eBook [PDF] Writing Effective Ecological Reports 1st Edition By Mike Dean
$ 30

Pearson Edexcel Advanced Subsidiary GCE In Chemistry (8CH0) Paper 2: Core Organic and Physical Chemistry Examiners’ Report Principal Examiner Feedback November 2021
$ 4.5

eBook [PDF] Buddhism in Court_ Religion Law, and Jurisdiction in China 1st Edition By Cuilan Liu
$ 29

Test Bank For What's That Sound by John Covach, Andrew Flory Chapter 1-15 Complete Guide 2023 updated.
$ 18

CJ 130 INTRO TO JUDICIAL PROCESS REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 10

eBook EPUB Rise and Shine, An Astrological Guide to How You Show Up in the World 1st Edition By Christopher Renstrom
$ 29
Tina Jones Skin Hair and Nails Completed Shadow Health Subjective
$ 8

NRNP 6560 Midterm exam with complete solutions
$ 10

Unit 4 Milestone 4.docx. 15 QUESTIONS AND RATIONALE ANSWERS. GRADED A+
$ 8

Science / Medicine / Hepatology - Liver Diseases (Questions And Answers)
$ 10

TEST BANK FOR Contract Law 6e By Mindy Chen-Wishart
$ 29

NFHS Basketball Rules Exam Part I Questions & Answers 2023 ( A+ GRADED 100% VERIFIED)
$ 6

D190 Task 1 revision 1.docx D190 Intro to Healthcare IT Systems A1 Plan for Determinin
$ 10

eBook American Constitutional Law The Bill of Rights and Subsequent Amendments (Volume II) 11e Ralph Rossum, Alan Tarr, Vincent Phillip Munoz
$ 29
(UMGC) NURS 300 Science & Research in Nursing Final Exam Guide Q & A 2024
$ 12

Week 5 SOAP NOTE PART 2| COMPLETE SOLUTIONS| NRP 531
$ 7

John Deere 240 and 250 Skid Steer Repair Technical Service Manual
$ 14.99

ATI RN Concept-Based Assessment Level 1 Online Practice
$ 17

TEST BANK Jazz Essential Listening by John Murphy - UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS
$ 19

eBook [PDF] Family Law and Practice 5th Edition By Grace Luppino, Justine Miller
$ 30
EDEXCEL A LEVEL 2022 ITALIAN QUESTION PAPER 2
$ 3

Surgical Case 5: Lloyd Bennett Documentation Assignments
$ 6

Dosage Calculation Practice Questions and Correct Answers
$ 10.5
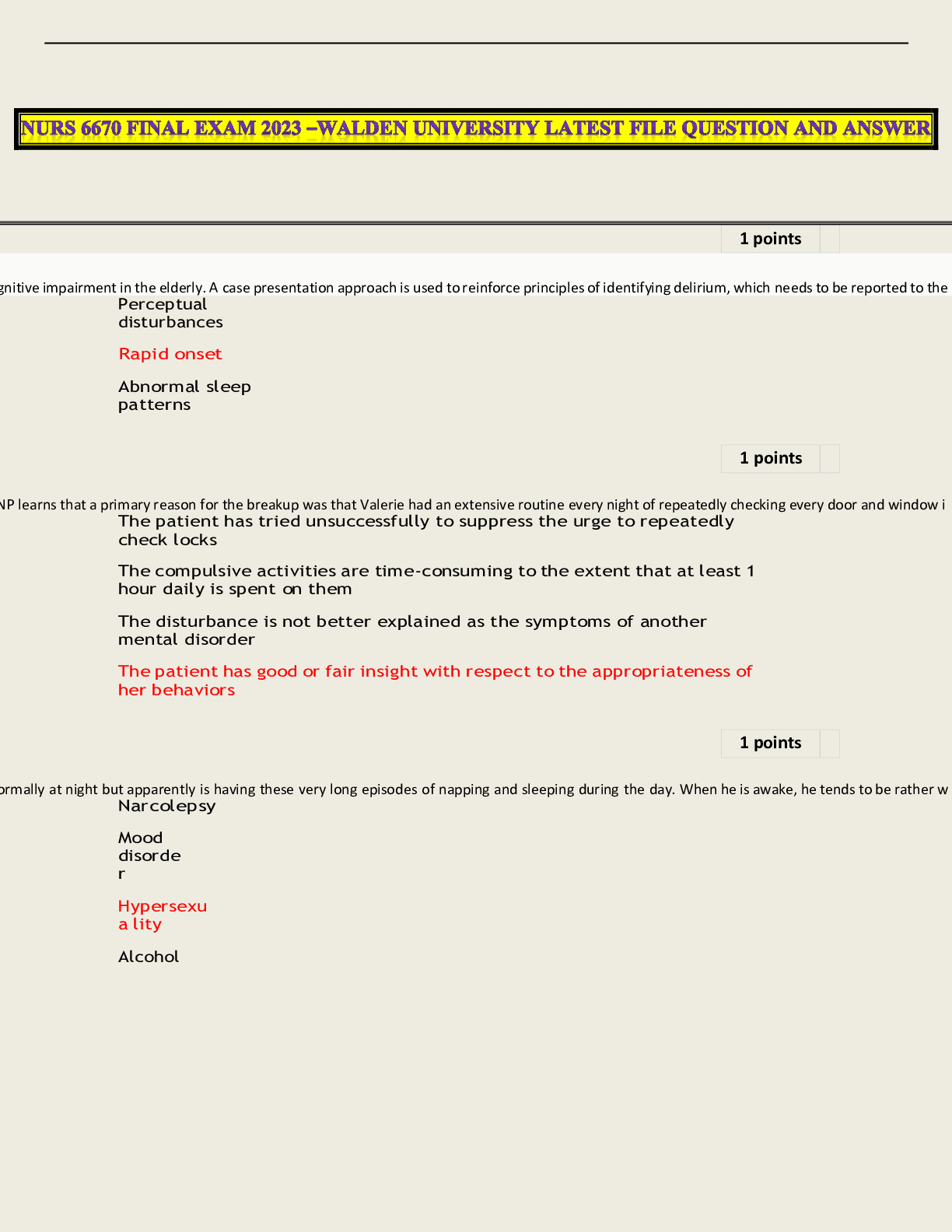
NURS 6670 FINAL EXAM WALDEN UNIVERSITY, 2023 SPRING QUESTION AND ANSWER LATEST FILE
$ 7.5

(eBook-PDF) Layered Nanomaterials for Solution-Processed Optoelectronics | ISBN: 9781032834689 and 1032834684 and eText ISBN: 9781040305393 and 1040305393 | Authored by Manjeet Singh, Ashish Kumar Singh, Balaram Pani | Published by CRC Press in 2025
$ 39.5

Current Mobile Technologies



.png)