*NURSING > QUESTIONS and ANSWERS > ISBAR Gestational Diabetes l100% Correct and Graded A (All)
ISBAR Gestational Diabetes l100% Correct and Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
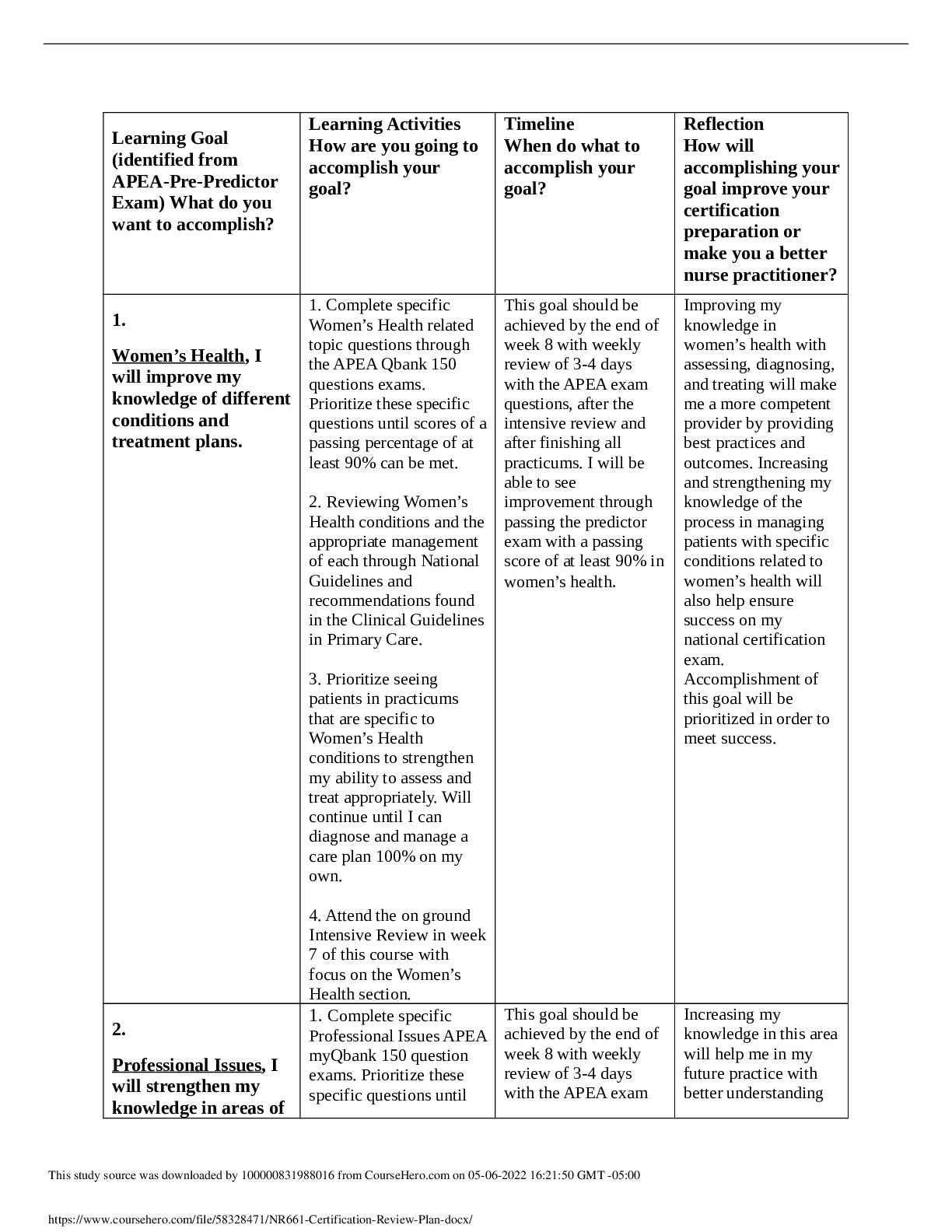
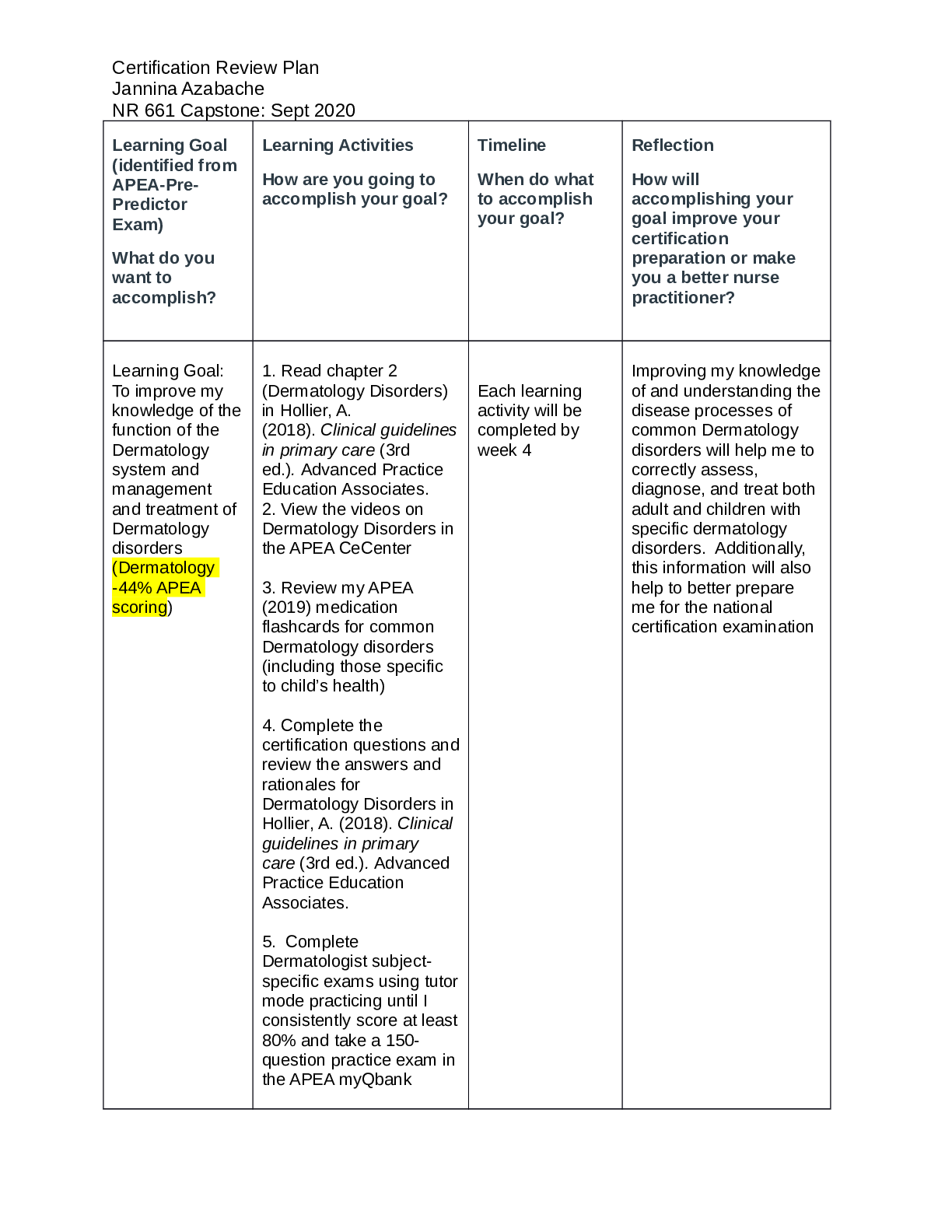
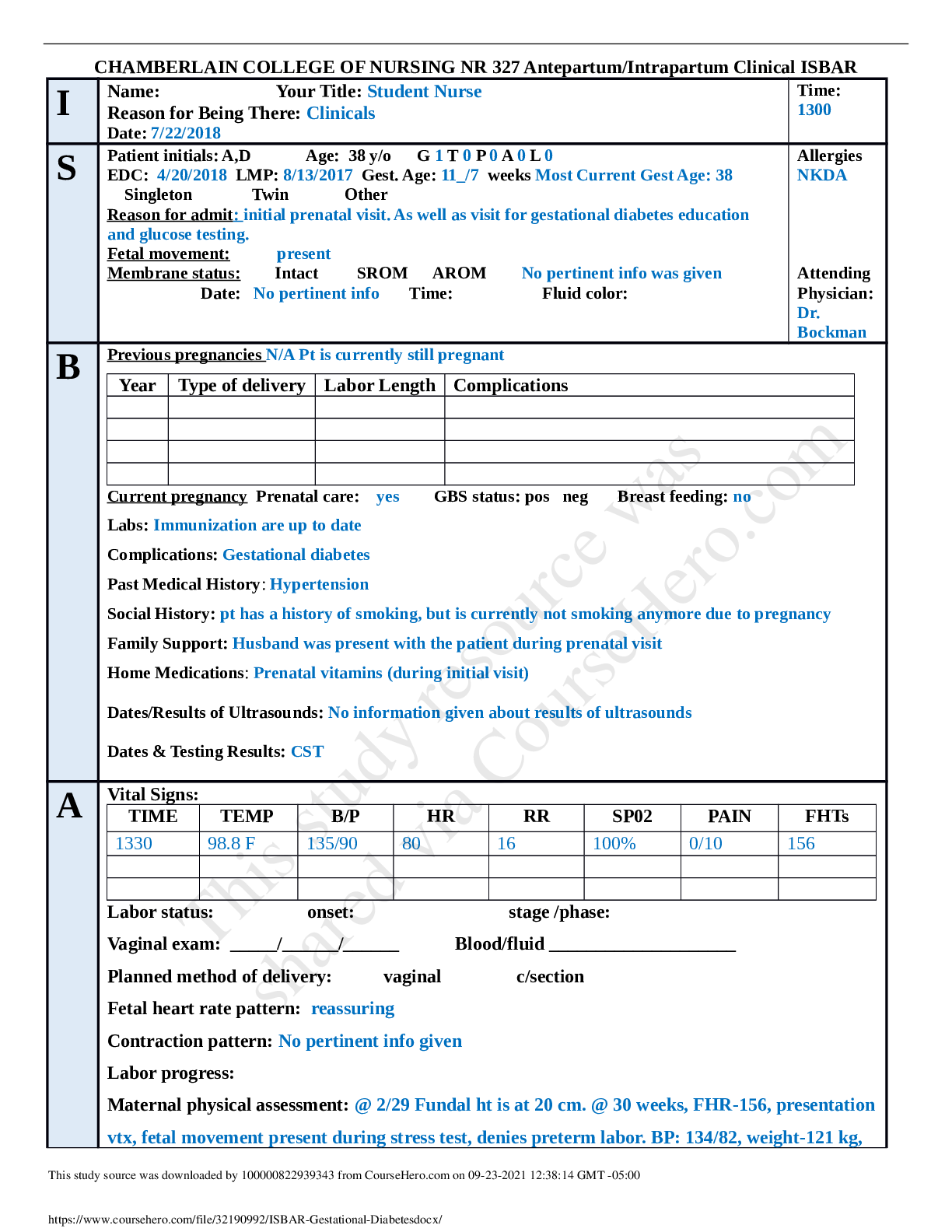
CHAMBERLAIN COLLEGE OF NURSING NR 327 Antepartum/Intrapartum Clinical ISBAR I Name: Your Title: Student Nurse Reason for Being There: Clinicals Date: 7/22/2018 Time: 1300 S Patient initials: A ... ,D Age: 38 y/o G 1 T 0 P 0 A 0 L 0 EDC: 4/20/2018 LMP: 8/13/2017 Gest. Age: 11_/7 weeks Most Current Gest Age: 38 Singleton Twin Other Reason for admit: initial prenatal visit. As well as visit for gestational diabetes education and glucose testing. Fetal movement: present Membrane status: Intact SROM AROM No pertinent info was given Date: No pertinent info Time: Fluid color: Allergies NKDA Attending Physician: Dr. Bockman B Previous pregnancies N/A Pt is currently still pregnant Year Type of delivery Labor Length Complications Current pregnancy Prenatal care: yes GBS status: pos neg Breast feeding: no Labs: Immunization are up to date Complications: Gestational diabetes Past Medical History: Hypertension Social History: pt has a history of smoking, but is currently not smoking anymore due to pregnancy Family Support: Husband was present with the patient during prenatal visit Home Medications: Prenatal vitamins (during initial visit) Dates/Results of Ultrasounds: No information given about results of ultrasounds Dates & Testing Results: CST A Vital Signs: TIME TEMP B/P HR RR SP02 PAIN FHTs 1330 98.8 F 135/90 80 16 100% 0/10 156 Labor status: onset: stage /phase: Vaginal exam: _____/______/______ Blood/fluid ____________________ Planned method of delivery: vaginal c/section Fetal heart rate pattern: reassuring Contraction pattern: No pertinent info given Labor progress: Maternal physical assessment: @ 2/29 Fundal ht is at 20 cm. @ 30 weeks, FHR-156, presentation vtx, fetal movement present during stress test, denies preterm labor. BP: 134/82, weight-121 kg, This study source was downloaded by 100000822939343 from CourseHero.com on 09-23-2021 12:38:14 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/32190992/ISBAR-Gestational-Diabetesdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com Glucose-trace, protein-negative, BG-378. Home monitoring: 200-422 mg/dL IVs: No IV given Current meds: prenatal vitamins, regular insulin (humulin) 25 units 3 times per day Labs: (List all Labs): immunizations up to date: rubella (titer) immune, varicella, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, influenza, pneumococcal. Activity:infant is reacting during stress test R Discharge planning needs: Dietary intake not to exceed 2,000 calories per day. Regular insulin (Humulin) 25 units 3 times per day. Bi-weekly non-stress test reactive. Plan of Care Complete the following information for ALL priority diagnosis (list dx in order of priority). Nursing Analysis/ Priority Diagnosis: 1 Risk for Altered Nutrition: Less than body requirements 2 Risk for maternal Injury 3 Risk for Fetal Injury 4 Deficient Knowledge Patient Goals: 1 Patient will know the nutritional education for maintaining blood glucose at optimal level. 