Earliest documented emergency medical service. - ANSWER In 1790 the French began transporting wounded soldiers from the battlefield.
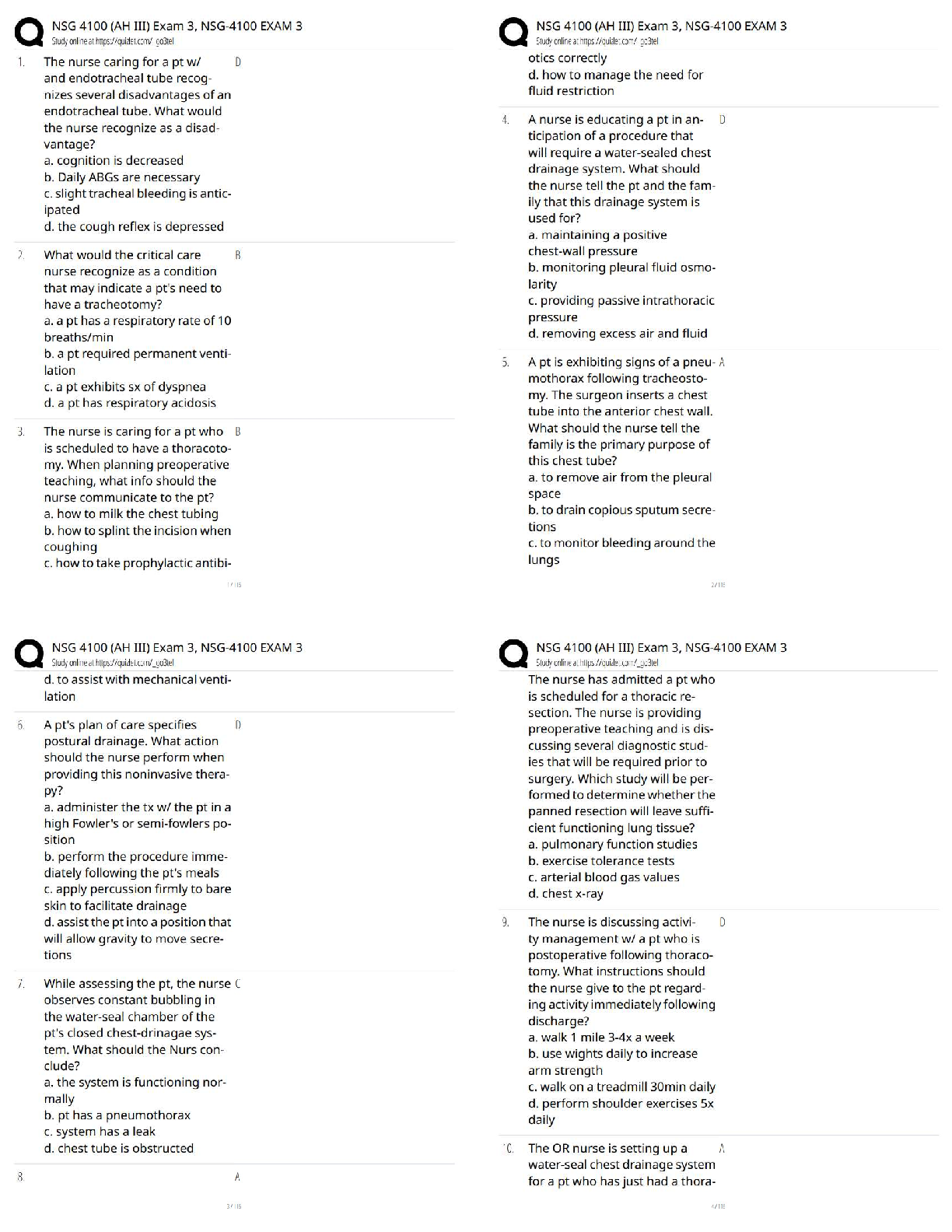
Who developed the first emergency medical standards? - ANSWER U.S. Department of Tra
...
Earliest documented emergency medical service. - ANSWER In 1790 the French began transporting wounded soldiers from the battlefield.
Who developed the first emergency medical standards? - ANSWER U.S. Department of Transportation
What is enhanced 911? - ANSWER Dispatchers are able to determine location of the caller.
