*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIOL 235 Midterm Exam 2 With Complete Solution(100% Verified) 185 Questions with 100% Correct Answer (All)
BIOL 235 Midterm Exam 2 With Complete Solution(100% Verified) 185 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
Document Content and Description Below
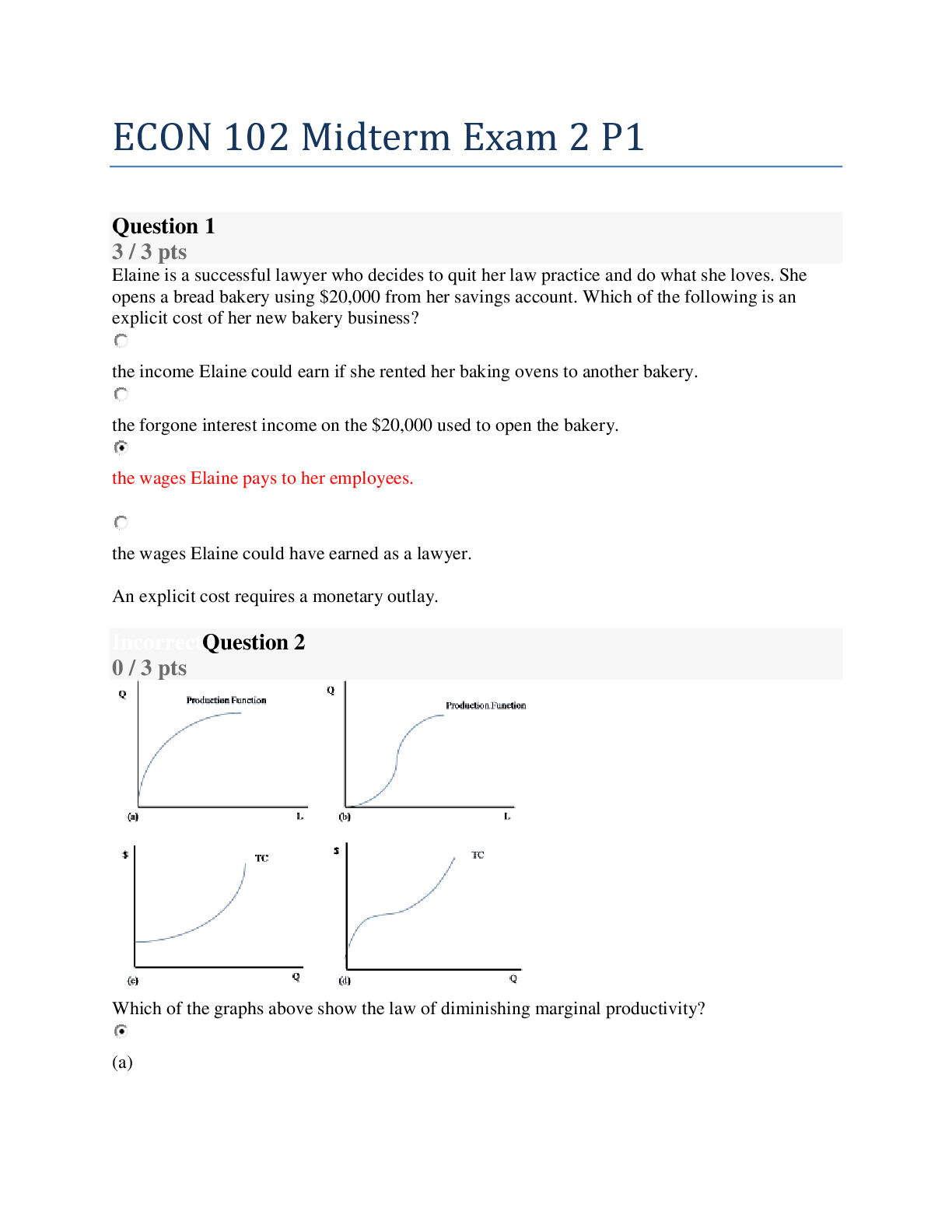
BIOL 235 Midterm Exam 2 With Complete Solution(100% Verified) 185 Questions with 100% Correct Answers 1. between the origin and insertion which is usually located proximally in limbs ? - ✔✔Origi... n 2. What happens during REVERSE MUSCLE ACTION? - ✔✔specific movements of the body the actions are reversed THEREFOR the positions of the origin and insertion of a muscle are switched 3. What is a mechanical advantage using the example of a lever? - ✔✔if the load is closer to the fulcrum and the effort is farther from the fulcrum only a small about of effort is needed to move the load 4. Bones serve as levers and joints serve as ________ for the lever - ✔✔fulcrum 5. Agonist (Prime Movers) _________ muscles while antagonist ____________ muscles - ✔✔contract, relax 6. What are muscles that contract and stabilize the intermediate joints called? - ✔✔synergists 7. What is a group of skeletal muscles, their blood vessels, and nerves called? - ✔✔Compartment 8. Origin an insertion of the masseter - ✔✔Origin = maxilla and zygomatic arch Insertion = angle and ramus of the mandible 9. What is the origin of the deltoid ? - ✔✔acromial extremity of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula 10. What are the 3 muscles that make up the hamstring ? - ✔✔semimebranosous, semitendinosus, biceps femoris11. What 4 muscles make up the Quads ? - ✔✔rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedialis 12. What do you call a small mass of nervous tissue that is made up primarily of neuron cell bodies? - ✔✔Ganglia 13. The somatic nervous system only sends impulses to ________ muscles - ✔✔skeletal 14. Fight or Flight is associated with which division of the autonomic nervous system? - ✔✔Sympathetic 15. What is the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into an action potential? - ✔✔electrical excitability 16. What type of neurons usually have several dendrite and on axon , and are norm ally found in brain and spinal cord as well as motor neurons? - ✔✔Multipolar 17. What type of neurons have one main dendrite and one axon as well as are primarily found in the retina of the eye, inner ear, and the olfactory area of brain? - ✔✔Bipolar 18. What type of neurons has dendrites and one axon that are fused together to form a continuous process that emerges from the cell body? - ✔✔Unipolar or Pseudounipolar 19. The processes of ________ make contact with blood capillaries, neurons, and the pia mater - ✔✔astrocytes 20. What neuroglia has these functions? 1. contain microfilaments that give them strength and allow them to support neurons 2. contributes to the effectiveness of BBB 3.in embyro, they secret chemicals that regulate things3. help maintain an appropriate chemical environment for nerve impulse generation 4. play a role in hearing and memory - ✔✔Astrocytes 21. What neuroglia resemble astrocytes but are smaller and contain fewer processes as well as are responsible fro forming nd maintiang myelin sheath? - ✔✔Oligodendrocytes 22. What neuroglia are small cells with slender processes that give them a spine like projections as well as act as phagocytes? - ✔✔Microglial Cells 23. What type of neurglia cells are cuboidal and columanr arranged in a single layer