NR 327 Maternal-Newborn Nursing Daily Assessment/Concept Map
Document Content and Description Below
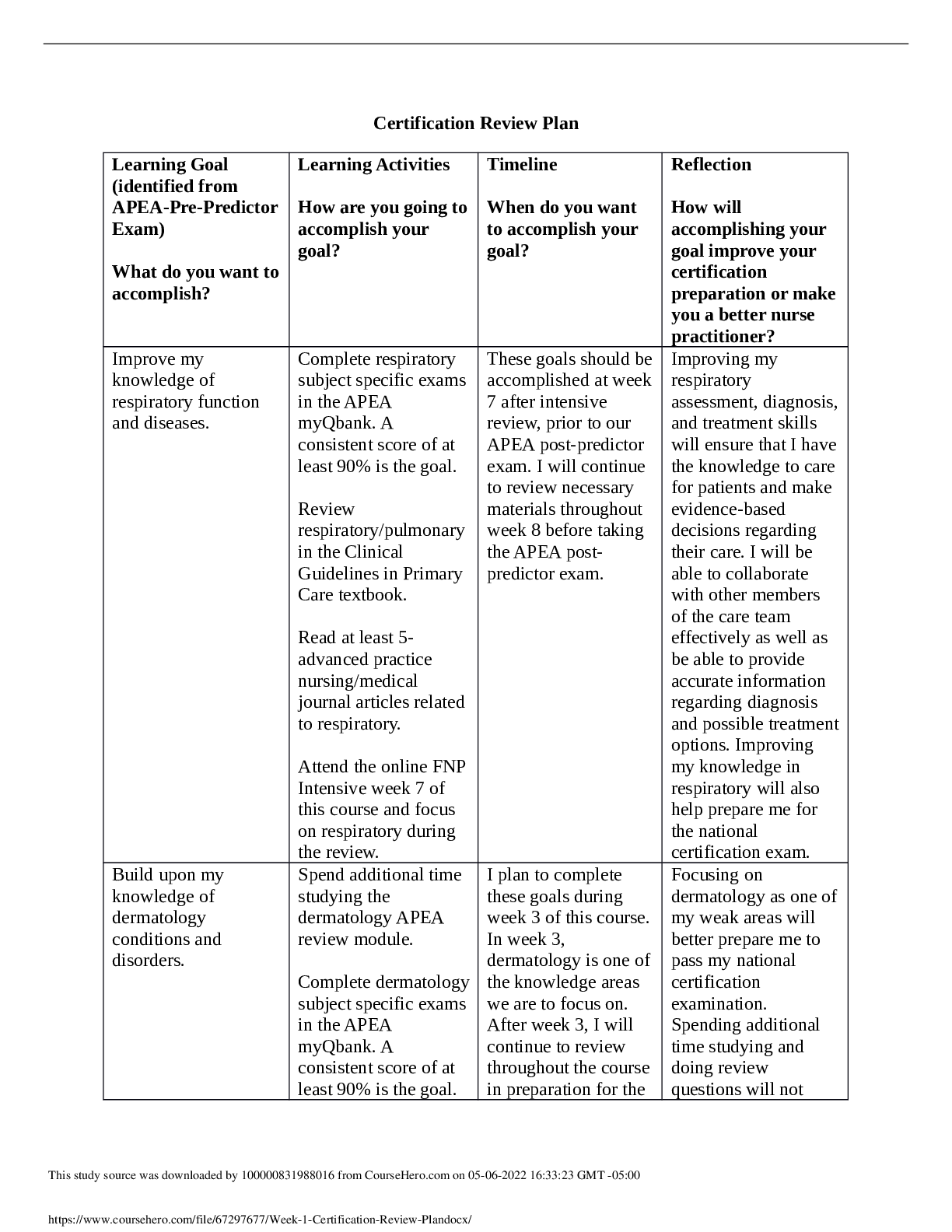
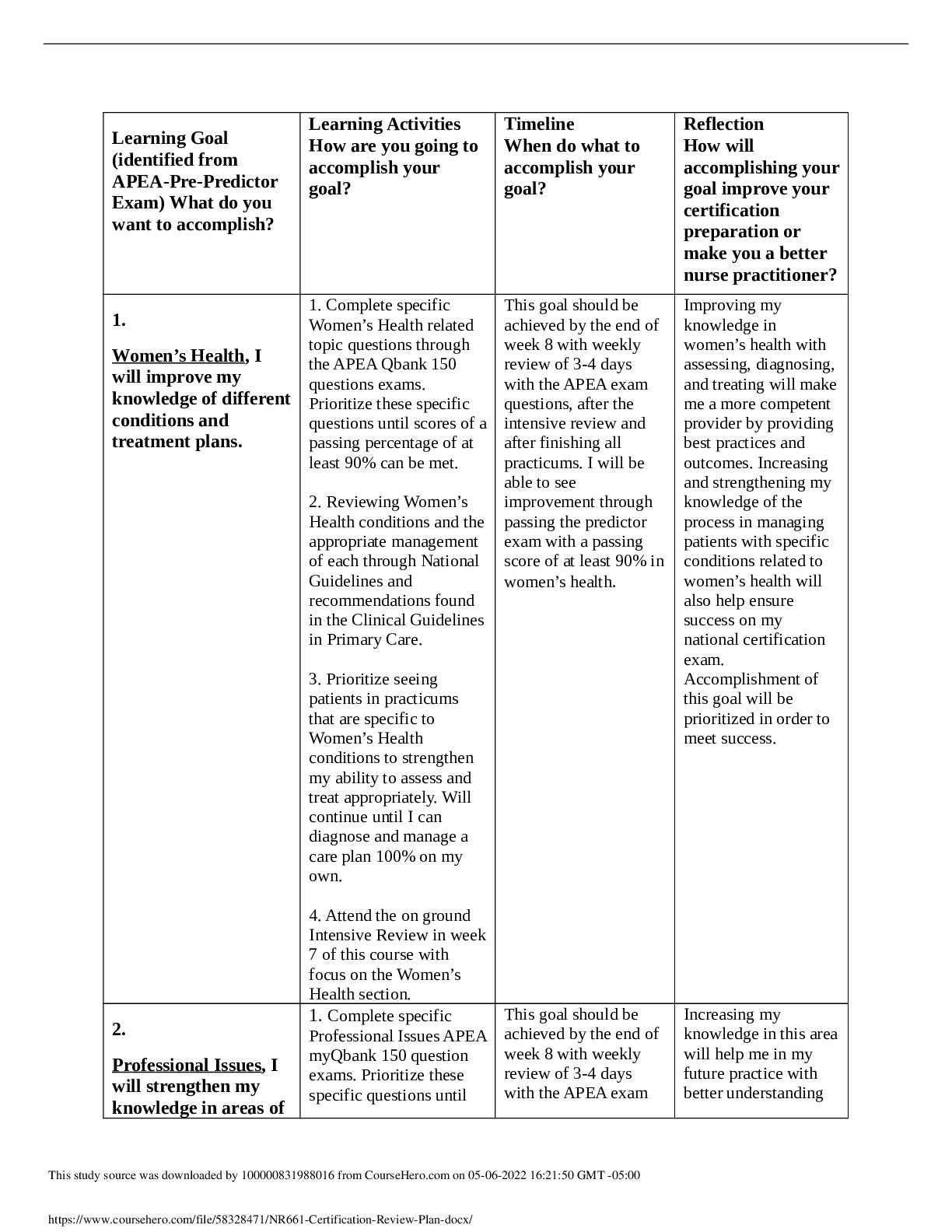
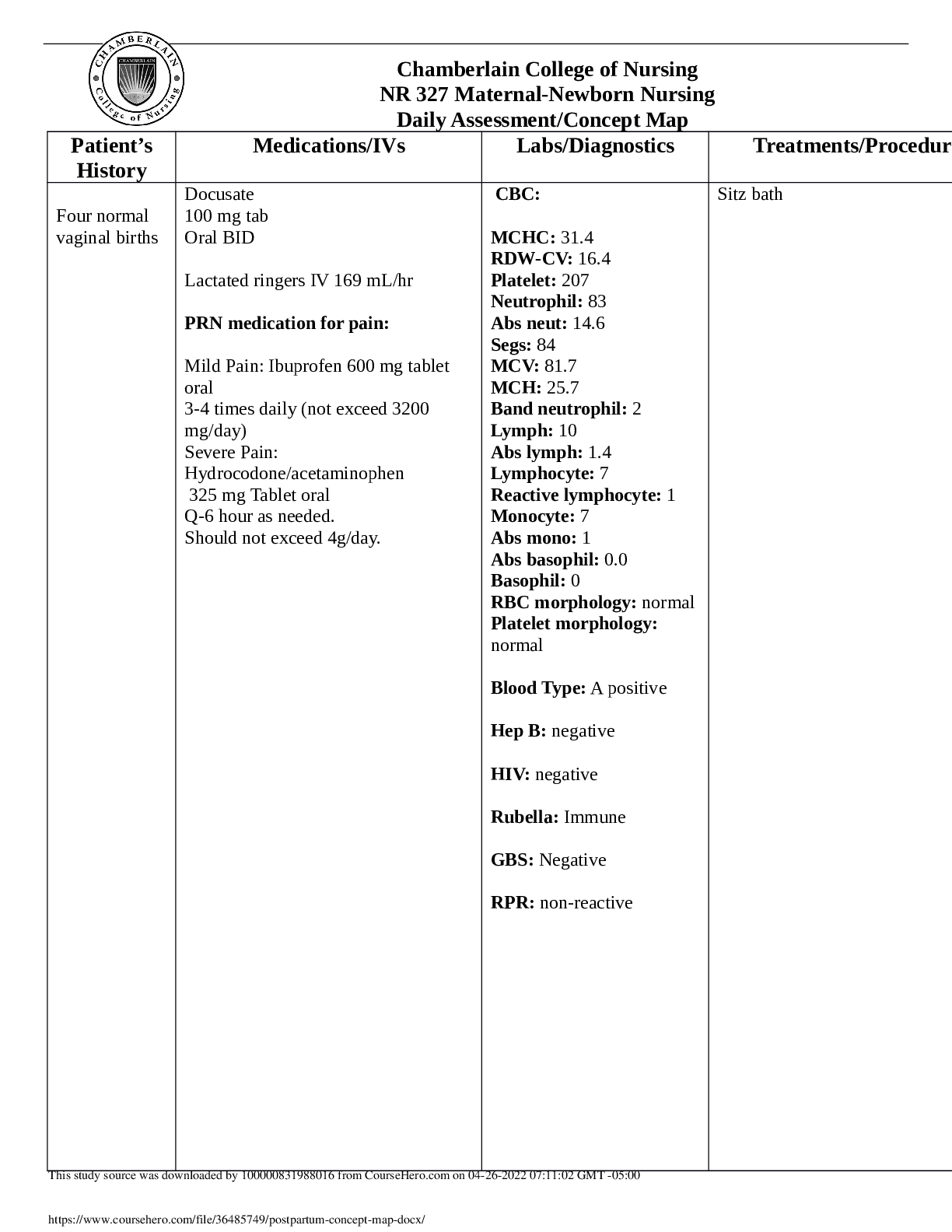
Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 327 Maternal-Newborn Nursing Daily Assessment/Concept Map Patient’s History Medications/IVs Labs/Diagnostics Treatments/ProcedurFour normal vaginal births Do ... cusate 100 mg tab Oral BID Lactated ringers IV 169 mL/hr PRN medication for pain: Mild Pain: Ibuprofen 600 mg tablet oral 3-4 times daily (not exceed 3200 mg/day) Severe Pain: Hydrocodone/acetaminophen 325 mg Tablet oral Q-6 hour as needed. Should not exceed 4g/day. CBC: MCHC: 31.4 RDW-CV: 16.4 Platelet: 207 Neutrophil: 83 Abs neut: 14.6 Segs: 84 MCV: 81.7 MCH: 25.7 Band neutrophil: 2 Lymph: 10 Abs lymph: 1.4 Lymphocyte: 7 Reactive lymphocyte: 1 Monocyte: 7 Abs mono: 1 Abs basophil: 0.0 Basophil: 0 RBC morphology: normal Platelet morphology: normal Blood Type: A positive Hep B: negative HIV: negative Rubella: Immune GBS: Negative RPR: non-reactive Sitz bath This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-26-2022 07:11:02 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/36485749/postpartum-concept-map-docx/ Newborn Data