Minimum level of certification to run on an ambulance crew. - ANSWER EMT
Evaluation of patient's condition is done by doing a ___. - ANSWER Patient Assessment
Who is responsible for scene safety? - ANSWER All crew members
A person who speaks on behalf of the patient. - ANSWER The Advocate
Assumes responsibility for all EMTs. - ANSWER The Medical Director
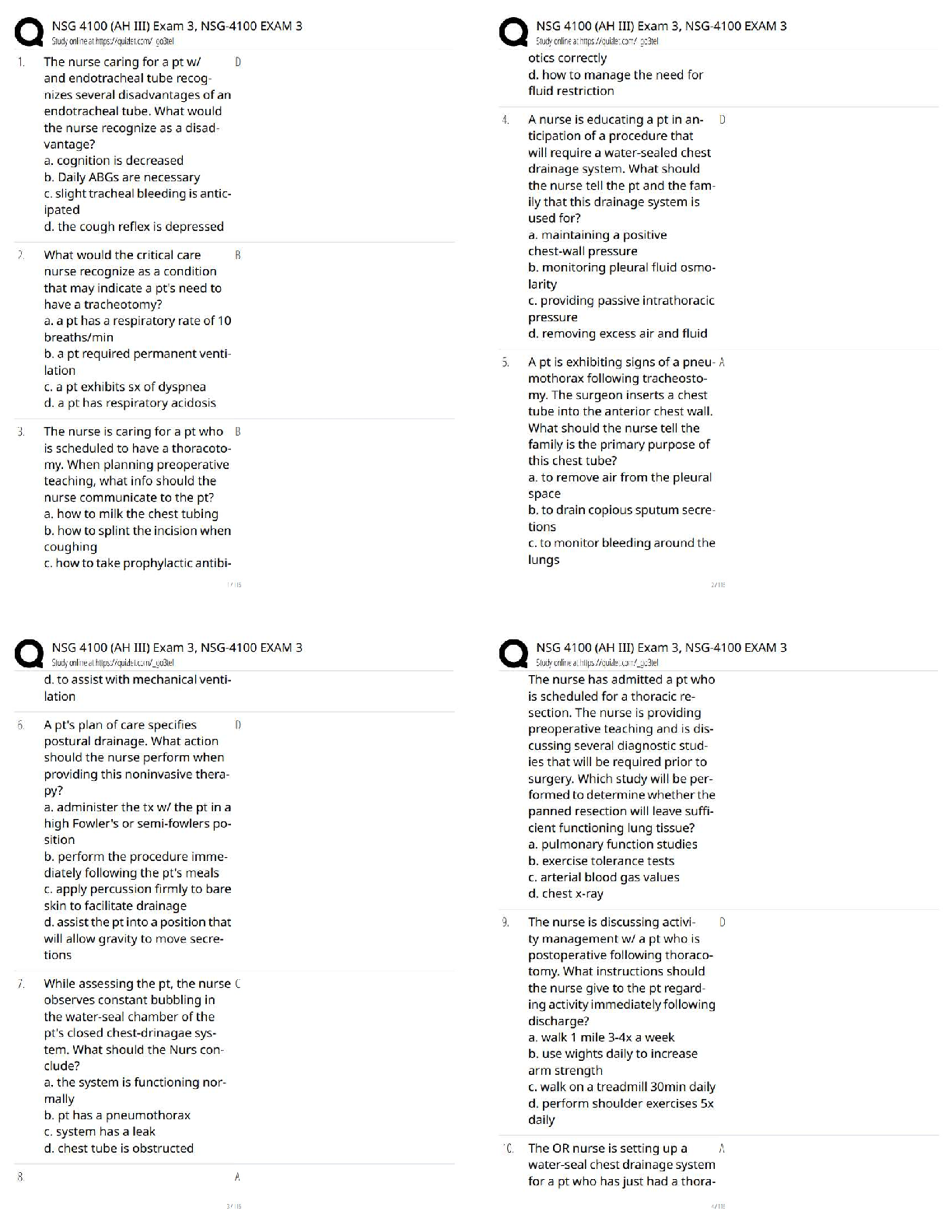
Any agent that causes disease is called a ______. - ANSWER Pathogen
How is Hepatitis A transmitted? - ANSWER Fecal-oral route
What part of the nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response? - ANSWER Sympathetic Nervous System
Levels of EMS - ANSWER EMR, EMT, AEMT, Paramedic
When lifting a patient, a basic principle is to: - ANSWER Know your own limitations
Preferred number of rescuers when using a stair chair. - ANSWER 3
Set of limitations that defines the legal actions and limitations placed on the EMT. - ANSWER Scope of Practice
Consent given by a school principal to treat a minor on behalf of the parents. - ANSWER In loco parentis (in place of the parent)
An EMT's legal and ethical obligation to provide care to a patient. - ANSWER Duty to Act
Act that governs patient confidentiality. - ANSWER HIPAA
EMTs role at a crime scene. - ANSWER Care of the patient
What is anatomy? - ANSWER The structures of the human body.
What is physiology? - ANSWER The function of the human body.