that possess microvilli and cilia? they produce and possibly monitor and assist in the circulation of CSF - ✔✔Ependymal Cells 24. What are the 2 types of neuroglia in the PNS? - ✔✔Schwann and satellite cells 25. What type of motor neuron directly supplies skeletal muscle fibers? - ✔✔lower motor neurons 26. What do all of these factors contribute to? 1. unequal distribution of ions in the ECF and cytosol 2. inability of most anions to leave the cells 3. electrogenic nature of the sodium potassium ATPases - ✔✔Resting membrane potential 27. Hyperpolarized cells are _______ negative inside ? - ✔✔More 28. What mode of travel by which graded potentials die out as they spread along the membrane ? - ✔✔decremental conduction 29. What kind of ion channels are found in nearly all cells, including dendrites, cell bodies, and axons of all types of neurons? - ✔✔Leak channels30. What kind of ion channel can be found in pain receptors? - ✔✔mechanically-gated channels 31. What refractory period causes voltage gated sodium channel activation gates are open as well as the voltage gated potassium channels are opening and then sodium channels are inactivating? - ✔✔absolute refractory period 32. Sodium channels are ______ and potassium channels are ________ during the relative refractory period ? - ✔✔closed, open 33. What do we classify based on amount of myelination, diameters, and propagation speeds? - ✔✔Nerve fibers 34. What is the largest nerve fiber? - ✔✔A fibers 35. What do you call a synapse that goes from an axon to cell body? - ✔✔axosomatic 36. What do you call a synapse between 2 axons? - ✔✔axoaxonic 37. Synchronization and faster communications are advantages of what? - ✔✔electrical synapses 38. Voltage gated channels are located on which synaptic neuron? - ✔✔the presynaptic neuron 39. An ISPS is a __________________potential - ✔✔hyperpoalrizing 40. What kind of receptor contain a NT binding site and an ion channel from the same protein? - ✔✔Ionotropic receptor 41. What are the 2 types of neurotransmitters? - ✔✔small-molecule NT & neuropeptide42. after an injury to a process of a normal peripheral neuron the nissel bodies break down into fine granular masses, what is this called? - ✔✔chromatolysis 43. The _____________________ is the space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal - ✔✔epidural space 44. What are the sub layers of the meninges? - ✔✔subdural space and subarachnoid space 45. What part of the spinal cord contains somatic motor nuclei which provide nerve impulses for contraction of skeletal muscles? - ✔✔the anterior (ventral) gray horns 46. Which gray horns contain autonomic motor nuclei which regulate activity of cardiac and smooth muscle as well as glands? - ✔✔the lateral gray horns 47. Dermatomes are areas of skin that provide sensory input to the CNS via the posterior roots of one pair of spinal nerves via the __________ nerve. - ✔✔trigeminal (V) 48. direct motor pathways cause _________ movements - ✔✔voluntary 49. What are the 5 parts of a reflex arc? - ✔✔1. sensory receptor 2. sensory neruon 4. integrating center 5. motor neuron 6. effector 50. What do you call an arrangement where sensiry nerve impulses enter the spinal cord on the same side from which the motor nerve impulses leave it? - ✔✔Ipsilateral reflex 51. What reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation - ✔✔tendon reflex52. What are these the functions of ? 