The nurse has obtained a unit of blood from the blood bank and has checked the blood bag properly with another nurse. Just before beginning the transfusion, the nurse assesses which priority item?
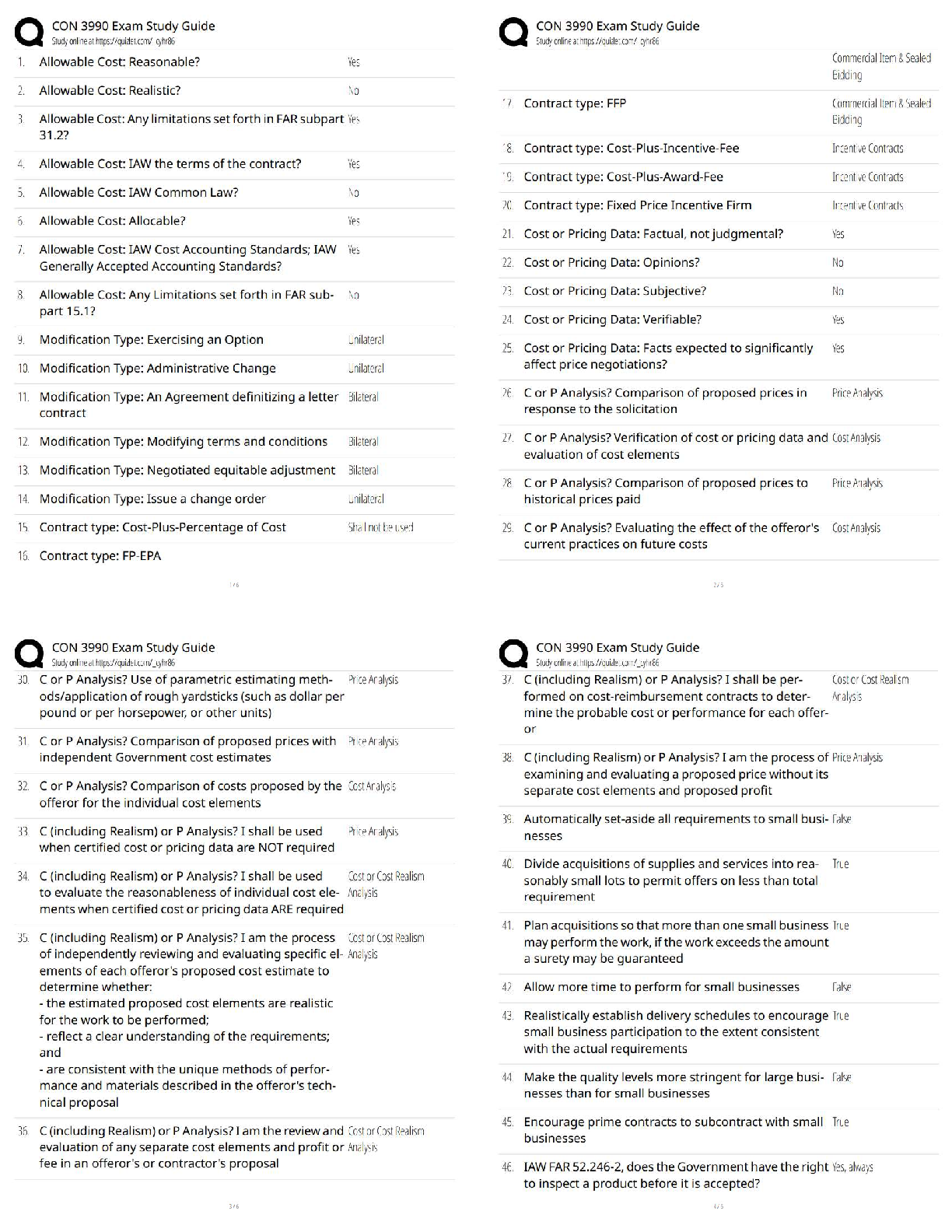