Medications Labs Treatments Date/Time of Birth: 11/11/17 at 09:34 Vaginal Delivery Weight: 6 lbs 6oz. Head Circumference: 33cm Abdomen Circumference: 33 cm Chest Circumference: 34 cm Erythromycin ophthalmic. 1 Application each eye, once 11/11/17 Phytonadione (Phytonadione (vitamin K) Ped. 1 mg/0.5 mL IM injection, once 11/11/17 Hepatitis. B Ped. Vaccine (Engerix-B) 10 mcg/0.5 mL IM injection Bilirubin Total: 5.6 Bilirubin Direct: 0.2 Erythromycin ophthalmic. 1 Application each eye, once 11/11/17 Phytonadione (Phytonadione (vitamin K) Ped. 1 mg/0.5 mL IM injection, once 11/11/17 Hepatitis. B Ped. Vaccine (Engerix-B) 10 mcg/0.5 mL IM injection This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-26-2022 07:11:02 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/36485749/postpartum-concept-map-docx/ This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 04-26-2022 07:11:02 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/36485749/postpartum-concept-map-docx/ Concept Map Fourth degree perineal laceration Pathophysiology Vaginal lacerations typically occur when baby’s head passes through the vaginal canal and is too large for the vagina to stretch around. Vaginal lacerations are graded in degrees. First-degree vaginal laceration is the least severe; it