(Walden University), Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
STAT 3001 Week 2 Assignment 2 (2021) (Walden University), Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A
$ 8
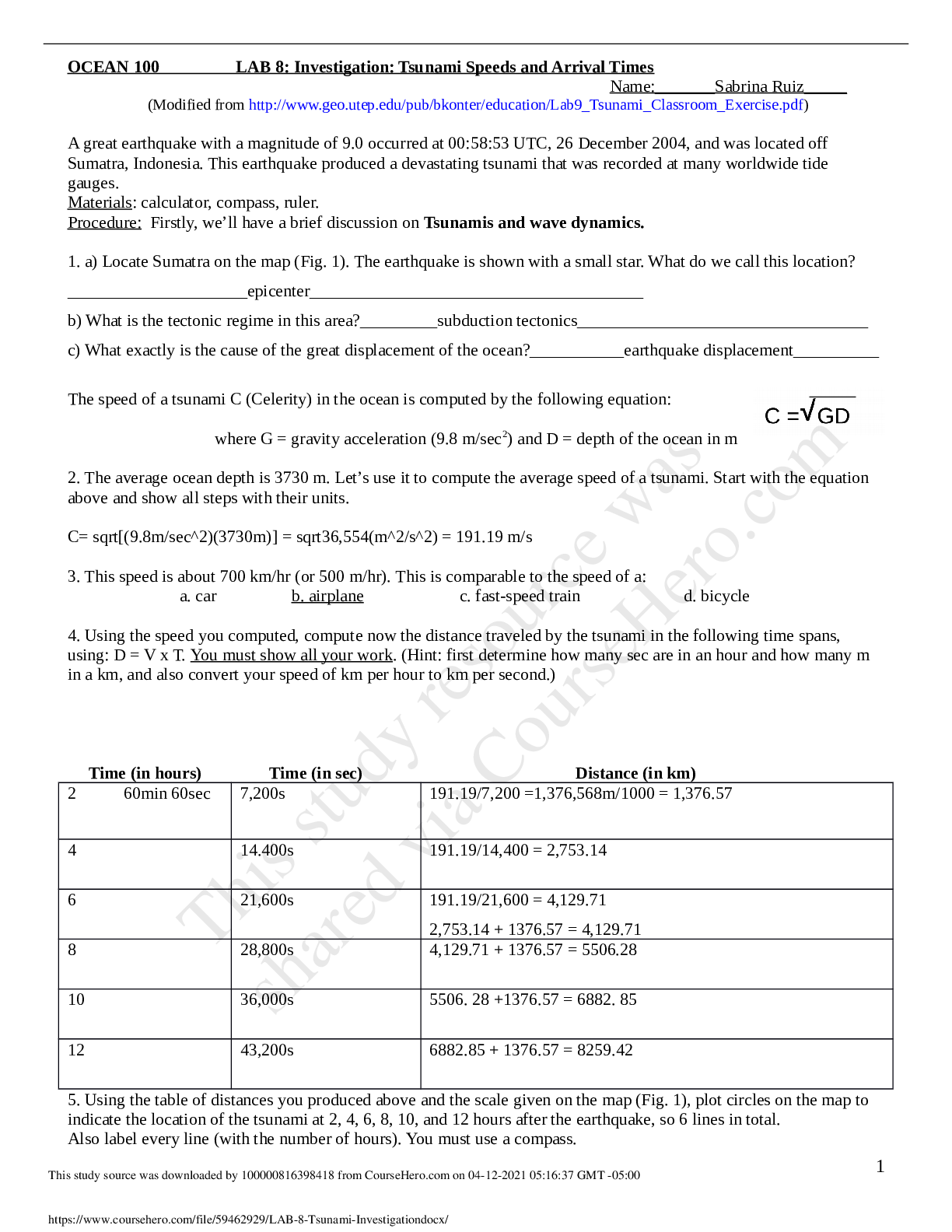
San Diego State University - OCEAN 100LAB 8 Tsunami Investigation
$ 5

eBook Sheehy's Emergency Nursing Principles and Practice 7e Emergency Nurses Association
$ 29

California POST Test #1 – Learning Domains 5, 15, 16, 20, and 39 Practice Questions 2025/2026
$ 20

[eBook] [PDF] Teaching Academic Writing for EAP Language Foundations for Practitioners 1st Edition BY Milada Walková
$ 25