1. mechanical protection 2. homeostatic function 3. circulation - ✔✔Cerebrospinal fluid 53. What do the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and the reticular formation make up? - ✔✔The brain stem 54. What carries out these functions? -control of the ANS -production of hormones -regulation of emotion and behavioral patterns and eating and drinking - control of body temp -regulation of circadian rhythms and states of consciousness - ✔✔the dicephalon which consists of the thalamus and the hypothalamus 55. the pineal gland is part of the ___________ system - ✔✔endocrine 56. What are the roles of the epithalamus? - ✔✔-secrets melatonin via the pineal gland -regulates blood pressure, fluid balance, hunger, and thirst 57. _________ are folds that occur due to the gray matter of the cortex enlarging much faster than the deeper white matter - ✔✔Gyri 58. What kind of tract contains axons that conduct nerve impulses between gyris in the same hemisphere? - ✔✔association tracts 59. what kind of tract contains axons that conduct nerve impulses from gyri in one cerebral hemisphere to corresponding gyri in other cerebral hemispheres? example = corpus callosum - ✔✔commissural tracts60. what is the name of the distorted map of the body located in the primary somatosensory area? - ✔✔the sensory homunculus 61. Where is the Broca`s speech area located? - ✔✔the frontal lobe close to the lateral cerebral sulcus 62. What brain waves when found in an awake adult represent brain damage? - ✔✔delta waves 63. What brain waves disappear during sleep? - ✔✔alpha waves 64. What waves normally occur in people experiencing with emotional stress or disorders? - ✔✔theta waves 65. How many cranial special sensory nerves are there? - ✔✔3 66. how many cranial motor nerves are there? - ✔✔5 67. How many cranial mixed nerves are there? - ✔✔4 68. These nerves carry axons of sensory neurons and are unique to the head with a cell body located in ganglia outside the brain - ✔✔special sensory nerves 69. ______________ is the conscious or subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environement - ✔✔sensation 70. These sensory receptors are bare dendrites that lack any structural specialization. Ex: receptors for pain, temp, itch, tickle - ✔✔Free nerve endings 71. What kind of receptors are associated with visceral sensation such as pressure and vibration? - ✔✔encapsulated nerve ending72. the sensation of hearing, visions, smell, taste, touch, pressure, vibration, temperature and pain are all conveyed by ______________ - ✔✔exteroceptors 73. Where are interoceptors found? - ✔✔in blood vessels, visceral organs, muscles, and the nervous system 74. What are the proprioceptors in skeletal muscles that are responsible for monitoring changes in the length of the muscles in stretch reflexes? - ✔✔muscle spindles 75. These are located at the junction of a tendon and a muscle - ✔✔tendon organs 76. These neurons conduct impulses from somatic receptors into the brain or spinal cord - ✔✔Firstorder neruons 77. These neurons conduct impulses from the brain stem and spinal cord to the thalamus - ✔✔second-order neurons 78. These neurons conduct impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side - ✔✔third-order neurons 79. Nerve impulses for touch, pressure, vibration, and conscious proprioception from the limbs, trunk, neck,, and posterior head ascend to the cerebral cortex along the __________________________ pathway - ✔✔posterior column-medial lemniscus 80. Nerve impulses fro pain, temperature, itch, and tickles ascend to the cerebral cortex along the ________________________ pathway - ✔✔anterolateral 81. Nerve impulses for most somatic sensation from the face, nasal cavity, oral