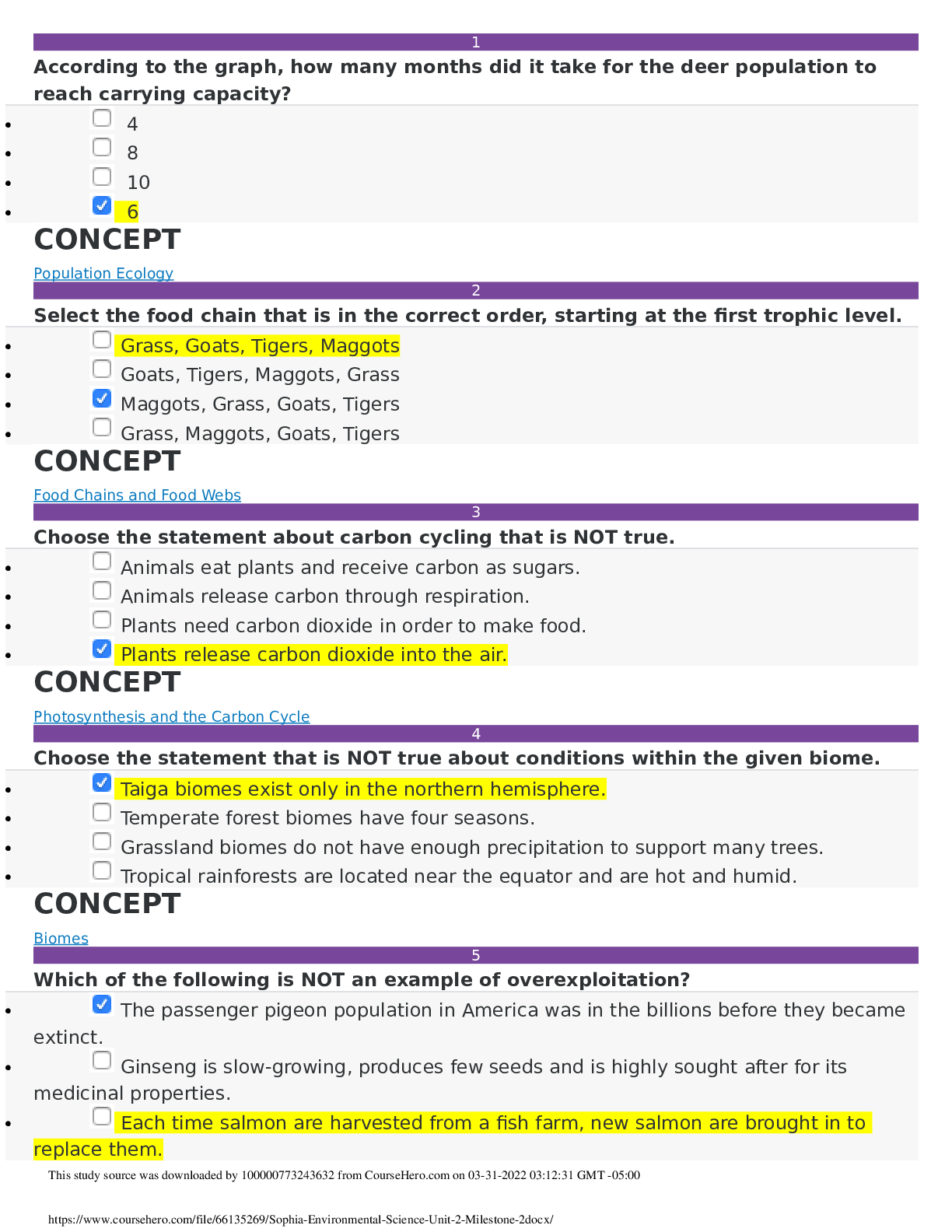
According to the graph, how many months did it take for the deer population to reach carrying capacity?
• 4
• 8
• 10
• 6
CONCEPT
Population Ecology
2
Select the food chain that is in the correct order, starti
...
According to the graph, how many months did it take for the deer population to reach carrying capacity?
• 4
• 8
• 10
• 6
CONCEPT
Population Ecology
2
Select the food chain that is in the correct order, starting at the first trophic level.
• Grass, Goats, Tigers, Maggots
• Goats, Tigers, Maggots, Grass
• Maggots, Grass, Goats, Tigers
• Grass, Maggots, Goats, Tigers
CONCEPT
Food Chains and Food Webs
3
Choose the statement about carbon cycling that is NOT true.
• Animals eat plants and receive carbon as sugars.
• Animals release carbon through respiration.
• Plants need carbon dioxide in order to make food.
• Plants release carbon dioxide into the air.
CONCEPT
Photosynthesis and the Carbon Cycle
4
Choose the statement that is NOT true about conditions within the given biome.
• Taiga biomes exist only in the northern hemisphere.
• Temperate forest biomes have four seasons.
• Grassland biomes do not have enough precipitation to support many trees.
• Tropical rainforests are located near the equator and are hot and humid.
CONCEPT
Biomes
5
Which of the following is NOT an example of overexploitation?
• The passenger pigeon population in America was in the billions before they became extinct.
• Ginseng is slow-growing, produces few seeds and is highly sought after for its medicinal properties.
• Each time salmon are harvested from a fish farm, new salmon are brought in to replace them.
• 25 million bison once roamed the American landscape; by 1880, only 1,091 remained.
CONCEPT
Overexploitation
6
Select the statement that refers to an exponential population growth model.
• This model considers a limited amount of natural resources when examining population growth.
• This graph is a more realistic model of population growth.