United States President’s Powers
$ 5

RDA Exam Questions And Answers Latest Update
$ 12
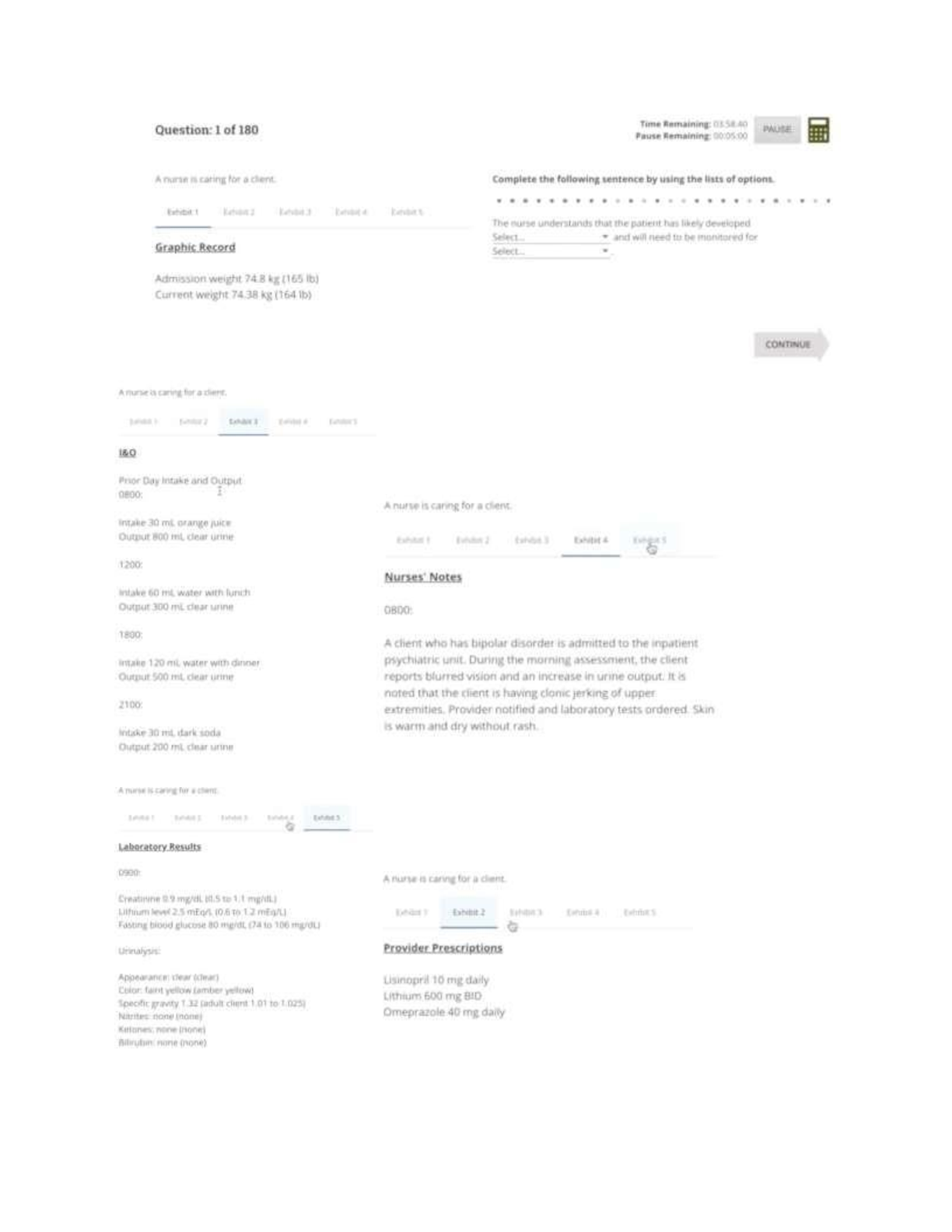
ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT RETAKE EXAM 2023
$ 17

Understanding Pathophysiology 7 th Edition Test Bank CHAPTER 1-44 QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 9.5

AQA A-level GEOGRAPHY 7037/1 Paper 1 Physical Geography Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final Mark Scheme
$ 10.5

BIBL 410 Weekly Study Questions 4 Liberty University answers complete solutions. BEST FOR 2021/2022
$ 7

eBook Photorealistic Colored Pencil Drawing Techniques: Step-by-Step Lessons for Vibrant, Realistic Drawings 1st Edition By e Cocomaru
$ 30

