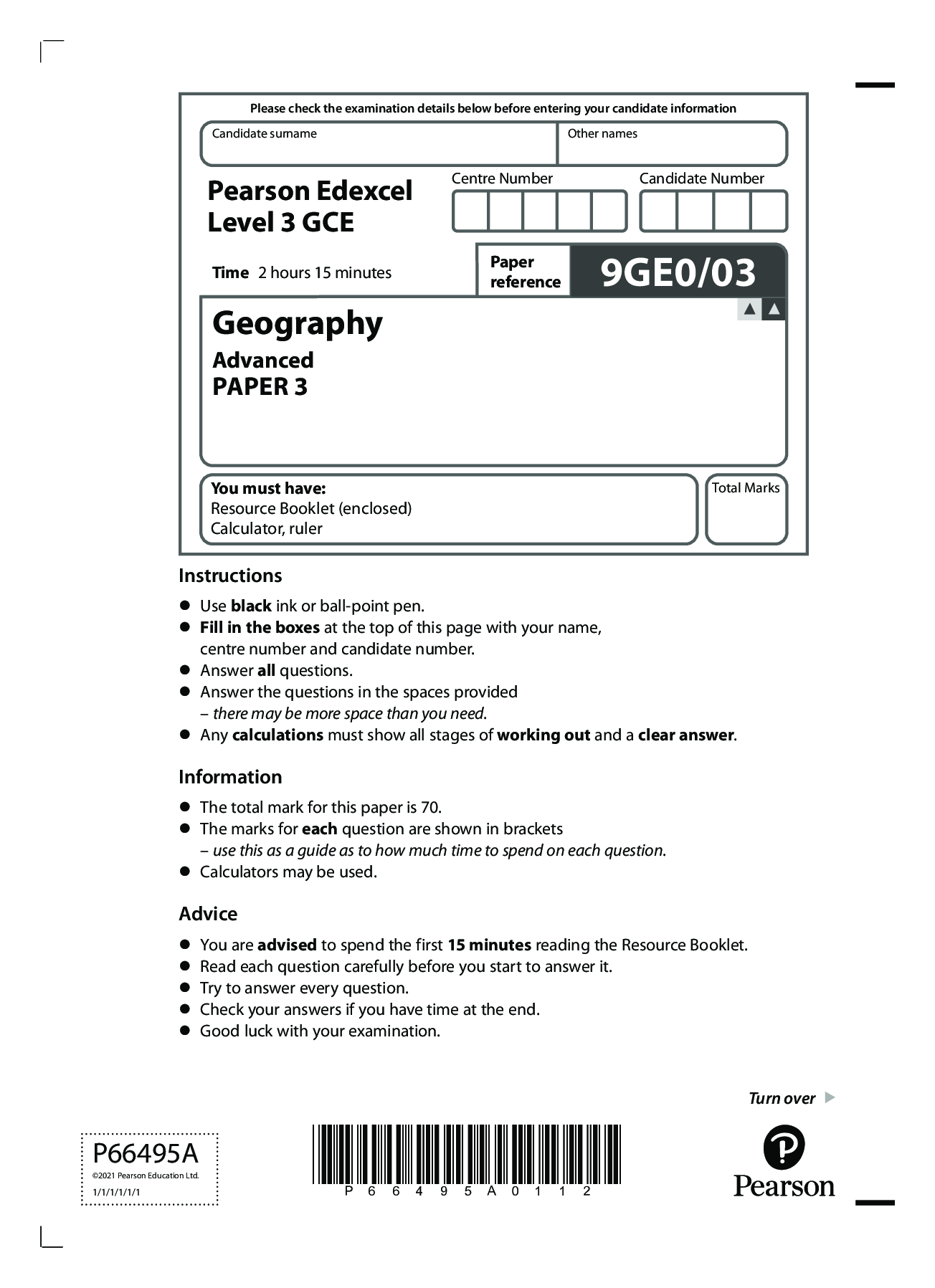
single line comment format - ANSWER --this is a single line comment
multi-line comment format - ANSWER /* this is
multi lines
comments
*/
capabilities of SQL select statements - ANSWER
--4.1 to select all th
...
single line comment format - ANSWER --this is a single line comment
multi-line comment format - ANSWER /* this is
multi lines
comments
*/
capabilities of SQL select statements - ANSWER
--4.1 to select all the columns/rows in a table use: - ANSWER SELECT *
FROM employees;
--4.2 to select specific columns - ANSWER SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID, DEPARTMENT_NAME
FROM DEPARTMENTs;
--4.3 using Arithmetic Expressions ( +,-,*,/) - ANSWER SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY
FROM
employees;
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, SALARY, sALARY+100, salary+(SALARY*0.10)
FROM
employees;
--4.4 to know null values - ANSWER --NULL IS A VALUE THAT IS UNAVAILABLE, UNASSIGNED, UNKNOWN, OR INAPPLICABLE.