2 Patient will verbalize the food that is healthy for gestational diabetics 3 Patient will repeat back the steps to using the glucometer after patient education Outcome Criteria: Outcome Criteria: 1 Patient will verbalize understanding of individual treatment regimen and the need for frequent self-monitoring 2 Patient will be free of signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (fruity breath, excess thirst) 3 Patient will maintain fasting serum blood glucose levels between 60-100 mg/dL 4 DX # Interventions Reasoning/Rationale Evaluation of intervention This study source was downloaded by 100000822939343 from CourseHero.com on 09-23-2021 12:38:14 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/32190992/ISBAR-Gestational-Diabetesdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com 1. Assess and record dietary pattern and caloric intake using a 24-hour recall. To help in evaluating client’s understanding and/or compliance to a strict dietary regimen. Pt states she will need to focus on her caloric intake to mostly be from carbohydrates during the patient education. 2. Assess understanding of the effect of stress on diabetes. Teach patient about stress management and relaxation measures. It has proven that stress can increase serum blood glucose levels, creating variations in insulin requirements. Pt states the importance of her not to be stressed during her pregnancy, she knows the result of stress to her baby like the result of high blood pressure. 3. Weight the client every prenatal visit. Encourage the client to periodically monitor weight at home between visits. Weight gain seves as an indicator for determining caloric adjustments. Pt has maintained a healthy weight gain of 1 kg every prenatal visit. 4. Observe for the presence of nausea and vomiting, especially during the first trimester. Nausea and vomiting may be brought about by a deficiency in carbohydrates, which may result in the metabolism of fats and development of ketosis. Pt states she knows the importance of carbohydrate intake for her gestational diabetes. 5. Teach and demonstrate client to monitor sugar using a fingerstick method. Insulin needs for the day can be adjusted based on periodic serum glucose readings. Note: Values obtained by reflectance meters may be 10-15% lower/higher than plasma levels. Pt was educated on the importance of switching sites for insulin injections. 6. Provide information regarding any required changes in diabetic management; e.g., use of humulin insulin only, changing from oral diabetic drugs to insulin, amount of carbohydrates to have a day. Metabolism and maternal needs fluctuates during gestational period, requiring close monitoring and adaptation. Research suggest antibodies against insulin may cross the placenta, causing inappropriate fetal weight gain. The use of Patients states that should should have 80-85% of her caloric intake from carbohydrates out of her 2,000 calories a day diet. This study source was downloaded by 100000822939343 from CourseHero.com on 09-23-2021 12:38:14 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/32190992/ISBAR-Gestational-Diabetesdocx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.com human insulin decreased the development of these antibodies. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 4 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 30, 2022
Number of pages
4
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
177