Cornell UniversityHADM 4280Earle Square.pptx
$ 15

ATI FUNDAMENTALS EXAM
$ 7

Pathophysiology Final Exam Questions And Answers 2022/2023
$ 10

TCOLE Prep TEEX Study Guide 2025
$ 29.5

2024 COLORADO POST STUDY GUIDE | Questions with Complete solution | Graded A+
$ 12
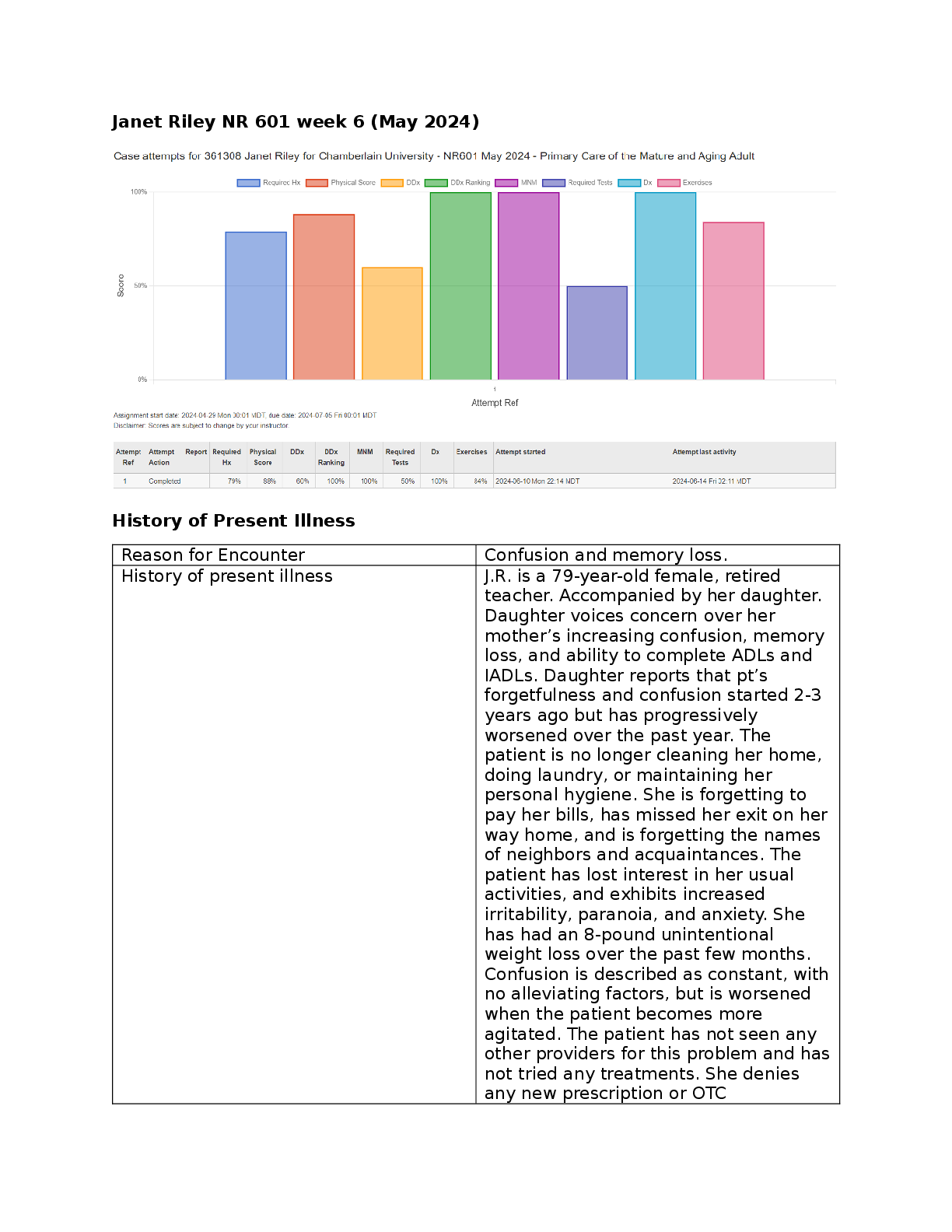
jr-ihuman-i-human-janet-riley
$ 30.5

Ihuman case study for tamika brayton
$ 35.5

eBook The Pocket Mentor for Video Game Writers 1st Edition By Anna Megill
$ 30

D279A ITSW 3110 User Interface Design OA (Qns & Ans) 2025
$ 13

eBook EPUB Cure for a Nightmare 1st Edition By Mr. Joseph James Van Landschoot
$ 29
.png)
PSY 520 Topic 7 Exercise:Chapter 19 and 20-Latest Update
$ 7

