Critical Thinking > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > 09 - WGU - C168 - Critical Thinking - Module 1, 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 Already Passed (All)
09 - WGU - C168 - Critical Thinking - Module 1, 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 Already Passed
Document Content and Description Below
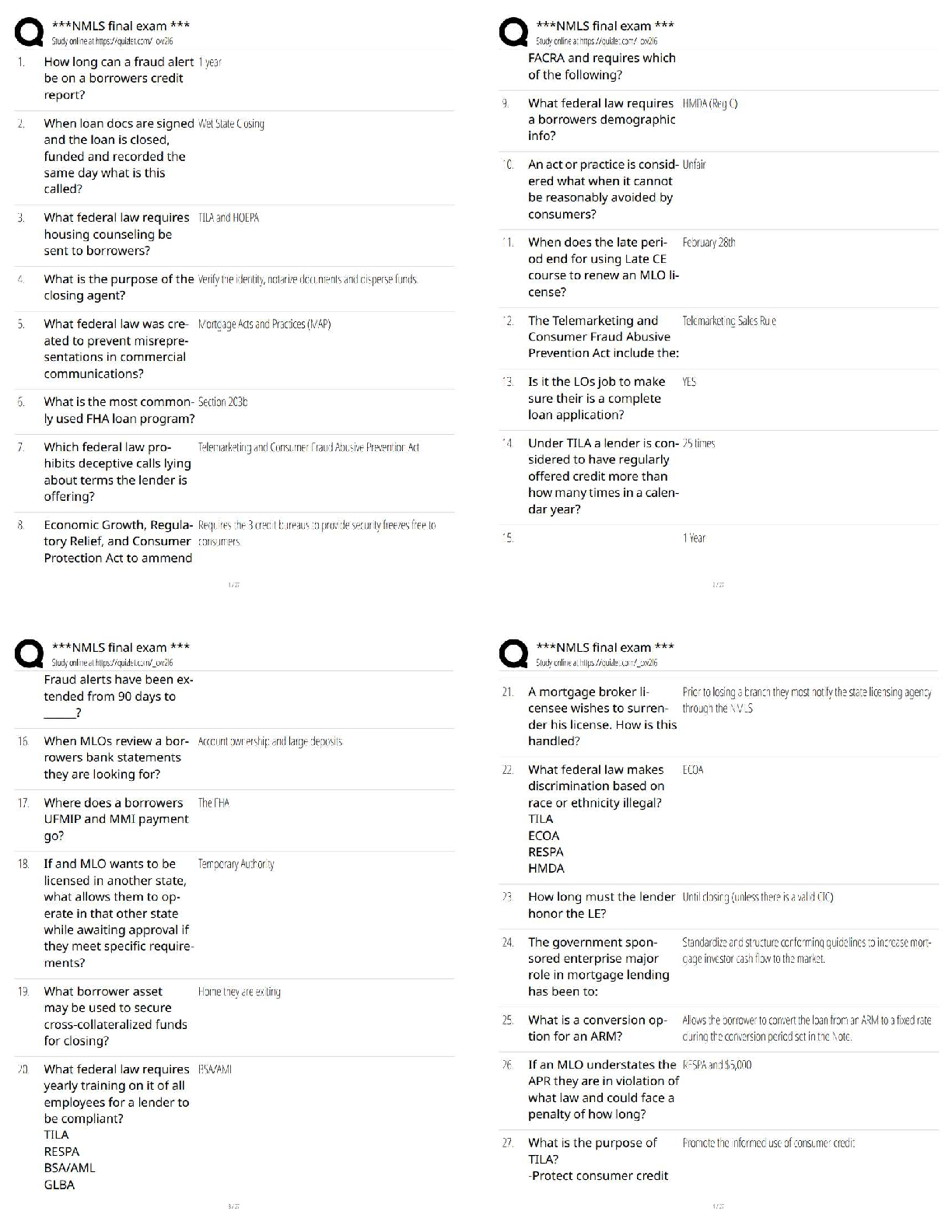
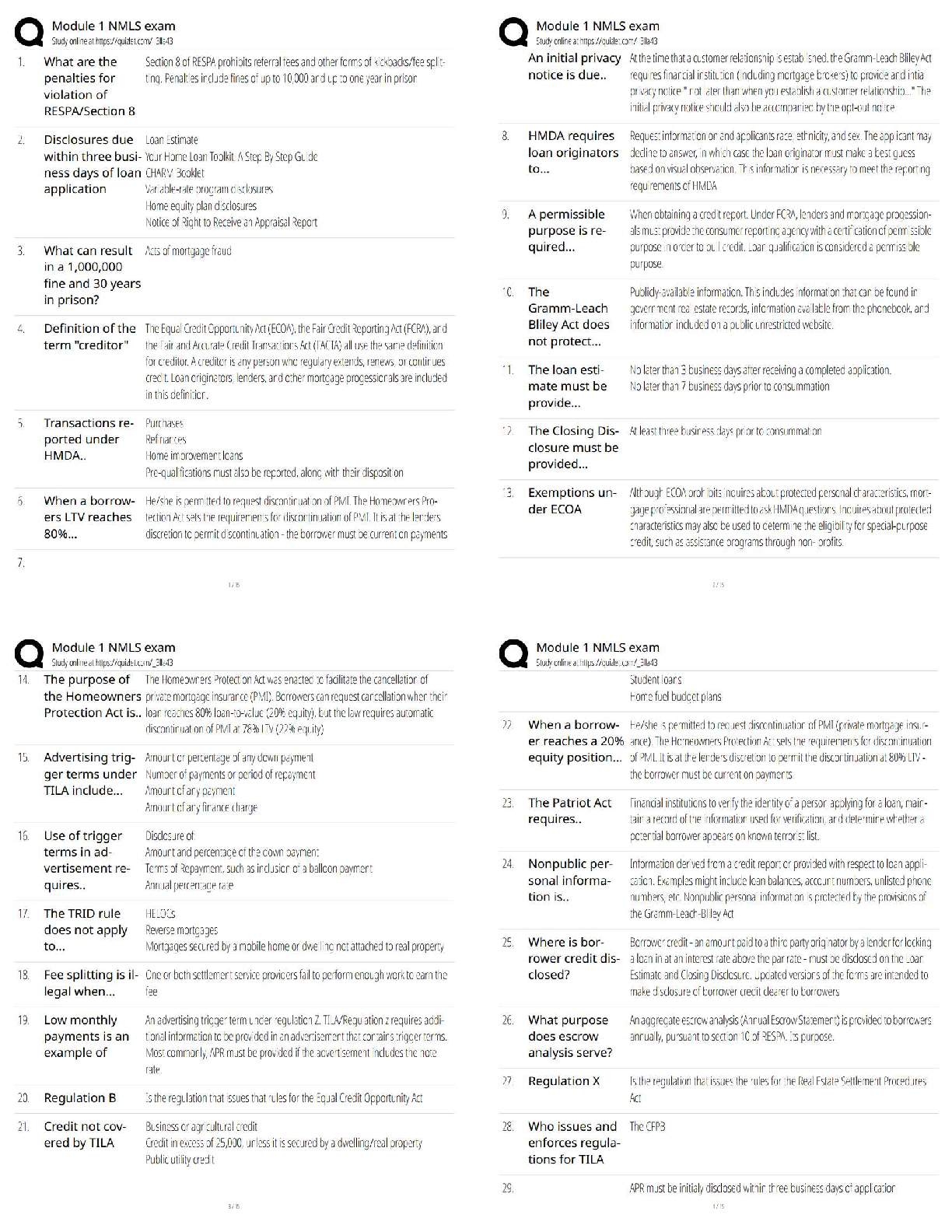
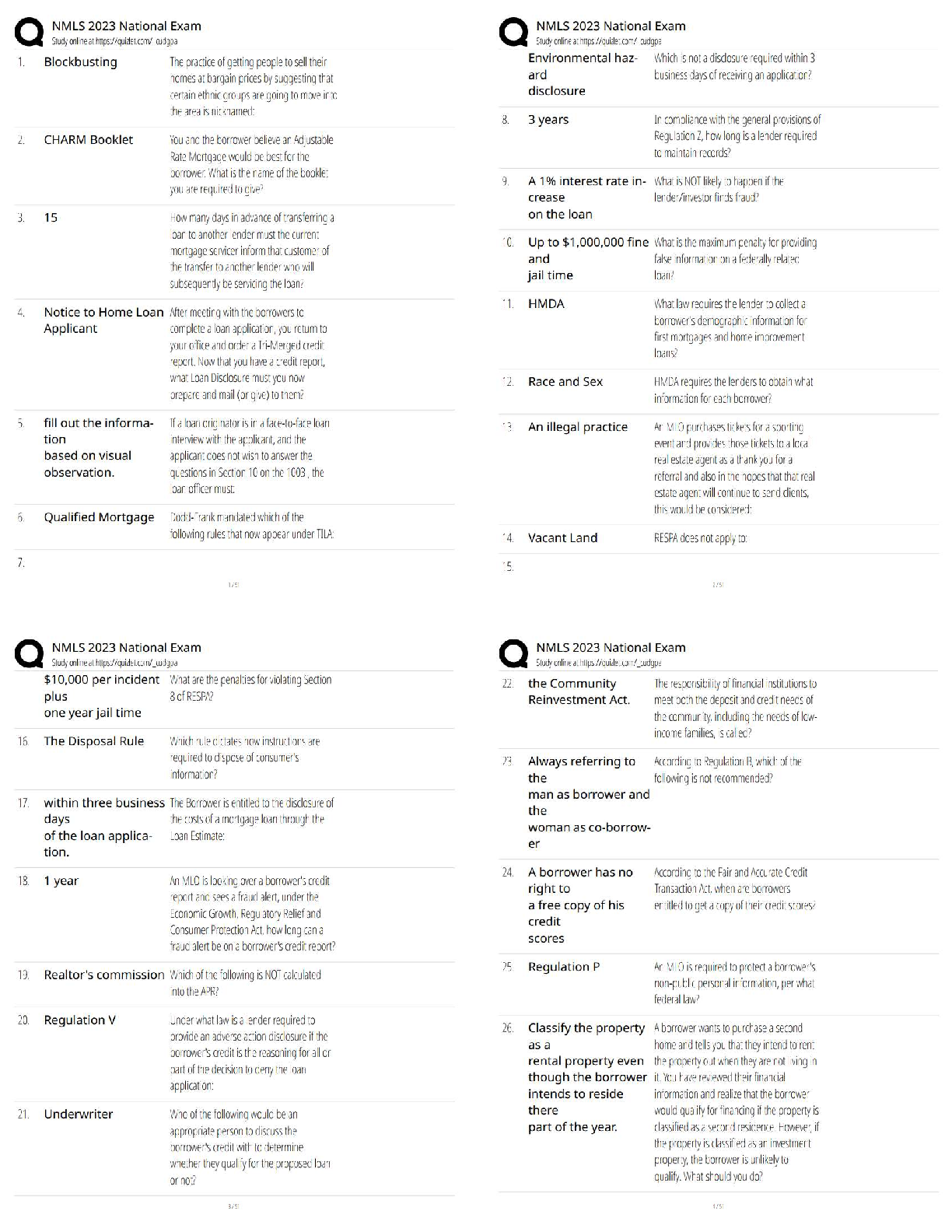
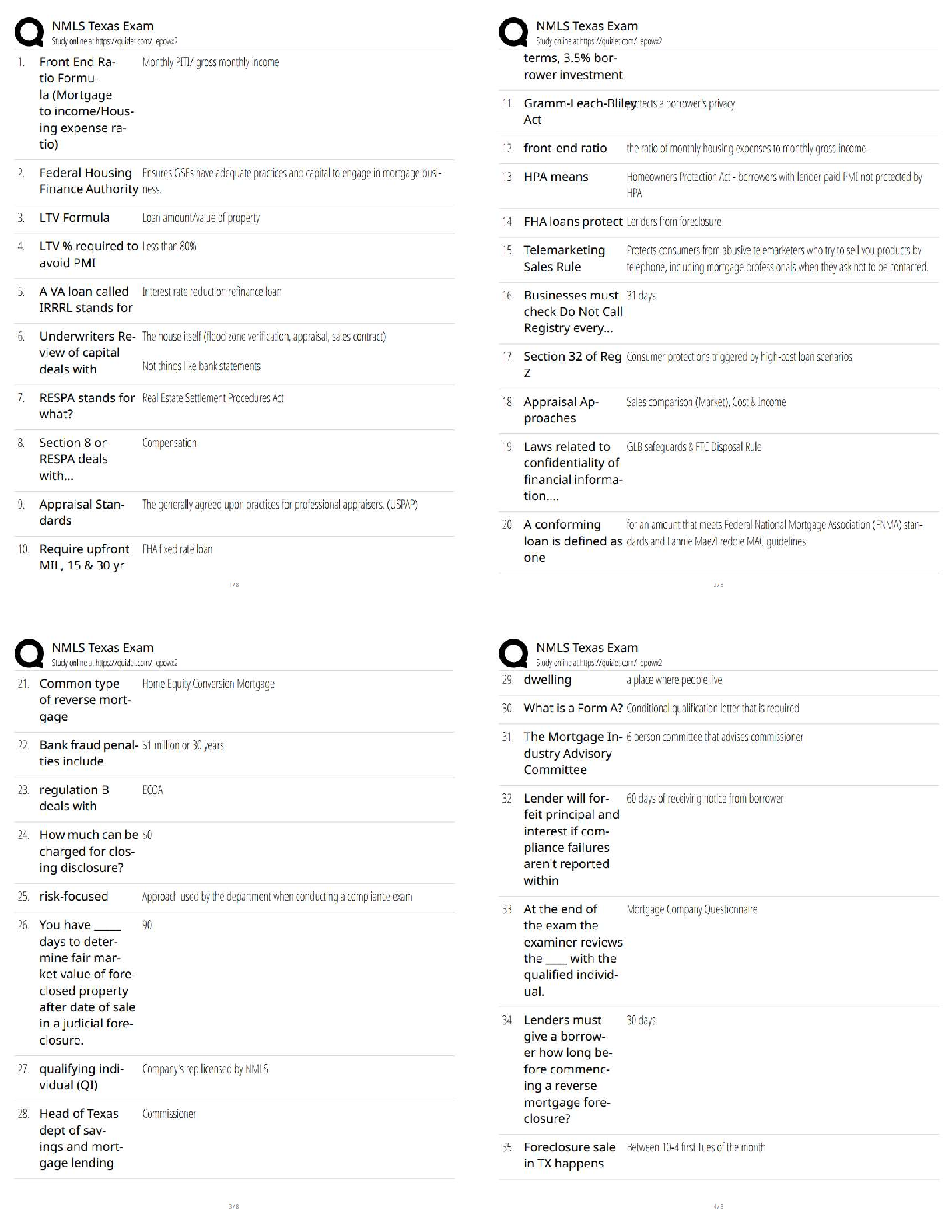
09 - WGU - C168 - Critical Thinking - Module 1, 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 Already Passed Critical thinking comprises three interlinking dimensions Correct Answer- Analyzing, evaluating, and improving Critical ... thinking is characteristically Correct Answer- self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, self-corrective Stereotype Correct Answer- A fixed or a oversimplified conception of a person, group, or idea Egocentrism Correct Answer- the tendency to view everything in relationship to oneself Sociocentrism Correct Answer- assumption that one's own social group is inherently superior to all others First-order thinking (ordinary thinking) Correct Answer- Spontaneous and non-reflective, contains insight, prejudice, good and bad reasoning Second-order thinking (critical thinking) Correct Answer- First-order thinking that is consciously realized (i.e., analyzed, assessed, and reconstructed) Weak sense critical thinkers Correct Answer- Ignore the flaws in their own thinking, Often seek to win an argument through intellectual trickery or deceit. Strong sense critical thinkers Correct Answer- Consistent pursuit of what is intellectually fair and just, strive to be ethicalFair mindedness Correct Answer- The commitment to consider al relevant opinions equally without regards to one's own sentiments or selfish interests. Intellectual unfairness