involves skin around the Perineal skin. First-degree lacerations don’t always require sutures and may heal on their own. Seconddegree laceration involves the Perineal muscles and often require sutures. Third-degree tears involve the area around the Perineal muscles to the muscles around the anus. These require surgical intervention to repair the perineum. Fourth-degree lacerations are the most severe. These tears involve the Perineal muscles, the anal sphincter, and the tissues around the rectum. Fourth-degree lacerations require surgical repair and take months to heal. Risk Factors Delivery of a large baby Previous pelvic surgery Abnormal position of a baby’s head Medications and treatments (Include nursing considerations) Application of ice (make sure patient does not leave the ice on skin for too long in order to avoid skin damage). Taking sitz bath (Demonstrate patient how to take a sitz bath, allow patient to do a return demonstration or repeat instructions). Performing perineal care (Advise patient not to take baths in order to avoid infection and instruct to wipe front to back.) Topical anesthetics (Instruct patient to maintain perineum clean prior to applying topical anesthetic). Oral analgesics (Instruct patient to take pain medication as needed) 3 Nursing diagnosis (2 physiological and 1 psychosocial MUST be prioritized) and 3 prioritized Nursing interventions for each Risk for infection related to broken perineum tissue -Monitor absolute neutrophil count -Implement measures to reduce the risk for infection (Meticulous hygiene, proper fluid intake, adequate nutritional status, initiate measures to prevent constipation) -Routinely monitor for signs and symptoms of infection (increase in temperatures, increased pulse, loss of appetite, increase in WBC, lethargy) Acute pain related to trauma to perineum during labor and delivery -Assess client for pain -Measures to reduce pain: relaxation, ice pack, administer analgesics, corticosteroids -Prevent constipation and straining (administer stool softeners, appropriate fluid intake Readiness for enhanced self-health management related to choices of daily living is appropriate for meeting goals -Provide information that is appropriate, relevant, and timely -Tailor information to the specific needs of individual client -Identify the client’s level of choice in decision-making [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 26, 2022
Number of pages
5
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 26, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
216