[eTextBook] [PDF] 101 Tips for Teaching Online BY Alex Kajitani
$ 25

Patho Final Sg - Summary - complete - Exam 1 and final exam study guide
$ 8.5
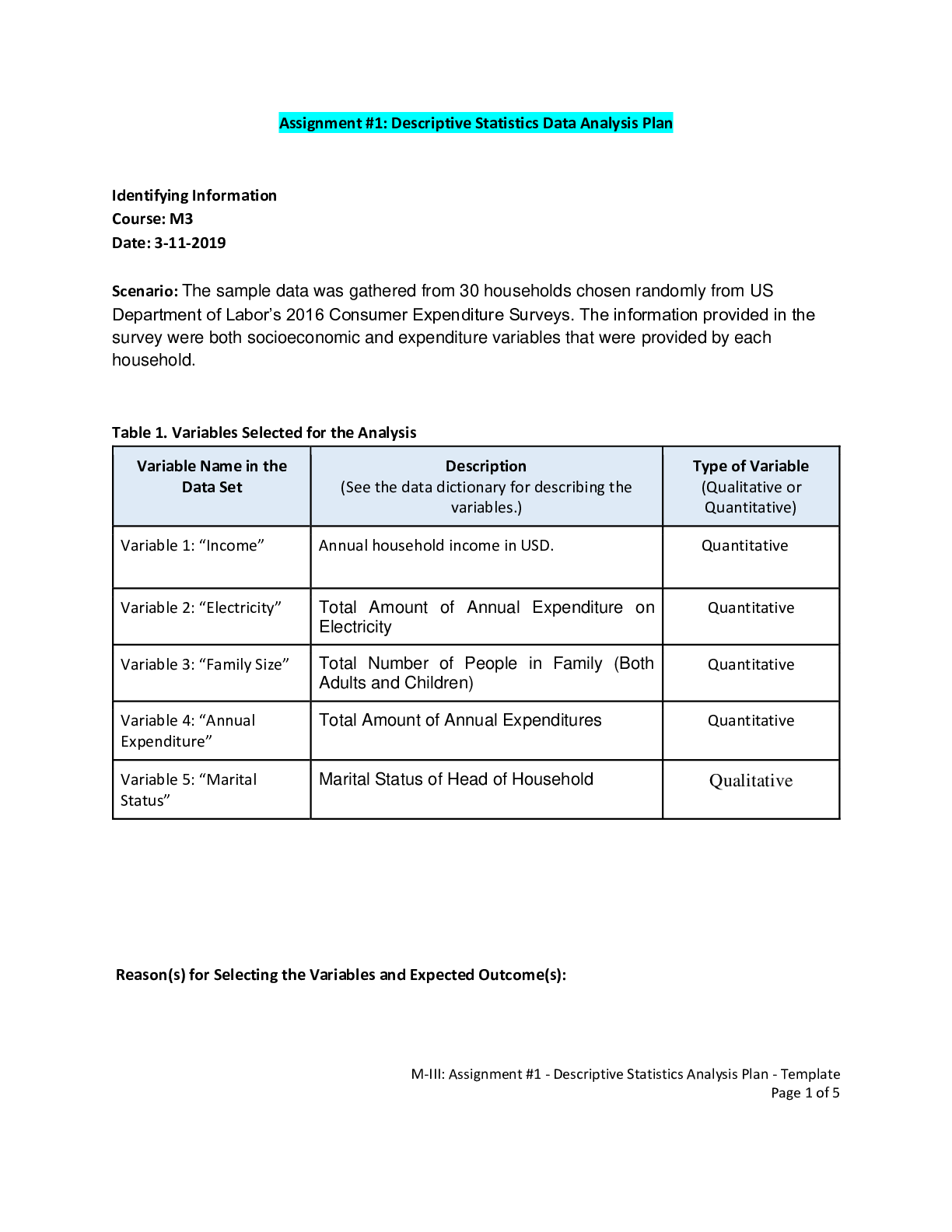
STA200-2019-Assignment1 Descriptive Statistics Data Analysis Plan.pdf
$ 15

NCCCO Signal Person Test Questions And Answers With Latest Solutions
$ 7.5

RDA Practice Exam #1 Questions And Answers
$ 10.5

ADMIN EXAM COMBINED QUESTIONS, Salesforce Admin, Salesforce Admin Spring17, Salesforce ADM 201 Prep 466 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 15

Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Design and Technology (Product Design) Advanced COMPONENT 1 QUESTION PAPER 2022
$ 5

Business Law, Text & Cases; The First Course, 14e Roger LeRoy Miller (Solution Manual)
$ 25

NR 360 Unit 7 Assignment Using ATI Resources Nurse’s Touch – Nursing Informatics & Technology Virtual Social Networks (Summer 2020)
$ 5
.png)
Liberty University - GOVT 220GOVT 220 Paper
$ 9

Dirty Talk Phrases by Adam Armstrong