Sharing information about a patient's history or condition. - ANSWER Breach of confidentiality
Medial - ANSWER Middle
Lateral - ANSWER Outside
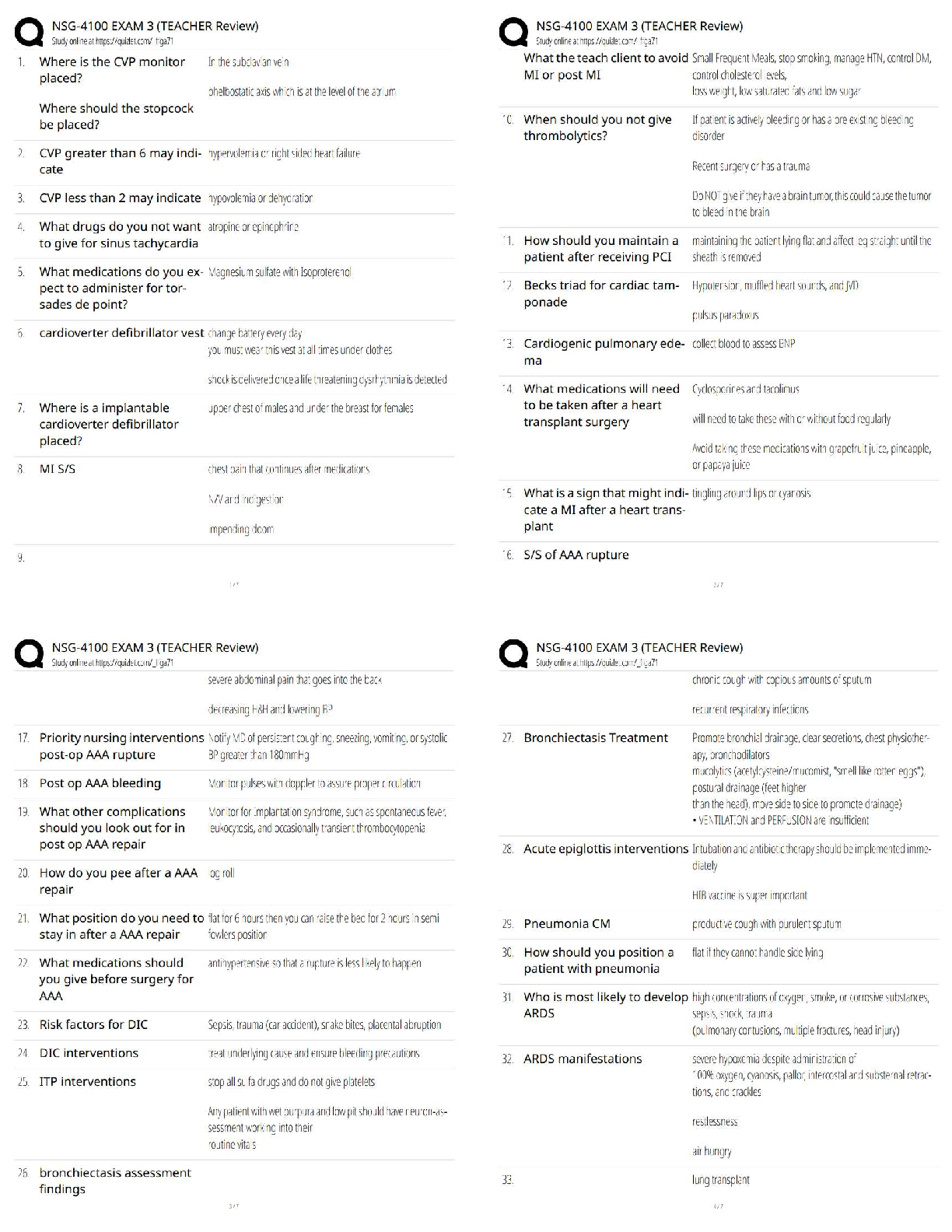
Standing erect, facing the observer, with arms down and the palms of the hands facing forward. - ANSWER Anatomical Position
Prone - ANSWER Face down
Supine - ANSWER Face up
Proximal - ANSWER Near to
Distal - ANSWER Away from
Patient is sitting straight up. - ANSWER Fowler's position
Shock is also called _____. - ANSWER Hypoperfusion
The two areas of the spine most easily injured. - ANSWER Cervical and Lumbar
Arteries always carry blood ______ from the heart. - ANSWER away
Veins always care blood _____ the heart. - ANSWER towards
The clotting components of blood. - ANSWER Platelets
The arteries the feed blood to the heart. - ANSWER Coronary arteries
The pressure created by the contraction of the left ventricle - ANSWER Systolic
The pressure remaining in the arteries when the left ventricle relaxes. - ANSWER Diastolic
The system of the body that produces chemicals and hormones that regulate most of the body's activities and functions. - ANSWER Endocrine System
Main function of the liver. - ANSWER Detoxifies harmful substances, stores sugar, and assists in the production of blood products.
