MCAT Biology 2022 Practice Questions AND ANSWERS ALL CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
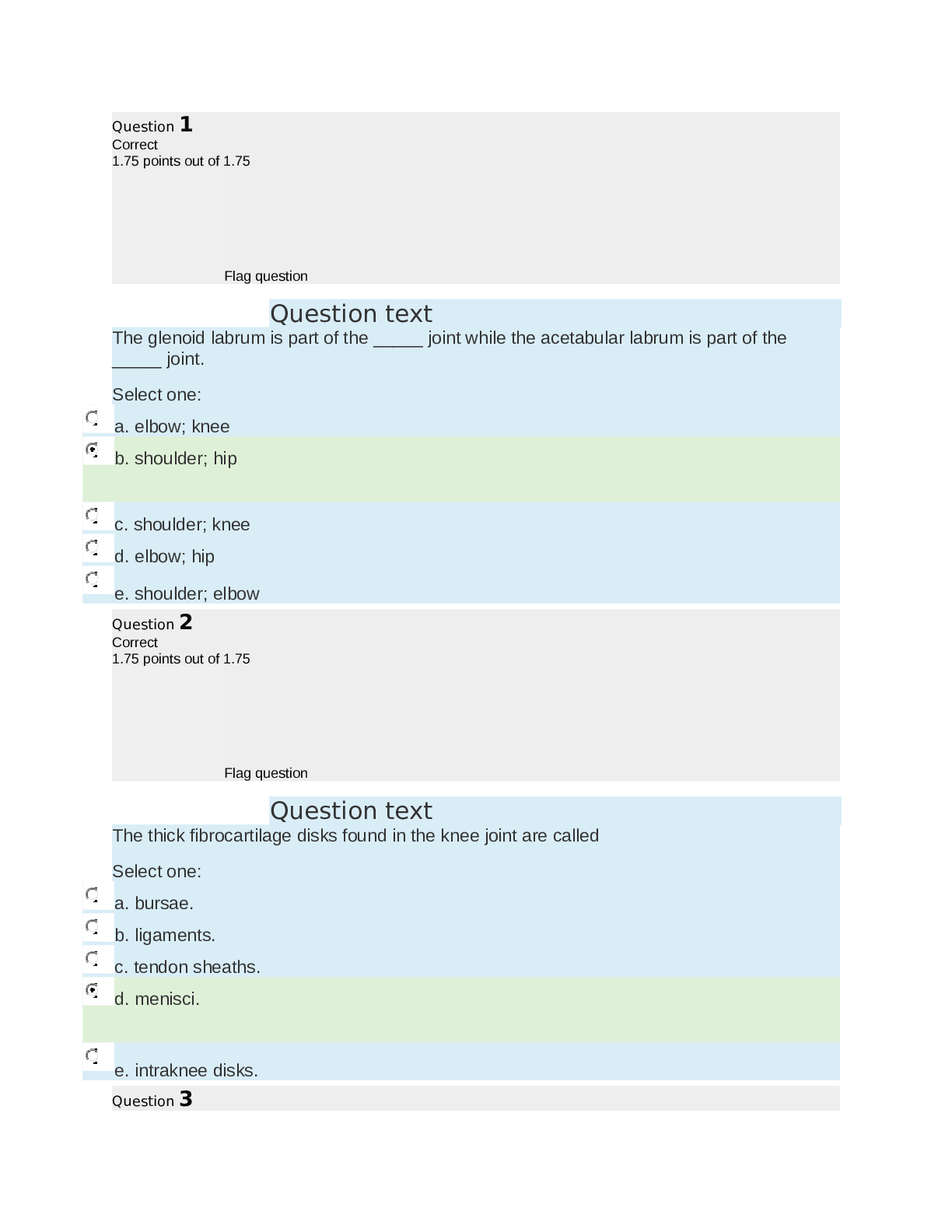
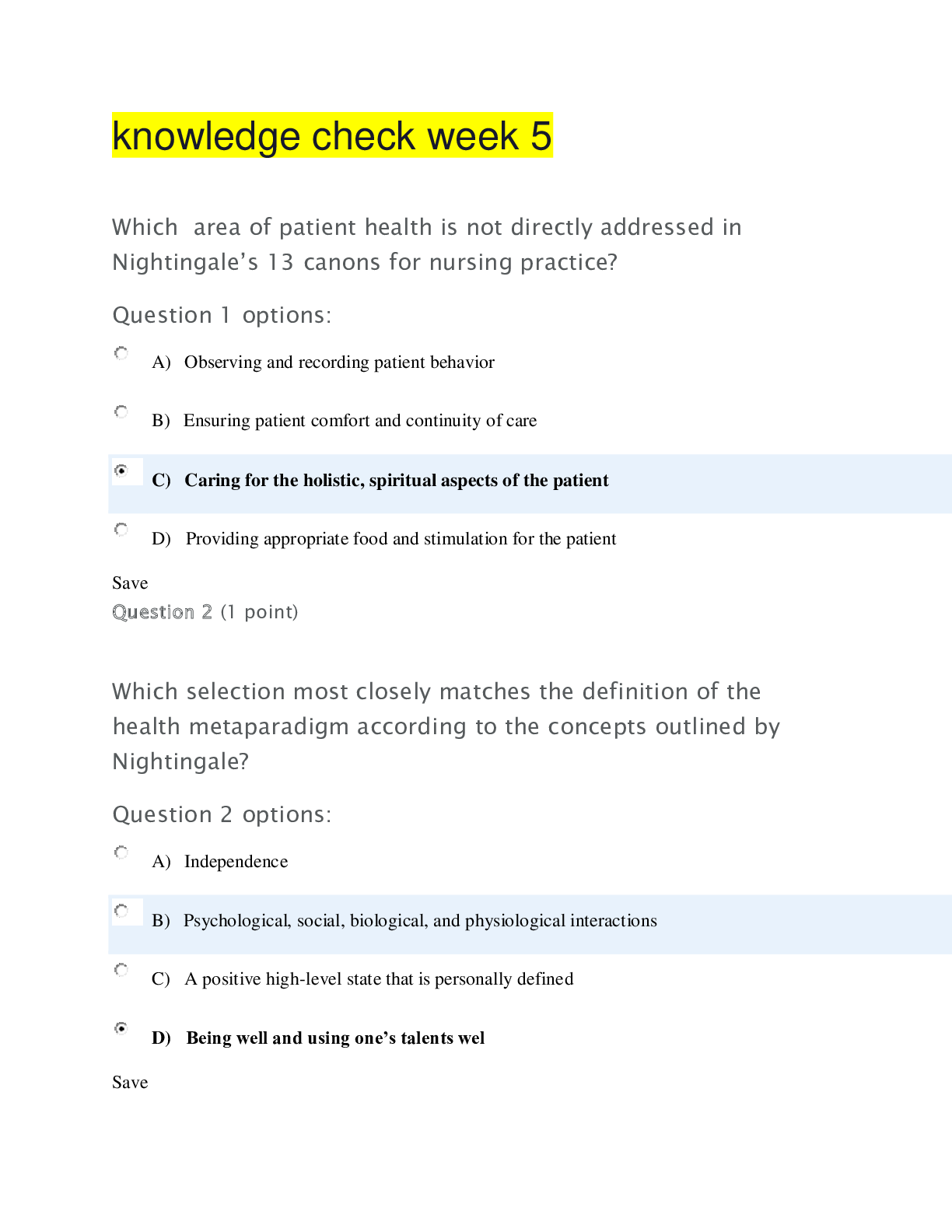
MCAT Biology 2022 Practice Questions the chemical reaction that breaks down all the major macro-molecules Correct Answer: Hydrolysis What is the strongest type of INTER-molecular bonds? Correct... Answer: Hydrogen bonds are the strongest intermolecular bonds.... diople-dipole bonds are weaker. . . Vander wall bonds are the weakest. Why is water a liquid at high temperatures? Correct Answer: Hydrogen bonding bonds the water molocules closer together. What is an ampipathic molecule? give an Example. Correct Answer: A molecule with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Example: PhoshpoLipid (Phospho=philic,lipid= phobic) What is a lipid? Correct Answer: A lipid is a biological molecule with low solubility in water. Lipid means fat. Liposuction is fat removal. Peptides are NOT lipids. What are the 6 major groups of lipids? Correct Answer: 1) fatty acids... the next 3 have a 3 carbon back bone: 2) Tri-glyceride 3) Phospholipids 4) Glycolipids 5) Steroids 6) Terpenes - A large class of organic compounds. examples: smelly pine oils, beer hops aroma and vitamin A. What is the structure of a Tri-glyceride? Correct Answer: triglicerides are esters. Composed from 3 carbon glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acid chains dangling. Each carbon chain is attached by an ester bond. What happens if you add water to an ester group in a Tri-glyceride? How is this reaction rate increased? Correct Answer: Water cleaves the ester bond into an alcohol and a carboxylic/ fatty acid. LIPASES speed are the enzyme that speed this reaction. in terms of water solubility, What is important to know about the longer the carbon chain in a Tri-glyceride when broken down? Correct Answer: longer carbon chains are less water soluble. In longer chains the polar carboxylic acid are less significant. How soluble is a Shorter chain fatty acids? Correct Answer: Shorter chain fatty acids are slightly water soluble. explain what is so