Correct Answer- Feel no responsibility to represent viewpoints with which they disagree fairly and accurately Intelectual humility Correct Answer- Commitment to discovering the extent of one's own ignorance on any issue Intellectual arrogance Correct Answer- Overestimation of how much one knows Intellectual Courage Correct Answer- Confronting ideas, viewpoints, or beliefs with fairness, even when doing so is painful Intellectual cowardice Correct Answer- Fear of ideas that do not conform to one's own Intellectual Empathy Correct Answer- Inhabiting the perspectives of others in order to genuinely understand them Intellectual self-centeredness Correct Answer- Thinking centered on self Intellectual Integrity Correct Answer- Holding oneself to the same rigorous intellectual standards that one expects others to meet Intellectual dishonesty Correct Answer- Marked by contradictions and inconsistencies of which the perpetrator is unconsciousIntellectual Perseverance Correct Answer- Working one's way through intellectual complexities despite frustrations inherent in doing so, Not giving up when confronted by complicated problems that don't lend themselves to easy solutions Intellectual laziness Correct Answer- Giving up quickly when confronted with a tough intellectual challenge Confidence in Reason Correct Answer- Proceeds from the belief that both the individual's and society's higher interests are best served by unfettered reason Intellectual distrust of reason Correct Answer- Lack of confidence in reason, Inclines us to assert the truth of our own beliefs, flawed though they might be Intellectual Autonomy Correct Answer- Thinking for oneself while adhering to standards of rationality Intellectual conformity Correct Answer- Intellectual dependence, Society rewards conformity of thought, which perpetuates the status quo (political, economic, or intellectual), while providing scant incentive for