---Null is not the same as zero or a blank space
SELECT last_name, job_id, salary, commission_pct
FROM EMPLOYEES;
--45 Arithmetic expressions containing a null value evaluate to null - ANSWER SELECT LAST_NAME, JOB_ID, SALARY, COMMISSION_PCT,COMMISSION_PCT+10
FROM EMPLOYEES;
--4.6 Defining a Column Alias ( Renames a column heading) - ANSWER SELECT LAST_NAME, LAST_NAME AS name, LAST_NAME lname, LAST_NAME " LAST nAME"
FROM EMPLOYEES;
--4.7 Concatenation Operator || Links columns or character strings
--Literal (A literal is a character, a number, or a date that is included in the SELECT statement) - ANSWER SELECT FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, FIRST_NAME || LAST_NAME "full name",
FIRST_NAME || ' ' || LAST_NAME "full name with space" --Using Literal Character Strings
from
EMPLOYEES;
SELECT FIRST_NAME||' work in department '|| DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM
EMPLOYEES;
SELECT FIRST_NAME||q'[ work in department]'|| DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM
EMPLOYEES;
SELECT FIRST_NAME||q'( work in department)'|| DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM
EMPLOYEES;
--4.8 using distinct - ANSWER SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES; -- this will pick all the DEPARTMENT_ID from table EMPLOYEES
SELECT DISTINCT DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES; -- only distinct values ????? ????????
--you can use many columns in distinct
SELECT DISTINCT DEPARTMENT_ID, JOB_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES
--4.9 DESCRIBE or DESC command - ANSWER --USE THE DESCRIBE COMMAND TO DISPLAY THE STRUCTURE OF A TABLE.
DESCRIBE EMPLOYEES;
DESC EMPLOYEES;
--5.1 to select all the rows and columns in table - ANSWER SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES;
--5.2 to Limiting the Rows That Are Selected, we use WHERE and it come always after the FROM clause - ANSWER --first look to the manual
SELECT *
FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID=90;
SELECT *
FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE salary=24000;
/* these you should know when using the where
Character strings and date values are enclosed with single quotation marks.
Character values are case-sensitive and date values are format-sensitive.
The default date display format is DD-MON-RR
*/
--5.3 using where in char column - ANSWER SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, last_name, JOB_ID
FROM
EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME='Steven';
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, FIRST_NAME, last_name, JOB_ID
FROM
EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME='steven'; -- the data is Case sensitive
--5.4 using where in date column - ANSWER SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE HIRE_DATE = '17-OCT-03' ;
--5.5 using the comparison operators - ANSWER SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE SALARY>=10000;
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE HIRE_DATE > '17-OCT-03' ;
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME>'Alberto';
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME>'Alberto'
order by FIRST_NAME;
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME<'Alberto'
order by FIRST_NAME;
--for more info refer to https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B12037_01/server.101/b10759/sql_elements002.htm
--5.6 using between and - ANSWER SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE SALARY BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; --always the lower limit first, then higher limit
--try to do the query by making the high limit first, no result
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE SALARY BETWEEN 20000 AND 10000;
--YOU CAN USE OPERATORS ALSO IN varchar COLUMNS
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME BETWEEN 'A' AND 'C'
order by FIRST_NAME;
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
order by FIRST_NAME
--5.7 using the in operator - ANSWER SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE SALARY IN (10000, 25000,17000);--the order is not important
--5.8 using the like operator - ANSWER /*8 using the like operator and it come usually with _ and %
% mean zero or more characters
_ mean one character
*/
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME LIKE 'S%'; --ALL THE FIRST NAME which sart with S
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME LIKE '%s'; --ALL THE FIRST NAME which end with s
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME LIKE '%am%'; --ALL THE FIRST NAME which include am
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME LIKE '_d%';-- the first_name which has d in second letter
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE FIRST_NAME LIKE '__s%';-- the first_name which has s in third letter
--now suppose there is value in any column co
[Show More]