special about Saturated Fatty Acids........Also, explain the melting point. Correct Answer: saturated fatty acids have only single, alkane bonds along the carbon chain. They have a straighter chain and have more van der wall forces, and therefor a higher melting point. explain what is so special about Unsaturated Fatty Acid.... Also, explain the melting point. Correct Answer: Unsaturated fatty acids have at least one double bond. They are not saturated with Hydrogen. they have a LOWER melting point. At room temperatures unsaturated fatty acids may be oily, like Healthy peanut butter. explain the phospho-lipids structure. Where are phoshpo lipids common? Correct Answer: Phospholipids are also built on a 3 Carbon backbone. One of the carbon has a Phosphate PO4 group. the other 2 carbons have carbon chains attached by a ester bond. This is the lollypop of the cell membrane. Esters have 2 oxygens. What regions are poplar nonpolar in a membrane? Correct Answer: 1)the phosphates are Polar, water lovin, hydro philic regions that face the outside. 2) Nonpolar, hydro phobic carbon chain regions face the inside. Explain glycolipids structure. Correct Answer: glycolipids have 3 carbon backbone with 2 Carbon chains attached by an ester group. THe third carbon has a carbohydrate What do steroids look like? Correct Answer: Slightly amphipathic 4 ring structures lipids are insoluble. So how do they move through the blood? Correct Answer: They are usually carried by lipoproteins, like HDL or LDL. What are the major classes of lipoproteins? Correct Answer: 1) Chylomicrons which are the largest 2) VLDLs these are low denstiy, but large. 3) LDLs 4) HDLs. these high density lipids are the smallest, and called good proteins. What are proteins made up of? Correct Answer: one or more chains of amino acids, perhaps in a crazy ass arrangement. describe amino acid structure. Correct Answer: Amino acids have 4 parts attached to the alpha carbon. 