FHR MONITOR questions and answers
Document Content and Description Below
FHR MONITOR
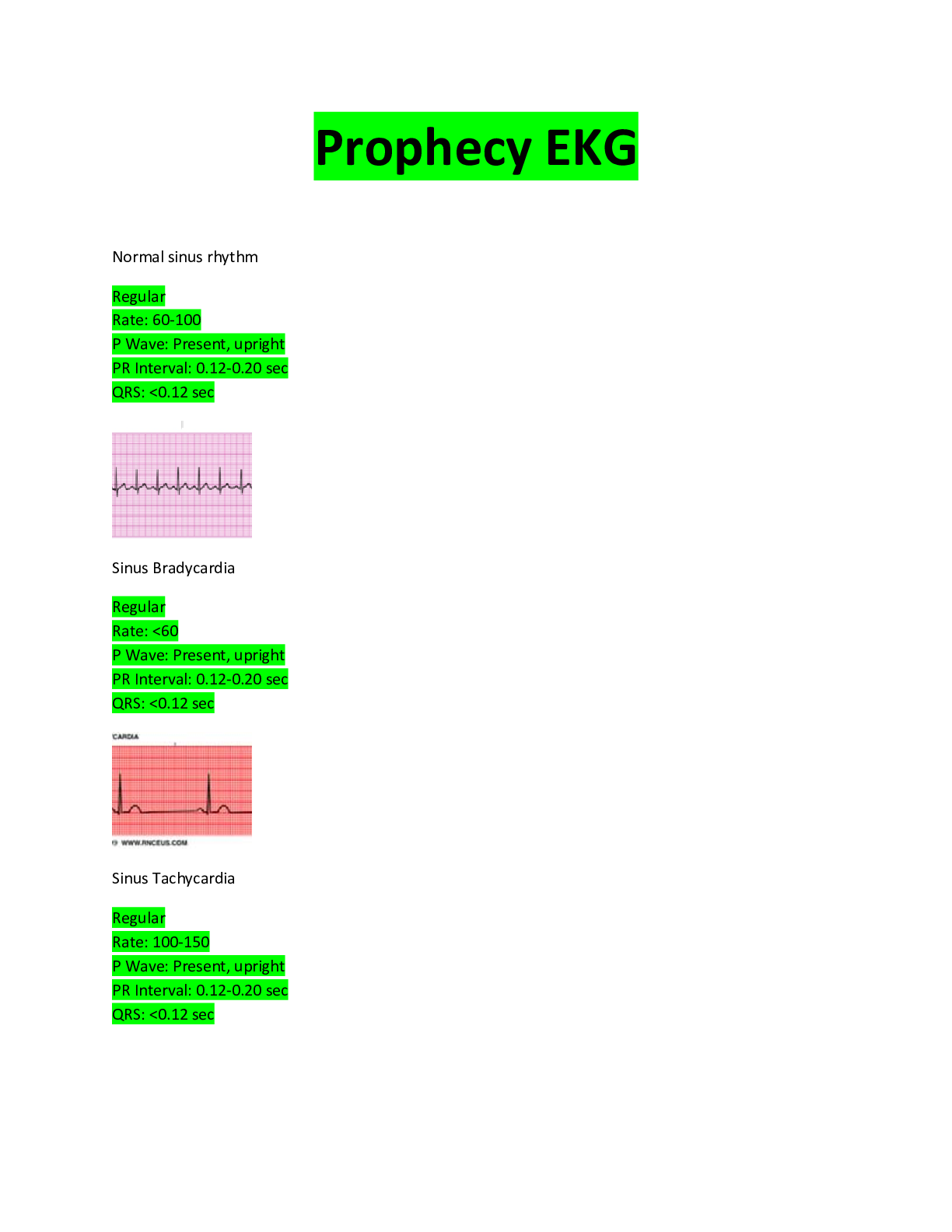
Explain how to identify the baseline FHR. Correct Answer: The baseline FHR is determined by approximating the mean FHR rounded to increments of 5 beats per minute during a ten minute
...
window. (There must be a 2 minute window of identifiable baseline segments)
Explain absent FHR variability. Correct Answer: amplitude range undetectable
Explain minimal FHR variability. Correct Answer: amplitude range greater than undetectable and less than or equal to 5 bpm
Explain Moderate FHR variability. Correct Answer: Amplitude range from 6 bpm to 25 bpm
Explain Marked FHR variability Correct Answer: amplitude range greater than 25 bpm
What are the causes of decrease baseline FHR variability in the mother? Correct Answer: Medications response, Drug response (CNS DEPRESSANTS, MORPHINE, DEMEROL, NUBAIN, STADOL, NEMBUTAL, and ALCOHOL
What are the causes of decrease baseline FHR variability in the fetus? Correct Answer: fetal sleep cycles, fetal CNS anomalies, prolonged or serve fetal hypoxia, cardiac anomalies, persistent fetal tachycardia, excessive/prolonged parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation
Explain Deceleration Correct Answer: FHR decrease of at least 15 bpm that last less than 2 minutes
Explain Prolonged Deceleration Correct Answer: FHR decrease of at least 15 bpm that lasts longer than 2 minutes but less than 10 minutes
What are the maternal causes of FHR Bradycardia? Correct Answer: maternal supine positioning, maternal hypotension, connective tissue diseases, and prolonged maternal hypothermia, medications (Inderal, atenolol, and labetolol
What are the fetal causes of FHR Bradycardia? Correct Answer: umbilical cord occlusion/prolapse, decompensating fetus, cardiac conduction defects, cardiac anatomic defects, congenital heart disease, maturity of parasympathetic nervous system, excessive/prolonged parasympathetic vagal stimulation
What are the maternal causes of FHR Tachycardia? Correct Answer: maternal fever/infection, dehydration, hyperthyroidism, anemia, maternal anxiety, cigarette smoking, medication or drug response (parasympatholytic drugs, beta sympathomimetic drugs, illicit drugs)
What are the fetal causes of FHR
Tachycardia? Correct Answer: prolonged fetal activity/stimulation, chronic fetal hypoxemia, compensatory response to transient fetal hypoxemia, chorioamnionitis, fetal cardiac abnormalities, supraventricular tachycardia, fetal anemia
Explain Accelerations. Correct Answer: A visually apparent, abrupt increase is defined as an increase from onset of acceleration to peak in less than 30 seconds. The peak must be greater than or equal to 15 bpm and the acceleration must last greater than or equal to 15 seconds.