true intellectual autonomy Tactics for the beginning critical thinker Correct Answer- Use "wasted" time, Handle one problem per day, Internalize intellectual standards, Keep an intellectual journal, Practice intellectual strategies, Reshape your character, Deal with your ego, Redefine the way you see things, Get in touch with your emotions, Analyze group influences on your life.Three Functions of the Mind Correct Answer- Thinking, Feeling, and Wanting Elements of reasoning are also called Correct Answer- the parts of thinking or fundamental structures of thought Universal elements are Correct Answer- Purposes, Questions, Assumptions, Implications, Information, Concepts, Inferences, Points of View Purposes Correct Answer- The goal or objective of reasoning Questions Correct Answer- What directs reasoning. All reasoning involves answering at least one question Assumptions Correct Answer- Beliefs that are taken for granted(taken to be true) in reasoning Implications and consequences Correct Answer- What follows from reasoning. Reasoning delivers us to a position or viewpoint about something. Information Correct Answer- What the facts are (what is true). We use it whenever we reason. Concepts Correct Answer- What are used to classify or categorize information(ideas)Inferences Correct Answer- The conclusion drawn from reasoning Points of view Correct Answer- The place from which reassoning occurs (perspective) Our purpose affects Correct Answer- How we ask questions How we ask questions affects Correct Answer- The information we gather The information we gather affects Correct Answer- The inferences we make from it What we infer from the information affects Correct Answer- How we conceptualize it How we conceptualize the information affects Correct Answer- The assumptions we make The assumptions we make affect Correct Answer- The implications that follow from our thinking The implications affect Correct Answer- How we see things—i.e., our point of view Intelectual relativity Correct Answer- Nothing is provable because everything is relative Standards of reasoning Correct Answer- The way we assess our reasoning to determine how well we are reasoning The standards are Correct Answer- Clarity, Accuracy, Relevance,Logic, Breadth, Precision, Significance, Fairness, Depth Clarity (clearness) Correct Answer- Reasoning that is clear in meaning and expression Accuracy Correct Answer- Reasoning that expresses how things actually are Precision Correct Answer- Reasoning that is specific, exact, and detailed Relevance Correct Answer- Reasoning that is focused on what is important to the issue or problem at hand Depth Correct Answer- Reasoning that addresses the complexities and fine details of an issue or problem Breadth Correct Answer- Reasoning that considers issues from all relevant viepoints. It always involves more as opposed to less. Logic Correct Answer- Reasoning that is ordered, supported, makes sense in a coherent and combined way and is also free of contradictions Significance Correct Answer- Reasoning that recognizes the order of importance of something Fairness Correct Answer- Reasoning that is justifiedSocratic questioning Correct Answer- A systematic, disciplined approach to asking questions aimed at assessing truth Questions of fact Correct Answer- Have definitive answers, only one correct answer, evidence and reasoning within single system, serve as basis of knowledge Questions of preference Correct Answer- Have a range of potential answers, which reflect personal and subjective views on a topic Questions of judgement Correct Answer- More than one answer, with some better than others, competing answers, evidence and reasoning within multiple systems Dimensions of Decision-Making Correct Answer- Figure out, and regularly rearticulate, your most fundamental goals, purposes, and needs. Take problems and decisions one-by-one. Figure out the implications of alternatives. Figure out the information you need and seek it. Draw reasonable inferences from the information you analyze and interpret. Figure out long- and short-term options and limitations (time, money, power). Consider pros and cons of options. Be strategic in your decision-making. Monitor the implications of your actions and shift strategy if need be. Dimensions of Problem-Solving Correct Answer- Figure out and regularly reevaluate your goals, purposes, and needs. Identify your problems explicitly, then analyze them. Figure out the information you need, and actively seek that information. Carefully analyze, interpret, and evaluate the information you collect.Figure out your options for action and evaluate them. Adopt a strategic approach to the problem, and follow through on that strategy. When you act, monitor the implications of your action as they begin to emerge. Two components in strategic thinking Correct Answer- Identification. Recognizing when your thinking is irrational or flawed. Intellectual action. Engaging and challenging your own thinking. Intellectual action requires figuring out Correct Answer- 1) what is going on in a situation; 2) options for action; 3) a justification for choosing an option; 4) ways to reduce the impact of irrational thinking. Mill's Methods of Determining Causation Correct Answer- Common factor, Single difference, Concomitant variation, Process of elimination Common factor Correct Answer- In analyzing causation, looking for a single shared factor Single difference Correct Answer- In analyzing causation, looking for a causal factor that is present in one situation but absent in another, similar, situation Concomitant variation Correct Answer- In analyzing causation, looking for a pattern of variation between a possible cause and a possible effect Process of elimination Correct Answer- In analyzing causation, successively ruling out noncausal factors until one correct causal factor remains Inert Information Correct Answer- Taking into the mind information, that, though memorized, we do not understand.We think we understand this information, but we don't and can't use it. Activated Ignorance Correct Answer- Taking into the mind, and actively using, information that is false, although we mistakenly think it is true. We mislearn or partially learn information or accept illogical beliefs and then act on them. Activated Knowledge Correct Answer- Taking into the mind, and actively using information that is true and also, when understood insightfully, leads us by implication to more and more knowledge. We bring significant ideas and knowledge into the mind and are able to apply them, systematically, to new situations. Unclear Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Clear Irrelevant Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Relevant Biased Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Fairly gathered and reported Inaccurate Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Accurate Insufficient Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Adequate Inconsistently applied Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Consistently Applied Unjustified Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard JustifiedContradictory Correct Answer- Common problem associated with the primary standard Consistent Evaluating information Correct Answer- This evaluation should take into account five key factors in establishing the accuracy and validity of information: Authority, Point-of-view, Transparency, Scope and Depth, Accuracy. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 14, 2022
Number of pages
23
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 14, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
147