1. the amino group, which is NH2 2. the R group, which is one of 20 choices 3. the Carboxylic acid or C O O the last thing attached to the Carbon is the Hydrogen. What are the basic amino acids? Correct Answer: Hal Histidine Arginine Lysine What are the acidic amino acids? Correct Answer: Aspartic acid and Glutamic acid What are the nonpolar amino acids? Correct Answer: Poor LTMG Is Venezuelan At Parties 1) Phenylalanine 2) Leucine 3) Tryptophan 4) Methionine 5) Glycine 6) Isoleucine 7) Valine 8) Alanine 9) Proline What is the primary structure of a protein? Correct Answer: Sequence of amino acids and Location of disulfide bonds between cistine residues What is the secondary structure of a protein? Correct Answer: 1) Twisting of the alpha helix 2) Beta sheets What is the tertiary structure of a protein? Correct Answer: 3D structure including bending What is the quaternary structure of a protein? Correct Answer: Multiple proteins in formation What are the five forces that create tertiary structure? Correct Answer: 1) Covalent 2) Disulfide bonding between cysteine residues (Bond itself creates tertiary structure) 3) H bonds 4) HPhob away from cytosol and Hphil interactions towards cytosol 5) Van Der Waals (dipoles, instantaneous dipoles) What levels of structure are disrupted during the denaturation process? Correct Answer: Secondary - quaternary What is the difference between a proteoglycan and a glycoprotein? Correct Answer: Glycoproteins: 1) Made of protein and carbohydrate 2) More stable than proteins 3) Often used in IS to bridge the cellular membrane. 4) Ratio - have more proteins Proteoglycans: 1) Special class of glycoprotein 2) Contain extra carbohydrates 3) Structure = protein with one or more glycosaminoglycan chains. 4) Ratio - have more carbs What is the empirical formula for any carbohydrate? Correct Answer: CH2O Describe the chemical structure of glucose Correct Answer: 1) Aldehyde 2) Has 4 chiral carbons 3) Fischer - R, L, R, R [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 37 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)

MCAT TESTS COMPILATION BUNDLE
MCAT TESTS COMPILATION BUNDLE
By Crum 2 years ago
$40.5
23
Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 06, 2022
Number of pages
37
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
93













.png)