cavity etc, ascend tot he cerebral cortex along the ______________________ pathway - ✔✔trigeminothalami 1. between the origin and insertion which is usually located proximally in limbs ? - ✔✔Origin 2. What happens during REVERSE MUSCLE ACTION? - ✔✔specific movements of the body the actions are reversed THEREFOR the positions of the origin and insertion of a muscle are switched 3. What is a mechanical advantage using the example of a lever? - ✔✔if the load is closer to the fulcrum and the effort is farther from the fulcrum only a small about of effort is needed to move the load 4. Bones serve as levers and joints serve as ________ for the lever - ✔✔fulcrum 5. Agonist (Prime Movers) _________ muscles while antagonist ____________ muscles - ✔✔contract, relax 6. What are muscles that contract and stabilize the intermediate joints called? - ✔✔synergists 7. What is a group of skeletal muscles, their blood vessels, and nerves called? - ✔✔Compartment 8. Origin an insertion of the masseter - ✔✔Origin = maxilla and zygomatic arch Insertion = angle and ramus of the mandible 9. What is the origin of the deltoid ? - ✔✔acromial extremity of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula 10. What are the 3 muscles that make up the hamstring ? - ✔✔semimebranosous, semitendinosus, biceps femoris11. What 4 muscles make up the Quads ? - ✔✔rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedialis 12. What do you call a small mass of nervous tissue that is made up primarily of neuron cell bodies? - ✔✔Ganglia 13. The somatic nervous system only sends impulses to ________ muscles - ✔✔skeletal 14. Fight or Flight is associated with which division of the autonomic nervous system? - ✔✔Sympathetic 15. What is the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into an action potential? - ✔✔electrical excitability 16. What type of neurons usually have several dendrite and on axon , and are norm ally found in brain and spinal cord as well as motor neurons? - ✔✔Multipolar 17. What type of neurons have one main dendrite and one axon as well as are primarily found in the retina of the eye, inner ear, and the olfactory area of brain? - ✔✔Bipolar 18. What type of neurons has dendrites and one axon that are fused together to form a continuous process that emerges from the cell body? - ✔✔Unipolar or Pseudounipolar 19. The processes of ________ make contact with blood capillaries, neurons, and the pia mater - ✔✔astrocytes 20. What neuroglia has these functions? 1. contain microfilaments that give them strength and allow them to support neurons 2. contributes to the effectiveness of BBB 3.in embyro, they secret chemicals that regulate things3. help maintain an appropriate chemical environment for nerve impulse generation 4. play a role in hearing and memory - ✔✔Astrocytes 21. What neuroglia resemble astrocytes but are smaller and contain fewer processes as well as are responsible fro forming nd maintiang myelin sheath? - ✔✔Oligodendrocytes 22. What neuroglia are small cells with slender processes that give them a spine like projections as well as act as phagocytes? - ✔✔Microglial Cells 23. What type of neurglia cells are cuboidal and columanr arranged in a single layer that possess microvilli and cilia? they produce and possibly monitor and assist in the circulation of CSF - ✔✔Ependymal Cells 24. What are the 2 types of neuroglia in the PNS? - ✔✔Schwann and satellite cells 25. What type of motor neuron directly supplies skeletal muscle fibers? - ✔✔lower motor neurons 26. What do all of these factors contribute to? 1. unequal