The most muscular and strongest part of the heart. - ANSWER Left Ventricle
Primary organs of the renal system. - ANSWER Kidneys
Carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs. - ANSWER Pulmonary artery
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. - ANSWER Pulmonary veins
A source of major airway obstruction in children. - ANSWER The tongue
The amount of air the moves in and out of the chest in one normal breathing cycle. - ANSWER Tidal volume
Tidal volume x Breaths per minute = ? - ANSWER Minute volume
What is ATP? - ANSWER The cell's internally created fuel that is responsible for powering all cellular function.
When glucose and other nutrients are converted into energy. - ANSWER Cellular Respiration
The byproducts of anaerobic respiration. - ANSWER Lactic acid and carbon dioxide
The byproduct of cellular respiration that is removed from the blood and released through exhalation. - ANSWER Carbon dioxide
The main control center of respiratory control. - ANSWER Medulla Oblongata
Pathway of air from the nose to the alveoli. - ANSWER nose, nasopharynx, pharynx, hypopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, alveoli.
A condition that is caused by a decreased number of red blood cells. - ANSWER Anemia
Respiratory drive is triggered by changes in levels of ___. - ANSWER Carbon dioxide
Birth to one year. - ANSWER Infancy
A reflex in an newborn where it throws its arms out when started. - ANSWER Moro reflex
Age group most concerned with body image - ANSWER Adolescence
High-pitched upper airway obstruction. - ANSWER Stridor
How to open the airway when a spinal injury is suspected. - ANSWER Jaw-thrust maneuver
How to insert an oropharyngeal airway. - ANSWER Insert towards the roof of the mouth, then rotate it 180 degrees.
Normal vital signs for a 4-year old. - ANSWER heart rate 80-130, respiratory rate 20-30, systolic pressure 70-100.
Signs of hypoxia - ANSWER Blue or gray skin, decreased LOC, confusion, restlessness.
Normal respiration rate for an adult. - ANSWER 12 to 20 per minute
Normal oxygen concentration via a non-rebreather mask. - ANSWER 15 liters per minute
When to replace an oxygen tank. - ANSWER 200L
AVPU - ANSWER Alert, Verbal, Pain, Unconscious
Place to check a pulse on a responsive adult patient. - ANSWER Radial
Place to check a pulse on an infant. - ANSWER Brachial
Place to check a pulse on an unresponsive adult. - ANSWER Carotid
Normal capillary refill time. - ANSWER Less than 2 seconds.
Normal adult blood pressure - ANSWER 120/80
How often should you re-assess vital signs on an unstable patient? - ANSWER Every 5 minutes
How often should you re-assess vital signs on a stable patient? - ANSWER Every 15 minutes
Contraindication - ANSWER A reason why you should not give a medication.
Medications an EMT can administer. - ANSWER Aspirin, oral glucose, oxygen, prescribed inhalers, nitroglycerin, epinephrine auto-injectors.
Function of aspirin - ANSWER Reduces the blood's ability to clot and reduces pain.
Why do you give nitroglycerin? - ANSWER It is given for angina pectoris.
How does an epipen work? - ANSWER Anaphylaxis causes vasodilation and low blood pressure. Epinephrine causes vasoconstriction that counteracts the effect.
What is the most important drug an EMT can give to a patient with signs and symptoms of miocardial infarction. - ANSWER Oxygen
What are the two shockable rhythms. - ANSWER V-fib, V-tach
Low blood sugar - ANSWER Hypoglycemia
High blood sugar - ANSWER Hyperglycemia
What is a febrile seizure? - ANSWER A seizure brought on in infants and young children caused by high fever.
Most common signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis. - ANSWER Respiratory difficulties, low blood pressure
Most common sound when ausclutating someone with anaphylaxis. - ANSWER Wheezing
Highest risk of accidental poisoning - ANSWER Toddlers
Signs and symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning. - ANSWER flu-like symptoms, nausea, vomiting, altered LOC, headache, dizziness.
What does activated charcoal do? - ANSWER It is an adsorbent that binds poisons to its surface, thus reducing the amount that gets absorbed into the bloodstream. It should not be used with strong acids or alkalis, lithium or iron tablets. It does not work on all poisons, and has no effect on alcohol poisoning.
What effect does alcohol have on the CNS? - ANSWER It acts as a depressant.
What are barbiturates? - ANSWER They are downers that depress the CNS.
OxyContin, percocet, and lortab are examples of ____. - ANSWER Narcotics used for pain control
Best treatment that an EMT can give for inhaled poisons. - ANSWER High-flow oxygen
Effects of Delirium tremens. - ANSWER Occurs when someone has been using alcohol for some time, then stops using it suddenly. Signs and symptoms include altered LOC, hallucinations, unusual behavior, and seizure activity.
How to do CPR on an adult. - ANSWER 30 compressions
[Show More]