6 biod 101 module 6 problem set
$ 17.5

Complete Learning Companion for Google Data Analytics – Course 1
$ 12.5

Extra Credit HESI Module 2 2022-2023
$ 15

Certified Professional Coding Test 2022 COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
$ 10.5
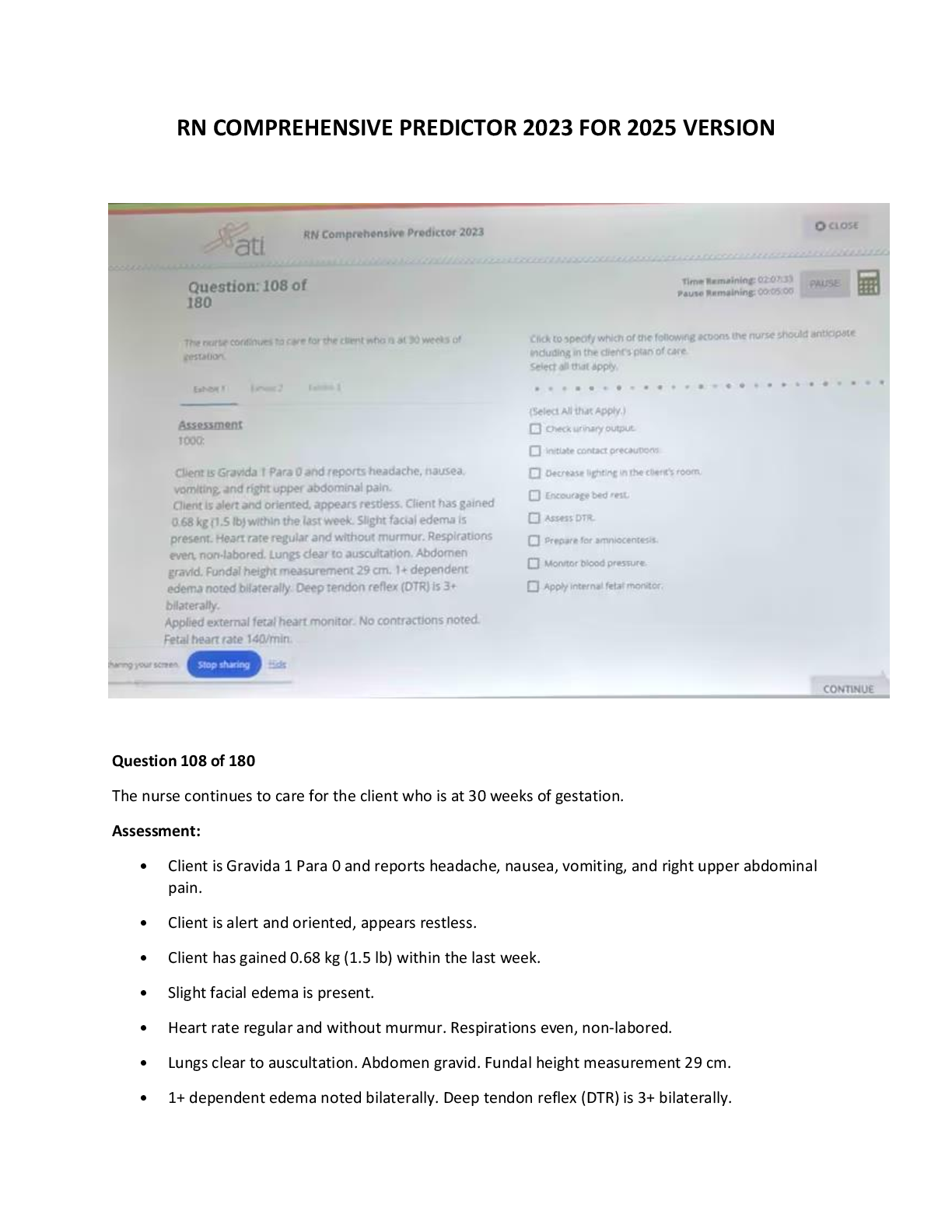
RN Comprehensive Predictor Retake Comprehensive Exam Study Guide
$ 20
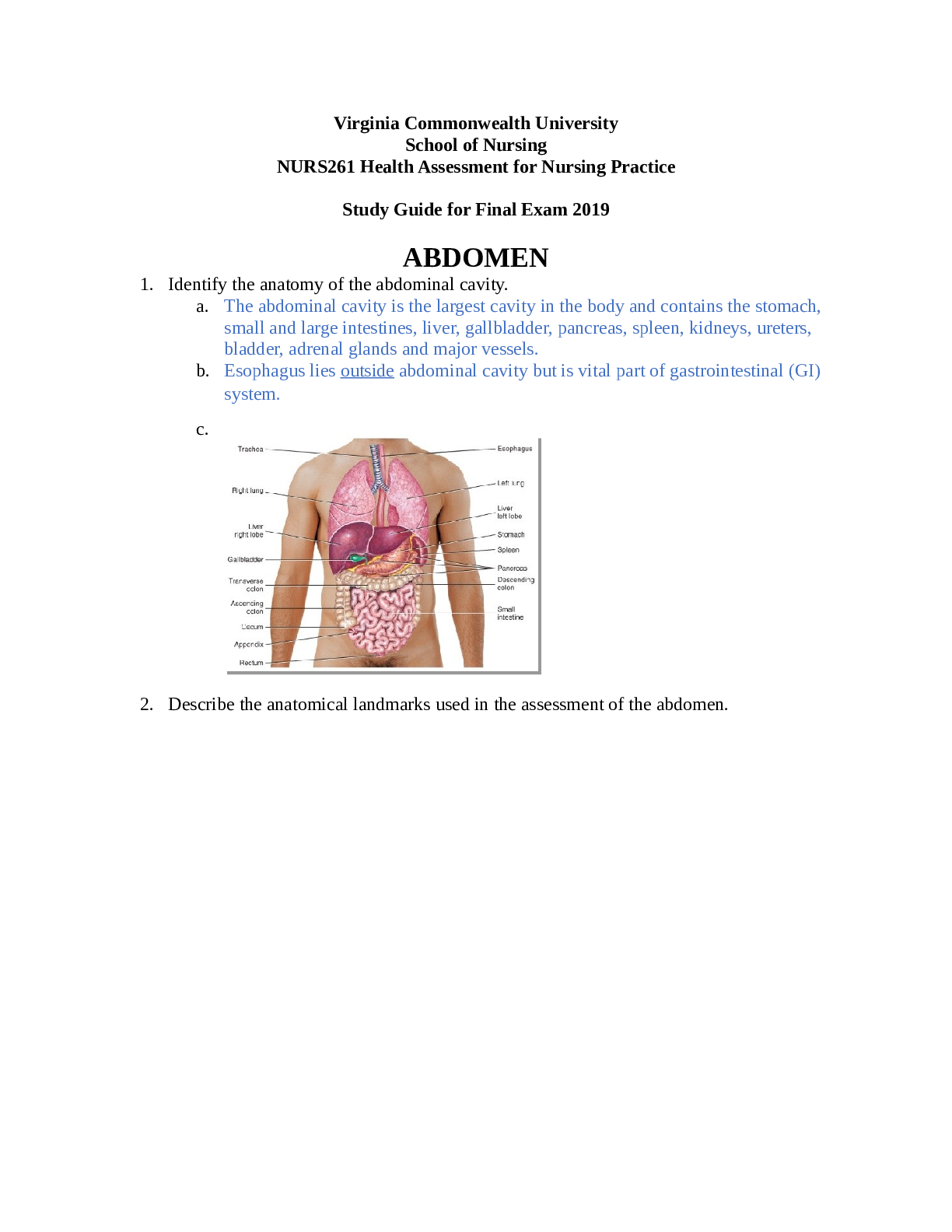
NURS 261 Final Exam Study Guide Spring 2019
$ 13

TEAS Nursing Entrance Exam Review Test Bank (answered) _Distinction Level Assignment Has everything.
$ 20

NR 602 Week 3 Immunization Case Study Assignment (GRADED A+)
$ 10
AQA GCSE CHINESE MANDARIN QUESTION PAPER 3 READING MAY 2023 FOUNDATION TIER
$ 2

(Combined) Module 6 Computer Concepts Exam, Computer Concepts Module 8, Computer Concept Module 9, Module 10 Computer Concepts Exam. With Complete Solution 2024
$ 15

Essential Elements of Public Speaking, 7th Edition, By Joseph A. DeVito (Solutions Manual )
$ 25

Solution Manual for Electronics and Communications for Scientists and Engineers 2nd Edition By Martin Plonus
$ 19

Explaining_Forensics.docx CJS/215: Introduc