distribution of ions in the ECF and cytosol 2. inability of most anions to leave the cells 3. electrogenic nature of the sodium potassium ATPases - ✔✔Resting membrane potential 27. Hyperpolarized cells are _______ negative inside ? - ✔✔More 28. What mode of travel by which graded potentials die out as they spread along the membrane ? - ✔✔decremental conduction 29. What kind of ion channels are found in nearly all cells, including dendrites, cell bodies, and axons of all types of neurons? - ✔✔Leak channels30. What kind of ion channel can be found in pain receptors? - ✔✔mechanically-gated channels 31. What refractory period causes voltage gated sodium channel activation gates are open as well as the voltage gated potassium channels are opening and then sodium channels are inactivating? - ✔✔absolute refractory period 32. Sodium channels are ______ and potassium channels are ________ during the relative refractory period ? - ✔✔closed, open 33. What do we classify based on amount of myelination, diameters, and propagation speeds? - ✔✔Nerve fibers 34. What is the largest nerve fiber? - ✔✔A fibers 35. What do you call a synapse that goes from an axon to cell body? - ✔✔axosomatic 36. What do you call a synapse between 2 axons? - ✔✔axoaxonic 37. Synchronization and faster communications are advantages of what? - ✔✔electrical synapses 38. Voltage gated channels are located on which synaptic neuron? - ✔✔the presynaptic neuron 39. An ISPS is a __________________potential - ✔✔hyperpoalrizing 40. What kind of receptor contain a NT binding site and an ion channel from the same protein? - ✔✔Ionotropic receptor 41. What are the 2 types of neurotransmitters? - ✔✔small-molecule NT & neuropeptide42. after an injury to a process of a normal peripheral neuron the nissel bodies break down into fine granular masses, what is this called? - ✔✔chromatolysis 43. The _____________________ is the space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal - ✔✔epidural space 44. What are the sub layers of the meninges? - ✔✔subdural space and subarachnoid space 45. What part of the spinal cord contains somatic motor nuclei which provide nerve impulses for contraction of skeletal muscles? - ✔✔the anterior (ventral) gray horns 46. Which gray horns contain autonomic motor nuclei which regulate activity of cardiac and smooth muscle as well as glands? - ✔✔the lateral gray horns 47. Dermatomes are areas of skin that provide sensory input to the CNS via the posterior roots of one pair of spinal nerves via the __________ nerve. - ✔✔trigeminal (V) 48. direct motor pathways cause _________ movements - ✔✔voluntary 49. What are the 5 parts of a reflex arc? - ✔✔1. sensory receptor 2. sensory neruon 4. integrating center 5. motor neuron 6. effector 50. What do you call an arrangement where sensiry nerve impulses enter the spinal cord on the same side from which the motor nerve impulses leave it? - ✔✔Ipsilateral reflex 51. What reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation - ✔✔tendon reflex52. What are these the functions of ? 