In the association rules method, the goal of rule selection is to find _________. A) rules that have a high level of support B) rules that have a high level of confidence C) only the rules that indicate a strong dependence between the antecedent and consequent item sets D) All of the above. 0.0/1.0 C 32. Areas in which the association rules can be applied include ________. A) shopping cart analysis B) medical diagnoses C) population demographics D) All of the above 1.0/1.0 D 33. In the association rules method, the _________ of a rule is the number of records that include both the antecedent and consequent item sets. A) strength B) support C) validity D) confidence 1.0/1.0 B 34. In the association rules method, the most common procedure for generating frequent item sets is _________. A) the Apriori algorithm B) the Gini Index C) the simplex method D) recursive partitioning 1.0/1.0 A 35. The form of an association rule is expressed in two parts called the _________ and the _________. A) subject; object B) primary; secondary C) antecedent; consequent D) condition; action 1.0/1.0 C 36. In the association rules method, the records of a dataset are commonly converted to __________ prior to analysis. A) third normal form B) pivot tables C) common logarithms D) binary matrix format 1.0/1.0 D 37. In the association rules method, a lift ratio of _________ indicated that the antecedent and consequent of a rule have no relationship beyond that of chance. A) 0 B) 1 C) ≤ 0 D) ≤ 1 1.0/1.0 B 38. Another term for the “association rules” method is __________. A) cluster analysis B) affinity analysis C) correlation matrix D) neural nets 1.0/1.0 B 39. Market basket analysis is commonly used in _________ systems. A) election polling B) recommender C) inventory control D) poulation demographic 1.0/1.0 B 40. In the association rules method, one approach to reducing the number of spurious rules due to chance effects is to ________. A) use a large dataset B) decrease the cutoff criteria for selection C) convert the data to binary matrix format D) normalize the data 1.0/1.0 A [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 22, 2020
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 22, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
154