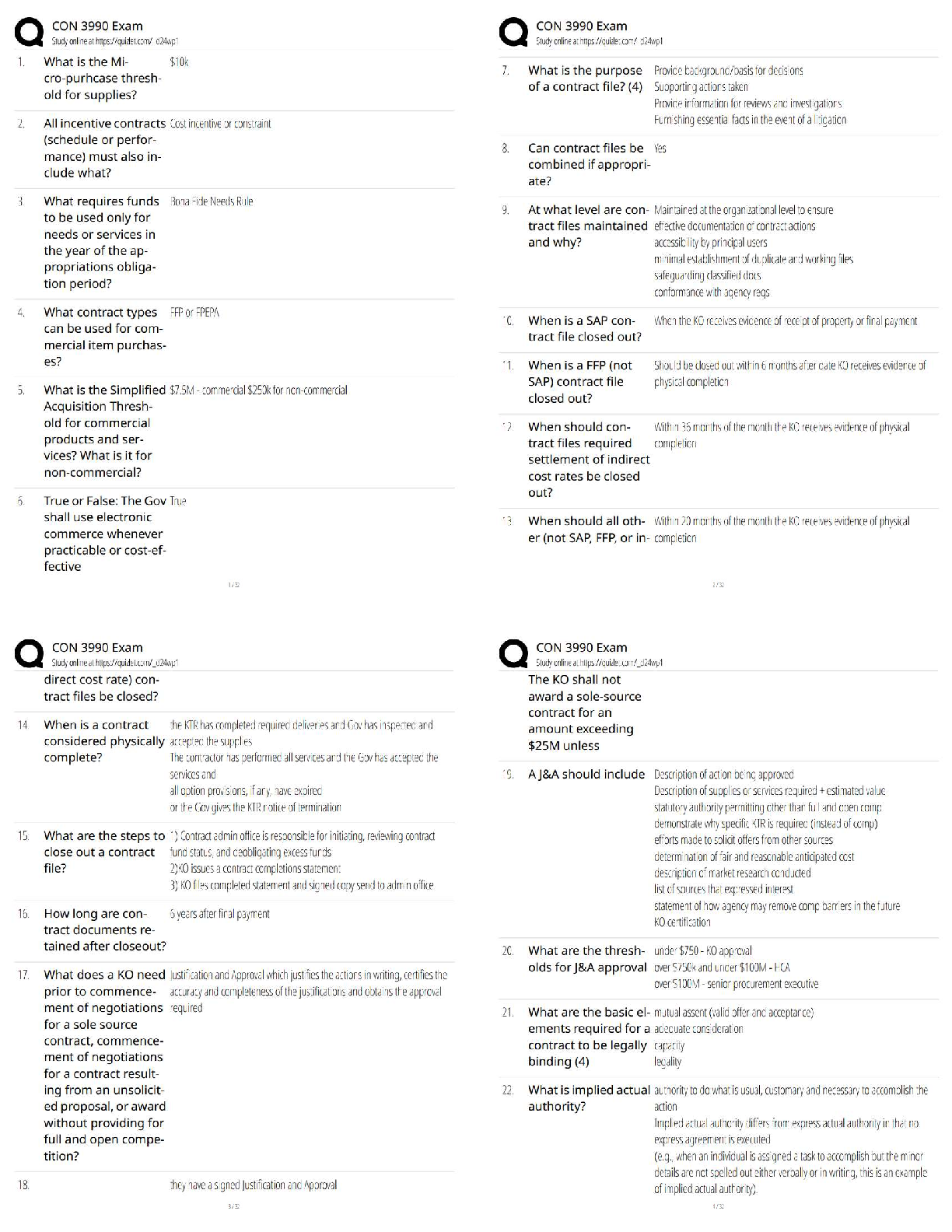
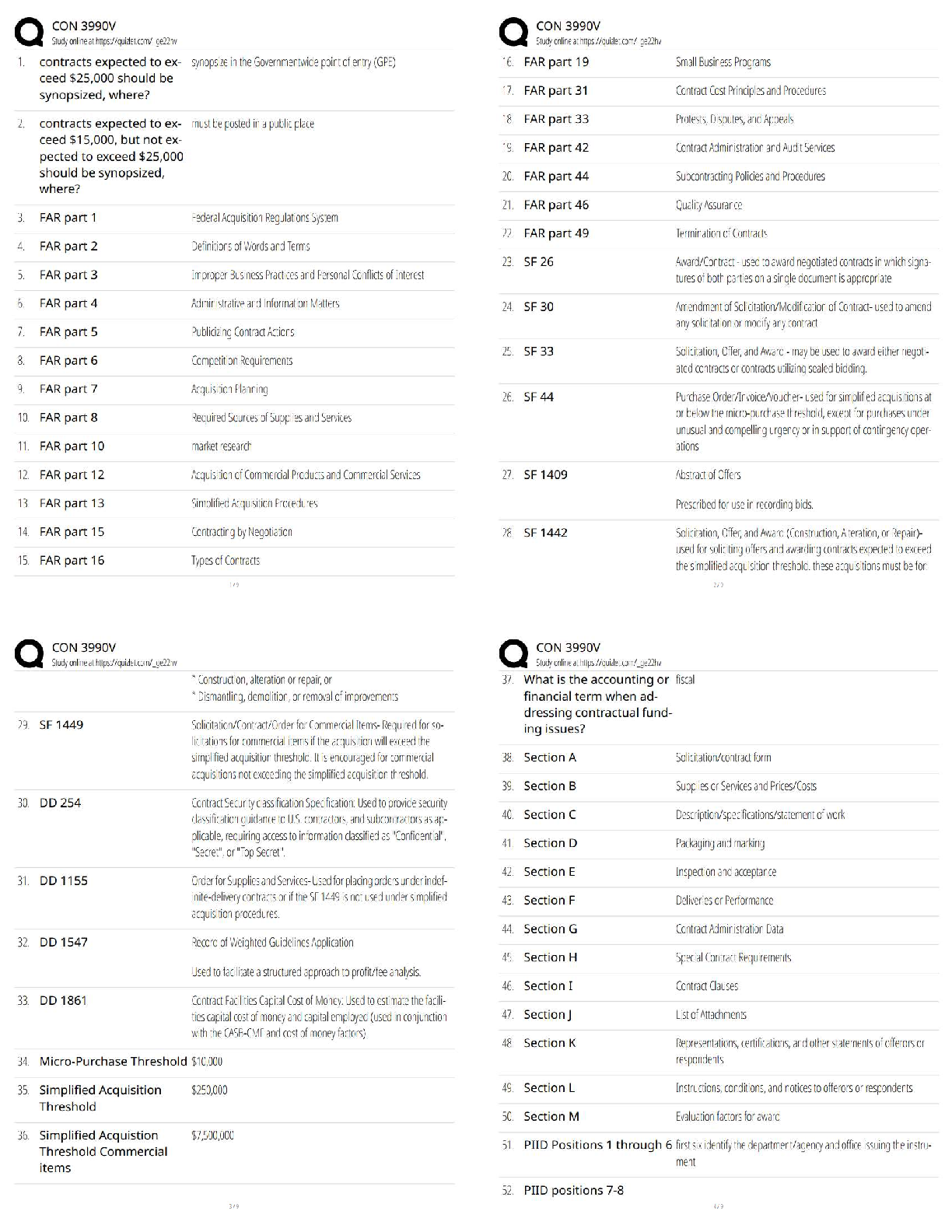
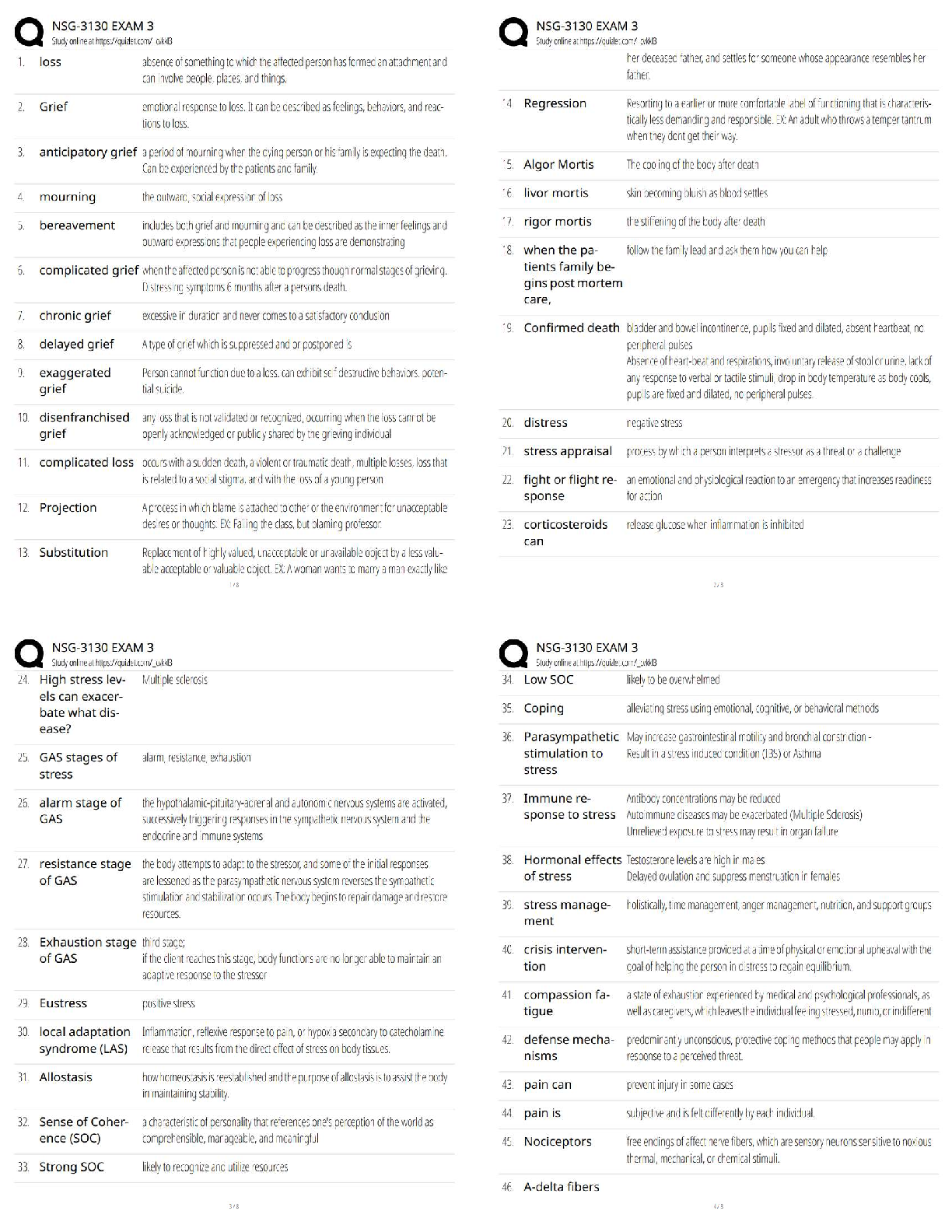
a. Vital signs
b. Ski
...
The nurse has obtained a unit of blood from the blood bank and has checked the blood bag properly with another nurse. Just before beginning the transfusion, the nurse assesses which priority item?
a. Vital signs
b. Skin color
c. Urine output
D. Latest hematocrit level - ANSWER A. vital signs
A change in VS during the transfusion from baseline may indicate that a transfusion reaction is occurring. This is why the nurse assesses vital signs before the procedure and again after the first 15 minutes.
The nurse has discontinued a unit of blood that was infusing into a client because the client experienced a transfusion reaction. After documenting the incident appropriately, the nurse sends the blood bag and tubing to which of the following departments?
a. Blood bank
b. Risk management
c. Environmental services
d. Infection control - ANSWER A. blood bank
The nurse returns the blood transfusion bag containing any remaining blood to the blood bank. This allows the blood bank to complete any follow-up testing procedures needed once a transfusion reaction has been documented. The other option identifies incorrect departments.
Packed red blood cells have been prescribed for a client with low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. The nurse takes the client's temperature before hanging the blood transfusion and records 100.6F orally. Which of the following is the appropriate nursing action?
a. Begin the transfusion as prescribed
b. Delay hanging the blood and notify the physician
c. Administer an antihistamine and begin the transfusion
d. Administer two tablets of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and begin the transfusion - ANSWER b. Delay hanging the blood and notify the physician
If the client's temperature is higher than 100F the unit of blood should not be hung until the physician is notified and has the opportunity to give further prescriptions. The physician will likely prescribe that the blood be administered regardless of the temperature, but the decision is not within the nurse's scope of practice to make.
A nurse is preparing medication for administration. In addition to the right medication, the nurse adheres to which of the following additional rights of medication administration. Select all that apply.
a. The right route
b. The right staff member
c. The right time
d. The right client
e. The right documentation
f. The right dose - ANSWER A, C, D, E, F
There are six rights to administering medications: The right medication, the right client, the right dose, the right route, the right time, and the right documentation.
A client is brought to the emergency department having experienced blood loss related to an arterial laceration. Fresh-frozen plasma is prescribed and transfused to replace fluid and blood loss. The nurse understands that the rationale for transfusing fresh-frozen plasma in this client is:
A. to treat the loss of platelets
B. to promote rapid volume expansion
C. That the transfusion must be done slowly
D. That it will increase the hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. - ANSWER B. to promote rapid volume expansion
Fresh-frozen plasma is often used for volume expansion as a result of fluid and blood loss. It does not contain platelets, so it is not used to treat any type of low platelet count disorder. It is rich in clotting factors and can be thawed quickly and transfused quickly. It will not specifically increase the hemoglobin and hematocrit level.
A client receiving a transfusion of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) begins to vomit. The client's blood pressure is 90/50 from a baseline of 125/78. The client's temperature is 100.8F orally from a baseline of 99.2F orally. The nurse determines that the client may be experiencing which complication of a blood transfusion?
a. Septicemia
b. Hyperkalemia
c. Circulatory overload
d. Delayed transfusion reaction - ANSWER A. Septicemia
Septicemia occurs with the transfusion of blood contaminated with microorganisms. Signs include chills, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, hypotension, and the development of shock. Hyperkalemia causes weakness, paresthesias, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and dysrythmias. Circulatory overload causes cough, dyspnea, chest pain, wheezing, tachycardia, and hypertension.
[Show More]