1. mechanical protection 2. homeostatic function 3. circulation - ✔✔Cerebrospinal fluid 53. What do the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and the reticular formation make up? - ✔✔The brain stem 54. What carries out these functions? -control of the ANS -production of hormones -regulation of emotion and behavioral patterns and eating and drinking - control of body temp -regulation of circadian rhythms and states of consciousness - ✔✔the dicephalon which consists of the thalamus and the hypothalamus 55. the pineal gland is part of the ___________ system - ✔✔endocrine 56. What are the roles of the epithalamus? - ✔✔-secrets melatonin via the pineal gland -regulates blood pressure, fluid balance, hunger, and thirst 57. _________ are folds that occur due to the gray matter of the cortex enlarging much faster than the deeper white matter - ✔✔Gyri 58. What kind of tract contains axons that conduct nerve impulses between gyris in the same hemisphere? - ✔✔association tracts 59. what kind of tract contains axons that conduct nerve impulses from gyri in one cerebral hemisphere to corresponding gyri in other cerebral hemispheres? example = corpus callosum - ✔✔commissural tracts60. what is the name of the distorted map of the body located in the primary somatosensory area? - ✔✔the sensory homunculus 61. Where is the Broca`s speech area located? - ✔✔the frontal lobe close to the lateral cerebral sulcus 62. What brain waves when found in an awake adult represent brain damage? - ✔✔delta waves 63. What brain waves disappear during sleep? - ✔✔alpha waves 64. What waves normally occur in people experiencing with emotional stress or disorders? - ✔✔theta waves 65. How many cranial special sensory nerves are there? - ✔✔3 66. how many cranial motor nerves are there? - ✔✔5 67. How many cranial mixed nerves are there? - ✔✔4 68. These nerves carry axons of sensory neurons and are unique to the head with a cell body located in ganglia outside the brain - ✔✔special sensory nerves 69. ______________ is the conscious or subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environement - ✔✔sensation 70. These sensory receptors are bare dendrites that lack any structural specialization. Ex: receptors for pain, temp, itch, tickle - ✔✔Free nerve endings 71. What kind of receptors are associated with visceral sensation such as pressure and vibration? - ✔✔encapsulated nerve ending72. the sensation of hearing, visions, smell, taste, touch, pressure, vibration, temperature and pain are all conveyed by ______________ - ✔✔exteroceptors 73. Where are interoceptors found? - ✔✔in blood vessels, visceral organs, muscles, and the nervous system 74. What are the proprioceptors in skeletal muscles that are responsible for monitoring changes in the length of the muscles in stretch reflexes? - ✔✔muscle spindles 75. These are located at the junction of a tendon and a muscle - ✔✔tendon organs 76. These neurons conduct impulses from somatic receptors into the brain or spinal cord - ✔✔Firstorder neruons 77. These neurons conduct impulses from the brain stem and spinal cord to the thalamus - ✔✔second-order neurons 78. These neurons conduct impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side - ✔✔third-order neurons 79. Nerve impulses for touch, pressure, vibration, and conscious proprioception from the limbs, trunk, neck,, and posterior head ascend to the cerebral cortex along the __________________________ pathway - ✔✔posterior column-medial lemniscus 80. Nerve impulses fro pain, temperature, itch, and tickles ascend to the cerebral cortex along the ________________________ pathway - ✔✔anterolateral 81. Nerve impulses for most somatic sensation from the face, nasal cavity, oral cavity etc, ascend tot he cerebral cortex along the ______________________ pathway - ✔✔trigeminothalami [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 14, 2022
Number of pages
20
Written in
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 14, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
163















.png)


.png)

.png)

.png)