Normal Uterine Contractions are: Correct Answer: less than or equal to five contractions in 10 minutes, an average over 30 minutes
Tachysystole contractions are: Correct Answer: greater than 5 contractions in 10 minutes average over a 30 minute window
Contraction intensity Correct Answer: strength of intrauterine pressure above baseline uterine tone
Contraction Frequency Correct Answer: interval between the beginning of one contraction and the beginning of the next one
Contraction Duration Correct Answer: length of time in seconds from the beginning of a contraction to its resolution
Periodic Patterns Correct Answer: Patterns in the FHR associated with contractions (acceleration or deceleration in the fetal hr that occur in direct association with uterine contractions)
Episodic Pattern Correct Answer: Patterns in FHR not associated with uterine contractions (a deceleration or acceleration in response to a vag exam, maternal vomiting, or fetal movements)
Fetal Tachycardia is indicative of Correct Answer: maternal or fetal infection, fetal hypoxia (ominous sign), anticholinergic drugs, and betasympathomimetic drugs, maternal illicit drugs such as cocaine, maternal anxiety, fetal anemia, maternal dehydration, amnionitits, and maternal hyperthyroidism
Fetal Bradycardia is indicative of Correct Answer: fetal hypoxia or stress, maternal hypotension after epidural initation, some fetus' have normal low baselines (investigate), tetanic uterine contractions, paracervical block, epidural and spinal anesthesia, maternal seizure, rapid descent, vigorous vaginal examination, maternal hypothermia, congenitial heart block, abruptio placenta, fetal arrhythmia (complete heart block)
Interventions for fetal bradycardia: Correct Answer: place on left side, increase fluids to counteract hypotension, stop oxytocin
What are the nursing interventions for early decelerations? Correct Answer: continue to monitor, may indicate the beginning of fetal descent and second stage of labor
If early decels are present early in labor this indicates? Correct Answer: possible fetopelvic disproportion
Late Decelerations are indicative of Correct Answer: fetal stress, hypoxia, placental insufficiency (cardiac disease, placenta pervia, abruptio placenta, PIH), supine position, maternal hypotension, uterine hyerstimulation
Late Decelerations nursing interventions Correct Answer: change maternal position, correct hypotension, increase IV fluid rates, dc oxytocin, administer o2 by face mask at 7-10 L/min, tocolytics as ordered if hyperstimulation is present, left side prosition, maintain good hydration with normal saline or LR, monitor for maternal hypotension (increase IV fluids?)
Variable decelerations are indicative of Correct Answer: cord compression (nuchal cord aka around fetal neck, short cord, long cord, prolapsed cord, knot in cord), hypoxia or hypercarbic states
Variable decelerations interventions Correct Answer: change maternal position, administer oxygen per face mask, vag exam to check prolapsed cord, notify physician, and prepare for amnionfusion order
decreased variability is indicative of Correct Answer: fetal sleep cycle ( lasting30-40mins each hour), depressant drugs, maternal and fetal hypoxia, cns abnormalities, maternal hypotension, uterine hyperactivity, cord prolapse, cord compression, abruption, fetal hemorrhage, fetal vagal stimulation, and uterine rupture , administration of dmerol valium or vistaril, fetal dysrhythmias or fetal anomalies, tachycardia, neurologic insult
Causes of marked variability Correct Answer: early mild hypoxia, fetal stimulation or activity, fetal breathing movements, advancing gestational age (30 weeks)
Prolonged decelerations are indicative of Correct Answer: acute hypoxia due to hyperstimulation, cord prolapse, hypotensionn, maternal hypoxia, rapid fetal descent
Prolonged decelerations nursing interventions Correct Answer: dc oxytocin, oxygen per mask at 7-10 L/min, reposition off cord if prolapsed, position changes, tocolytics for hypertonic contractions, notify physician, increase IV fluids
A fetoscope is used for Correct Answer: auscultation of fetal heart tones after 18 weeks
What are the common reasons for internal fetal monitoring used? Correct Answer: baby is difficult to keep on the monitor, baby has an abnormal hr or is having decelerations in its HR, and patient is having contractions but accurate info as to their actual strength is needed to determine whether the pt needs oxytocin to make them stronger and more effective
A fetal scalp electrode and an IUPC are only used
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages