SLHS 603 Final Exam 2022 with complete solution
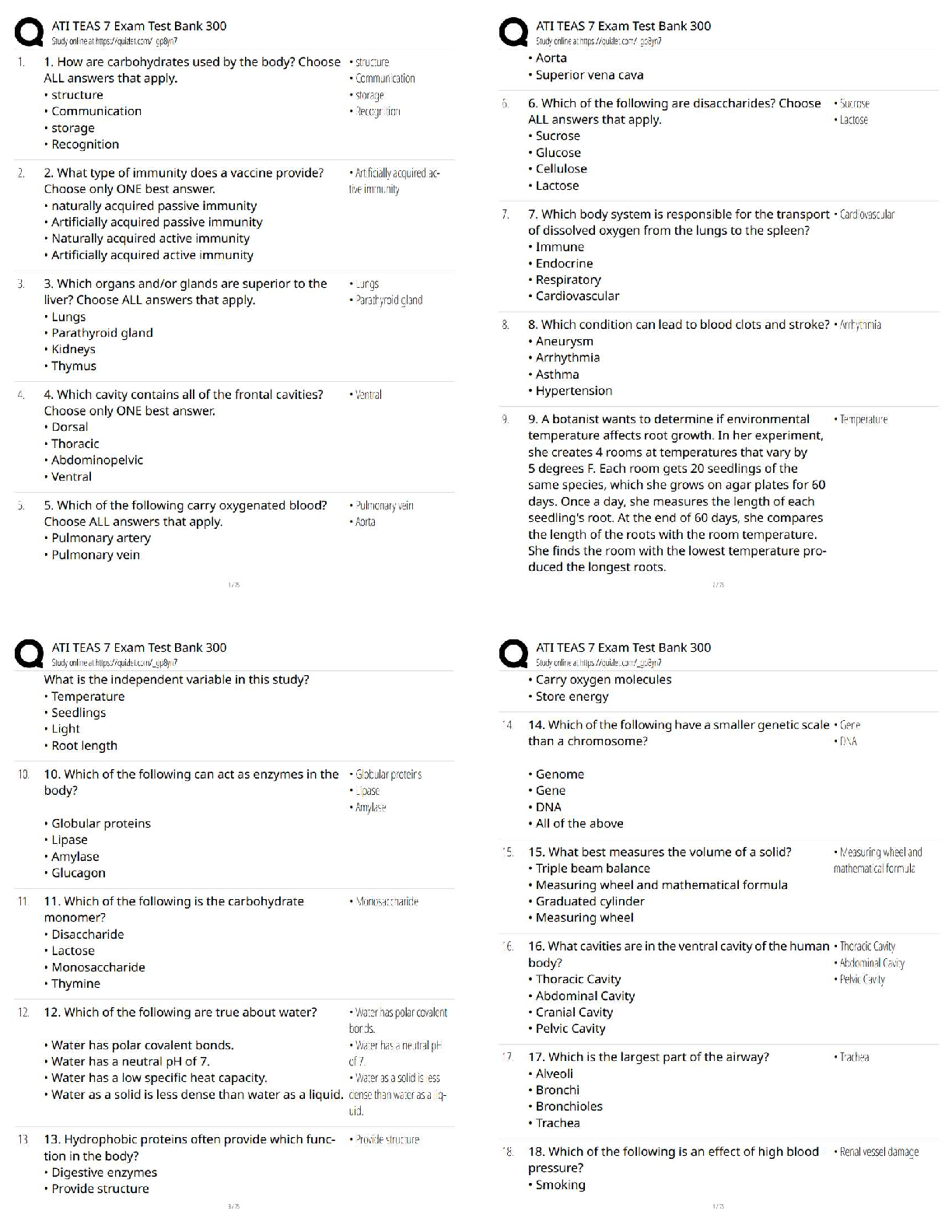
1. Understand the criteria to be a candidate for the contrast approaches (ex: vowel errors, distortion errors of several phonemes, or loss of phonemic contrasts, etc)
c
...
SLHS 603 Final Exam 2022 with complete solution
1. Understand the criteria to be a candidate for the contrast approaches (ex: vowel errors, distortion errors of several phonemes, or loss of phonemic contrasts, etc)
contrast/multiple oppositions approach -Answer- - candidate for multiple oppositions: deficits in both motor/articulation skills related to contrastive use of phonemes (so deficits in from/production and function of the sound system). -this approach targets several error sounds that are represented in a collapse of phonemes
-collapse of phonemes: several target sounds are represented by the same substitution error sound ex: /t/ for k, s, sh, ch
candidate for minimal oppositions:
-best suited for preschool age children with several substitution errors
candidate for maximal oppositions:
-one known speech sound vs one maximally opposing sound not known/produced by the child
empty set: two maximally opposing sounds unknown to the child.
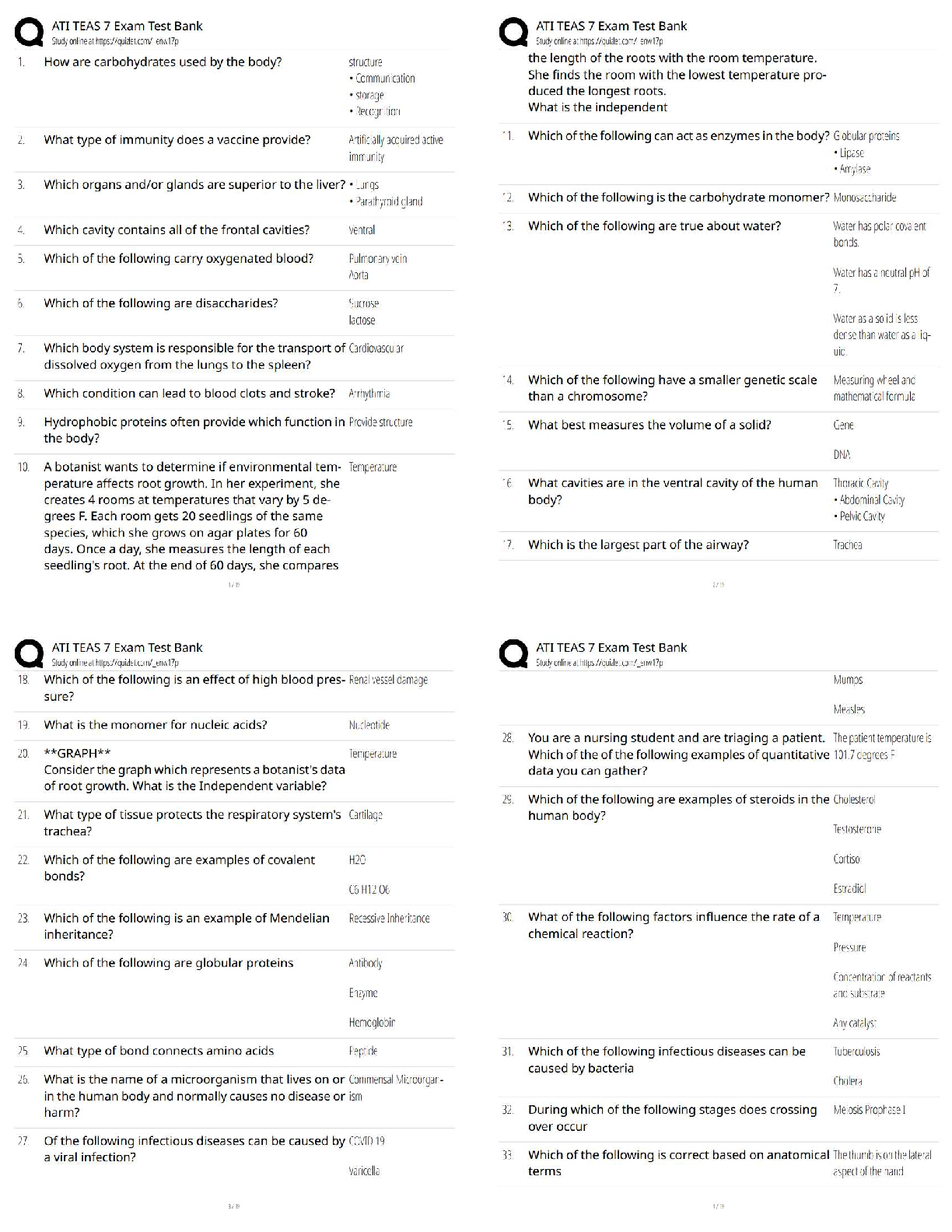
1. Understand how the contrast approaches utilize the concept of minimal pairs as the stimuli for intervention by highlighting the function of phonemes to create different meanings. -Answer- -contrastive therapy approach uses contrasting word pairs instead of individual sounds. This emphasizes sound contrasts needed to differentiate one word from the other.
-these approaches are: minimal oppositions contrast, max opposition contrast, empty set, multiple oppositions
1. Target selection for minimal oppositions intervention is based on what?? -Answer- -typically highlight the error and the substitution.
-consistent substitution errors, differ by one feature, additional consideration given to developmental norms, stimulability, and impact on intelligivlity,
-typically selects 3-5 word pairs for production practice
-minimal pairs that are minimally opposed (differ by one feature aka: place, manner, voicing).
-best suited for preschool age children with several subsititution errors
-child must be able to detect/hear the minimal differences in the word pairs
1. Be able to identify word pairs that are considered minimal oppositions and describe how they differ -Answer- -minimal pairs differ by one phoneme
-minimal oppositions differ by one distinctive feature: place, manner, or voicing. ex: two vs do; beak vs beat, pack vs tap; tan vs can; take vs cake.
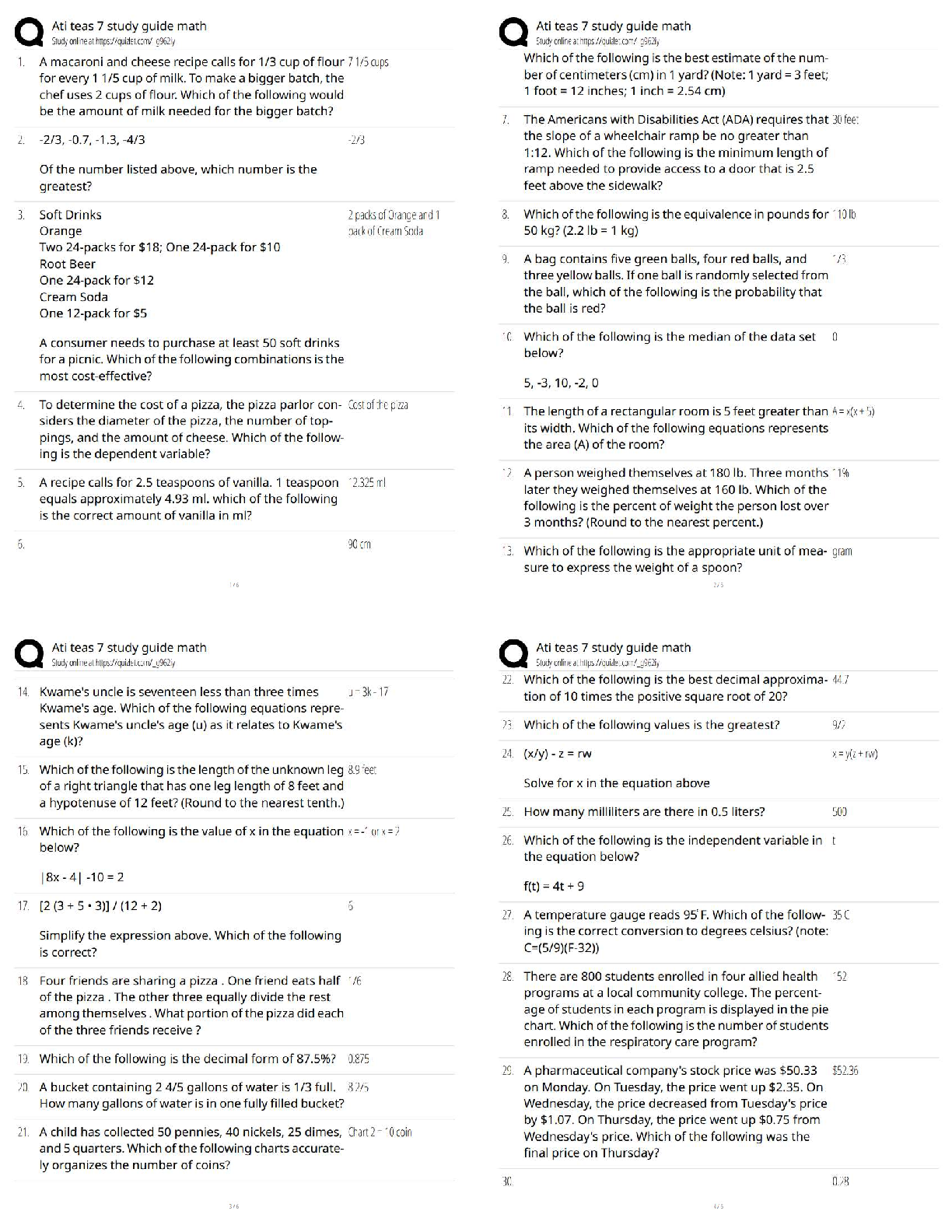
Target selection for maximal oppositions contrast approach is made on the basis of the amount of predicted change expected in the child's phonological system. This continuum is based on target selection across three parameters. Name the parameters -Answer- targets based on being maximally opposed.
-major class features: obstruent vs sonorant or even C vs V
-nonmajor class features: distinctive features (place, manner, and voicing)
-whether the sound is in the child's inventory or not
one sound that the child knows compared to a maximally opposing sound not known or produced by the child.
ex: /m/ vs /s/- obstruent vs sonorant and s is not in their inventory. maybe choose bc fricatives imply stops.
Describe the empty set in reference to a contrastive approach -Answer- similar to maximal opposition contrasts but uses pairs of words containing TWO max opposing sounds that are unknown to the child. ideally obstruent vs sonorant ex: /l/ vs /s/
-word pairs can be nonwords too for empty set
Both: familiarize child with novel words. then phase 1: imitation of contrasts (like drill play-card games). phase 2: spontaneous production
1. Which of the contrastive approaches is predicted to result in the least amount of change to the child's phonological system? -Answer- minimal oppositions -the child learns the least amount of new info
most change is two new phonemes with a major class difference -empty set
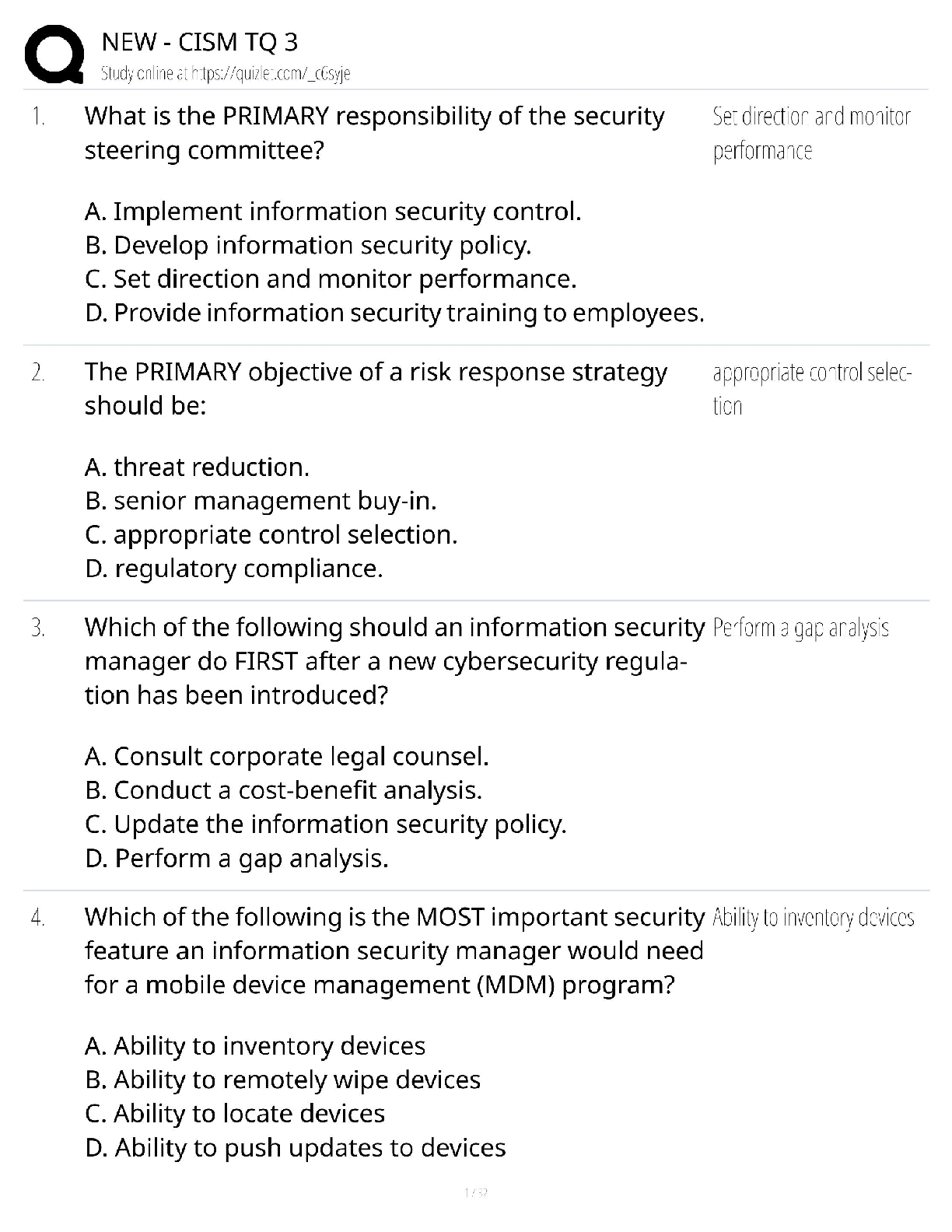
1. When given a case study with phonemes missing from the inventory or a collapse of contrasts, be ready to identify pairs of phonemes that would be considered maximal contrasts representing an empty set or multiple oppositions. -Answer-
1. Name the 4 phases of the multiple oppositions contrast approach in the appropriate sequence. -Answer- Phase 1: familiarization and production of targets
-child learns aobut target sounds (snake sound). child learns the vocab (pictures, sentences). production of the contrasts in imitation of the clinician (placement cues, metaphors).
Phase 2: production of contrasts during interactive play
-imitate clinician's production of contrasts. target the words into play (farm, house, picnic).
Phase 3: contrasts used in communicative contexts
-target words arranged in concentration style game or matching card game
phase 4: conversational recasts
-clinician presents conversational recasts to allow child to self-correct errors. so you ask them to retell the story that has the words they need to say like (go, doe, row).
-Answer- target selection for multiple oppositions approach:
-targets are selected from the phoneme collapse. select phonemes from different sound classes to promote within and across class generalization. develop multiple treatment sets for the set of phonemes
ex: /b/ for /d m s sh/. one set would be boo, do moo sue shoe. the other set could be bee. dee me. see. she
1. Know the type of client that would benefit from the Core vocabulary approach. -Answer- -used with children with inconsistent speech sound production who may be resistant to more traditional therapy approaches.
ex: child might pronounce duck as du, gu, dut.
-these inconsistent errors may be due to impaired assembly of the phonological plan, the sequence of phonemes needed for speech output
-this inability to plan the sequence of phonemes in the absence of oral-motor symptoms of childhood apraxia of speech
1. What is the goal of the Core Vocabulary approach? -Answer- -focuses on whole-word production
-goal: to generate a phonological sequence that results in consistent productions. make the words more consistent; not perfect.
-Goal: to teach the child how to generate a consistent phonological sequence for words during spontaneous speech. Therefore consistency and not accuracy is the long term goal p.228
1. Be familiar with the differences between horizontal, vertical and cyclical intervention approaches. -Answer- vertical: intense practice on one or two targets until the child reaches a specific criterior levle (usually conversational level) before proceeding to the next target or targets (really intense 1-2 targets)
[Show More]