• This model considers carrying capacity when examining population growth.
• The slope of the graph in this model is steepest near the top.
CONCEPT
Population Ecology
7
Choose the statement that is NOT true about energy and trophic levels.
• Sunlight provides the energy for primary productivity.
• Secondary production introduces no additional energy into the food chain.
• Ten is considered the maximum number of trophic levels in an ecosystem.
• Photosynthesis converts sunlight into sugars.
CONCEPT
Food Chains and Food Webs
8
Which of the following is a strategy associated with restoration ecology?
• Studying an environment closely to determine ways to maintain biodiversity and a healthy ecosystem.
• Creating a new wilderness area to limit human interactions with an endangered species.
• Examining the biological structures of living and non-living components in a given environment.
• Reintroducing native plant and animal species to a piece of land devastated by deforestation.
CONCEPT
Conservation Biology & Restoration Ecology
9
Environmental scientists cite several challenges to protecting endangered species.
Which of the following is NOT a difficulty faced by those working to protect an endangered species?
• There is no legislation in the United States to protect species identified as endangered.
• It is difficult to enforce protection policies in some environments.
• People aren’t that interested in protecting animals they do not consider valuable.
• Identifying danger for a species may come too late to reverse the danger.
CONCEPT
Endangered Species
10
Choose the statement about deforestation that is NOT true.
• The water cycle is affected.
• Soil erosion degrades the land.
• Climate is unaffected.
• Impacts are local, regional and global.
CONCEPT
Forests and Deforestation
11
Choose the true statement about the nitrogen cycle.
• Bacteria take nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into sugars.
• Nitrogen is contained in the leaves of plants such as peanuts, soybeans and clover.
• Nitrogen makes up about 22% of the atmosphere's composition.
• Animals release nitrogen through urination and by dying.
CONCEPT
Water and Nitrogen Cycles
12
Which statement is characteristic of an invasive species?
• A species that has been domesticated.
• A species that remains in its original environment.
• A species that has natural predators and competitors.
• A species that can reproduce rapidly.
CONCEPT
Native and Non-Native Species
13
Select the statement that is an example of a species providing an ecosystem service.
• Wolves promote biodiversity and natural balance by eating deer and other animals.
• Earthworms aerate the soil and create pathways for root growth under farmers’ fields.
• After mice invaded a home, the homeowner used humane traps to release the mice into the wild.
• When a whale is injured, other whales will support it out of the water so it can breathe.
CONCEPT
The Role of Individual Species
14
It was raining as we began our long hike. We took a trail to the east and left the ocean behind us. Soon we were in a large grove of eucalyptus trees. Coming out of the forest, the trail became rocky and the incline became steep. The rain had stopped, but now I was chilly.
“I wish the climate would make up its mind,” I grumbled.
My mother, a biologist and nature lover, gently corrected me. “Weather is what’s happening at the moment, dear. Climate is weather a certain area has over years.”
Which of the following best describes why the temperature has dropped?
• Rain along the coastline is following them.
• The hikers are climbing to a higher elevation.
• The hikers are walking into a valley.
• A large lake is nearby.
CONCEPT
Earth's Features
15
Which of the following is a renewable resource?
• Natural gas
• Gemstones
• Ethanol
• Coal
CONCEPT
Natural Resources
16
Large rocks at the back of a beach cause the wind speed to slow. Windblown sand begins to drop and build small sand piles, which create another windbreak and more sand is deposited. Gradually, salt-tolerant grasses will begin to stabilize the sand dune with a vast network of root systems.
The process described is called __________.
• community ecology
• ecosystems ecology
• primary succession
• secondary succession
CONCEPT
Community Ecology
17
Which list correctly orders the examples of organism, population, community and ecosystem?
• Tundra, moss, reindeer that eat moss, rocks and ice
• Elephant herd, grasslands, lions in the grasslands, river and trees
• Deer, herd of deer, deer and trees in forest, rocks and ponds around the forest
• Tadpole, pond, frog, fish and insects in the pond
CONCEPT
Ecology
18
Choose the example of a decomposer in the food chain.
• A head of lettuce grows in a garden
• A wildcat consumes the rabbit
• A rabbit eats lettuce growing in a garden
• An earthworm consumes a wilted lettuce leaf in a trash pile
CONCEPT
Ecosystems Ecology
19
Which of the following is an example of symbiosis?
• A blue jay uses a nest built by another jay.
• Rabbits and deer both consume grass.
• Bats snatch mosquitoes out of the air.
• A honeybee takes pollen from a flower.
CONCEPT
Community Ecology
20
Select the example that describes a non-native species.
• This particular species of orchid has remained within the same environment for hundreds of years.
• Populations of deer and wolves in Arizona have evolved in relationship with each other.
• Domestic livestock multiplied rapidly throughout eastern North America after their introduction by English colonists.
• A species of parrot has evolved to occupy a key niche within the Amazon rainforest ecosystem.
CONCEPT
Native and Non-Native Species
21
Population ecologists study which of the following characteristics?
• Temperature regulation, nutrition and metabolism of organisms.
• Composition, distribution and interaction of species in a given area.
• Number, density, age, and sex of organisms.
• Atmosphere, rocks, water and living organisms.
CONCEPT
Ecology
22
Which statement accurately describes the "savanna" biome?
• This biome features high levels of biodiversity and is located near the equator.
• This biome features a level of permafrost and a short growing season during the winter.
• This biome features forests and grasslands that go dormant during the winter.
• This biome features tropical grasslands and is located near the equator.
CONCEPT
Biomes
[Show More]